Here we are providing Class 12 Chemistry Important Extra Questions and Answers Chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids. Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions are the best resource for students which helps in Class 12 board exams.
Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 12 Important Extra Questions Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Important Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their reactivity in nucleophilic addition reactions: ethanal, propanal, propanone, butanone. (CBSE Delhi 2012)
Answer:
butanone < propanone < propanal < ethanal
Question 2.
Which of the following compounds would undergo the Cannizzaro reaction? Benzaldehyde, Cyclohexanone, 2- Methylpentanal. (CBSE Sample Paper 2019)
Answer:
Benzaldehyde
Question 3.
Draw the structure of semicarbazone of cyclopentanone. (CBSE 2019C)
OR
Draw the structure of the product formed when propanal is treated with zinc amalgam and concentrated hydrochloric acid.
Answer:
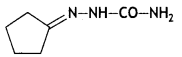
OR
Question 4.
Write the IUPAC name of the following: (CBSE AI 2012)
![]()
Answer:
Pent-2-enal.
Question 5.
Write the structure of 3-methylbutanal. (CBSE Delhi 2013)
Answer:
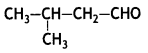
Question 6.
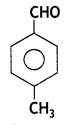
Write the structure of the p-Methylbenzal- dehyde molecule. (CBSE Delhi 2013, 2014)
Answer:
Question 7.
Draw the structure of the compound whose IUPAC name is 4-chloropentan 2-one. (CBSE Delhi 2008, CBSE AI 2011, 2013, 2014)
Answer:
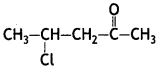
Question 8.
Draw the structural formula of a 1-phenyl propane-2-one molecule. (CBSE 2010)
Answer:
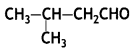
Question 9.
Draw the structure of 3-methylbutanal. (CBSE 2011, CBSE Delhi 2013)
Answer:
![]()
Question 10.
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their reactivity in nucleophilic addition reactions:
ethanal, propanal, propanone, butanone. (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
butanone < propanone < propanal < ethanal
Question 11.
Write the IUPAC name of (CBSE 2012)
Ph — CH = CH — CHO.
Answer:
3-Phenyl prop-2-en-al.
Question 12.
Rearrange the following compounds in the increasing order of their boiling points:
CH3 – CHO, CH3 – CH2 – OH, CH3 – CH2 – CH3 (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
CH3CH2CH3 < CH3CHO < CH3CH2OH
Question 13.
Ethanol is soluble in water. Why? (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
Ethanol is soluble in water because of hydrogen bonding between the polar carbonyl group of ethanal and water molecules:
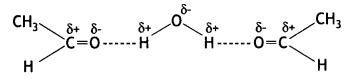
Question 14.
Write the IUPAC name of the compound (CBSE Delhi 2014)
![]()
Answer:
3-Hydroxybutanoic acid
Question 15.
Write the IUPAC name of the compound (CBSE Delhi 2014)
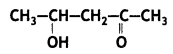
Answer:
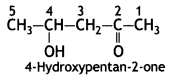
Question 16.
Write the IUPAC name of the compound (CBSE Delhi 2014)
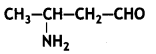
Answer:
3-Aminobutanal
Question 17.
Write the IUPAC name of the following compound: (CBSE AI2019)
![]()
Answer:
But-3-en-2-one
Question 18.
Write the IUPAC name of the following compound: (CBSE AI 2019)
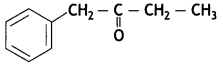
Answer:
1-Phenylbutan-2-one.
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Important Extra Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Write structures of compounds A and B in each of the following reactions: (CBSE Delhi 2019)
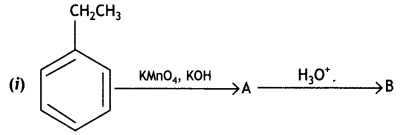
Answer:
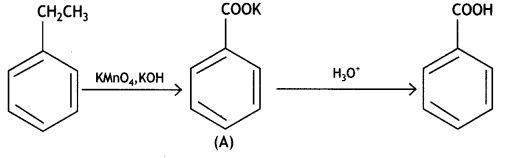
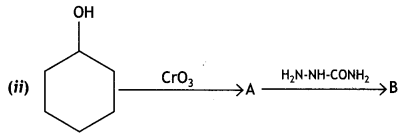
Answer:
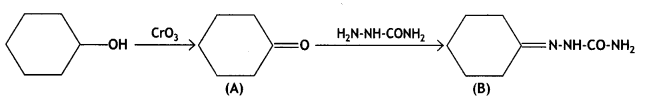
Question 2.
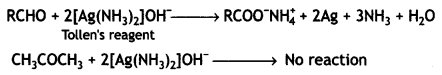
What is Tollen’s reagent? Write one use of this reagent. (CBSE 2010)
Answer:
The ammoniacal solution of silver nitrate is called Tollen’s reagent. It is used as an oxidizing reagent and helps to distinguish between aldehydes and ketones. Aldehydes are oxidized by Tollen’s reagent whereas ketones are not.
Question 3.
Name the reagents used in the following reactions: (CBSE Delhi 2015)
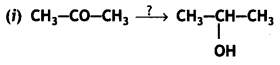
Answer:
Lithium aluminium hydride, LiAlH4
![]()
Answer
Alkaline potassium permanganate (KMnO4), KOH
Question 4.
Distinguish between
C6H5CH = CH – COCH3 and C6H5CH = CH CO CH2 CH3 (CBSE AI 2016)
Answer:
Heat both the compounds with NaOH and l2. C6H5CH = CHCOCH3 gives yellow ppt of iodoform. C6H5CH = CHCOCH2CH3 does not give yellow ppt. of iodoform.
Question 5.
Arrange the following in the increasing order of their reactivity in nucleophilic addition reactions.
CH3CHO, C6H5CHO, HCHO (CBSE AI 2016)
Answer:
C6H5CHO < CH3CHO < HCHO
Question 6.
Write the product in the following reaction: (CBSE AI 2017)
![]()
Answer:
![]()
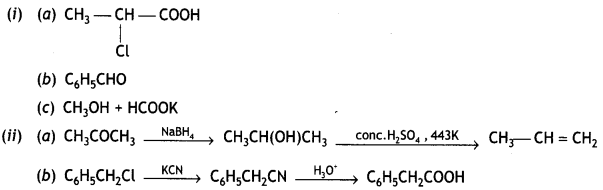
Question 7.
Write the structure of the products formed: (CBSE Sample Paper 2019)
(a) CH3CH2COOH ![]()
Answer:
CH3 – CH(Cl) – C00H
(b) C6H5COCl ![]()
Answer:
C6H5CHO
Question 8.
Name the reagents in the following reactions: (CBSE AI 2015)
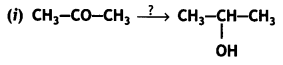
Answer:
Lithium aluminium hydride, LiAlH4
![]()
Answer:
Alkaline potassium permanganate (KMnO4), KOH
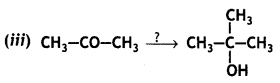
Answer:
CH3 Mg Br, H3O+
![]()
Answer:
Cl2, P (Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction)
Question 9.
Predict the organic products of the following reactions:
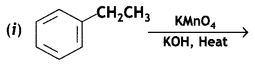
Answer:
Answer:
Answer:
Answer:
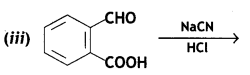
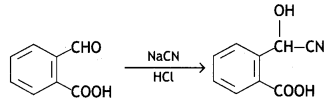
Question 10.
Describe how the following conversions are carried out:
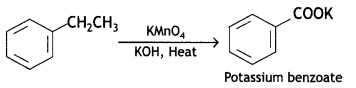
(i) Toluene to benzoic acid
Answer:
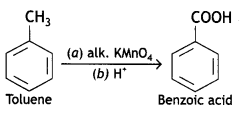
(ii) Bromobenzene to benzoic acid (CBSE AI 2013)
Answer:
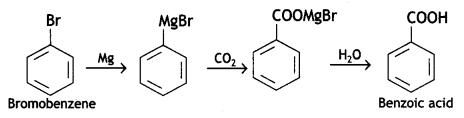
(iii) Ethylcyanide to ethanoic acid
Answer:
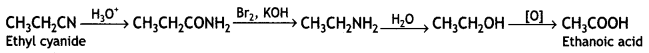
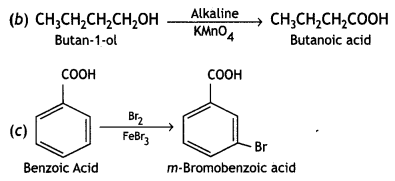
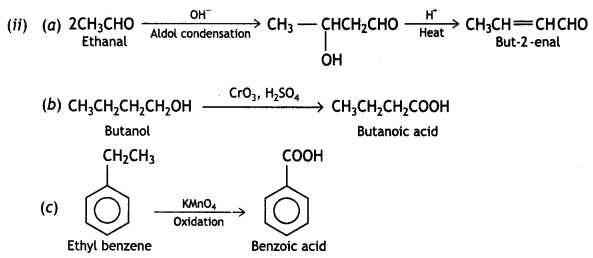
(iv) Butan-1-ol to butanoic acid (CBSE Delhi 2010)
Answer:
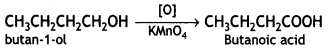
Question 11.
Write the structures of A, B, C, and D in the following reaction: (CBSE AI 2016)
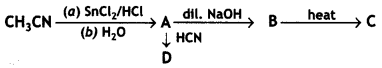
Answer:
Question 12.
Aromatic carboxylic acids do not undergo Friedel Crafts reaction. Explain. (CBSE Al 2018)
Answer:
Aromatic carboxylic acids do not undergo Friedel Crafts reaction because -COOH group is deactivating and the catalyst aluminum chloride (Lewis acid) gets bonded to the carboxyl group.
Question 13.
pKa value of 4-nitrobenzoic acid is lower than that of benzoic acid. Explain. (CBSE AI 2018)
Answer:
Due to the presence of a strong electron-withdrawing (-NO2) group in 4-nitrobenzoic acid, it stabilizes the carboxylate anion and hence strengthens the acid. Therefore, 4-nitrobenzoic acid is more acidic than benzoic acid and its pKa value is lower.
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Important Extra Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1.
Complete the following reactions:
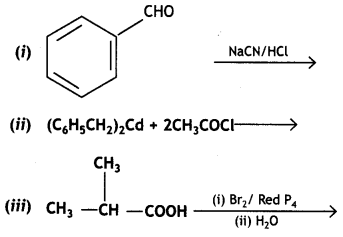
Or
Write chemical equations for the following reactions:
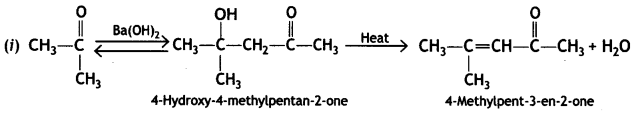
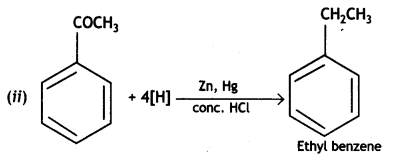
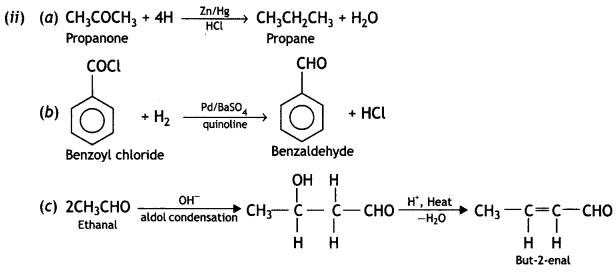
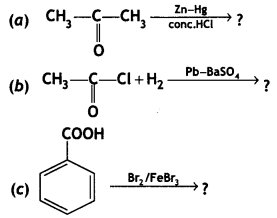
(i) Propanone is treated with dilute Ba(OH)2.
(ii) Acetophenone is treated with Zn(Hg)/Conc. HCI
(iii) Benzoyl chloride is hydrogenated in presence of Pd/BaSO4. (CBSE Delhi 2019)
Answer:
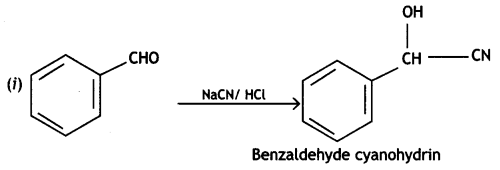
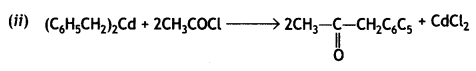
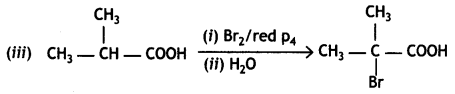
Or
![]()
Question 2.
Predict the products of the following B reactions: (CBSE Delhi 2015)
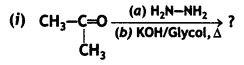
Answer:
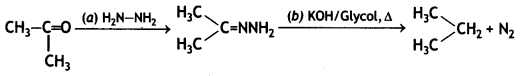
![]()
Answer:
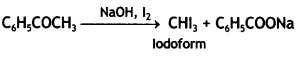
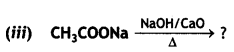
Answer:
Question 3.
Predict the products of the following reactions: (CBSE 2015)
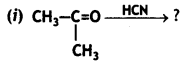
Answer:
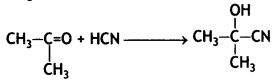
![]()
Answer:
![]()
![]()
Answer:
![]()
Question 4.
What happens when
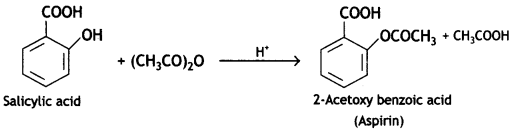
(a) Salicylic acid Is treated with (CH3CO)2O/H+?
Write a chemical equation in support of your answer. (CBSE AI 2019)
Answer:
Salicylic acid is treated with acetic anhydride In the presence of H+ to give aspirin.
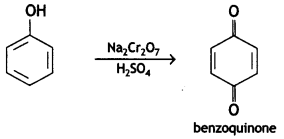
(b) Phenol is oxidized with Na2Cr2O7/H+?
Answer:
Phenol in the presence of acidified sodium dichromate gives benzoquinone.
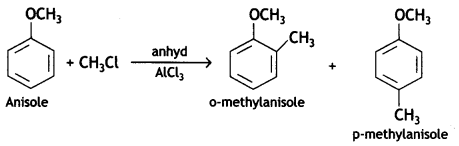
(C) Anisole Is treated with CH3Cl/anhydrous AlCl3?
Answer:
Question 5.
Draw the structures of the following compounds:
(i) 3-Methylbutanal
Answer:
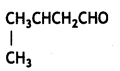
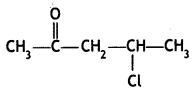
(ii) 4-Chlocopentan-2-one
Answer:
(iii) 4-Methylpent-3-en-2-one
Answer:
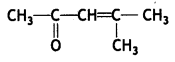
(iv) p-Methyl benzaldehyde (CBSE AI 2014)
Answer:
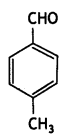
Question 6.
How will you bring about the following conversions in not more than two steps?
(i) Propanone to propene (CBSE Delhi 2017)
Answer:
Propanone to propene
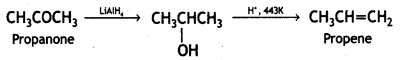
(ii) Propanal to butanone
Answer:
Propanal to butanone
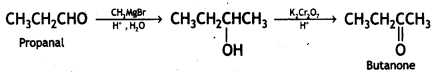
(iii) Benzaldehyde to benzophenone
Answer:
Benzaldehyde to benzophenone
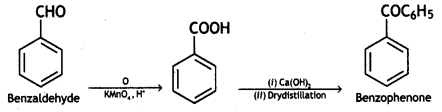
(iv) Benzaldehyde to 3-phenyl propan – 1-ol
Answer:
Benzaldehyde to 3- phenyl propan -1 -ol
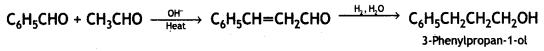
(v) Benzaldehyde to α-hydroxyphenyl acetic acid
Answer:
Benzaldehyde to α-hydroxyphenyl acetic acid
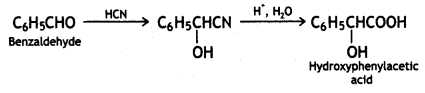
(vi) Ethanol to 3-hydroxybutanal
Answer:
Ethanol to 3-hydroxybutanal
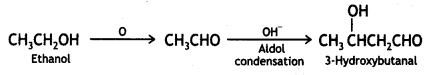
Question 7.
Convert the following:
(i) Ethanal to propanone. (CBSE AI 2018)
Answer:
Ethanal to propanone
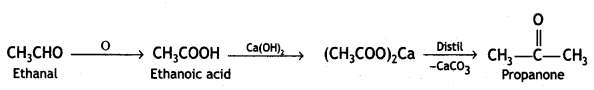
(ii) Ethanal to lactic acid.
Answer:
Ethanal to lactic acid
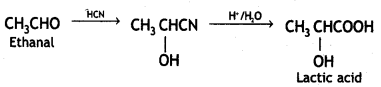
(iii) Ethanal to 2-hydroxy-3-butenoic acid.
Answer:
Ethanal to 2-hydroxy-3-butenoic acid
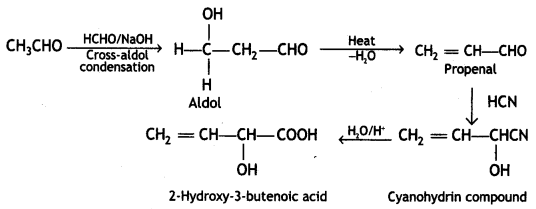
(iv) Acetaldehyde to formaldehyde.
Answer:
Acetaldehyde to formaldehyde
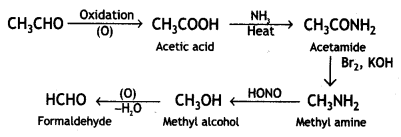
(v) Formaldehyde to acetaldehyde.
Answer:
Formaldehyde to acetaldehyde
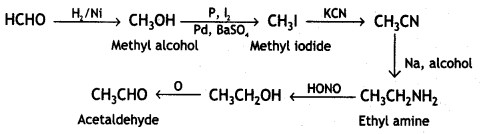
(vi) Acetaldehyde to crotonic acid.
Answer:
Acetaldehyde to crotonic acid
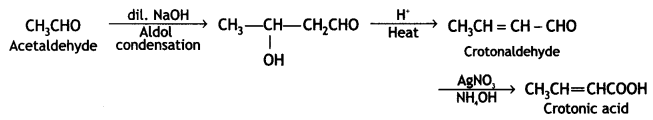
Question 8.
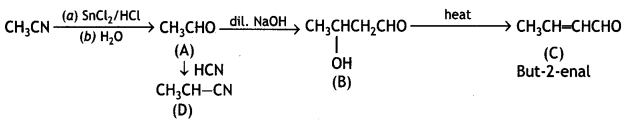
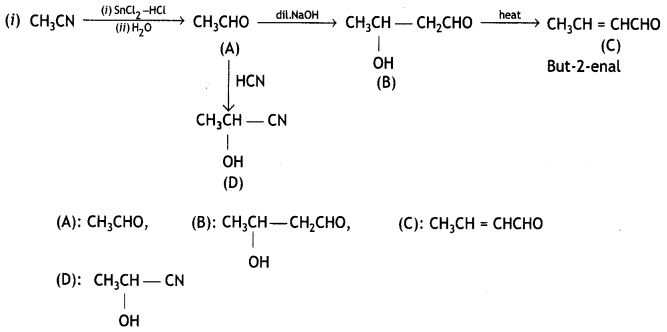
A compound ‘X’ (C2H4O) on oxidation gives ‘Y’ (C2H4O2). ‘X’ undergoes haloform reaction. On treatment with HCN ‘X’ forms a product ‘V which on hydrolysis gives 2-hydroxy propanoic acid.
(i) Write down structures of ‘X’ and ‘Y’.
(ii) Name the product when ‘X’ reacts with dil NaOH.
(iii) Write down the equations for the reactions involved. (CBSE Sample Paper 2007)
Answer:
Compound ‘X’ (C2H4O) is oxidized to ‘Y’ (C2H4O2). Since it undergoes a haloform reaction, it must be acetaldehyde.
(i) X = CHCHO Y = CH3COOH
On treatment with HCN, X gives cyanohydrin which on hydrolysis gives 2-hydroxypropanoic acid.
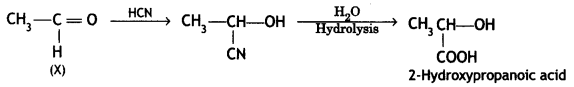
(ii) When ‘X’ reacts with dil. NaOH, undergoes an aldol condensation reaction forming aldol which on heating gives but-2-enal.
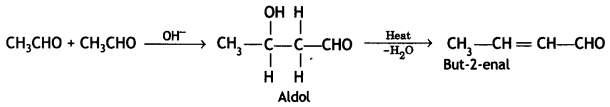
(iii) Equations for reactions
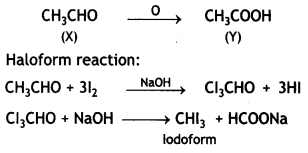
Other equations are given above.
Question 9.
Complete the following reactions:
![]()
Answer:
![]()
Answer:
![]()
Answer:
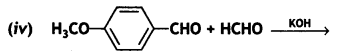
Answer:
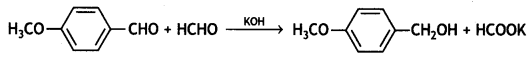
![]()
Answer:
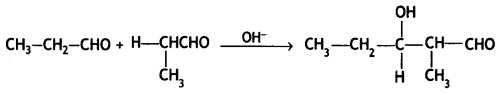
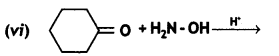
(CBSE Sample Paper 2017 – 2018)
Answer:
![]()
(CBSE Delhi 2013)
Answer:
![]()
![]()
(CBSE AI 2013)
Answer:
![]()
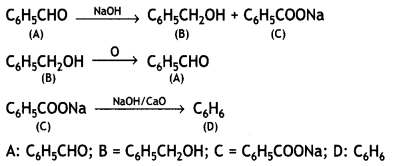
Question 10.
(i) An organic compound (A) has a characteristic odor. On treatment with NaOH, it forms two compounds (B) and (C). Compound (B) has molecular formula C7H80 which on oxidation gives back (A). The compound (C) is a sodium salt of an acid. When (C) is treated with soda lime it yields an aromatic hydrocarbon (D). Deduce the structures of (A), (B), (C) and (D). Write the sequence of reactions involved.
Answer:
The compound A is C6H5CHO, benzaldehyde having a characteristic odor. The reactions are:
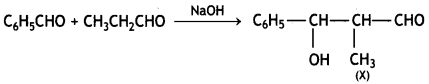
(ii) Complete each synthesis by filling the missing starting materials, reagents, or products. (X and Z).
(a) C6H5CHO + CH3CH2CHO NaOH ![]() X
X
Answer:
(b) CH3(CH2)9 COOC2H5 ![]() CH3(CH2),CHO
CH3(CH2),CHO
Answer:
![]()
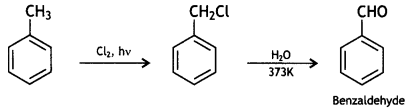
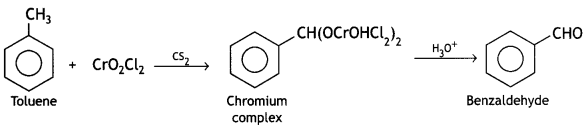
(iii) How will you bring about the following conversions in not more than two steps?
(a) Toluene to benzaldehyde
Answer:
(b) Ethylcyanide to 1-phenylpropanoid. (CBSE Sample Paper 2011)
Answer:
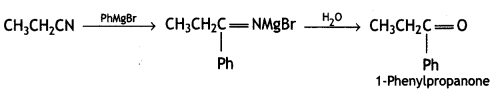
Question 11.
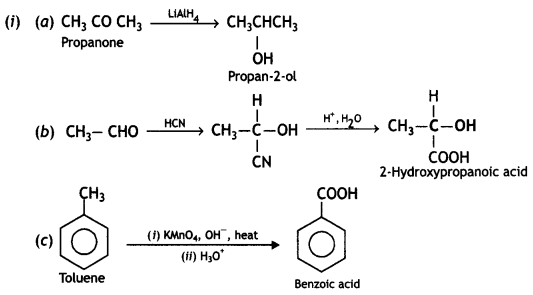
(i) How do you convert the following?
(a) Ethanal to propanone
(b) Toluene to benzoic acid
OR
(ii) (A), (B), and (C) are three non-cyclic functional isomers of a carbonyl compound with molecular formula C4H8O. isomers (A) and (C) give positive Tollens’ test whereas isomer (B) does not give Tollens’ test but gives positive iodoform test. Isomers (A) and (B) on reduction with Zn(Hg)/conc. HCI gives the same product (D).
(a) Write the structures of (A), (B), (C), and (D).
(b) Out of (A), (B), and (C) isomers, which one is least reactive towards the addition of HCN? (CBSEAI 2018)
Answer:
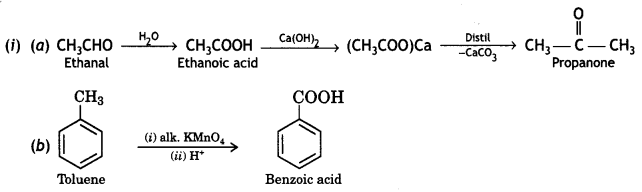
OR
(ii) (a) Out of A, B, and C, (A) and (C) give positive Tollens’ test, and therefore, these are aldehydes. (B) does not give Tollens’ test and therefore, it is a ketone, with a group because it gives positive iodoform test. Thus, the three isomers are:
a group because it gives positive iodoform test. Thus, the three isomers are:
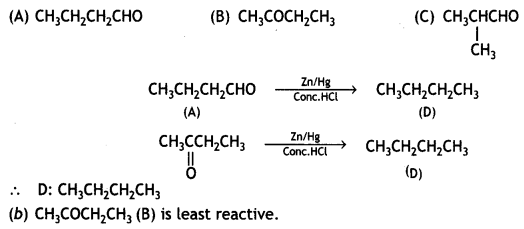
Question 12.
Predict the products of the following reactions:
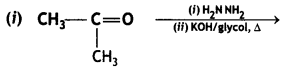
(CBSE Delhi 2015)
Answer:
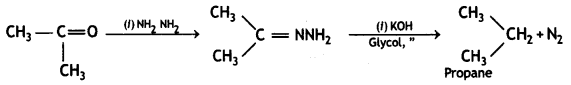
![]()
(CBSE Delhi 2015)
Answer:
![]()
![]()
(CBSE AI 2015)
Answer:
![]()
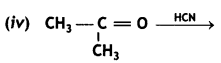
(CBSE AI 2015)
Answer:
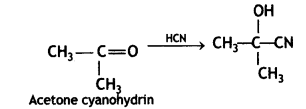
(CBSE AI 2017)
Answer:
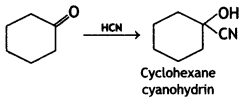
(CBSE AI 2017)
Answer:
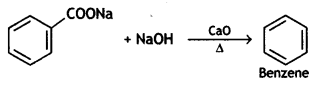
Question 13.
Write the structures of A, B, C, D, and E in the following reactions: (C8SE Delhi 2016)
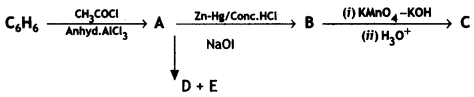
Answer:
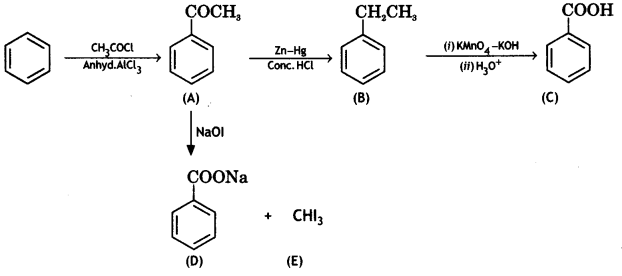
Question 14.
(a) Give chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
(i) Ethanal and Propanone.
(ii) Pentan-2-one and Pentan-3-one.
(b) Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their acid strength: Benzoic acid, 4- Nitrobenzoic acid, 3,4 -Dinitrobenzoic acid, 4- Methoxybenzoic acid.
OR
Compare the reactivity of benzaldehyde and ethanal towards nucleophilic addition reactions. Write the cross aldol condensation product between benzaldehyde and ethanal. (CBSE Sample Paper 2019)
Answer:
(a) (i)
| Experiments | Ethanal | Propanone |
| 1. Tollen’s Test: Warm the organic compound with freshly prepared ammoniacal silver nitrate solution (Tollen’s reagent). | A bright silver mirror is produced. | No silver mirror is formed. |
| 2. Fehling’s Test: Heat the organic compound with Fehling’s reagent. | A reddish-brown precipitate is obtained. | No precipitate is obtained. |
| Anyone test |
Acetaldehyde (Ethanal) and Acetone (Propanone)
(i) Acetaldehyde gives silver mirror with Tollen’s reagent.
![]()
Acetone does not give this test.
(ii) Acetaldehyde gives red ppt with Fehling solution.
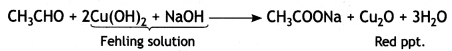
(ii) Pentan-2-one and Pentan-3-one
| Experiment | Pentan-2-one | Pentan-3-one |
| Iodoform Test: The organic compound is heated with iodine in presence of sodium hydroxide solution. | A yellow precipitate is obtained. | No yellow precipitate is obtained. |
Pentan-3-one and Pentan-2-one
(i) Pentan-2-one forms yellow ppt with an alkaline solution of iodine (iodoform test), but pentane-3-one does not give iodoform test.
CH3COCH2CH2CH3 + 3I2+ 4NaOH → CH3CH2CH2COONa + CHI3 + 3H20 + 3NaI
(ii) Pentan-2-one gives white ppt with sodium bisulphite while pentan-3-one does not.
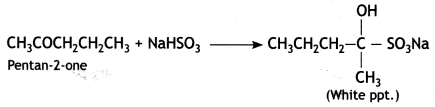
Or any other suitable test.
(b) 4- Methoxybenzoic add < Benzoic acid < 4- Nitrobenzoic acid < 3,4-Dinitrobenzoic acid Effect of substituents on acidic strength of acids. The substituents have a marked effect on the acidic strength of carboxylic acids. The nature of substituents affects the stability of the conjugate base (carboxylate ion) and hence affects the acidity of the carboxylic acids.
In general, electron-withdrawing groups (EWG) increase the stability of the carboxylate ion by delocalizing the negative charge and hence increase the acidity of the carboxylic acid. Conversely, electron-donating groups (EDG) decrease the stability of the carboxylate ion by intensifying the negative charge and hence decrease the acidity of the carboxylic acid.
OR
The carbon atom of the carbonyl group of benzaldehyde is less electrophilic than the carbon atom of the carbonyl group present in ethanol. The polarity of the carbonyl group is reduced in benzaldehyde due to resonance hence less reactive than ethanal.
Aromatic Aldehydes and Ketones
In general, aromatic aldehydes and ketones are less reactive than the corresponding aliphatic analogs. For example, benzaldehyde is less reactive than aliphatic aldehydes. This can be easily understood from the resonating structures of benzaldehyde as shown below:
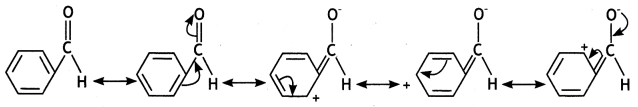
It is clear from the resonating structures that due to the electron releasing (+I effect) of the benzene ring, the magnitude of the positive charge on the carbonyl group decreases, and consequently it becomes less susceptible to the nucleophilic attack. Thus, aromatic aldehydes and ketones are less reactive than the corresponding aliphatic aldehydes and ketones.
However, amongst aromatic aldehydes and ketones, aromatic aldehydes are more reactive than alkyl aryl ketones which in turn are more reactive than diaryl ketones. Thus, the order of reactivity of aromatic aldehydes and ketones is:
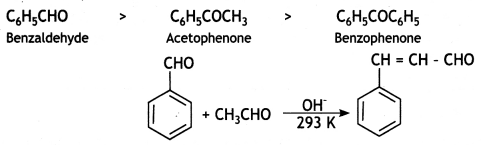
Question 15.
(i) Illustrate the following name reaction giving a suitable example:
(a) Clemmensen reduction
(b) Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction
(ii) How are the following conversions carried out?
(a) Ethylcyanide to ethanoic acid
(b) Butan-1-ol to butanoic acid
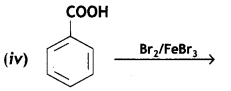
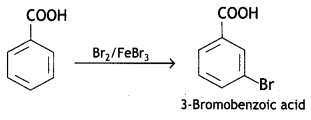
(c) Benzoic acid to m-bromobenzoic acid .
OR
(i) Illustrate the following reactions giving a suitable example for each.
(a) Cross aldol condensation
(b) Decarboxylation
(ii) Give simple tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
(a) Pentan-2-one and Pentan-3-one
(b) Benzaldehyde and Acetophenone
(c) Phenol and Benzoic acid (CBSE Delhi 2012)
Answer:
(i) (a) Clemmensen reduction
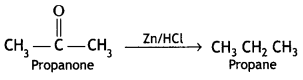
(b) Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction
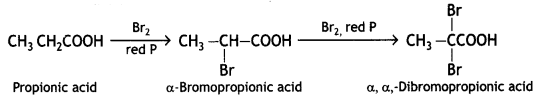
(ii)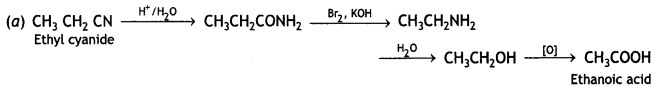
OR
(i) (a) Cross Aldol condensation
![]()
(b) Decarboxylation
![]()
(ii) (a) Pentan-2-one and pentan-3-one can be distinguished by iodoform test
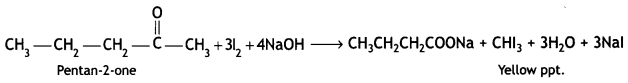
Pentan-3-one does not give this test.
(b) Benzaldehyde and acetophenone: Benzaldehyde forms a silver mirror with ammoniacal silver nitrate solution (Tollen’s reagent).
![]()
Acetophenone does not react with Tollen’s reagent.
(c) Phenol and Benzoic acid: Benzoic acid reacts with NaHC03 to give effervescence due to the evolution of CO2.
![]()
Phenol does not give effervescence.
Question 16.
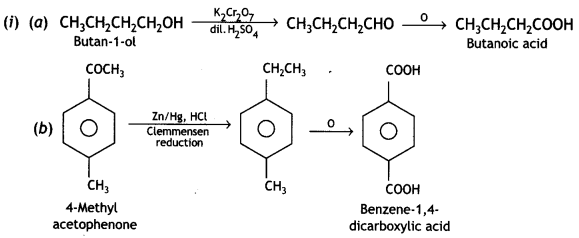
(i) Write a suitable chemical equation to complete each of the following transformations:
(a) Butan-1-ol to butanoic acid
(b) 4-Methylacetophenone to benzene-1, 4-dicarboxylic acid.
(ii) An organic compound with molecular formula C9H10O forms 2,4-DNP derivative, reduces Toilen’s reagent, and undergoes Cannizzaro’s reaction. On vigorous oxidation, it gives 1, 2-benzene dicarboxylic acid. Identify the compound.
OR
(i) Give chemical tests to distinguish between (a) Propanol and propanone
(b) Benzaldehyde and acetophenone
(ii) Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their property as indicated:
(a) Acetaldehyde, Acetone, Methyl tert-butyl ketone (reactivity towards HCN)
(b) Benzoic acid, 3,4-Dinitrobenzoic acid, 4-Methoxybenzoic acid (acid strength)
Answer:
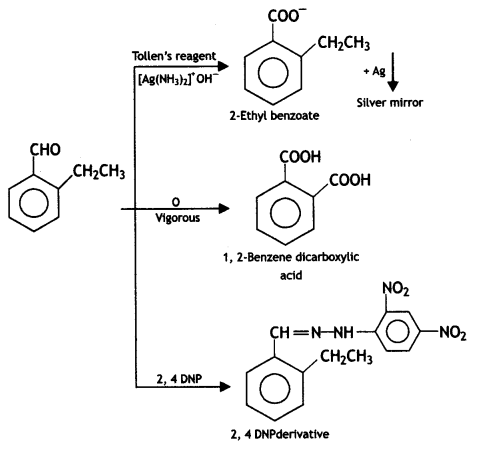
(ii) The given compound forms a 2,4-DNP derivative. Therefore, it is an aldehyde or ketone. Since it reduces Tollen’s reagent, it must be an aldehyde. The compound undergoes Cannizzaro’s reaction, so it does not contain hydrogen. On vigorous oxidation, it gives 1,2-benzene dicarboxylic acid, which means that it must be containing an alkyl group at 2-position with respect to the CHO group on the benzene ring.
The molecular formula suggests it should be
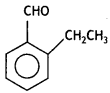 (2- Ethytbenza(dehyde)
(2- Ethytbenza(dehyde)
Answer:
(i) (a) Propanone gives iodoform test but propanol does not. When propanone is heated with aqueous sodium carbonate and iodine solution, a yellow precipitate of iodoform is obtained.
![]()
Propanol does not give this test.
(b) Acetophenone forms yellow ppt. of iodoform with an alkaline solution of iodine (iodoform test). Benzaldehyde does not react.
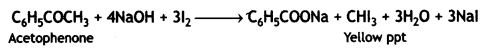
(ii) (a) Methyl tert-butyl ketone < Acetone < Acetaldehyde.
(b) 4-Methoxybenzoic acid < Benzoic add < 3, 4-Dinitrobenzoic acid.
(c) (CH3)2CHCOOH < CH3CH(Br)CH2COOH < CH3CH2CH(Br)COOH
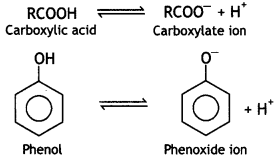
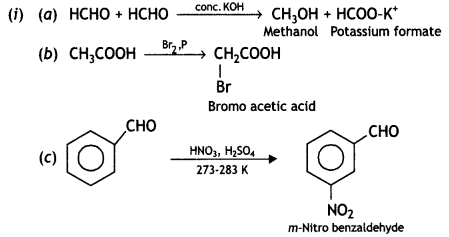
Question 17.
(i) Although phenoxide ion has more resonating structures than carboxylate ion, the carboxylic acid is a stronger acid than phenol. Give two reasons.
(ii) How will you bring about the following conversions?
(a) Propanone to propane
(b) Benzoyl chloride to benzaldehyde
(c) Ethanal to but-2-enal
OR
(i) Complete the following reactions:
![]()
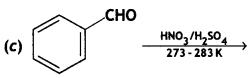
(ii) Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
(a) Ethanal and Propanal
(b) Benzoic acid and Phenol (CBSE AI 2013)
Answer:
(i) The carboxylic acids are stronger acids than phenols. The difference in the relative acidic strengths can be understood if we compare the resonance hybrid structures of carboxylate ion and phenoxide ion.
The resonance hybrids may be represented as:

(a) The electron charge in the carboxylate ion is more dispersed in comparison to the phenoxide ion since there are two electronegative oxygen atoms in the carboxylate ion as compared to only one oxygen atom in the phenoxide ion.
(b) Carboxylate ion is stabilized by two equivalent resonance structures in which negative charge is on more electronegative 0 atoms. But phenoxide ion has non-equivalent resonance structures in which the negative charge is also on a less electronegative carbon atom.
Therefore, the carboxylate ion is relatively more stable as compared to the phenoxide ion. Thus, the release of H+ ions from carboxylic acid is comparatively easier or it behaves as a stronger acid than phenol.
OR
(ii) (a) Ethanal gives a yellow ppt. of iodoform on heating with iodine and NaOH solution whereas propanal does not give.
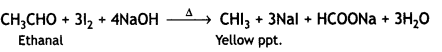
(b) Benzoic acid reacts with NaHC03 to give effervescence due to the liberation of CO2.
C6H5COOH + NaHCO3 → C6H5COONa + H20 + CO2
Phenol does not give effervescence.
Phenol gives violet color with FeCl3 solution but benzoic acid does not give such color.
Question 18.
(i) How will you convert the following:
(a) Propanone to Propan-2-ol
(b) Ethanal to 2-hydroxypropanoic acid
(c) Toluene to benzoic acid
(ii) Give a simple chemical test to distinguish between:
(a) Pentan-2-one and Pentan-3-one
(b) Ethanal and Propanal
OR
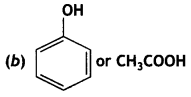
(i) Write the products of the following reactions:
(ii) Which acid of each pair shown here would you expect to be stronger? (CBSE AI 2013)
(a) F – CH2 – COOH or Cl – CH2 – COOH OH
Answer:
(ii) (a) Pentan-2-one forms yellow ppt. with an alkaline solution of iodine (iodoform test), but pentane-3-one does not give iodoform test.
![]()
(b) Ethanal gives a yellow ppt. of iodoform on heating with iodine and NaOH solution whereas propanal does not give.
![]()
OR
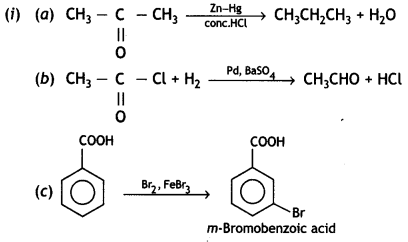
(ii) (a) FCH2COOH
(b) CH3COOH
Question 19.
(a) Predict the main product of the following reactions:
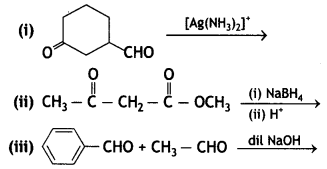
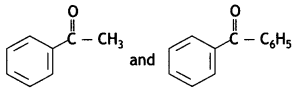
(b) Give a simple chemical test to distinguish between
(c) Why is alpha (a) hydrogen of carbonyl compounds acidic in nature?
OR
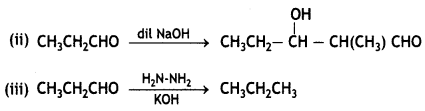
(a) Write the main product formed when propanal reacts with the following reagents:
(i) 2 moles of CH3OH in presence of dry HCI
(ii) Dilute NaOH
(iii) H2N – NH2 followed by heating with KOH in ethylene glycol
(b) Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their property as indicated:
(i) F – CH2COOH, O2N – CH2COOH, CH3COOH, HCOOH – acid character
(ii) Acetone, Acetaldehyde, Benzaldehyde, Acetophenone — reactivity towards the addition of HCN (CBSE AI 2019)
Answer:
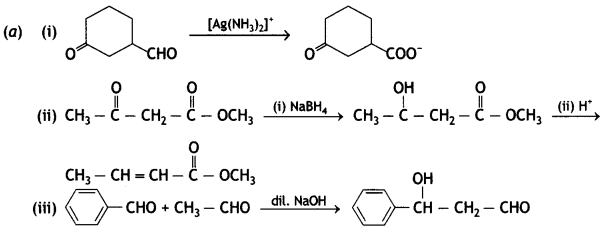
(b) On adding NaOH/l2 and heat, acetophenone gives yellow ppt of iodoform but benzophenone does not.
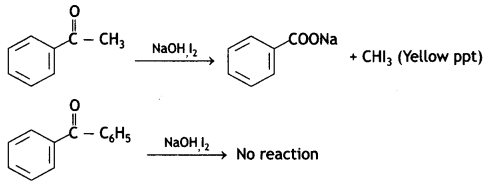
(c) α – hydrogen of carbonyl compounds is acidic because of the electron-withdrawing nature of the carbonyl group.
OR
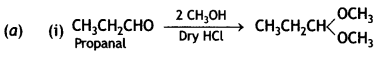
(b) (i) CH3COOH < HCOOH < FCH2COOH < NO2-CH3 COOH
(ii) Acetophenone < Benzaldehyde < Acetone < Acetaldehyde
Question 20.
(a) An organic compound with the molecular formula C7H60 forms a 2,4-DNP derivative, reduces Tollen’s reagent, and undergoes the Cannizzaro reaction. On oxidation, it gives benzoic acid. Identify the compound and state the reactions involved.
(b) Give chemical tests to distinguish between the following pair of compounds:
(i) Phenol and propanol
(ii) Benzoic acid and benzene
OR
(a) Predict the products of the following:
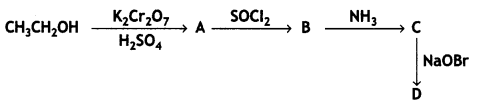
(b) Arrange the following in increasing order of acidic character: (CBSE 2019C)
HCOOH, CF3COOH, ClCH2COOH, CCl3COOH
Answer:
(a) Compound = Benzaldehyde or C6H5CHO
Reaction
Reaction with 2,4-DNP
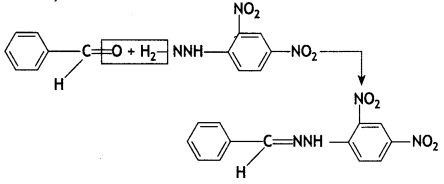
With Tollens reagent
RCHO + 2[Ag(NH3)2 ]+ + 30H– → RCOO– + 2 Ag + 2H2O + 4NH3 (where R = – C6H5)
Cannizzaro
![]()
(b) (i) FeCl3 test: Add 2 drops of neutral FeCl3 to both the compounds separately. Phenol gives violet color.
![]()
(ii) Sodium bicarbonate test: Add NaHCO3 to both the compounds: Benzoic acid reacts with NaHCO3 to give effervescence due to liberation of CO2.
C6H5COOH + NaHCO3 → C6H5COONa + H2O + CO2
OR
(a) A = CH3COOH
B = CH3COCl
C = CH3CONH2
D = CH3NH2
(b) HCOOH < ClCH2COOH < CCl3COOH < CF3COOH
- the electron-withdrawing substituents disperse the negative charge on carboxylate ion and stabilize it and thus, increase acidity.
- the electron-releasing substituents intensify the negative charge of the carboxylate ion, destabilize it and thus, decrease the acidity.
Question 21.
(i) Give chemical tests to distinguish between:
(a) Propanal and propanone
(b) Benzaldehyde and acetophenone
(ii) How would you obtain:
(a) But-2-enal from the ethanal
(b) Butanoic acid from butanol
(c) Benzoic acid from ethylbenzene? (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
(i) (a) Propanal gives a silver mirror with Tollen’s reagent.
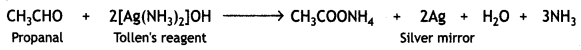
Propanone does not give this test.
(b) Benzaldehyde forms a silver mirror with ammoniacal silver nitrate solution (Tollen’s reagent). Acetophenone does not react.
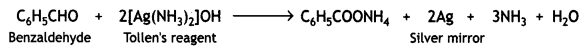
Question 22.
(i) Describe the following giving linked chemical equations:
(a) Cannizzaro reaction
Answer:
Aldehydes that do not contain any a-hydrogen atom (e.g. benzaldehyde, formaldehyde) undergo self- oxidation and reduction reaction on treatment with cone, solution of caustic alkali. In this reaction, one molecule is oxidized to acid while another molecule is reduced to an alcohol.
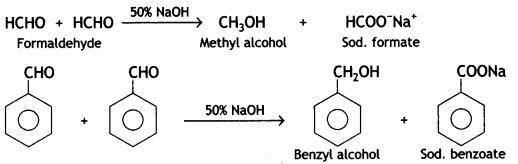
(b) Decarboxylation
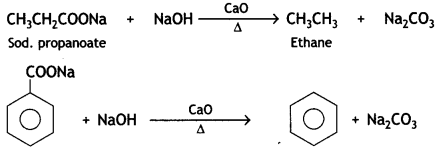
Answer:
The process of removal of a molecule of C02 from a carboxylic acid is called decarboxylation. It is usually carried out by heating a mixture of carboxylic acid or its sodium salt with soda lime (NaOH + CaO).
(ii) Complete the following chemical equations: (CBSE Delhi 2011)
Answer:
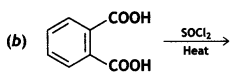
Answer:
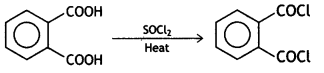
![]()
Answer:
![]()
Question 23.
(i) Give chemical tests to distinguish between the following:
Benzoic acid and ethyl benzoate.
Answer:
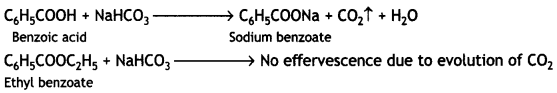
(a) When treated with NaHCO3 solution, benzoic acid gives brisk effervescence while ethyl benzoate does not
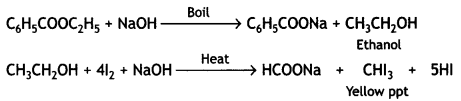
(b) Ethyl benzoate on boiling with an excess of NaOH gives ethyl alcohol which on heating with iodine gives yellow ppt. of iodoform.
(ii) Complete each synthesis by giving missing reagents or products in the following:
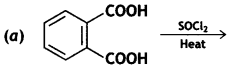
Answer:
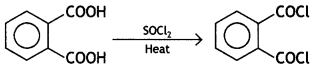
![]()
Answer:
![]()
![]()
(CBSE 2011)
Answer:
![]()
Question 24.
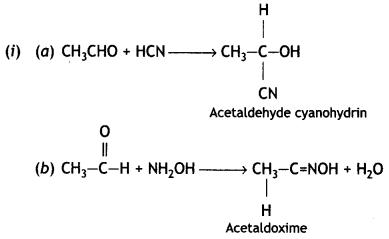
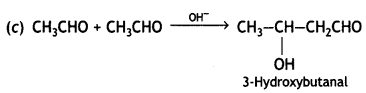
(i) Write the products formed when CH3CHO reacts with the following reagents:
(a) HCN
(b) H2N – OH
(C) CH3CHO in the presence of dilute NaOH
(ii) Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
(a) Benzoic acid and Phenol
(b) Propanal and Propanone
OR
(i) Account for the following:
(a) Cl – CH2COOH is a stronger acid than CH3COOH.
(b) Carboxylic acids do not give reactions of the carbonyl group.
(ii) Write the chemical equations to illustrate the following name reactions:
Rosenmund reduction
(iii) Out of CH3CH2—CO—CH2 – CH3 and CH3CH2 — CH2 — CO — CH3, which gives iodoform test? (CBSE 2014)
Answer:
(ii) (a) Add neutral FeCl3 in both the solutions, phenol gives violet color with FeCl3 solution, but benzoic acid does not give such color.
(b) Add an ammoniacal solution of silver nitrate (Tollen’s reagent) in both the solutions, propanal gives silver mirror whereas propanone does not.
![]()
OR
(0) Chlorine is an electron-withdrawing atom (-I effect). It withdraws the electrons from carbon to which it is attached and therefore, this effect is transmitted throughout the chain. As a result, electrons are withdrawn more strongly towards oxygen of 0—H bond and promotes the release of the proton.

Consequently, ClCH2COOH is a stronger acid than CH3COOH.
(b) Carboxylic acids do not give the characteristic reactions of the carbonyl group (>C = 0) as given by aldehydes and ketones. In carboxylic acids, the carbonyl group is involved in resonance, as follows:
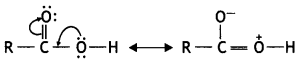
Therefore, it is not a free group. But no resonance is possible in aldehydes and ketones. They give the characteristic reactions of the group.
(ii) Rosenmund reduction. Acid chlorides are converted to corresponding aldehydes by catalytic reduction. The reaction is carried out by passing through a hot solution of the acid chloride in the presence of palladium deposited over barium sulfate (partially poisoned with sulfur or quinoline).
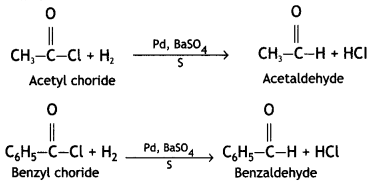
The poisoning of palladium catalyst decreases its activity and it does not allow the further reduction of an aldehyde into alcohol.
(iii) CH3CH2CH2COCH3 gives iodoform test
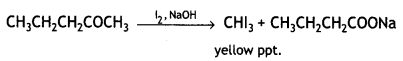
Question 25.
(i) Write the structures of A, B, C, and D in the following reactions:
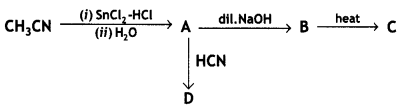
(ii) Distinguish between:
(a) C6H5 – CH = CH – COCH3 and C6H5 – CH = CH – CO CH2CH3
(b) CH3CH2COOH and HCOOH
(iii) Arrange the following in the increasing order of their boiling points:
CH3CH2OH, CH3COCH3, CH3COOH
OR
(i) Write the chemical reaction involved in the Etard reaction.
(ii) Arrange the following in the increasing order of their reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reaction:
CH3 – CHO, C6H5COCH3, HCHO
(iii) Why pKa of Cl-CH2-COOH is lower than the pKa of CH3COOH?
(iv) Write the product in the following reaction.
![]()
(v) A and B are two functional isomers of compound C3H6O. On heating with NaOH and l2, isomer A forms a yellow precipitate of iodoform whereas isomer B does not form any precipitate. Write the formulae of A and B. (CBSE 2016)
Answer:
(ii) (a) Heat both the compounds with NaOH and l2, C6H5 CH = CHCOCH3 gives yellow ppt. of iodoform. C6H5CH = CHCOCH2CH3 does not give yellow ppt. of iodoform.
(b) Add ammoniacal AgNO3 solution (Tollen’s reagent), HCOOH gives silver mirror while CH3CH2COOH does not.
(iii) CH3COCH3 < CH3CH2OH < CH3COOH
OR
(i) Etard’s reaction
(ii) C6H5COCH3 < CH3CHO < HCHO
(iii) Chlorine is an electron-withdrawing group (-I inductive effect).
It withdraws the electrons from the C to which it is attached and this effect is transmitted throughout the chain. As a result, the electrons are withdrawn more strongly towards 0 of the O-H bond and promote the release of the proton. Consequently, Cl — CH2COOH is more acidic than acetic acid.
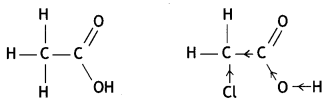
Therefore, pKa of ClCH2COOH is less than that of CH3COOH.
(iv) CH3 CH2 CH = CH CH2 CN ![]() CH3 CH2 CH = CH CH2 CHO
CH3 CH2 CH = CH CH2 CHO
(v) Two isomers are CH3COCH3 and CH3CH2CHO
Since A forms yellow ppt. of iodoform on heating with NaOH and l2, it is CH3COCH3.
CH3COCH3 + 3I2 + 4NaOH → CHI3 + CH3COONa + 3Nal + 3H2O
B does not give iodoform, it is CH3CH2CHO.
A: CH3COCH3 B: CH3CH2CHO
Question 26.
Write the structures of A, B, C, D, and E in the following reactions:
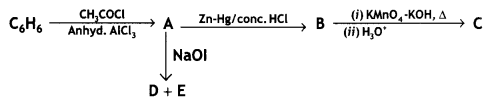
OR
(i) Write the chemical equation for the reaction involved in the Cannizzaro reaction.
(ii) Draw the structure of the semicarbazone of ethanal.
(iii) Why pKa of F-CH2-COOH is lower than that of Cl – CH2 – COOH?
(iv) Write the product in the following reaction:
CH3 – CH = CH – CH2CN ![]()
(v) How can you distinguish between propanal and propanone? (CBSE Delhi 2016)
Answer:
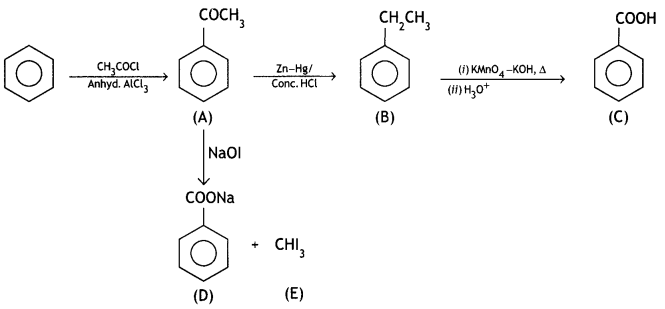
OR
(i) Cannizzaro’s reaction: Aldehydes that do not contain a-hydrogen undergo self-oxidation and reduction on treatment with cone. KOH.
![]()
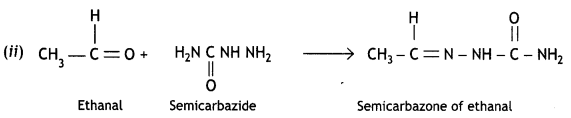
(iii) Fluorine is more electronegative than Cl and therefore, will have a greater electron-withdrawing effect (-I effect). As a result, the carboxylate ion will be stabilized to a larger extent and therefore fluoro acetic acid will be a stronger acid than chloroacetic acid. Hence, the pKa of FCH2COOH will be lower than that of ClCH2COOH.
(iv) CH3 — CH = CH — CH2 CN ![]() CH3 CH = CH CH2 CHO
CH3 CH = CH CH2 CHO
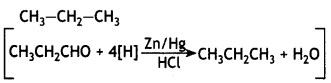
(v) Propanal gives red ppt with Fehling solution but propanone does not.
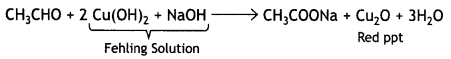
Question 27.
(i) Give reasons :
(a) HCHO is more reactive than CH3-CHO towards the addition of HCN. (CBSE 2018C)
(b) pKa of O2N—CH2—COOH is lower than that of CH3—COOH.
(c) Alpha hydrogen of aldehydes and ketones is acidic in nature.
(ii) Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds :
(a) Ethanal and Propanal
(b) Pentan-2-one and Pentan-3-one
OR
(i) Write the structure of the product(s) formed :
(a) CH3 — CH2 — COOH ![]()
(b) C6H5COCl ![]()
(c) 2HCHO ![]()
(ii) How will you bring the following conversions in not more than two steps :
(a) Propanone to propene
(b) Benzyl chloride to phenyl ethanoic acid
Answer:
(i) (a) Due to + I effect of the methyl group is CH3CHO.
(b) Due to – I effect of the nitro group in nitroacetic acid.
(c) Due to the strong electron-withdrawing effect of the carbonyl group and resonance stabilization of the conjugate base.
(ii) (a) Add NaOH and l2 to both the compounds and heat, ethanal gives yellow ppt of iodoform.
(b) Add NaOH and l2 to both the compounds and heat, pentan-2-one gives yellow ppt of iodoform.
OR