Here we are providing Class 12 Chemistry Important Extra Questions and Answers Chapter 15 Polymers. Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions are the best resource for students which helps in Class 12 board exams.
Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 15 Important Extra Questions Polymers
Polymers Important Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Define the term ‘homopolymerisation’ giving an example. (CBSE Delhi 2012)
Answer:
The polymers formed from one type of monomers and having same repeating units are called homopolymers. For example polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polythene.
Question 2.
Give one example of condensation polymer. (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
Nylon-6, 6
Question 3.
Which of the following is a natural polymer? (CBSE 2014)
Buna-S, Proteins, PVC
Answer:
Proteins.
Question 4.
Based on molecular forces what type of polymer is neoprene? (CBSE 2014)
Answer:
Elastomer.
Question 5.
Which of the following is a fibre?
Nylon, Neoprene, PVC (CBSE 2014)
Answer:
Nylon
Question 6.
Draw structure for the polymer used for the manufacture of non-stick utensils. (CBSE2019C)
Answer:

Question 7.
What is the primary structural feature necessary for a molecule to make it useful in a condensation polymerisation reaction? (CBSE AI 2010)
Answer:
The monomers must be bifunctional i.e. contain two functional groups.
Question 8.
Arrange the following polymers in the increasing order of tensile strength. Nylon 6, Buna-S, Polythene. (CBSE Sample Paper 2010)
Answer:
Buna – S < Polythene < Nylon 6.
Question 9.
What type of reaction occurs in the formation of Nylon 6,6 polymer? (CBSE Sample Paper 2019)
Answer:
Condensation
Question 10.
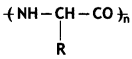
Is a homopolymer or R copolymer? (CBSE 2019C)
Answer:
Homopolymer
Question 11.
Identify the Monomers of the following polymer:
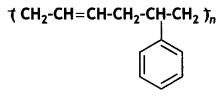
Answer:
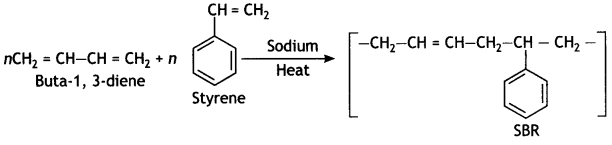
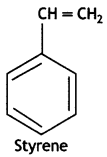
Buta-1,3-diene, styrene.
It is obtained by the polymerisation of buta-1, 3-diene and styrene in the ratio of 3: 1 in the presence of sodium.
Polymers Important Extra Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Draw the molecular structures of the monomers of
(i) PVC
Answer:
PVC : CH2 = CH – Cl (Vinyl chloride)
(ii) Teflon (CBSE 2010)
Answer:
Teflon : F2C = CF2 (Tetrafluoroethene)
Question 2.
Mention two important uses of each of the following : (CBSE Delhi 2011)
(i) Bakelite
Answer:
Uses of bakelite:
- Used for making combs, fountain pens, barrels, electrical switches and handles of utensils.
- Soft bakelites are used for making glue for binding wooden laminated planks in varnishes.
(ii) Nylon 6
Answer:
Uses of Nylon 6:
- It is used for making tyre cords.
- It is used for making fabrics and ropes.
Question 3.
Draw the structure of the monomer for each of the following polymers:
(i) Nylon 6
Answer:
The monomer of Nylon-6:
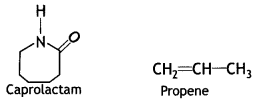
(ii) Polypropene (CBSE Delhi 2012)
Answer:
The monomer of polypropene:
Question 4.
Differentiate between thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Give one example of each. (CBSE Delhi 2010, 2012) Answer:
Thermoplastics when heated become soft and more or less fluid. These can be moulded into any desired shape. The thermoplastics ‘ can be processed again and again.
The intermolecular forces in thermoplastics are intermediate between those of elastomers and fibres.
On the other hand, thermosetting plastics on heating become hard and insoluble masses. These cannot be moulded into the desired shape and cannot be reprocessed. The intermolecular forces in thermosetting are strong and there are cross-links that hold the molecules in place so that heating does not allow them to move freely.
The common examples are:
- Thermoplastics: Polythene, polystyrene and polyvinyl chloride.
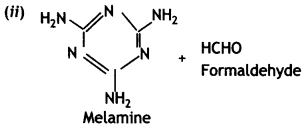
- Thermosetting: Bakelite and melamine formaldehyde.
Question 5.
Write the name of monomers used for getting the following polymers: (CBSE 2014)
(i) Bakelite
Answer:
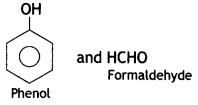
Phenol and formaldehyde
(ii) Neoprene
Answer:
2-Chloro-1,3-butadiene(chloroprene)
Question 6.
Write the name of monomers used for getting the following polymers: (CBSE 2014)
(i) Terylene
Answer:
Ethylene glycol, terephthalic acid
(ii) Nylon-6, 6
Answer:
Hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid.
Question 7.
Write the name of monomers used for getting the following polymers: (CBSE 2014)
(i) Teflon
Answer:
Tetrafluoroethylene
(ii) Buna-N
Answer:
1, 3-butadiene and acrylonitrile
Polymers Important Extra Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1.
Write the structures of monomers used for getting the following polymers:
(i) Nylon-6,6
(ii) Glyptal
(iii) Buna-S
OR
(i) Is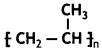 it a homopolymer or copolymer? Give reason.
it a homopolymer or copolymer? Give reason.
(ii) Write the monomers of the following polymer:
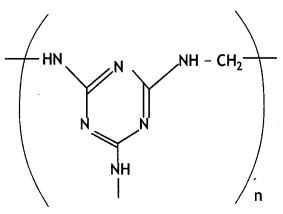
(iii) What is the role of the Sulphur in the vulcanization of rubber? (CBSE Delhi 2019)
Answer:
(i) Nylon-6,6
Hexamethylenediamine: NH2 – (CH2)6 – NH2 and Adipic acid
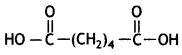
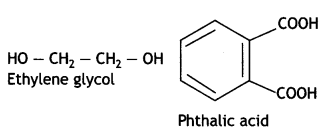
(ii) Glyptal
(iii) Buna – S
CH2 = CH — CH = CH2
1, 3 Butadiene
OR
(i) It is a homopolymer because it has only one monomer.
(iii) Sulphur makes the rubber hard, tough with greater tensile strength and non-sticky by forming sulphur crosslinks.
Question 2.
(a) Write the names of monomers of the following polymer:
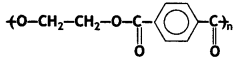
Answer:
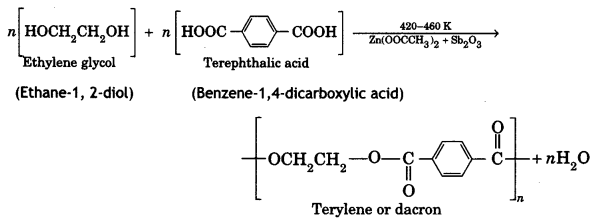
Ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid or Ethane-1,2- diol and Benzene 1, 4- dicarboxylic acid.
Terylene: It is a polymer of ethylene glycol (ethane-1,2-diol) and terephthalic acid (benzene-1, 4-dicarboxylic acid). It is obtained by heating a mixture of ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid at 420 to 460 K in the presence of zinc acetate-antimony trioxide, [Zn(OOCCH3)2 + Sb2O3] catalyst. It is known as terylene or dacron.
(b) What does part 6,6 mean in the polymer Nylon-6,6?
Answer:
It represents 6 carbon atoms present in both the monomer units.
Nylon-6,6: The monomer units of nylon-6,6 are hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid. It is prepared by condensation of hexamethylene diamine with adipic acid under high pressure and high temperature.
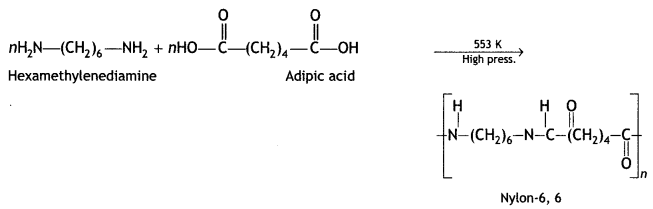
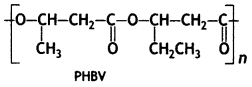
(c) Give an example of a Biodegradable polymer. (CBSE 2019C)
Answer:
Poly-p-hydroxybutyrate-co-p-hydroxy valerate (PHBV).
It is a copolymer of 3-hydroxybutyric acid and 3-hydroxypentanoic add, in which the monomer units are joined by ester linkages.
Question 3.
Explain the following terms giving a suitable example for each :
(i) Elastomers
Answer:
Elastomers: These are polymers in which the polymer chains are held together by weak intermolecular forces. Because of the presence of weak forces, the polymer can be easily stretched. However, a few cross-linked are also introduced in the chains which impart the property of regaining the original positions after the stretching force is released. A common example is vulcanised rubber.
(ii) Condensation polymers
Answer:
Condensation polymers: A polymer formed by the condensation of two or more than two monomers is called condensation polymer. In this type, each monomer generally contains two functional groups, and condensation takes place by the loss of molecules such as H20, HCl, etc. Common examples are nylon-6, nylon-6,6, bakelite, terylene and alkyl resins.
(iii) Addition polymers (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
Addition polymers: A polymer formed by the direct addition of repeated monomers is called an addition polymer. In this type, the monomers are unsaturated compounds and are generally derivatives of ethene. In addition, polymers have the same empirical formula as their monomers. For example, the addition of polymers polyethene or polypropylene are obtained as:
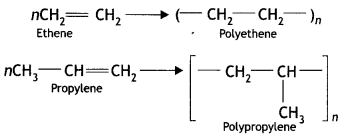
Question 4.
Write the names and structures of the monomers of the following polymers:
(i) Buna-S
Answer:
Buna-S:
1, 3-Butadiene: CH2 = CH – CH == CH2
Styrene: C6H5CH = CH2
(ii) Neoprene
Answer:
Neoprene:
Chloroprene: CH2 = C – CH = CH2
(iii) Nyton-6, 6 (CBSE Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Nylon 6, 6:
- Adipic acid: HOOC (CH2)4 COOH
- Hexamethylenediamine: NH2(CH2)6NH2
Question 5.
Write the names and structures of the monomers of the following polymers:
(i) Bakelite
Answer:
Bakelite:
- Phenol:
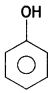
- Formaldehyde: HCHO
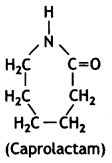
(ii) Nylon-6
Answer:
Nylon-6:
Caprolactam
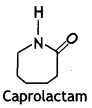
(iii) Polythene (CBSE Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Polythene: Ethene: CH2 = CH2.
Question 6.
(i) What is the role of benzoyl peroxide in the polymerisation of ethene?
(ii) Identify the monomers in the following polymer:
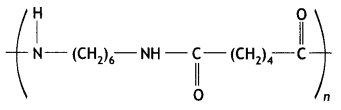
(iii) Arrange the following polymers in the increasing order of their intermolecular forces: Nylon-6, 6, Polythene, Buna-S
OR
Write the mechanism of free radical polymerisation of ethene. (CBSE 2016)
Answer:
(i) Benzoyl peroxide acts as a free radical generator. In the presence of benzoyl peroxide, phenyl free radical is formed which initiates the chain initiation step.
![]()
(iii) Buna-S < Polythene < Nylon 6, 6
OR
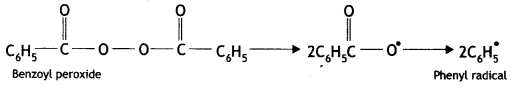
Mechanism
(i) Chain initiation step:
(ii) Chain propagating step:
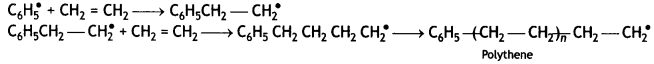
(iii) Chain termination step:
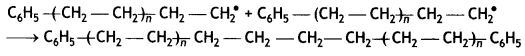
Question 7.
Write the names and structures of the monomers of the following polymers:
(a) Neoprene
Answer:
Chloroprene CH2 = C — CH = CH2
(b) Bakelite
Answer:
C6H5OH(Phenol) and HCHO (formaldehyde)
(c) PVC (CBSE 2019C)
Answer:
Polyvinyl chloride CH2 = CH – Cl
Question 8.
Write the structures of monomers used to obtain the following polymers:
(a) Natural rubber
(b) PVC
(c) Nylon-6,6
OR
Write the mechanism of free radical polymerisation of ethene. (CBSE AI 2019)
Answer:
(a) Natural rubber: 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene
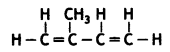
(b) PVC: vinyl chloride
CH2 = CH – Cl
(c) Nylon-6,6:
HOOC-(CH2)4 – COOH (Adipic acid)
NH2 — (CH2)6 — NH2
(Hexamethylenedlamine)
OR
Chain Initiation Step:
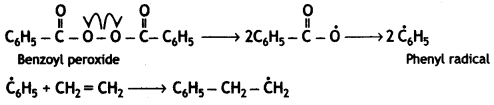
Chain propagation:
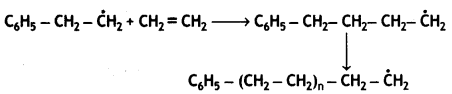
Chain termination step
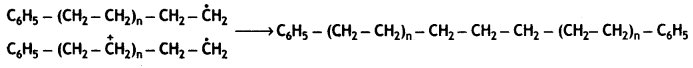
Question 9.
Write the structures of monomers used to obtain the following polymers:
(a) Buna-S
(b) Glyptai
(c) Nylon-6
OR
(a) Arrange the following polymers in increasing order of their intermolecular forces: Polyvinylchloride, Neoprene, Terylene
(b) Write one example of each of
(i) Natural polymer
(ii) Thermosetting polymer
(c) What is the significance of numbers 6,6 in the polymer Nylon-6,6? (CBSE Al 2019)
Answer:
(a) Buna-S
CH2 = CH – CH = CH2 (1,3-Butadiene) and C6H5CH = CH2 (Styrene)
(b) Glyptal
HO – CH2 — CH2 — OH (Ethylene glycol) and
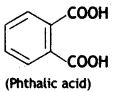
(c) Nylon-6
OR
(a) Neoprene < Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) < Terylene
(b) (i) Isoprene
(ii) Bakelite
(c) The numbers ‘6, 6’ signifies that both the monomers of nylon-6, 6 have six carbon atoms.
Question 10.
What is a biodegradable polymer? Give an example of a biodegradable aliphatic polyester. (CBSE AI 2013)
Answer:
Polymers that are degraded by micro-organisms within a suitable period so that the polymers and their degraded products do not cause any serious effects on the environment are called biodegradable polymers. For example,
Poly β – hydroxybutyrate – co – β – hydroxy valerate (PHBV)
Question 11.
Write the names and structures of the monomers of the following polymers:
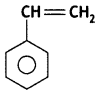
(i) Polystyrene
Answer:
Polystyrene: Styrene:
(ii) Dacron
Answer:
Dacron:
- Ethylene glycol: HOCH2CH2OH
- Terephthalic acid:
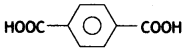
(iii) Teflon
Answer:
Teflon:
Tetrafluoroethene: F2C = CF2
Question 12.
Write the names and structures of the monomers of the following polymers:
(a) Teflon
Answer:
Tetrafluoroethylene, CF2 = CF2

(b) Terylene
Answer:
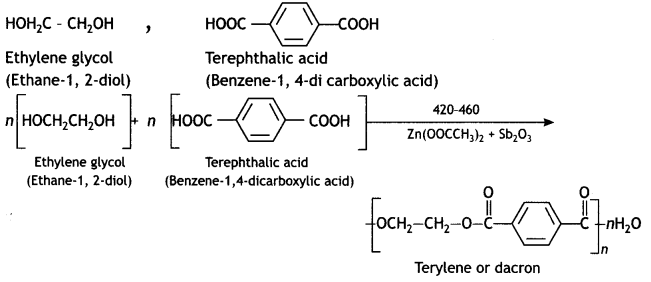
(c) Buna-N
Answer:
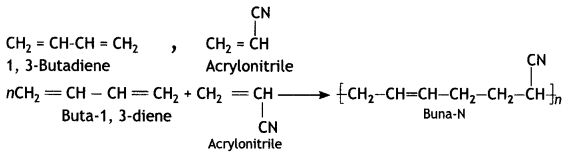
Question 13.
Write the structures of monomers used to obtain the following polymers:
(a) Neoprene
(b) PHBV
(c) Bakelite
OR
(a) Arrange the following polymers in decreasing order of their intermolecular forces:
Bakelite, Polythene, Buna-S, Nylon-6,6
(b) Write the monomers of the following polymer:
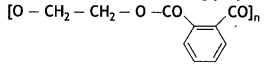
(c) What is the structural difference between high-density polythene (HDP) and low-density polythene (LDP)? (CBSE AI 2019)
Answer:
(a) Neoprene:
Chloroprene
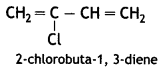
(b) PHBV

(c) Bakelite
OR
(a) Buna-S < potythene < Bakelite < Nylon-6,6
(b) HO — CH2 — CH2 — OH and
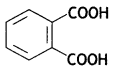
(c) Low-density polythene (LDP) consists of highly branched chain molecules. Due to branching, the polythene molecules do not pack well and therefore, it has low density.
High-density polythene (HDP) consists of linear chains and therefore, the molecules can be closely packed. Hence, it has a high density.
Question 14.
What are high density and low-density polythene?
Answer:
High-density polythene is obtained by heating ethene at about 333-343 K under a pressure of 6-7 atm in the presence of a catalyst such as triethylaluminium and titanium tetrachloride (known as Zeigler-Natta catalyst)
![]()
This polymer consists of linear chains and therefore the molecules can be closely packed in space. It, therefore, has a high density (0.97g/cm3) and a higher melting point (403K). It is harder, tougher and has greater tensile strength than low-density polythene.
Low-density polythene (LDP) is prepared by free radical addition and hydrogen atom abstraction. It consists of highly branched chain molecules. Due to branching, the polythene molecules do not pack well and therefore it has low density (0.92 g/cm3) and low melting point (384 K). Low-density polythene is transparent. It has moderate tensile strength and high toughness. It is chemically inert.
Question 15.
Discuss the mechanism of free radical addition polymerisation.
Answer:
A large number of unsaturated compounds such as alkenes or dienes and their derivatives are polymerised by this process. The polymerisation takes place through the generation of an initiator, which is a molecule that decomposes to form free radicals. The commonly used initiator is t-butyl peroxide.
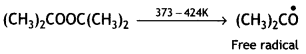
The addition occurs as
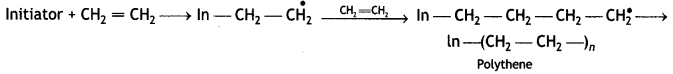
For example, most of the commercial addition polymers are obtained from alkenes and their derivatives,
![]()
The general model of polymerisation is:
Chain initiation step:
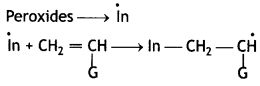
Chain Propagating Step:
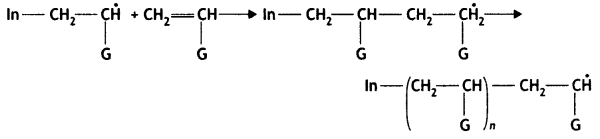
Chain terminating step
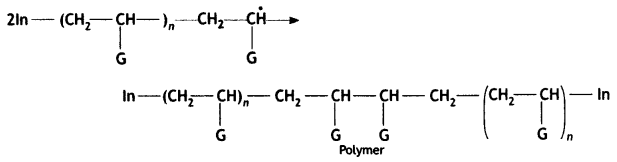
Question 16.
List some important differences between natural rubber and vulcanised rubber.
Answer:
Differences between natural rubber and vulcanised rubber:
| Natural rubber | Vulcanized rubber |
| 1. Natural rubber is soft and sticky. | 1. Vulcanized rubber is hard and non-sticky. |
| 2. It has low tensile strength. | 2. It has a high tensile strength. |
| 3. It has low elasticity. | 3. It has high elasticity. |
| 4. It can be used over a narrow range of temperature (from 10°C to 60°C). | 4. It can be used over a wide range of temperature (-40°C to 100°C). |
| 5. It has low wear and tears resistance. | 5. It has high wear and tears resistance. |
| 6. It is soluble in solvents like ether, carbon- tetrachloride, petrol etc. | 6. It is insoluble in all the common solvents. |
Question 17.
(a) What is the difference between two notations: nylon-6 and nylon-6,6? Give their synthesis.
Answer:
Nylon-6 has only one compound having 6-carbon atoms while nylon-6,6 refers to a polymer obtained from 6-carbon atoms of dicarboxylic acid (adipic acid) and 6-carbon atoms of diamine (hexamethylene diamine).
Nylon-6 is synthesised from caprolactam as
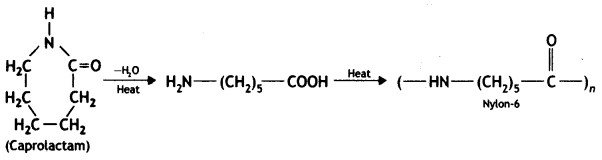
Nylon-6,6 is synthesised from hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid.
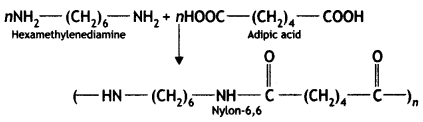
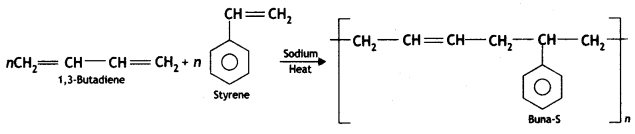
(b) How is Buna-S prepared?
Answer:
Buna-S is obtained by copolymerisation of styrene and 1, 3-butadiene.
Question 18.
Write the names and structures of the monomers of the following polymers:
(i) Buna-S
Answer:
1, 3-Butadiene: CH2 = CH — CH = CH2
Styrene: C6H5CH = CH2
(ii) Buna-N
Answer:
1, 3-Butadiene: CH2 = CH – CH = CH2
Acrytonitnie: CH2 = CH — CN
(iii) Dacron
Answer:
- Ethylene glycol:
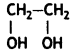
- Terephthalic acid:
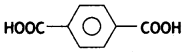
(iv) Neoprene.
Answer:
Chloroprene:
![]()