By going through these CBSE Class 11 Accountancy Notes Chapter 12 Applications of Computers in Accounting, students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Applications of Computers in Accounting Notes Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 12
Computers are becoming indispensable in our day-to-day life. It has brought a complete revolution in every sphere of human activity. It becomes an essential tool of today’s society.
Examples of their increasing uses are; reservation in railway and air tickets, to forecast weather, preparing customer’s bill, diagnosing diseases, recording the monetary transaction of customers in the bank, etc. In fact, computers have become indispensable in almost every field of communication, commerce, industry, science and research, technology, transport.
Computers are not used only by engineers, scientists, and mathematicians but even in the typesetting for printing, TV programming, film editing, music composing, etc.
Both in the commercial and personal areas, there are so many works which we are not able to do. due to lack of time. The computer makes it possible by doing our work speedily and efficiently. Computers are nowadays being used on a large scale in business houses for a number of functions. They are used for recording and posting transactions, maintaining journals, ledgers, stock records, pay-rolls, wages records, purchases and sales records, etc. The computer performs all the accounting operations at a phenomenal speed and with a high degree of accuracy.
Limitations of a Computer System:
- Lack of common sense.
- Lack of feelings.
- Lack of IQ (Intelligence Quotient).
- Lack of decision-making.
- Complex and rigid procedure.
- Installation cost.
- Frequent changes.
- Costly maintenance.
- Unemployment.
- Loss of data: Backup required.
Difference between Human and Computer:
Following are the differences between Human and Computer:
- Memory: Human memory is limited however computer’s memory has no limits.
- Speed: is faster than human.
- Repetitive task: can be performed by computers errorlessly.
- Computers do not possess mind and work as directed by a human. It has no impact of emotions however human is emotional and decides on its own, which computers cannot.
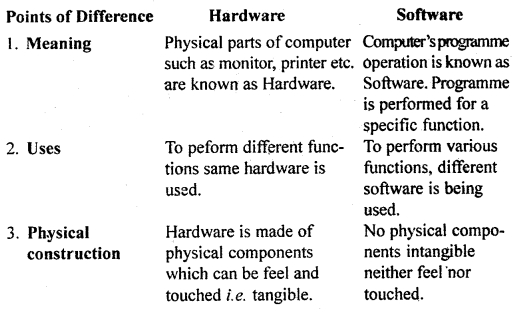
Difference between Hardware and Software:
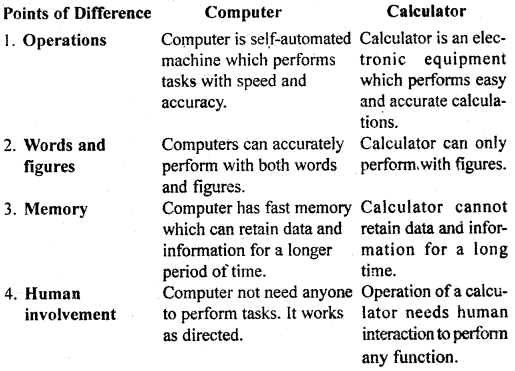
Difference between Computer and Calculator
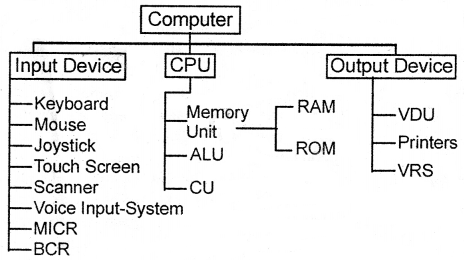
Components of Computer:
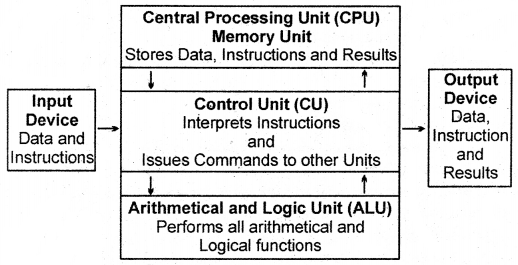
The computer is an electronic device that stores and processes information to give meaningful results. It takes information from an input device and after processing the information, gives the processed information to an output device.
Three basic components of a computer are:
- Input Device
- Central Processing Unit (CPU)
- Output Device.
Need of Computer in Accounting or Evolution of Computerised Accounting:
In past, the business transactions were limited so that they were handled manually. Trader himself or by taking the service of Accountant to maintain the books of accounts such as cashbook, journal, and ledger. As the economy starts growing, the trades also developed and the number of transactions starts increasing.
With the help of scientific development, new machines were invented which perform the large work in a short time, for e.g. billing the machine. With the substantial increase in the number of transactions, the technology advanced further. The success of a growing organization with the complexity of transactions tended to depend on resource optimization, quick decision-making, and control. Such a system of maintaining accounting records becomes convenient with the computerized accounting system.
Computers are required in accounting for the following tasks:
- To note down business transactions.
- Processing and maintaining payrolls.
- Maintaining personal records.
- Keeping effective stock control.
- Invoicing of sales.
- To maintain ledgers of creditors.
- To make bills.
- To prepare accounts of credit and debit.
- Classification of accounting transactions through sorting; merging and updating.
- Prepare reports in the form of ledger accounts and balance sheets.
- Stores accounting.
Automation of Accounting Process:
An organization is a col section of interdependent decision-making units that works for the achievement of common goals. Every organization, as a system, performs the same function that accepts inputs and transforms them into outputs. Information system facilitates the decision-making regarding allocation of resources.
The information thus becomes the most important resource in business. With the increasing use of information systems in organizations. Transaction Processing Systems (TPS) have started playing important role in supporting business operations. A large number of devices are now available to automate the input process for TPS.
Transaction Processing System:
They can perform and records the daily routine transactions which are necessary to conduct the business.
Process of TPS
- Collection of data.
- Validation of data
- Manipulation of data
- Storage of data
- Generation of output
- Query support.
Features of Computerised Accounting System:
- Online input and storage of accounting data.
- Automatically update the ledger etc.
- Printout of purchases and sales invoices.
- Grouping of accounts.
- Instant Reports like Stock Statement, Trial Balance, Trading and Profit, and Loss A/c, Balance Sheet, Value Added Tax (VAT), Payroll, etc.
- Codification of accounts and transactions.
Management Information System (MIS) and Accounting Information System (AIS):
Accounting information is one of the most important information used by the management in taking decisions. However, the scope of accounting information is limited. Accounting information when contained in a computerized environment is called an accounting information system.
However, management information system is a much broader term and incorporates many functional information systems like production, marketing, research, and development, etc., besides accounting information systems.
A management information system is an information system that generates, accurate, timely, and organized information to help managers make decisions, control processes, solve problems, supervise activities and track progress.
An accounting information system identifies, collects processes, and communicates the economic information of an organization to a wide variety of users. Every accounting system is a part of an accounting information system where AIS is part of a management information system.
Meaning of Computer:
The dictionary meaning of computer is “an electronic calculating machine”. This meaning of computer does not reflect upon the true capabilities of a computer. A computer is a very versatile machine capable of performing diversified functions at an incredibly fast speed with accuracy.
It converts raw data into meaningful information. The data is fed into the computer and in case of need, it can be retrieved and converted into output.
A computer is an electronic machine that operates on given instruction and PROCESSES the INPUT DATA, to convert it into some OUTPUT.
“A computer is a data processor that can perform substantial computation, including numerous arithmetical and logical operations, without intervention by a human operator during the run.” – International Standards Organisation
‘‘A computer is a device capable of solving problems by accepting data, performing described operations on the data, and supplying the results of these operations. —U.S. Institute
Thus, a computer is an electronic device, in which a lot of information or data can be stored so Jhat the data can be used in the future. It can also perform various calculations at a very high speed.
Elements of Computer System
A Computer System is a combination of six elements:
- Hardware
- Software
- People.
- Procedure
- Data
- Connectivity.
1. Hardware: The hardware of a computer may be classified under the following categories:
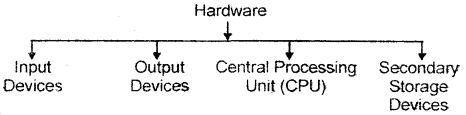
They are further classified as follows:
Input Devices
- Keyboard
- Mouse
- Joystick
- Touch Screen
- Scanner
- Voice Input System
- Magnetic Ink Character Reader (MICR)
- Bar Code Reader (BCR)
Output Devices:
- Monitor or Visual Display Unit (VDU)
- Printers
- Voice Response System (VRS)
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
- Storage Unit
- Control Unit
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
Secondary Storage Devices
- Hard Disk
- Floppy Disk
- Compact Disk
- DVD (Digital Visual Disc)
2. Software: A set of programs, which is used to work with hardware is called its software. There are six types of software which are following:
- Operating System
- Utility Software
- Application Software
- Language Processors
- System Software
- Connectivity Software.
3. People: People are basically those individuals who use computers to develop, maintain and use the information system. They are also called live-ware of the computer. The main categories of people involved with the computer system are:
- System Analysts
- Computer Operators
- Programmers.
4. Procedures: The procedures are the various operations performed in a certain way in order to achieve some desired results.
There are basically three types of procedures:
- Software-oriented
- Hardware-oriented
- Internal procedure.
5. Data: The data is therefore processed and organized to create information that is relevant and can be used for decision-making.
6. Connectivity: The element of connectivity refers to the way in which a computer system is connected to other electronic devices and link-ups such as satellite links, internet, telephone lines, etc.
Capabilities or Features of a Computer System
1. High Speed: A computer can perform millions of operations in one second. The calculations will be error-free.
2. Automatic IHachine: Once the data are fed into the computer, it executes the instructed functions without human intervention.
3. Accuracy: This machine is extremely accurate. Its operations are error-free and the information derived from that is more reliable.
4. Reliability: Computer can perform jobs of repetitive nature any number of times. They are immune to tiredness, boredom, or fatigue. Therefore, they are more reliable than human beings.
5. Versatility: A computer can perform a wide variety of jobs simple as well as complex.
6. Storage: The storage capacity, of a computer, is so large that it can store any volume of information or data for being processed.
7. Scientific Approach: The computer operates scientifically and never gets emotional while solving problems.
8. Work on Special Language: A computer can perform many functions by giving or programming in any one language of computers, which are developed in order to feed the information and data into a computer.
9. Logical decision: Computer has the capability to make decisions that are based on certain conditions.
10. Use of Binary System: The computer uses a two-way system known as Binary System, not the decimal system.

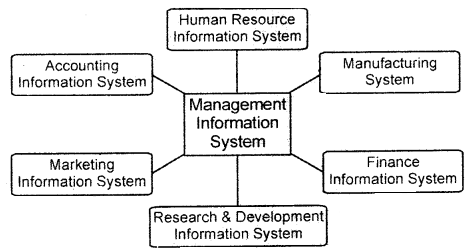
Relationship of Management Information System with other functional Information Systems
Designing of Accounting Reports: When the related information is summarised to meet a particular need it is called a report. It must be effective, efficient, and useful for decision-making.
Every accounting report must be able to fulfill the following features:
- Relevance
- Accuracy
- Completeness
- Timeliness
- Summarisation.
Types of Reports
- Summary Reports
- Customer Reports
- Supplier Reports
- Demand Reports
- Exception Reports
- Responsibility Reports.
Steps in Designing Reports
- Definition of objectives
- Structure or format of the report
- Querying with database
- Finalizing the report.
Data Interface between the Information System:
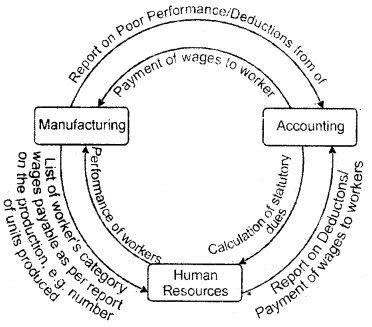
I. Relationship between Accounting Information System (AIS), Manufacturing Information System and Unman Resource Information System.
II. Relationship between AIS and Marketing Information System: Marketing and Sales Department perform following activities:
- Inquiry Process
- Creating Contacts
- Order Taking
- Dispatching Goods
- Billing
The accounting sub-system transaction cycle includes:
- Processing of sales order
- Credit Authorisation
- Keeping custody of goods
- Stock Position
- Dispatch Details
- Accounts Receivable etc.
III. Relationship between AIS and Manufacturing Information
System: Production Department performs the following activities:
- Preparing plans, schedules ‘
- Issue of material requisition forms
- Issue of job cards
- Issue of stock
- Handling of vendor invoices
- Payment to vendors/suppliers
The accounting sub-system transaction cycle includes:
- Processing purchases order
- Advance payment
- Stock Updation
- Accounts payable etc.
Application of Computer in Accounting
Although computers influence every field of accounting, however, its usage in normal modes is mentioned below:
(a) Recording of Business Transactions
(b) Accounting of Debtors
(c) Stores Accounting
(d) Pay-toll Accounting.
(a) Problems that arise due to manual accounting such as complexity, percentage of error, delayed work can be easily rectified using a computer in accounting. Computers can automatically generate ledger postings of business transactions. Using computers, can therefore completely maintain ledger accounts.
(b) Debtors account can easily be maintained via computers. Computers can generate accurate figures for the debtor’s account. They can also be used to prepare reminders to debtors in order to timely collect debt.
(c) Stores Accounting: In stores accounting, the contribution of computers is appreciable. They can be used for
- Daily Stock Position
- Price of Stock
- Need of goods to be credited.
(d) Payroll Accounting: To generate pay of employees in an organization, wages, salary, bonus, allowances, etc. are calculated. Furthermore, employee provident fund, income tax, etc. is deducted from salary. Traditional manual accounting is difficult and bound to make errors that can be made easy, fast, and accurate through the use of payroll accounting.
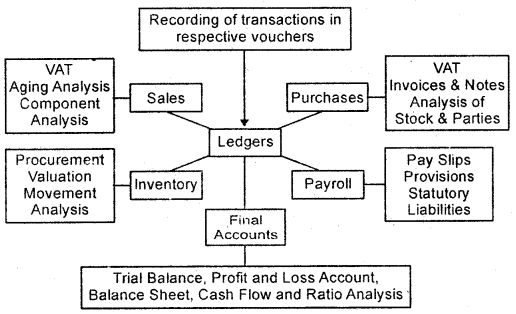
Components Of Computerised Accounting Software System