Here we are providing Class 10 Geography Chapter 6 Extra Questions and Answers Manufacturing Industries was designed by subject expert teachers. https://ncertmcq.com/extra-questions-for-class-10-social-science/
Manufacturing Industries Class 10 Extra Questions Geography Chapter 6
Question 1.
What are light industries?
Answer:
The industries which use light raw’ materials and produce light goods like electric fans, sewing machines, television sets etc. are known as light industries.
Question 2.
Name four important cotton textile centres of Maharashtra.
Answer:
The four important cotton textile centres of Maharashtra are the following:
- Mumbai,
- Sholapur,
- Pune,
- Wardha.
Question 3.
Name two important sugar-producing states of India?
Answer:
The two most important sugar-producing states in India are the following:
- Uttar Pradesh,
- Maharashtra.
Question 4.
Name two iron and steel producing plants each of Karnataka and West Bengal.
Answer:
Two iron and steel producing plants of Karanataka are-
- Vijaya Nagar,
- Bhadravati.
Two iron and steel producing plants of West Bengal
- Durgapur,
- Burnpur.
Question 5.
Name five electronic goods-producing centres of India.
Answer:
Five electronic goods-producing centres of India are the following:
- Bangalore,
- Mumbai,
- Hyderabad,
- Delhi,
- Chennai.
![]()
Question 6.
What is the annual production of cement in the country at present?
Answer:
The annual production of cement in the country at present is 100 million tonnes.
Question 7.
How many software technological parks are there in India?
Answer:
18.
Question 8.
What is meant by DWT?
Answer:
DWT stands for deadweight tonnage. It is the unit for weighing of an empty ship.
Question 9.
How many dry docks are there in India?
Answer:
17.
Question 10.
How much crude oil is produced by India?
Answer:
India produces about 27 million tonnes of crude oil.
Question 11.
Why are the most of the Jute mills of India located at West Bengal?
Answer:
Most of the Jute mills are located at West Bengal because of the following reasons:
- Closeness of the jute producing areas.
- Cheap labour.
- Banking and insurance facilities.
- Availability of abundant water for processing of jute.
- Inexpensive water transport.
- Desired port facilities for export.
Question 12.
Describe the distribution of shipbuilding industry in India?
Answer:
1. Shipbuilding is a large industry requiring huge capital.
2. In India, at present there are five major shipbuilding centres.
3. These are namely
- Vishakapatnam,
- Kolkata,
- Kochi,
- Mumbai,
- Margmago.
4. All of these are in public sector.
5. The maximum size of ships that can be constructed at Kochi and Vishakhapatnam are 100000 DWT and 50000 DWT respectively.
Question 13.
How does industrial pollution degrade environment?
Answer:
In one hand industries make great contributions in the economic development of the country. On the other hand, industries also increase pollution and degrade environment.
![]()
Question 14.
Point out the burning problems of the cotton textile industry?
Answer:
The burning problems of the cotton textile industry today are the following:
- Scarcity of good quality water.
- Obsolete machinery.
- Erratic power supply.
- Low productivity of labour.
- Stiff competition with synthetic fibre industry etc.
Question 15.
In which countries are the Indian cotton textiles mainly exported?
Answer:
India mostly exports its cotton textile in the form of readymade garments. Indian cotton textile is mainly exported to the United States of America, UK, Russia, France, East European countries, Nepal, Singapore and the various African countries.
Question 16.
Why is manufacturing sector considered the backbone of development in India.
Answer:
Manufacturing sector is considered the backbone of development in general and economic development in particular mainly because:
- Manufacturing industries not only help in modernising agriculture, which forms the backbone of our economy, they also reduce the heavy dependence of people on agricultural income by providing them jobs in secondary and tertiary sectors.
- Industrial development is a precondition for eradication of unemployment and poverty from our country. This was the main philosophy behind public sector industries and joint sector ventures in India. It was also aimed to bring down regional disparities by establishing industries in tribal and backward areas.
- Export of manufactured goods expands trade and commerce and brings in much needed foreign exchange.
- A country that transforms its raw materials into a wide variety of finished goods of higher value is prosperous. India’s prosperity lies in increasing and diversifying its manufacturing industries as quickly as possible.
Question 17.
Classify Industries.
Answer:
Industries may be classified as follows: On the basis of source of raw materials used:
- Agio based: Cotton, Woollen, Jute, Silk textile, Rubber and Sugar, tea, coffee, edible oil
- Mineral-based: Iron and steel, cement, aluminium, machine tools, petrochemicals.
According to their main role:
- Basic or key industries which supply their products or raw materials to manufacture other goods e.g. iron and steel and copper smelting, aluminium smelting.
- Consumer Industries that produce goods for direct use by consumers sugar, toothpaste, paper, sewing machines, fans etc.
On the basis of capital investment:
A small scale industry is defined into reference to the maximum investment allowed on the assets of a unit. This limit has changed over a period of time. At present, the maximum investment allowed is rupees one crore. If investment is more than one crore on any industry than it is known as large scale industry.
On the basis of ownership:
- Public sector, owned and operated by government agencies-BHEL, SAIL.
- Private-sector industries owned and operated by individuals or a group of individuals TISCO, Bajaj Auto Ltd., Dabur Industries.
- Joint sector industries which are jointly run by the state and individuals or a group of individuals. Oil India Ltd. (OIL) is jointly owned by public and private sector.
- Cooperative sector industries are owned and operated by the producers or suppliers of raw materials, workers or both. They pool in the resources and share the profits or losses proportionately, such as sugar industry in Maharashtra, Coir industry in Kerala.
Based on the bulk and weight of raw material and finished goods:
- Heavy industries such as Iron and Steel.
- Light Industries that use light raw materials and produce light goods such as electrical industries.
![]()
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Paper is manufactured from :
(a) Wood
(b) Yarn
(c) Cotton
(d) Raw-wool.
Answer:
(a) Wood
Question 2.
One of the following is not an agro-based industry:
(a) Automobile
(b) Silk
(c) Sugar
(d) Edible oil
Answer:
(a) Automobile
Question 3.
The first textile mill was established in 1854 at the following place:
(a) Kanpur
(b) Mumbai
(c) Ahmedabad
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Mumbai
Question 4.
India exports yarn to the following country:
(a) Brazil
(b) Pakistan
(c) Bangladesh
(d) Japan
Answer:
(d) Japan
![]()
Question 5.
Jute mills in India are:
(a) 170
(b) 70
(c) 270
(d) 370.
Answer:
(b) 70.
Map Skills
Question 1.
Show the textile industries on the outline map of India.
Or
Locate on the outline map following industries:
- Cotton textile industries
- Jute textile industries
- Woolen textile industries
- Silk textile industries
- Synthetic textiles.
Answer:
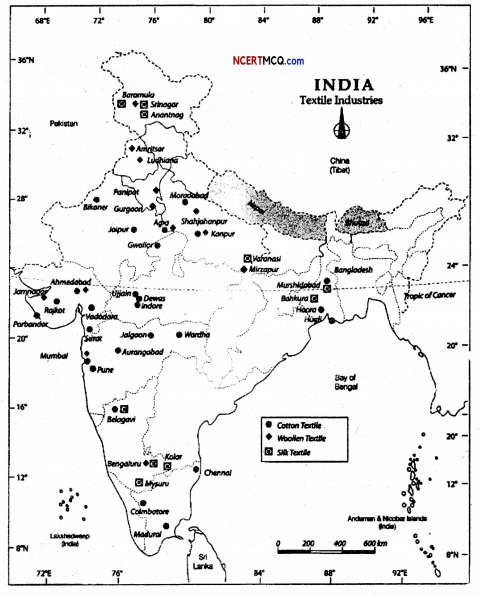
Question 2.
Point out following industries on an outline map of India:
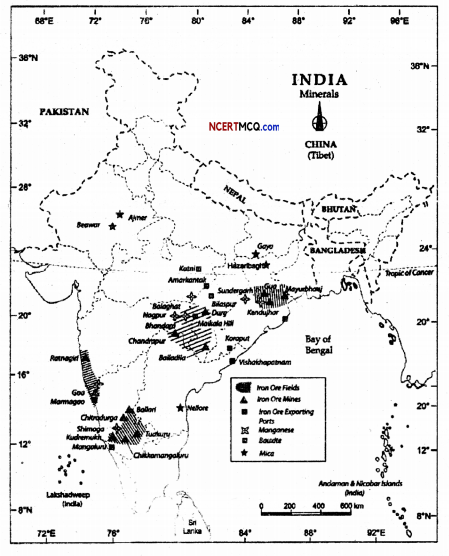
- Iron and steel industries.
- Locomotives
- Railway coaches
- Shipbuilding
- Automobiles
- Machine tools
- Electric gadgets.
Answer:
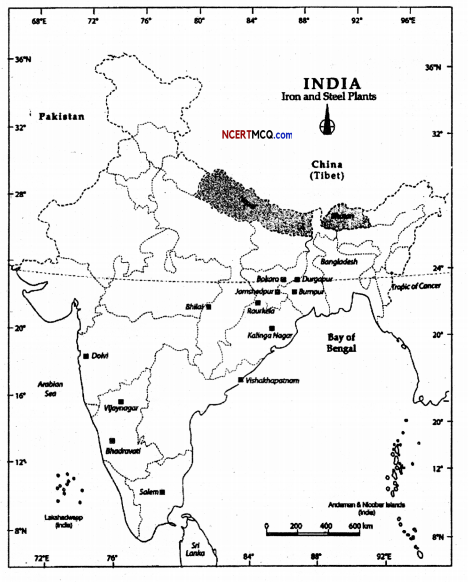
Question 3.
On an outline map of India show the following mineral-based industries:
- Cement
- Fertilisers
- Defence Equipments
- Chemicals
- Heavy electricals
- Petrochemicals.
Answer: