Here we are providing Class 12 Business Studies Important Extra Questions and Answers Chapter 11 Marketing. Business Studies Class 12 Important Questions are the best resource for students which helps in class 12 board exams.
Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 11 Important Extra Questions Marketing
Marketing Important Extra Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1.
What are Marketing and selling? Also, differentiate between the two.
Answer:
Many people confuse ‘Selling’ for marketing They consider these two terms as one and same. Marketing refers to a large set of activities of which selling is just one part. For example, a marketer of television, before marketing the sale does a lot of other activities such as planning the types and model of television to be produced, the price at which it would be sold, and selecting the distribution outlets at which the same would be available, etc. In short, marketing involves a whole range of activities relating to planning, pricing promotion, and distribution of the products that satisfy customers’ needs.
The function of selling, on the other hand, is restricted to the promotion of goods and services through salesmanship, advertising, publicity, and short-term incentives so that title of the product is transferred from seller to buyer or in other word product is converted into cash.
The Major differences between Selling and Marketing are listed below
1. Part of the Process Vs Wider term: Selling is only a part of the process of Marketing and is concerned with promotion and transferring possession and ownership of goods from the seller to the buyer Marketing is a much wider term consisting of a number ofactiviti.es such as identification of the customer. Need, developing the products to satisfy these needs fixing prices, and persuading the potential buyers to buy the same thus selling is merely a part of marketing.
2. Transfer of title Vs Satisfying Customer Need: The main focus of selling is on affecting the transfer of title and possession of goods from sellers to consumers or achieving maximum satisfaction of the customer’s needs and wants.
3. Profit, Through Maximising Sales Vs Customer Satisfaction: All selling activities are directed as Maximising sales and thereby the profit of the firm. In another word, the emphasis is on profit maximization through the maximization of sales. Marketing on the other hand is concerned with customer satisfaction and thereby increasing profit in the long run. Marketing organization thus attaches the highest importance to customer satisfaction as a route to profit maximization.
4. Start and End of the Activities Selling activities start after the product has been developed while marketing activities start much before the product is produced and continue even after the product has been sold.
5. Difference in the Emphasis: In selling the emphasis is on bending the customer according to the product while in marketing the attempt is to develop the product and other strategies as per customer needs.
6. Difference in the Strategies: Selling involves efforts like promotion and persuasion while marketing uses integrated marketing efforts involving strategies in respect of product promotion, pricing, and physical distribution.
Question 2.
Mention in brief the role of Marketing in the Context of the Indian economy?
Answer:
AM profit or pursue some improvement of quality of life or promotion of cause say UNICEF working for the Welfare of children or Help age working for the cause of senior citizens whether it is a profit organization or non-profit organization Marketing plays an important role in achieving its objectives. Marketing plays an important role from its help the individual consumers in raising their standard of living by making available the product and services that satisfy their need and want.lt also plays a significant role in the economic development of a nation. The role of marketing in different situations may be described in brief as follows.
The modern concept of marketing plays a significant role in achieving the objectives of a firm, ft emphasizes that customer satisfaction is the key to the survival and growth of an organization in the contemporary competitive marketing environment. By adopting a marketing organization, an organization-whether profit-making or non-profit making can achieve its goals in the most effective manner, it helps in focusing the activities of an organization or the need and wants of the customers. For example, what products or services will be marketed by a firm will depend upon what do its customers need. Thus an analysis of the need of the customers shall be undertaken in order to decide what to produce and sell.
The product will then be designed according to the need of the potential buyers and be made available through the outlets are convenient to customers and are priced at a level which the target customers can afford. In other words marketing as a business philosophy help in serving the customers by satisfying their needs. It is a well-known fact that a satisfied customer is the most valuable asset of a firm. Thus marketing plays a crucial role in the survival and growth of a firm.
O Role in Economy: Marketing plays a significant role in the development of an economy, it acts as a catalyst in the economic development of a country, and helps in raising the standards of living of people.
The development of a nation can be judged by the level of standard of living of its people. Another important criterion, which is related to the first one is the per capita income of an average citizen of a country. On this basis, an underdeveloped country may be stated to be which is characterized by factors like poverty, Scarcity of goods and services predominance of agriculture, etc.
Marketing can play a significant role in the economic development of a nation. It can inspire people to undertake new activities and to set up enterprises for producing goods that are needed by customers. Marketing can help in overcoming obstacles posed by high prices due to imbalances in the level of production and consumption It can also ensure smooth flow of goods through efficient physical distribution arrangements.
In other words, marketing can help in finding out the right type of products and services that a firm should manufacture the places where it should make such products available for sale. The price at which the product should be sold and the channels that should be used for moving the products to the ultimate place of consumption or use. This linkage between the business and consumption centers accelerates the economic activity leading to higher incomes more consumption and increased saving and investment.
Question 3.
Explain the important characteristics of a good brand name?
Answer:
Characteristics of Good Brand Name: Choosing the right brand name is not an easy decision what makes this decision important is the fact that once a brand name is chosen and the product is launched in the market. Changing the brand name is very difficult. So getting it right the first time is very essential following are some of the considerations which should be kept in mind while choosing a brand name.
- The brand name should be short easy to Pronounce, spell, recognized, and remember e.g. ponds, VIP, Rin, Vim Etc.
- A brand should suggest the product’s benefits and qualities. It should be appropriate to the product’s functions, e.g. Rasika, Genteel, Promise, My fair Lady, and Boost.
- A brand name should be distinctive e.g. Liril, sprit, Safari, Zodiac;
- The brand name should be adaptable to packaging or Labelling requirements to different advertising media and to different languages.
- The brand name should be sufficiently versatile to accommodate new products, which are added to the product line e.g. Maggie, Colgate;
- It should be capable of being registered and protected legally; and
- The chosen name should have to stay power ie; it should not get out of data.
Question 4.
Explain the term sales promotion and mention, in brief, the merits and limitations of sales promotion.
Answer:
Sales Promotion refers to short-term incentives which are designed to encourage the buyers to make immediate purchase of a product or service these include all promotion effort other than advertising, personal selling, and publicity, used by a company to boost its sale sales promotion activities include offering a cash discount, sales contests, tress gift offers and free sample distribution, sales promotion include only those activities that are u$ed to provide short term. incentives to boost the sales of a firm.
Merits of Sales promotion:
- Attention ValueSales promotion activities attract the attention of the people because of the use of incentives.
- Useful in New Product Launch Sales Promotion tools can be very effective at the time of introduction of a new product in the market. It includes people to break away from their regular buying behavior and try the new product.
- Synergy in total promotional efforts Sales Promotion activities is designed to Supplement the personal selling and advertising efforts used by a firm and add to the overall effectiveness of the promotion efforts of a firm.
Limitation of Sales promotion:
- Reflects CrisisIt a firm frequently rely on Sales promotion, it may give the impression that it is unable to manage its sales or that there are no takers of its product.
- Spills Product Image Use of Promotion tools may affect the image of a product. The buyers may start feeling that the product is not of good quality or is not appropriately priced.
Question 5.
Differentiate between the old and new concept of Marketing?
Answer:
The difference between the new and old Marketing. The concept may be made clear as to under
1. Orientation: – The old concept is production-oriented because it emphasizes production on the other hand new concept insists on the consumer’s need for satisfaction and therefore it is consumer-oriented.
2. Scope of Marketing Production and sales were the main
activities included scope. The scope of Marketing under the new concept has been widened to include the pre-production and after-sales problems.
3. Targets: In the old Marketing concept the main target of the firm was to earn profit through more and more production and higher sales volume whereas in the modern concept of Marketing the target of the firm is to earn more profit through customer satisfaction.
4. Market Research: There is no scope of Market research in the old concept of the market whereas, in a new concept of Marketing, market research is a must to know the needs, wants and behavior of the consumers so as to produce goods and services accordingly.
5. Inter-departmental Integration: Under the old concept of Marketing different departments of the firm independent and has no Integration with the Marketing department. They were mainly concerned with the production and not with the sales. A new concept of Marketing has now changed the view. Now activities of each department are directed by the Marketing department and the various department are better integrated with the Marketing department.
6. Consumer Welfare The new concept is fully dedicated to consumer welfare. The main responsibility of Marketing is to raise the standard of living of the society through consumer welfare and consumer satisfaction. There was no place for consumer welfare under the old concept of Marketing.
From the above-mentioned point, it is clear that: The old concept of Marketing is referred to as a system where more and more emphasis was laid on the production of commodities. It was based on the idea that consumers would buy what the seller produces. The modern concept on the other hand concentrates on the satisfaction of the need of customers and the need there. The seller produces what the buyer need and thus new concept emphasizes customers and their need satisfaction. The main point of difference between these two concepts has been explained in the following lines.
Old Concept of Marketing:
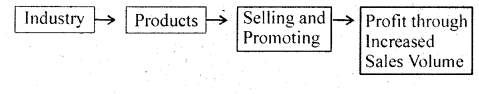
New Concept of Marketing:
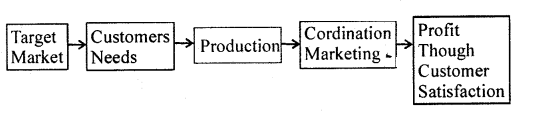
Before embarking on the production work, the new concept of Marketing starts by finding out the requirement of customers. The businessman has to earn profit by selling and satisfying the customer with the product’s quality.
The Modern Concept of Marketing In India: On the question of the application of the Modem concept of Marketing in India, various scholars are of the view that it does not apply to India. They put forward undermentioned logics in support of their answer
- Production if India is not according to the taste and needs of the consumers.
- The marketing program does not include after-sales service.
- The Concept that “We must have profit irrespective of the fact that consumer feels satisfied or not is adopted in India.
However, consumers are of the opinion that the modem concept of Marketing applies in India due to the following reasons:
- Many producers produce products after identifying the need of consumers.
- After-sale services are provided such as a guarantee on products.
- There are many manufacturers who are not solely concerned with a profit motive.
- Advertisement and other sales-promotion activities are undertaken by producers, so as to enhance the standard of living of consumers.
Judging and Comparing the two thoughts on Marketing in India, it can be deduced that Modern Marketing Concept applies in India in a partial way. Modern Marketing concepts will play a crucial role in India with the expansion of education, urbanization of the population, increase in per-capital income, and improvement of the standard of living.
Question 6.
Explain in brief the objectives and importance of Physical Distribution Management?
Answer:
The Scope elf Physical Distribution System and its Components
The Marketing process is not complete simply by creating a super product and by creating a customer at the right time and place is an equally important function in Marketing. In the process of Marketing, this vital function is called Physical distribution. Physical distribution means the process of delivering the product to the user or Consumer Promptly safety and its time.
The following are the components of the Physical distribution system:
- Distribution Planning and accounting
- Inbound Transport
- Receiving
- Inventory Management
- In-plant Warehousing
- Order processing
- Packaging/repackaging where applicable
- Dispatch of goods
- Outbound transport
- Field warehousing
- Customer service
- Communication.
Physical distribution components or activities can be used as elements of Marketing strategy. Recognization of Physical distribution service can bring about better customer service. Increase in sales cost reduction and higher profit Margin.
In this full scope for a manufacturer, Physical distribution would involve not only the movement of finished goods from the end of the production line to the final customer but also the flow of raw materials from the supplier to the factory. Similarly, dealers and traders will manage the flow of goods into their shelves as well as from their shelves to the customer’s home or stores.
Importance of Physical Distribution Management – It is a physical distribution that provides place-utility and time-utility to products. In other words, it is the physical distribution that makes the product available at the right place and at the right time thereby Maximising the company’s chance to sell the product and strengthen its competitive position. If any product mode in any place could be consumed in its entirety at the very place of production and at the very time of production, there would no need for Physical distribution for that product.
But such products are very rare. In practice, almost every product gets consumed at places and times that, are different from those of their manufacture. They have to be carried t to places of consumption, they have to be stored and they have to be distributed.
The activity of Physical distribution is necessary for modern Marketing due to the following reasons
1. Control on Distribution CostUnder an efficient system of Physical distribution, a detailed analysis of transportation and storage cost is made in view of controlling or minimizing the distribution cost. It aims at reducing the sale price to the consumer for this purpose stress is laid on improvement in packaging control over channels of distribution simplification of the distribution system and technical improvement:
2. Increase in Sales Volume Marketing Management has realized that there is a definite connection between merchandising programs and physical distribution services (Particularly delivery service and order processing service). Customer often gives more importance to physical distribution than to price and promotion service. Physical distribution is considered by customers second in importance 1 to produce quality a reason for purchasing from a certain firm. Better J Physical distribution service gives higher overall customer satisfaction.
In other words, customers’ buying behavior hinges on the offer of adequate Physical distribution service.
3. Coordination of Demand and SupplyPhysical distribution facilitates the coordination between management got the benefits of a lower and higher level of customer service and thereby could reduce their operating expenses by 10 to 15 percent Many other competing firms were also compelled to adopt Scientific Management of physical distribution service. Thus many companies have now started giving more attention to the management of physical distribution operations in an integrated manner.
4. Product PlanningIncreasing competition in Marketing has necessitated the proper attention to be paid on product planning, production advertisement, and sales promotion, etc. but only this is not enough for an enterprise to get success in its marketing efforts. It also becomes necessary that the goods and services produced by the enterprise must be made available to the consumers at the right time and right place for this reason. Marketing executives of today have come to realize the importance of physical distribution.
5. Important in Marketing Physical distribution system is now recognized as an integral part of Marketing. Hence the marketing concept must apply to the management of physical distribution revolving around customer need can add the utility or want-satisfying power, viz, the availability of product at the right place and time, and at the lowest possible cost.
6. Need for customer satisfaction Physical distribution is not only a cost, it should be regarded as one of the tools in competitive Marketing. A Marketer can attract additional customers and maintain existing customers by offering better and dependable service or lower prices with fair service through improvement in the physical distribution package. The marketer has to evolve an appropriate physical distribution process that will fulfill the objective of adequate customer satisfaction.
7. Stabilisation of Prices The Marketing function of warehousing inventory, control, transport, protective packaging physical handling order processing, etc. is now managed as an integrated whole. An effective physical distribution package gives the customers the service they expect and at the same time, it assures profitable sales. Control oversupply position may help to stabilize the prices in the market. It at any time demand exceeds the supply available in the Market additional supplies can be released from the warehouses on the contrary if the supply position improves the production may be kept in storage in order to arrest the fall in prices.
8. Management Science The development of Management science or operations research has made possible the integration of Physical distribution functions. Physical distribution problems have a large number of variables that are readily measurable. Operations research techniques can be easily applied to secure the solution to the physical distribution problem.
Question 7.
What is market segmentation?. Mention in brief the criteria for market segmentation.
Answer:
Definitions of Market Segmentation:
Following are the definitions of market segmentation:
1. According to, Philip Kotler “Market segmentation is the subdividing of a market into homogeneous subsets of customers, where any subset may be a distinct marketing mix.”
2. According to William J. Stanton “Marketing segmentation consists of taking the total heterogeneous market for a product and dividing it into several sub-markets or segments, each of which tends to be homogeneous in all significant aspects.”
3. According to Rustan S. Davar” Market may be classified in several ways depending on the customer characteristics. Customers may be grouped on the basis of how they use a product or service. This grouping of customers can also be broken up in terms of age, sex, income level, education, or geographical in terms of sales territories. This grouping of buyers or segmenting the market is described as Market segmentation.”
4. According to Cundiff and Still: “Market segments are a grouping of consumers according to such characteristics as income, age, degree of urbanization, race or ethnic classification, geographic location or education.
5. According to Alan A. Robert”Market segmentation is the strategy of dividing markets in order to conquer them.”
6. According to Amerian Marketing Association “Market segmentation refers to dividing the heterogeneous markets into smaller customer divisions having certain homogeneous characteristics that can be satisfied by the firm.”
Basis or Criteria For Market Segmentation: Market segmentation being the key input in a firm’s marketing planning process the important issue is how to identify these market segments. Unfortunately, there is no one best way of segmenting the markets. That is why marketing managers are expected to examine a variety of segmentation criteria so as to identify those that will be most effective in defining their markets. The most prevalent basis for segmentation of the market in several countries broadly industrialized, have the prime objective of buying the product/item.
On the basis of this objective, the product market can be divided into two segments. These are
- Ultimate Consumer
- Industrial Consumer
The reason behind the division of the product market lies in the differentiation of consumers’ nature quantum of purchase, the factors influencing purchase, and the marketing efforts made by the seller.
The above division of market segmentation is used by Cundiff and Still. They have mentioned the following criteria for market segmentation:
| Bases for Consumer Product | Bases for Industrial Product |
| 1. Income of the Consumer. | 1. Kinds business |
| 2. Age of the Consumer | 2. Usual purchasing procedure |
| 3. Sex of the Consumer | 3. Size of user |
| 4. Degree of urbanization of the consumer | 4. Geographical market segmentation. |
| 5. Geographical market segmentation | |
| 6. Education attainment of the consumer | |
| 7. Religion of the consumer. |
Philip Kotter h1s mentioned the following criteria for market segmentation:
- Geographic Segment
- Demographic Segment
- Psychographic Segment
- Benefit Segment
- Marketing Segment
- On the basis of Volume
- Basis of Brand Loyalty
1. Geographic Segment: The first most popular criterion for segmenting the market may be the geographical segmentation of the whole operational area. The markets are divided on the basis of geographical factors such as area, climate, and the density of population. According to area states may be taken the basis for segmentation. Each state may be recognized as a separate market. The area may further be segmented in rural, town, and urban areas or where the market is international, the division may be a national or international market.
On the basis of climate, markets may be on hill and plain areas. For example, the North-Western cities of India may be important market segments for a manufacturer of woolen textile. Such type of segmentation is best where the customers are stretched over a vast area and the production is done on large scale. the producer may design his marketing strategies taking the characteristics of the individual markets into consideration.
2. Demographic Segment: On this basis, a seller does the segmentation by taking into consideration the age, income, sex, occupation, education, religion, size of family, nationality and the social class, etc, and thus, makes the separate groups. Demographic variables have been popularly made the basis for market segmentation for a long. It is, therefore, necessary to give them a wide description as under
1. Income: Income is a very important factor affecting the nature, attitudes, preferences, and behavior of consumers. Therefore, a market can be segmented on the basis of the income of consumers. Consumers can be divided into three parts on the basis of income
- High-income group,
- Middle-income group;
- Low-income group.
The consumers of the high-income group stress the design, fashion, quality, and the feeling of social prestige. The consumers of the middle-income group stress the durability and utility of products, while the consumers of the low-income group stress the price and quality. Different models of television sets are examples of this type of segmentation.
2. AgeAge is one of the most important factors for segmenting the market. The producer should know for what age group his product would be most suited so that he can plan his pricing polity, advertisement policy, marketing policy, and strategy accordingly. For example, some breakfast products are aimed to suit the tastes of children while others are attractive to consumers within a broader range of ages. Similarly, the cloth market or garment market may be segmented on the basis of age as children, young, adults, and old.
3. Sex Markets may also be divided on the basis of sex, i.e., ladies and gents. Some products are exclusively produced for women while others are for men. For example, lipstick is meant for women and on the other hand, shaving cream is only for men. Because the attitudes, needs, mental and physical attributes, and motivational factors are different in men and women, advertisement strategy may differ for both types of products.
Personality, sense of family security, and social prestige are some of the factors which are given top priority in an advertisement for a product meant exclusively for men. On the other hand, beauty and purchasing ability are some factors for advertising a product meant for women.
4. Educational level The consumers can be divided on the basis of educational levels such as educated, semi-educated, and uneducated, and the marketing activities and strategies are worked out accordingly. For example, a book market may be segmented on the basis of primary, high school, degree, and professional course books.
5. Business or profession It is also an important factor on which market of a product can be divided. Businessmen, employed persons, and professionals are examples of such classification. Employed persons may further be sub-grouped as clerks, officers, teachers, and executives. Similarly, professionals may be sub-grouped as doctors, advocates, chartered accountants, etc.
6. Caste or religion India is a country having a number of varieties of communication, castes, sub-castes, and religions. The feelings, attitudes, and lifestyles of the consumers of different castes and religions are different. Therefore, a market can be segmented on the basis of caste or religion.
3. Psychographic Segment: The characteristics of psychographic buyers are also the basis for market segmentation. These characteristics are added to the personality of the buyers. Customers’ behavior regarding several products is found to be different. The reason for this difference is related to the customer’s personality. For example, some buyer wants to buy new products while some among them prefer second hand or cheap products. The lifestyle of people too influences the buying trends.
4. Benefit Segment: When consumers buy a particular product they have their expectations. Such expectations differ from product to product and from consumer to consumer. These benefits can be durability, economy, efficiency, prestige, etc. For example, a shampoo market may have 4 benefits-cleanliness, economy, protection (protein, enriched, and anti-dandruff), and cosmetic (long silky hair) benefits.
Each segment favors a certain brand. The company can study these features and decide to which segment they want to comply with and should know the characteristics of that segment and the major existing competitive brands. The company can also search for new benefits and launch a brand that delivers them. Benefits segmentation usually implies that a company should focus on satisfying one benefit group.
5. Marketing Segment: Elements of marketing can also be made a basis for market segmentation. They are of different kinds for example,
- buyers with price consciousness,
- buyers influenced by the quality and variety of the product.
A seller will have made different efforts of marketing for each type of market segment.
6. Volume: Market segmentation can be made on the basis of the quantum of the product proposed for buying, for example, customers buying bulk quantity, medium quantity, and Lesser quantity. Flour purchased by a customer for domestic needs and for hotel use may be from different segments.
7. Brand Loyalty can also be made a basis for the market segmentation. The sellers first try to introduce the characteristics of loyal buyers and then endeavor to make them the buyer. However, segmentation of the market is not always possible on the basis of mere brand loyalty.
Question 8.
Explain the various objectives of packaging?
Answer:
Objectives of Packaging:
1. Attraction: As far as possible, the package must possess attraction value, as attraction is the main objective of packaging, so that it may attract customers towards the products concerned.
2. Protection: The second objective of packaging is to provide safety to the product. In other words, the package must protect the contents of the product until it is consumed. The package keeps the product fresh and clean. It protects from adverse effects of weather, temperature, dampness, insects, contamination, breakage, evaporation, leakage, etc. It preserves the flavor and color of the product. It also prevents theft and pilferage.
3. Convenience: The consumers, as well as the middlemen, want packages that are easy to carry, use and dispose of. A good package facilitates easy transportation; storage, display, and usage. Pouch packing is very popular nowadays due to convenience.
4. Economy The next important objective of packaging is economy. Here economy means economic use of the product. The consumer can take out the only quantity to be used at a time and thus, wastage can be avoided.
5. Sales Promotion The objective of packaging is to promote the sale of the product. Whatever is written on the packing acts as an advertisement and sales promotion.
6. Other objectives of packaging are as under,
- It improves the image of the product and thus increases the profit.
- It maintains the utility of the package even after the product packed is consumed.
- Owing to data of manufacturing and the expiry printed on the packing, the freshness or expiry of products can be identified.
Question 9.
Differentiate between Branding and Trade Marks.
Answer:
Difference between Brand and Trade Mark: Difference between brand and trademark can be made on the basis of the following points
1. Registration: Registration of a brand is not essential while registration for a trademark is essential. A brand is called a trademark only when it is registered.
2. Scope: The scope of a brand is limited while the scope of a trademark is very wide. Any business firm can use different brands for its different products while it uses only one trademark for all of them.
3. Legal protection: Brand can be copied by other competing concerns. No legal actions can be taken against them but if trademark denotes the manufacturer who got it registered. So trademark can be used with every brand. ‘
4. Nature: All brands are not trading marks but all trademarks are the brands. Thus, the word brand is more comprehensive than the trademark.
5. Use: Brand can be used by all that but the trademark can be used by the business firm that got it registered in the name of the firm.
In simple words, the main difference between brand and trademark is that brand is not registered, whereas trademark is always registered under Trade and Merchandise Mark Act, 1958.
Question 10.
Explain the term skimming the cream pricing strategy and low penetration pricing strategy and the reasons for adopting the two?
Answer:
Skimming the cream Pricing Strategy: It is also known as the “High Initial Price Strategy”. Under this strategy, the price of a new product is determined very high. Such prices continue to be high till the competitors begin to enter the market. As soon as competitors enter the market, the pioneer producer reduces the price of his product. This strategy is based on a plea that substantial expenses are incurred on research, advertising, and sales promotion activities and the competitors are also absent in the initial price is determined for a product.
By this strategy, the investment made for the development of the product may be quickly realized. The pricing strategy is useful in the case of innovating and specialty products. The manufacturers of computers, mobile phones, calculators, electronic watches, and electronic appliances used this strategy very successfully for pricing their products.
The main reasons for adopting the Skimming the cream strategy are as follows:
- To recover the heavy amount of expenditure incurred by the firm on the research, development production, advertising, and sales promotion of the new product.
- To get the highest possible return on capital invested till the competitors enter the market.
- To get the advantage of a monopoly situation in the market.
- To attract the consumers of the high-income group.
- To try the market for the product at a high rate, because it is easy to reduce it than to raise it.
- When the initial cost of production is very high.
- Suitable for pricing luxury products, because it creates social status.
- A high introductory price will produce greater rupee sales and profits than a low introductory price.
Low Penetration Pricing Strategy: Under this strategy, the price of a new product is determined low to speed up its sales and therefore widening the market base. Low price is used as a major tool for rapid penetration into the market to hold a position. This pricing strategy is adopted where there seem to be no distinctive classes of customers with different price, elasticity, and when advantages of mass production drastically reduce the costs, and when the product is not an innovative product but a simple product.
This strategy aims at capturing the market at the very outset. And if there is already a competing product, it aims at capturing the major share of the market. The best example ever seen of this strategy is the pricing of NIRMA washing powder. This strategy also discourages competitors from entering the market. Another feature of this strategy is that when the new product gains popularity or when its market is expanded, the price of the product is increased.
The main reasons for adopting a low penetration strategy are as follows
- Less cost of research, development, and production.
- To avoid the competition or to face the competition successfully.
- To avoid government interference
- To get the economics of large scale production by increasing the sales.
- To attract the customers of low-income groups, which are large in number.
- The demand for new products is highly elastic even in the introductory stage.
- To expand the market.
- To obtain large profit.
Comparison of Skimming the cream and low penetration Pricing strategies: Skimming the cream means high initial price and low penetration means low initial price. Now the question arises, which of the two strategies should be followed for price determination of a new product. To compare the two strategies or to answer this question we should consider a number of things.
For example, if excess expenses are made on new product development, advertising, and sales promotion, and there are no prospects for competition in near future, demand for the product is less elastic and the product is related to the consumer of the high-income group, then the marketer should follow, high initial price strategy. Contrary to it, if no many expenses are incurred on new product development, advertising, and sales promotion and there are high prospects for competition in near future, demand for a product is more elastic and the product is related to the consumers of the low-income group than the marketer should follow low initial price strategy.
For revolutionary new products that have large potential markets, penetration pricing is usually the most appropriate strategy. This is because the existence of a large potential market is almost certain to attract many larger competitors soon after the introduction of a new product. Penetration pricing helps to discourage prospective competitors contrary to it, if marketer expects that competitors will need considerable time and will meet great difficulties in coming up with their own version of the product, then, of course, price skimming is an appropriate strategy. Hence, the selection of the strategy depends upon the needs of the circumstances.
Question 11.
Give the objectives of Physical Distribution of consumers and Industrial Products?
Answer:
Objectives of Physical Distribution: Like any other marketing mix component, physical distribution has two broad objectives to attain.
- Maximization of customer satisfaction
- Minimization of costs
Physical distribution is concerned with getting the right product to the right place, at right time at the lowest cost. In other words, efficiency and satisfactory services are key goals of physical distribution. The Physical distribution function has the following objectives.
1. To provide better customer services: Customer services are the services provided to the consumers from the time of order placed by them till the products are delivered to them, it also includes after-sale services. In physical distribution customer service consists of providing the right product at the right time and at the right place. However, a high level of customer satisfaction can be attained through a distribution system.
2. To reduce cost: Cost reduction is an important objective of physical distribution. By intelligently managing the physical distribution system and determining the optimum number and locations of warehouses, transportation schedules and modes, material handling, increasing stock turnover, correcting inefficient procedures in order processing and moving offices, plants, retail outlets to low-cost locations, economics can be brought in various costs. By reducing the cost, the profit margin can be improved. This advantage can be shifted to the consumer by lowering the prices.
3. To increase sales: Another objective of physical distribution is to make available the products which have regular demand and also have contingency plans for quick order processing of items so that the product is not out of supply even in the stock or offseason. Moreover, firms can attract additional customers by offering better service or by charging lower prices, this will increase the sales volume of the firm.
4. To create utilities: The physical distribution function by warehousing and transportation creates time and place utility. Warehousing system is known for creating time utility by holding the products from the time of their production till their consumption. Whereas, transportation creates place utility making products more useful by bringing them to the places where they are needed. The main objective is the maximization of customer satisfaction and profits to the firm.
5. To establish a differential advantage over rivals: A firm can establish an advantage over its rivals by performing customer services more effectively, such as arranging rapid and reliable delivery, avoiding errors in order processing, and delivering undamaged products and satisfactory services.
6. To develop a communication system: To develop a communication system which permits the traveling salesmen to transmit orders on a regular basis, so that customer’s inquiries on the order status can be responded to within the shortest possible time and order may also be executed within time.
7. To attain price stability: By physical distribution, the objective of price stabilization can be achieved. With the help of transport and warehousing facilities, an adjustment can be made between the demand and supply of products, and thus, the price fluctuations can be prevented.
8. To increase reputation: With the help of efficient physical distribution management, a firm is able to increase its reputation among buyers and competitors. Buyers like those firms who are able to fulfill their orders as per specification and within the time limit with the help of physical distribution ‘no stock’ situation can be avoided and quality of goods produced can be improved. Better services are always welcomed by the customers.
Question 12.
Explain in brief the importance of promotion mix in marketing?
Answer:
Importance of Promotion in Marketing: Promotion plays an important role in stimulating demand and sales of the product. Its importance may be gathered from the following facts
1. In depression, the importance of promotional activities is greater because, at such a time, the main problem is that of sales of goods and services.
2. The activity of promotion has become important because of the widening of the market. With the physical distance between producers and consumers and also the increase in the number of prospective buyers, the promotion has gained importance. The producer is now to inform all prospective consumers to capture a major share of the market.
3. There are a number of channels of distribution. The producer should not only inform the consumers but he should also inform about the product to the middlemen because they have to present the goods to the middlemen next in the hierarchy and to the consumers. The middlemen should be well versed in the characteristics of the goods.
4. In modern times, there is cut-throat competition in every field. New and new products and producers are entering the market and every producer wants to sell his products first. In order to meet the competition, the producer is to make the customers/prospective customers of his products and their outstanding features along with a comparative view of the competitor’s products. This helps the consumers to select the right type of product.
5. Promotion expenses are the highest of all the marketing expenses. They should be properly and strictly controlled and should be paid due attention.
Question 13.
Explain the term personal selling and its important functions?
Answer:
- “Personal selling consists of contacting prospective buyer of the product personally.” – Richard Buskirk
- “Personal selling is an oral presentation in conversation with one or more prospective purchases for the purpose of making sales.” – American Marketing Association
- “Personal selling consists of individual, personal communication, in contrast to mass relatively impersonal communication of advertising, sales promotion and other promotional tools.” – William J. Stanton
- “Personal selling is basically a method of communication. It involves not only individual but social behavior each of the person, also in face contrast-salesman and prospect influences the other.” -Cundiff and Still
From the above definitions, we can conclude that personal selling is the art of convincing prospects to buy the given product and services. It is the ability to handle the people to demand the product. It is the science and art of understanding human desires and pointing the ways to their fulfillment. It is the ability to convert human needs into wants. The purpose of personal selling is not to ensure the present sales alone, but to win a regular customer.
Functions of Personal selling is an oral presentation in a face to face conversation with one or more prospective customers for the purpose of making sales. The main functions of personal selling are as follows: ‘
1. Making Sales The first and the foremost function of personal selling is to make sales both to old and new customers.
2. Keep Sales records Another important function of personal selling is to keep the complete record of the sale. This record is sent to the manufacturer.
3. Achieving Sales targets Another function of personal selling is to achieve the Sales targets by increasing the Sales Volumes.
4. Collection of Statistics The Salesman collects the data pertaining to the product, from the market on regular basis and sends it to the manufacturer.
5. Advertising new product The salesman sells in the market, the new products with his skills and expertise and create demand for the new product.
6. Demonstration of products Under personal selling the seller physically demonstrates the product, explains its working and features to the customer, and tries to persuade him to buy the product. The customer buys the product after being satisfied with the demonstration.
7. Increase in goodwill The Salesman provides several services apart from selling under personal selling. These services increase the popularity of the company and the Salesman both.
8. Executive function The experienced Salesman provides training to the new Salesman and assist the management in selling the problems relating to marketing.
9. Customer services The functions of personal selling also include, rendering customer services, such as: to introduce the products, explain the right use of the product, convince the customers about the quality of the product, remove doubts of the customers, etc.
10. Other services Under personal selling the Salesman not only perform the selling activities but other services like market research, complaints redressal, repairs, etc. are also performed by the Salesman.
11. Winning customer’s confidence Modem personal selling aims at educating the customer and providing a solution to his problems. The salesman also provides after-sale services. This helps in winning the confidence of the customers.
12. Persuasion of customers The customer is not to be pressurized but influenced favorably by the Salesman. A Salesman must have the ability to .convince the people to buy the product.
Question 14.
Give the importance of Sales promotion as a tool of enhancement in Sales?
Answer:
Importance of Sales Promotion: In recent years, the importance of Sales promotion has increased to a greater extent. The amount spent on Sales promotion now equals the amount spent on advertising. The Sales promotion increase is due to the changes in the marketing environment. The importance of sales promotion increase is due to the thinking of new ideas for creating a favorable condition of selling promoting sales and future expansion of sales. It is a part of marketing strategy. It is essential for the survival of a manufacturer.
More and more promotional activities are required to induce the consumers to purchase more and more products and thus they produce the demand.
In today’s competitive world, promotional activities play an important role which can be judged from the following facts:
1. Effective Sales support: Basically sales promotion policies supplement the. efforts of personal and impersonal sales-manship (advertising). It is found that good sales promotion materials make the salesman’s effort more productive. Activities reduce his time spent in prospecting and reduce the turndowns.
2. Faster product acceptance: Most of the sales promotion devices (such as contests, premium coupons, etc.) can be used faster than the other promotion methods such as advertisement.
3. Distance between producers and consumers: Due to prevalent market conditions mass selling is quite impossible without promotional activities. The distance between producers and consumers has so widened in present days that to get them acquainted with the product, promotional activities are necessary.
4. Selling in imperfect markets: Every market is an imperfect market. In imperfect market conditions, the product cannot be sold easily only on the basis of price differentiation. It is a promotional activity that provides information about the differences, characteristics, and multitudes of the products of various competitors in the market. The customer is attracted to purchase the goods on the basis of such information. Thus, promotional activities are necessary for selling products successfully.
5. Intense competition: The intense competition has necessitated the sales promotional activities. When one manufacturer increases its promotion spending and adopts an aggressive strategy in creating a brand image, others are also forced to follow the suit. This leads virtually to a ‘promotion-war’. It actually leads to a price reduction of standard goods.
6. Increased trade pressures: The growth of large-scale retailers such as supermarkets, chain stores, etc. have brought greater pressure on manufacturers for support and allowance. So, in order to aid the retailer and also to ensure their share of shelf space, many manufacturers have taken to sales promotion activities.
7. Increased standard of living and employment opportunities large scale production is the theme of the day. Sales promotion is always the result of large scale production. But this could be achieved only with appropriate methods of large scale selling. Large scale selling is possible only with the help of promotional activities.
In this way, promotional activities increase the standard of living by providing better goods at a lower rate (due to large scale production and selling). As the promotional activities cannot be performed without the help of an effective sales force and specialists in the field, employment opportunities are open for a large number of people.
8. Traffic-building: Traffic-building implies encouraging more inflows of new buyers and repurchasers. Traffic-building objective is attained by offering incentives to the buyers like special sales, retailer coupons, and premiums, weekly special, etc.
Marketing Important Extra Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1.
What is Packaging? Explain the importance and functions of packaging?
Answer:
Packaging: One of the most important developments affecting the business world in recent years has been in the area of packaging. Many products, which we thought could never lend themselves to packing because of their nature, have been successfully packed e.g. pulses, ghee, milk, salt, cold drinks, etc. Packaging refers to the act of designing and producing the container or wrapper of a product, packaging plays a very important role in the marketing success or failure of many products, particularly the consumer non-durable products.
In fact, if one makes an analysis of the reasons for the success of some of the successful products in the recent past, it can be noted the packaging has played its due role. For example, it was one of the important factors is the success of products like Maggie Noodles, Uncle Chips, or Crax Wafers.
Importance of Packaging: Packaging has acquired great significance in the marketing of goods and services, because for the following reasons
1. Rising standards of Health and Sanitation: Because of the increasing standards of living in the country, more and more people have started purchasing packed goods as the chances of adulteration as such goods are minimized.
2. Self-Service Outlets: The self-service retail outlets are becoming very popular, particularly in major cities and towns. Because of this, some of the traditional roles assigned to personal selling in respect be promotion have gone to packaging.
3. Innovational Opportunity: Some of the recent development in the area of packaging have completely changed the marketing scene in the country. For example, milk can now be stored for 4-5 days without refrigeration in the recently developed packing materials. Similarly, in the area of pharmaceuticals, soft drinks, etc, lots of new innovations have come in respect of packaging. As a result, the scope for the marketing of such products has increased.
4. Product Differentiation: Packaging is one of the very important means of creating product differentiation. The color, size, materials, etc. of the package makes a real difference in the perception of customers about the quality of the product. For example, by looking at the package of a product say paint or hair oil one can make some guess about the quality of the product contained in it.
Functions of Packaging:
As stated above, packaging performs a no. of functions in the marketing of goods. Some of the important functions are as follows
1. Product Identification: Packaging greatly helps in the identification of the products. For example, Colgate in red color, or Ponds Cream jar can be easily identified by its package.
2. Product Protection: Packaging protects the contents of a product from spoilage, breakage, leakage, pilferage, damage, climatic effect, etc. This kind of protection is required during storing, distribution, and transportation of the product.
3. Facilitating the use of the Product: The size and shape of the package should be such that it should be convenient to open, handle and use for the consumers. Cosmetics, medicines, and tubes of toothpaste are good examples of this.
4. Product Promotion: Packaging is also used for promotion purposes. A startling color scheme, photograph, or typeface may be used to attract the attention of the people at the point of purchase. Sometimes it may work even better than advertising. In self-service stores, this role of packaging becomes all the more important.
Question 2.
What is the pricing of a product? Explain the important factors affecting the pricing of a product?
Answer:
Pricing: When a product is bought, some money is paid for it. This money represents the sum of values that consumers exchange for the benefit of having or using the product and is referred to as the price of the product. Similarly, money paid for the services such as fare for the transport service, premium for an insurance policy, and fee to a doctor for his medical advice represent the price of these services. Price may therefore be defined as the amount of money paid by a buyer (or received by a seller) in consideration of the purchase of a product or a service.
Factors affecting Price Determination: There is a number of factors that affect the fixation of the price of a product. Some of the important factors in this regard are discussed below:
1. Product Cost: One of the most important factors affecting the price of a product or service is cost. This includes the cost of producing, distributing, and selling the product. The cost sets the minimum level or the floor price at which the product may be sold. Generally, all marketing firms strive to cover all their costs, at least in the long run. In addition, they aim at earning a margin of profit over and above the costs.
In certain, circumstances, for example, at the time of introducing a new product or while, entering a new market, the product may be sold at a price, which does not cover all the costs. But in the long run, a firm cannot survive unless at least all its costs are covered.
There, are broadly three types of costs: viz fixed costs, variable costs, and semi-variable costs. Fixed costs are those costs, which do not vary with the level of activity of a firm says the volume of production. or sale. For example, the rent of a building or the salary of a sales manager remains the same whether 1000 units or 10 units are produced in a week.
Those costs which vary in direct proportion with the level of activity are called variable costs, for example, the cost of raw materials, labor, and power is directly related to the quantity of I goods produced. Let us say if the cost of wood for manufacturing one chair comes to Rs. 100/- the cost of wood, for 10 chairs would be Rs 1000/- obviously, there will be no cost of wood if no chair is produced.
Semi variable costs are those costs that vary with the level of activity but not in direct proportion with it change in the volume of sale.
Total costs are the sum total of the fixed variable and semi-variable costs for the specific level of activity say the volume of sales or quantity produced.
2. The Utility and Demand: While the product costs set the lower limits of the price, the utility provided by the product and the intensity of demand of the buyers sets the upper limit of price, which a buyer would be prepared to pay. In fact, the price must reflect the interest of both the parties to the transaction the buyers and the seller. The buyers may be ready to pay up to the point where the utility from the product is at least equal to the sacrifice made in terms of the price paid. The seller would, however, try to at least cover the costs. According to the law of demand, consumers usually purchase more units at a low price than at a high price.
The price of a product is affected by the elasticity of demand of the product. The demand is said to be elastic if a relatively small change in price results in large changes in the quantity demanded. Here numerically the price elasticity is greater than one. In the case of inelastic demand, the total revenue increases when the price is increased and goes down when the price is reduced. If the demand for a product is inelastic, the firm is in a better position to-fix higher prices.
3. Extend of Competition in the market: Between the lower limit and the upper limit where would the price settle down. This is affected by nature and the degree of competition. The price will tend to reach the upper limit in case there is a lesser degree of competition while under conditions of free competitors the price will tend to be set at the lowest level.
Competitor’s prices and their anticipated reactions must be considered before fixing the price of a product. Not only the price but the quality and the features of the competitive products must be examined carefully, before fixing the price.
4. Government and Legal Regulations: In order to protect the interest of the public against unfair practices in the field of price-fixing, the government can intervene and regulate the price of commodities. The government can declare a product as an essential product and regulate its prices. For example, the cost of a drug manufactured by a company having a monopoly in the production of the same was Rs. 20/- per strip of ten and the buyer is prepared to pay any amount for it say Rs. 200/-.
In the absence of any competitor, the seller may be tempted to export the maximum amt. of Rs. 200/- for the drug and intervene to regulate the price. Usually, in such a case, the govt does not allow the first to charge such a high price and intervene to regulate the price of the drug. This can be done by the govt, by declaring the drug as an essential commodity and regulating its prices.
5. Pricing objectives: Pricing objectives are another imp. factor affecting the fixation of the price of a product or a service. Generally, the objective is stated to be to maximize the profits. But there is a difference in maximizing profits in the short run and in the long run. If the firm decides to maximize profits in the short run, it would tend to charge maximum price and its products. But if it is to maximize its total profit in the long run, it would opt for a lower per-unit price so that it can capture a larger share of the market and earn greater profits through increased sales.
Apart from profit maximization, the pricing objectives of a firm may include:
(a) Obtaining market share leadership: If a firm objective is to obtain a larger share of the market, it will keep the price of its products at lower levels so that a greater no. of people are attracted to purchase the products.
(b) Surviving in a competitive market: If a firm is facing difficulties in surviving in the market? because of intense competition or the introduction of a more efficient substitute by a competitor, it may resort to discounting its products or running a promotion campaign to liquidate its shock, and
(c) Attaining product quantity leadership: In this case, normally higher prices are charged to cover high quality and high cost of Research and Development.
Thus, the price of firm products and services is affected by the pricing objective of the firm.
6. Marketing Method Used: The price fixation process is also affected by other elements of marketing such as distribution system quality of salesman employed, quality and amount of advertising, sales promotion efforts the type of packaging product differentiation, credit facility, and customer service provided. For example, if a company provides free home delivery, it has some flexibility in fixing prices. Similarly, the uniqueness of any of the elements mentioned above gives the company competitive freedom in fixing the prices of its products.
Question 3.
Mention the important features or characteristics of personal selling?
Answer:
Characteristics of Personal selling: Following are some imp. characteristics of personal selling
- Personal selling is a method of sales communication.
- Personal selling includes commercial and social behavior.
- Personal selling includes both selling functions and non-selling functions.
- It involves the persuasion of customers.
- It involves winning buyers’ confidence.
- It aims at providing information and services to buyers.
- It is a two-way process and benefits both buyers and sellers.
- It helps in solving the problems of the buyers and satisfying their needs.
- Personal selling is an educative process. It tells consumers the way in which they can satisfy their needs.
- Personal selling is more flexible and adaptable. Because of face communication, the salesman adjusts himself and his sales talks according to the need, desires, and behavior of the consumers.
Role of Personal Selling: Personal selling plays a very important role in the marketing of goods and services. The importance of personal selling to businessman, customers, and society may be described as below:
Importance to Businessmen: Personal selling is a powerful tool for creating demand for a firm’s products and increasing their sales. The importance of personal selling to a business organization may be described as follows
1. Effective Promotional tool: Personal selling is a very effective promotional tool that helps in influencing the prospects about the merits of a product and thereby increasing its sales.
2. Flexible tool: Personal selling is more flexible than other tools of promotion such as advertising and sales promotion. It helps business persons in adopting their offer in varying purchase situations.
3. Minimise wastage of efforts: Compared with other tools of promotion, the possibility of wastage. of efforts in personal, selling is minimum. This helps the business, persons in bringing economy in their efforts.
4. Consumer attention: There is an opportunity to detect the loss of consumer attention and interest in a personal selling situation. This helps a business person, in successfully completing the? sale.
5. Lasting relationship: Personal selling helps to develop a lasting relationship between the salespersons it the customers, which is very important for achieving the objectives of a business.
6. Personal rapport: The development of personal rapport with customers increases the ‘ competitive strength of a business organization.
7. Role in the introduction stage: Personal selling plays a very important role in the introduction stage ( of a new product as it helps in persuading customers about the merits of the product.
8. Link with customers: Salespeople play their different roles, namely persuasive role, service role, and informative role, and thereby link a business firm to its customer’s importance to Customers
This role of personal selling becomes more imp. for the illiterates and rural customers who do not have many other means of getting product information.
The customers are benefited from personal selling in the following ways
- Help in identifying needs: Personal selling helps the customers in identifying their needs and wants and in knowing how these can best be satisfied.
- Latest market information: Customers get the latest market information regarding price changes product availability and shortage and new product introduction which helps them in taking the purchase decisions in a better way.
- Expert advice: Customers get expert advice and guidance in purchasing various goods and services which help them in making a better purchase.
- induces Customers: Personal selling induces customers to purchase new products that satisfy their needs in a better way and thereby helps to improve their standards of living.
Importance of society: Personal selling plays a very productive role in the economic progress of a society. The more specific benefits of personal selling to society are as follows
1. Converts latent demand: Personal selling converts latent demand into effective demand. It is through this cycle that the economic activity in the society is fostered, leading to more jobs, more incomes, and more products and services. That is how economic growth is influenced by personal selling.
2. Employment opportunities: Personal selling offers greater income and employment opportunities to unemployed youth.
3. Career opportunities: Personal selling provides an attractive career with greater opportunities for advancement and job satisfaction as well as security, respect, variety, interest, and independence to young men and women.
4. Mobility of Salespeople: There is a greater degree of mobility in salespeople, which promote travels and tourism in the country.
5. Product standardization: Personal selling increases product standardization and uniformity in consumption patterns in a diverse society.
Question 4.
“Money spent on advertising is an investment not waste.” Explain the statement by giving the merits/advantages of advertising?
Answer:
Money spent on advertising is an investment
or
Imp. and Advantages of Advertising
It is an era of advertising. No business or industrial enterprise can survive without advertising in the modern business world, because in every business and industrial activity there is cut-throat competition.
To face and win this competition successfully, it becomes imperative for every enterprise that it advertises what it has and what it wants to sell to the consumers. Advertising is useful not only for the business and industrial enterprise but for the whole community as a whole.
Advertising broader the knowledge of the consumers. With the aid of advertising, consumers find and buy necessary products without much waste of time. This speeds up the sales of commodities, increases the efficiency of labor in distribution, and diminishes the cost of selling. It is an accepted fact that without the market stimulus of heavy advertising, consumers might have waited another sixty years for the product evaluation that took place in less than ten years-it took after all over sixty years from the Invention of the Safety razors before the first acceptable stainless steel blades appeared in the market. These words are more than enough to justify the potentialities of advertising in’ the field of the modem marketing system.
Importance and Advantages of Advertisement:
| Advantages to Producers | Advantages to Middleman | Advantages to Consumers | Advantages to Society |
| 1. Increase in Sale | 1. Helpful in Selling | 1. Increase Knowledge | 1. Rapid economic development |
| 2. Lower Costs | 2. Helpful in searching middleman | 2. Easy purchase | 2. Increase in standard-of-living. |
| 3. Reduction in production selling expenses | 3. Helpful in facing competition | 3. Information regarding avail of goals. | 3.Increase in employment |
| 4. Reduced distribution expenses | 4. Earning sources | 4. Cheap quality goods | 4. Increase in knowledge |
| 5. Increase in demand | 5. Increase in goodwill | 5. Increase in standard of living | 5. Quality product |
| 6. Creation of goodwill | 6. Development of civilization | ||
| 7. Steady demand | 7. Helpful in foreign trade | ||
| 8. Prepare the ground for the new product | 8. Helpful in the development of the newspaper | ||
| 9. To receive efficient workers | 9. Reduction in costs | ||
| 10. To increase profit | 10. Others |
Advantages to Producers:
1. Increase in Sales: By creating the demand for new products, increasing the demand
for existing products, and maintaining the demand for products in all seasons and at all times, advertising helps in increasing the sales of an enterprise.
2. Lower cost: Production cost and marketing cost both can be reduced by manufacturing the product on large scale .because the demand rises through advertising and supply can only be given by manufacturing them on a large scale.
3. Reduction in Production and selling expenses: Selling cost per unit is reduced due to increased sale volume, consequently production cost and overheads are also reduced due to mass production and sale.
4. Reduction in Distribution expenses: Due to large scale selling distribution cost is also reduced.
5. Increase in Demand: Advertising helps in increasing the demand for existing products because it reminds the consumers of a product again and again.
6. Creation of Goodwill: Advertising helps in the creation of goodwill. It increases the sales and increases in sales mean the increase in no. of customers which is apparently the result of the increase in goodwill of the concern.
7. Steady Demand: Advertising helps in stabilizing the demand for a product in all the seasons and all the time. It is only because of advertising that people like to consume eggs, tea, coffee, etc in summer also.
8. Preparation of the ground for New Products: Whenever a producer produces, a new product advertising helps him in creating demand for his product because it is the advertising through which a producer explains the merits of his products to the consumers. It is also the advertisement through which a producer proves the superiority of his products in comparison to the similar products of competitors.
9. To employ efficient workers: As the demand for products is increased through advertising, the employer working with the firm is motivated. This helps in the recruitments of efficient workers.
10. Increase in Profits: Increase in sales results in increased profits also, and thus the enterprise achieves the object of maximizing profits.
Advantages to Middleman:
- Helpful in selling: Easy sale of the products is possible since consumers are aware of the product and its quality through advertisements.
- Helpful in searching middleman: Able middleman can be appointed through the advertisements.
- Helpful in facing competition: Advertising helps the middleman in facing competition successfully. It introduces the products into the market and creates the demand for the products.
- Earning sources: Advertising stabilizes demand. Customers are thereby available throughout the year which ensures permanent income to the middleman.
- Increase in goodwill: The reputation created is shared by middlemen also because they need not spend anything on the advertising of already a well-advertised product.
The advantage to consumers:
- Increase in knowledges: Advertising helps the customers to know about the existence of various products and their prices. They can choose from the various brands to satisfy their wants. Thus, they cannot be exploited by the sellers. Advertising educates people about new products and diverse – uses.
- Easy purchase: Advertising makes it very convenient for the consumers to make their purchases because they take the decision well in advance about the commodity to purchase.
- Cheap and quality goods: The goods advertised are cheap and of standard quality. Advertising induces the manufacture to improves quality because otherwise, the customers will switch to competitor’s products.
- Increase in standard of living: Advertising stimulates the consumption of varied and new products. More the consumption more will be the standard of living of the consumers. Advertising induces the manufactures he improves the quality of their products through research and development. This ensures a supply of products of better quality to the consumers.
Advantages to Society and Nation:
1. Rapid Economic development: Due to advertising sales of products increase in the market, it helps in increasing the scale of production. Large scale production brings industrial progress and prosperity. Advertising also encourages art and design in the country. Due to advertising employment opportunities, research and development also help in the rapid economic development of a country.
2. Increase in standard of living: Advertising promotes the standard of living of the people by increasing the variety and quality in consumption as a result of sustained research and development activities by the manufactures.
3. Increase in employment opportunities: Advertising provides employment to persons engaged in writing, designing, and issuing advertisements. Increased employment brings additional income to the people, which stimulates more demand. Employment is further generated to meet the increased demand.
4. Increase in knowledge: Advertising is very educative. It provides complete information about, the products of their uses to the society. In the words of the late President Roosevelt of the U.S.A. “Advertising brings to the greatest no. of people-actual knowledge consuming useful things.” It is essentially a form of education and the progress of civilization depends on education.
5. Good quality products: Confidence of the public towards the product gets stability through advertisement. This is the reason, the manufacturer is not inclined to end such confidence of the public and enters only goods quality of products or the market. It increases productivity.
6. Development of Civilisation: In the Age of globalization advertising plays a vital role in foreign trade. Exports and imports are possible only due to advertising.
7. Helpful in the development of newspaper: Advertising provides an imp. source of revenue to the publishers of newspapers and magazines. It enables them to increase the circulation of their publication by selling them at lower rates. People are also benefitted because they get publications at cheaper rates.
8. Reduced cost: As already stated cost of production is reduced due to large-scale production. Society also benefits from sour rates of products.
From the above discussion, it is clear that there are a number of advantages of advertising. It is beneficial to all the concerned – Producers, middlemen, customers, and consumers. In this time of throat competition, it is not enough to produce quality products at low costs, it is also necessary that it should be made known to the customer for whose it is produced.
Question 5.
Explain in detail the various pricing policies of a product?
Answer:
Pricing Policies Policies are guidelines for achieving the objectives. Therefore, different policies are framed and adopted for achieving the different objectives. Thus price policy is framed and adopted ‘policies provide the framework and consistency needed by the company to make reasonable, practicable, and effective pricing decisions. It helps the company to attain its pricing objectives.
Any good pricing policy must be aimed at offering a reasonable price to the consumer, ensuring a fair return on investment, and provide, price stability. While adopting the price policy trade traditions, customer preferences, their buying motives, purchase frequency, level of competition, nature of the product, amount of discount and allowances to be given, etc. must be considered.-There are a number of pricing Policies, a brief explanation of them is as follows:
A. On the basis of Cost and Demand. There are two price policies
- Cost-oriented pricing policy: This policy assures that no product is sold at a loss since the I price covers the full, coat incurred. Pricing under this policy is based on simple arithmetic i.e.; adding a fixed percentage to the Unit Cost.
- Demand-oriented pricing policy: Under the policy of a product is based upon its demand in the market. For instance, a high price is charged when and where the demand is high and a low price is charged when and where the demand is low. This policy is more suited to small business units and mostly in the case of non-standardized products.
B. On the basis of Price-Level.There are three price policies:
Meeting Competition Policy: If the price is the main basis of competition, then companies adopt this policy and adjust their prices 1 according to that of competitions. If the competitors change their price, the company will do the same. Such a policy is adopted in the case of highly competitive goods. One important feature of the policy is that it may not have any relationship to its cost and demand of the
Under the Market policy: It is a policy in which a company keeps its prices less than those prevailing in the market. Under the market, the policy is adopted when a company wants to enter the market on wants to expand it. Sometimes, a company has low costs because TtSsProducts is of lower quality and therefore, the price of products is usually kept low than those of competitors. At other times, lower prices may be substituted for promotional efforts used by its competitors.
Above the Market policy: Under this policy, the company ‘ eeps? its prices more than those prevailing in the market. This policy is adopted by companies who either enjoy a good reputation in the market or offer a unique product.
The customers get attracted to the company because of its high prestige. Such a company spends highly on advertising. Sometimes, manufacturers keep more than above price to give some more margin to profit to a middleman in return for their aggressive marketing efforts.
C. On the basis of Flexibility.
There are two pricing policies
1. One price Policy: Under this policy, one price is charged from all types of customers irrespective of volume or conditions of purchase. Price is fixed in this policy. It is a fair trade practice. Such a policy helps in clearly estimating the sales and profits. This policy helps in bargaining as such saves time and selling expenses. These companies, who follow this policy lays emphasis on the product’s quality and customs service.
2. Flexible pricing policy: Under this policy, different buyers are charged different prices for the same product. The difference in price depends upon the bargaining power of buyer and seller, place on delivery market conditions, and many other such factors. It is generally adopted in the case of sub-standard products. This policy makes the seller free to adjust the price according to the prevailing market circumstances. In certain cases, the product may be prepared on the basis of specification or design given by the buyer. In such a case, the price has to be negotiated and then fixed.
D. On the basis of Geographical Conditions.
There are six pricing policies
1. Uniform delivery pricing policy is also known as’F.O.R.’ (Free on the rail) or ‘Destination price’ or ‘Postage stamp’ pricing policy. Under this same price is charged from all the buyers irrespective of their location. In other words, the buyers do not bear directly the freight and other charges because the price includes such charges. They actually add in full or average of total freight charges for all the nation to the price quoted. Such a pricing system is used where transport costs are a major change on the seller’s total cost structure as a case of medicines.
2. Production point pricing policy It is that type of pricing policy in which the firm quotes ‘Ex-factory’ or Free on rail’ price. It does not bear the transportation cost, in the case of ex-factory price, the buyer bears all the transportation costs both freight and cartage from the factory point, whereas in the case of F.O.R. price, the firm bears the freight charges up to the railway station as the transport agency.
After that, the buyer has to meet, freight and cartage. It is also called as ‘Free on, Board’ (F.O.B) pricing policy. In simple words, under this policy, the price of the product includes only the price of the product. All the expenses of transportation from the price of the product. All the expenses of transportation from the place of the seller to the place of buyers are paid by the buyer himself.
3. Zonal delivery pricing policy Under this policy, the company divides the country into different zones and quotes uniform prices for each zone. The prices are uniform within a zone. But these prices differ from zone to zone, because of differences in transportation costs, local taxes, etc. The company adds average transportation cost to the basic price to arrive at the zonal price. Such a price benefits the buyer living at a distant place within a zone.
4. Basepoint pricing policy: It implies partial absorption of the transport cost by the company. One or more geographical locations are selected as base points from which the transport costs are, calculated. The buyers pay the er-factory price plus freight calculated from. the nearest base point. This price policy is normally the collective decision of all the firms.
5. Freight absorption pricing policy: To penetrate distant marked a seller may be willing to absorb part of the freight cost. Thus, under the freight absorption policy, the price of a product includes its actual price and a part of transportation cost. Therefore, the total expenses to be incurred on transportation of goods are divided into \ two parts – a part of these expenses is paid by the seller and the remaining part is paid by the buyer. A freight absorption strategy is adopted to offset the competitive disadvantages of F.O.B. or er-factory pricing.
6. Home delivery pricing policy This policy is gaining popularity in cities. Under this policy, dealers quote the price of a product and delivered the goods at the door-step of the customer. Dealers of television, fridge, air-condition, washing machines, steel furniture, and Haryana merchants usually adopt a home delivery pricing policy.
E. On the basis of Speciality:
On the basis of the specialty of the product, market conditions, trade -conditions, different sellers use the following pricing policies:
1. Skimming pricing policy: It involves setting a very high, price for a new product initially and to reduced the price gradually as competitors enter the market. The initial high price serves to skim the cream of the market. This is a policy of recovering the product^ generally adopted in the case of an innovative product.
2. Penetration pricing policy: This policy aims at capturing the market as soon as possible, therefore, the prices are kept at a low level. It helps in the initial stage or till the product is accepted by the majority of the population.
3. Price lining policy: Under this policy, various products are v priced according to their quality standards. The products may be classified as good, better and best – Different prices are charged for different qualities. The price lining has attraction both for the consumers and the retailers. The consumer’s buying decisions are simplified since the no. of prices from which he must make a selection is limited. The retailers also find this policy attractive because it helps them to plan their buying decisions.
4. Full-line pricing policy: When a manufacturer produces a product in different sizes or models and is unable to calculate the fixed expenses incurred on each type of product separately, he priced his product according to sizes or their demand.
5. Unit pricing policy: Under this policy price of the package and price per unit are mentioned on the package. For example, a toothpaste of 100 grams bears the price of a 100 grams package and also the price of 1 gm. This policy facilitates the consumers to make their buying decision and there is no scope of any bargaining.
6. Bait pricing policy to kinds of products are manufactured under this policy i.e. low price products. The marketer attracts the consumer by showing low price products. Thus, low prices act as bait for attracting customers.
7. Psychological Pricing policy: Under this policy prices are forced in such a manner that they have some psychological effect on buyers. Certain consumers have a feeling that high period products are indicated of high quality. As such, they demand high priced products. For example, diamonds, electronic products, cosmetics, etc. The pricing of products according to their quality standards as superior, fine, or economical also puts psychological pressure on consumers.
8. Old Pricing policy: It is another form of psychological pricing policy. Under this policy price is ending in an odd no. or a price just under a round number i.e. setting the price at an off amount such as Rs. 199.95 instead of Rs. 200 or Rs.5.990 instead of 6,000. The rationale for this policy is that consumers perceive off prices as a better buy. Even extensive products appear less expensive when the period in this way. This policy gives the feeling that the company is true to the last paisa, and results in an increase in sales.
9. Customary pricing: The policy is one that is based on the customs prevailing in the market. The prices are fixed to suit local conditions. Such products are typically standard ones. The price of sweets, soft drinks, bread, and other eatables are based on customary pricing policy.
10. Prestige pricing policy: Generally, the prestige pricing policy is adopted in the case of luxury products where the salesman is successful in creating a prestige of his product in the consumer’s mind. In this case, prices so fixed are generally higher than the prevailing market price. Sometimes, to show that our product is a quality product, market fix higher price for his product in comparison to competitors. Because customers judge the quality of a product by its price. If the price is high, they assume that quality is good. This policy is only useful when actually the quality of the product is genuine and high.
11. Captive pricing policy: In a captive pricing policy, the basic product is priced low, often below cost, but the high markup on supplies required to operate the basic product compensates for that low price. The loss on the basic product is recovered in profits from the sale of the required supplies. This policy is adopted by the newspaper. A newspaper costs, more to produce and distribute than the price charged from the subscribers, but increased circulation encouraged by the low price leads to more advertising revenue and greater overall profit.
12. Loss leader pricing policy Under this policy, few popular products are temporarily offered at low prices with a
view to attracting customers. Such products are termed as loss leaders.
13. Leader pricing policy The business firm who wants to present itself pioneer in the industry take the initiative in fixing the price and other firms follow it. This is generally adopted in oligopolistic market conditions where there are few sellers and these products are identical.
14. Monopoly pricing policy: Monopoly pricing policy is adopted when one company has single-handed control over the entire supply, there are a large number of buyers blit only one seller. The product is unique with no close substitutes. The competition is totally is absent and the seller has a free hand in fixing the price. Monopoly prices are generally considered as high prices.
15. Discriminating pricing policy: Under this policy, the marketer sells the same product at different prices to different buyers. This discrimination may be on basis of the use of product type of customer, the difference in a geographical area, etc.
16. Dual pricing policy Under dual pricing policy, a producer is required to sell a part of his production, under compulsion, to the govt, or its authorized agency at a substantially low price.
17. Administrated pricing policy Prices fixed by the govt, of goods sold through fair price shops are administered prices. This policy favors the welfare of low-income group people.
18. Sealed bid pricing policy Big firms or the govt, calls for competitive bids when they want to purchase certain products or specialized terms. The lowest bidder gets the work.
19. Break-even pricing policy The level of output of which the total revenue will be equal to the total cost is known as the break-even point. Sales over this point will yield profit. The sale must be above the break-even point quantity.
20. Promotion pricing policy This policy is based on its sales promotion method. For instance, take the case of ‘Grand Reduction Sale’ which is intended to revive the memory of the customs who might have stopped buying the products they used to buy in past. In this case, the seller tries to get rid of old and outdated stock.
Question 6.
Explain the various methods of determining the price of a product?
Answer:
Methods of Determining Prices There are many methods for the determination of the price of products. For the convenience of study, these methods can be divided into two parts:
- Methods of determining the price on the basis of cost.
- Methods of determining the price on the basis of market conditions.
1. Methods of determining the price on the basis of cost: The cost of production of a product is the most important variable and most, an important determinant of its price. There may be many types of costs such as Fixed cost, the variable cost, total cost, avg. cost, and marginal cost, etc.
An analytical study of these costs must be made for t determining the price of a product. Methods of determining the price on the basis of cost are as under
1. Cost-plus pricing method This is the simplest and easiest method of price determination. Under this system of pricing the average, I total cost of each unit of production is calculated, and to it is added the desired margin of profit, and selling is done at this ultimate price.
Cost-plus, pricing involves making a cost estimate and adding a margin to cover making expenses and profit. For example, a manufacturer may set the price for a new product by estimating the producer’s per unit total costs and then adding a certain percentage to provide a gross margin (i.e. expenses of net profit).,
Thus, under this method, the price per unit of product is calculated by adding desired profit to the total cost per unit. Under this policy, the price per unit can be calculated as under:

The amount of desired profit varies from enterprise to enterprise, product to product, and time to time. Some business enterprises determine a certain percentage of profit and calculate the price per unit of their product by adding this much percentage of profit to the cost of production, such as
Price per unit = Total Cost + 10% Profit.
This method assumes that no product is sold at a loss. This method is used when there is no competition in the market or when the cost of production of a product of all the manufacturers is almost equal. This method is used by retail traders also. This method of pricing is based on simple arithmetic of adding a fixed percentage of profit to the unit cost. Thus, the retail price of a product can be the cost of the manufacturer plus the margin of profit of the wholesaler plus s the margin of profit to the retailer. Therefore, this method is also known as “The sum of margin method”.
2. Marginal or Incremental Cost pricing Method Linder this method, price is so set that it covers only the marginal costs and not the total costs. When a new product is introduced, such a method is usually adopted. By this method, labor may be kept employed even during slack seasons. However, this method cannot be followed for long as the fixed cost has also to be taken into consideration. If certain products are period on this basis and others on a cost-plus basis, then some customers would be required to pay higher, prices while others would get the product at the cost of the last unit.
3. Break-Even Analysis: Break-even points is the volume of sales at which the total sales revenue of the product is equal to its total cost. In other words, it can also be said that the break-even point is the volume of sales at which there is no profit and no loss. Therefore, this method is also known as the’ profit No loss Pricing Method’.
Under this method, break-even price (B.E.P.) can be calculated as under

4. Rate of Return of Target pricing method: Under this method, first of all, an arbitrary desired rate of profit on the capital employed/invested is determined by the enterprise. The total desired profit is then calculated on the basis of this rate of return. The total desired profit is then added to the total cost of production and thus, the price per unit of the product is determined. In short, this method is good only when there is no competition in the market. The rate of investment is decided arbitrarily.
2. Methods of determining the price on the basis of market conditions: The price of a product must be determined keeping in view the conditions prevailing in the market. If market conditions are not duly considered before determining the price of products, the marketing objectives of the enterprise can’t be achieved.
Following are the methods of price determination based on market conditions:
1. Pricing to meet Competitions: Under this method, the price of a product is determined on the basis of the price of a competitor’s products. This method is used when the firm is new in the market. ; This method is used when there is tough competition in the market.
The method is based on assumption that a new product will create: demand only when its price is competitive. In such a case, the film follows the market trader.
2. Price below Competitive level: Under this method, the pricing firm determines the price of its. products below the competitive level i.e. below the price of the same products of the competitors. This policy pays where customers are price conscious and the method is used by new firms entering the market.
3. Pricing above Competitive level: Under his policy, the seller may set higher than avg. prices for his product to convey an impression that his products are above avg. equality. The buyer may pay this price in the belief that it is of higher quality.
Manufacturers sometimes keep more than average price to give some margin of profit to a middleman in return for the latter’s aggressive sales promotion. For a consumer product to compete successfully at a price above the market, it must either be so strongly differentiated that consumers believe it is superior to a competitive brand, or middleman must enthusiastically and heavily promote.
4. Purchasing power pricing method: Some commercial undertakings determine the product price by keeping in mind the purchasing power of their consumers. This method is generally used for the determination of the price for fashionable products.
Question 7.
Explain the various methods/Tools of Sales Promotion?
Answer:
Types, Methods/Tools of Sales Promotion: For a marketer resorting to sales promotion, a variety of tools and techniques are available. Sales promotion letters, catalogs, point of purchase displays, customer service programs, demonstrations, free samples discounts, contests, sweepstakes, premiums, and coupons are the Commonly employed methods of sales promotion.
Sales promotion can be divided into the following kinds:
- Consumer/Customer Promotion Methods.
- Dealer Sales Promotion
- SalesForce.
1. Consumer/Customer Promotion Methods: Consumer promotion methods of sales promotion are the methods that directly encourage consumers to buy the product in more and more quantity. These methods may be as follows
1. Distribution of free samples: Under this method, the producer distributes free samples of the product to the consumer. They are also given to introduce a new product and expand the market. It increases the sales volume when the product is a new one to the customers. It is an effective device in which the product is purchased often, i.e. soaps, detergents, tea or coffee, etc. It is a method of demand creation, sampling gives a chance to the consumers to compare the products with other substitutes. Samples are given to doctors by medical representatives.
The samples may be delivered door to door, sent by mail, picked up in a store, attached to another product, etc. It is the most effective way to introduce a new product.
However, sampling is not always a good marketing strategy. It is not justified in the case of
(a) Well established product.
(b) a product that is not the superior in-store way to competing products or whose points of superiority would not easily be recognized by the consumers.
(c) a product with a slow turnover.
(d) a product with a narrow margin of profit.
(e) a highly fragile, perishable, or bulky product.
2. Coupons: A coupon certificate that reduces the price. When a buyer gives a coupon to the dealer, he gets the products at a lower price. Coupons are accepted as cash by retailers coupons normally perform two specific functions for the manufacturer. Firstly, they enthuse the consumers to exploit the bargain. Secondly, they serve as an inducement to the channel for stocking the items. The manufacturer thus succeeds in attracting consumers as well as in promoting the channel to stock the merchandise by introducing coupons. They are useful for introducing a new product as well as for strengthening the sale of an existing product.
According to John F. Luick and Zieglar, “A coupon is a certificate that when presented for redemption at a retail store, entitles the bearer to a stated saving in the purchase of a specific product.”
3. Price Reduction or price off promotion: It stimulates sales during a slump season. It gives a temporary, discount to the consumers, i.e. goods are offered at a rate less than the labeled rate. Fans are sold at a reduced rate in the rainy season.
For example, Hawkins pressure cookers have come up with several sales promotion schemes during the last few years. In one of these schemes, Hawkins announced.
Upto Rs. 150/- off on a new Hawkins in exchange for any old pressure cooker.
4. Contests: These may be conducted to attract new customers or to introduce a new product by asking the prospects to state in a few words why they prefer a particular product. For entering into the contest, the prospect is first required to purchase a product and submit the evidence (e.g. a label or package or card wanted to the product) with an entry form for a contest. Through such contests, even the persons who are not inclined to purchase otherwise, also get interested in using the product.
According to John. F. Lick and W.L. Zieglar, “A contest is sales promotion device in which the participants compete for a prize or prizes on the basis of their skill in fulfilling a certain requirement, usually analytical or creative.”
Sponsor companies on the T.V. are adopting the quiz and contest route as a profitable means of establishing brand equality over a period of time. lit programs like Philips Top ten, four with, Close-up brand equity has been used as a format. These programs have gained considerable popularity and they will be remembered for along time. T.V. has gained a substantial audience in India.
5. Demonstration: It is the introduction to educate the consumers in the manner of using the product. It is a promotional tool that attracts the attention of consumers. When products are complex and of a technical nature, the demonstration is necessary, e.g. computers field machinery, electrical pumping set, etc. The demonstration is done in front of consumers for mixy, wet grinder in retail shops, etc.
6. Premium It is a temporary price reduction wealth increases the instinct of the buyers. Products are offered free or at a reduced cost as an inducement for purchasing. It is offered to consumers for consumer goods like soap, brush, paste, washing powder, glucose, etc. For instance, when the customer buys two soaps, a soapbox is given free along with the soaps. The soapbox is a premium, It certain cases, the price is reduced. The reduced amount is a premium.
According to George Wuistopto is “A Premium is an item of Merchandise that is offered at cost or at relatively low cost as a bonus to purchases of a particular product.”
According to Alfred Gross, “A premium is an article of merchandise or another thing of value offered as an inducement to purchase a product or service.”
7. Money Refund Offers: If the purchaser is not satisfied with the product, a part or all of the purchaser’s money will be refunded. It is stated on the package. It will create new users and will strengthen brand loyalty. Some times, the money will be refunded, if 10 top covers or 10 empty bottles or 10 packages are sent a book to the manufacturers.
8. Trade fairs and Exhibitions: India is a country in which various fairs and exhibitions are organized at different levels in different parts. Some producers take part in these fairs and exhibitions and display their products.
9. Special Prizes: Under this method, every purchase of the product is given a prize coupon during a certain period. All the coupons distributed during this period are put into a box and a lottery is drawn therefrom. The winners are given some attractive prizes. There, this scheme also compels the consumers to purchase and use the product.
10. Bonus Stamps: Such bonus stamps are issued to the consumers by the retailers or manufacturer in proportion to their purchases. The consumer goes on collecting stamps until he has sufficient quantity to obtain the desired merchandise in exchange for the stamps.
11. Buy-Back Allowance: Allowance is given following a previous trade deal. That is, a trader deal offers a certain amount of money for a new purchase based on the purchased quantity. It prevents a decline in the post-trade deal. Buyer’s Motivation is increased because of their co-operation on the first trade deal, for example when Cinthol and Mav soaps are purchased, the salesman gives one mug and two coupons free.
12. After-Sale Service Under this method, the producer gives a guarantee to the consumers to maintain the product for a certain specified period.
2. Dealer Sales Promotion: Dealer promotion methods include all the methods which are adopted with a view to encouraging the dealers and distributors to purchase and resell the product in more and more quantity. Dealer promotion methods include the following methods
1. ContestThis is an indirect way of hosting the sales. This is in the form of the window display, store display, etc. The prize is awarded for outstanding achievements.
2. Buying Allowance Discount The buying allowance or discount is offered to the dealer to induce him to buy the manufacturer’s product.
3. Premium Premium is a product usually offered free at less than its price to encourage consumers to buy other products.
4. Incentive By using this method, producers announce some incentives to their salesman so that they may take maximum interest in the sale of the product.
5. Loan Facility The producer allows credit to their dealers, based on the quantity purchased by them. This enables them to purchase bulk quantities.
6. Advertising Allowance The allowance is offered to the dealer to display the manufacturer’s product.
7. GiftRalli Fan Co. arranges for a free holiday.
8. Point of purchase The point of purchase display is the silent salesman that calls the attention to the product in the hope of buying action.
9. Dealers listed promotion This method induces dealers to stock the products and consumers are encouraged to buy the products from the listed dealers.
10. Training Through this method, producers train their selling force.
Try Once: