Here we are providing Class 12 Chemistry Important Extra Questions and Answers Chapter 16 Chemistry in Everyday Life. Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions are the best resource for students which helps in Class 12 board exams.
Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 16 Important Extra Questions Chemistry in Everyday Life
Chemistry in Everyday Life Important Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Name a substance that can be used as an antiseptic as well as a disinfectant. (CBSE 2019C)
Answer:
Phenol / C6H65OH
Question 2.
Differentiate between disinfectants and antiseptics. (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
Both antiseptics and disinfectants kill or prevent the growth of microorganisms. Antiseptics are applied to living tissues (cuts, wounds). But disinfectants are applied to inanimate objects only (floor, instruments).
The same substance can act as an antiseptic as well as a disinfectant by varying the concentration of the solution used. For example, 0.2% solution of phenol acts as an antiseptic and its 1% solution is a disinfectant.
Question 3.
What is the cause of a feeling of depression in human beings? Name a drug that can be useful in treating this depression. (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
The cause of depression in human beings is a low level of noradrenaline. Because of the low level of noradrenaline, the signal-sending activity of the hormones becomes low and the person suffers from depression. Phenelzine is useful in treating this depression.
Question 4.
Name one substance that can act as both:
(i) Analgesic and antipyretic. (CBSE Sample Paper 2012)
Answer:
Aspirin
(ii) Antiseptic and disinfectant. (CBSE Sample Paper 2011)
Answer:
Phenol
Question 5.
What is the tincture of iodine? What is its use? (CBSE 2019C)
Answer:
2 – 3% iodine solution of alcohol-water is called tincture of iodine. It is a powerful antiseptic and is applied on wounds.
Question 6.
(a) Which one of the following is a food preservative?
Equanil, Morphine, Sodium benzoate. (CBSE Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Sodium benzoate
(b) If the water contains dissolved Ca2+ ions, out of soaps and synthetic detergent, which will you use for cleaning clothes? (CBSE AI 2013)
Answer:
Synthetic detergent.
Question 7.
Among the following which one acts as a food preservative?
Aspartame, Aspirin, Sodium benzoate, Paracetamol
Answer:
Sodium benzoate.
Chemistry in Everyday Life Important Extra Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1.
What are food preservatives? Name two such substances. (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
Food preservatives are chemical substances that are added to food materials to prevent spoilage and to retain their nutritive value for long periods. For example, sodium benzoate, potassium metabisulphite.
Question 2.
(i) Why is bithional added to soap?
Answer:
Bithional acts as an antiseptic agent and reduces the odors produced by the bacterial decomposition of organic matter on the skin.
(ii) Which class of drugs is used in sleeping pills? (CBSE AI 2018)
Answer:
Tranquilizers.
Question 3.
(i) What class of drug is Ranitidine?
Answer:
Antacid
(ii) Which of the following is an antiseptic?
0. 2% phenol, 1% phenol(CBSE AI 2013)
Answer:
0.2% phenol: antiseptic; 1% phenol: disinfectant
Question 4.
Give one example for each of the following:
(i) An artificial sweetener whose use is limited to cold drinks.
Answer:
Aspartame.
(ii) A non-ionic detergent. (CBSE Sample Paper 2011)
Answer:
Ester of stearic acid and polyethylene glycol
CH3(CH2)16COO(CH2CH2O)nCH2CH2OH
Question 5.
Sleeping pills are recommended by doctors to the patients suffering from sleeplessness but it is not advisable to take their doses without consultation with the doctor. Why? (CBSE Sample Paper 2011)
Answer:
Most of the drugs taken in doses higher than recommended may cause harmful effects and act as poison leading to death. Therefore, a doctor must always be consulted before taking any medicine, who will advise the patient for proper and safe doses of the drug.
Question 6.
Why do soaps not work in hard water? (CBSE Delhi 2011)
Answer:
Hard water contains calcium and magnesium salts. Therefore, in hard water soap gets precipitated as insoluble calcium and magnesium soaps which being insoluble stick to the cloth as gummy mass and blocks the ability of soap to remove oil or grease from the cloth.
Question 7.
Explain the following term with one suitable example:
Antifertility drugs (CBSE 2010)
Answer:
Antifertility drugs. These are the chemical substances used to control the pregnancy. These are also called oral contraceptives birth control pills. The common drugs used as antifertility drugs are norethindrone, ethynylestradiol (nostril), mifepristone, ormeloxifene, etc.
Chemistry in Everyday Life Important Extra Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1.
(i) What type of drug is used in sleeping pills?
(ii) What type of detergents is used in toothpaste?
(iii) Why is the use of alitame as an artificial sweetener not recommended?
OR
Define the following terms with a suitable example in each:
(i) Broad-spectrum antibiotics
(ii) Disinfectants
(iii) Cationic detergents (CBSE Delhi 2019)
Answer:
(i) Tranquilizers
(ii) Anionic detergents
(iii) With alitame, it is difficult to control the sweetness of food to which they are added.
OR
(i) Broad-spectrum antibiotics: These are the antibiotics that are effective against several types of harmful microorganisms and are used for curing a variety of diseases, for example, chloramphenicol.
(ii) Disinfectants: The chemical substances which are used to kill microorganisms but cannot be applied on living tissues are called disinfectants, for example, phenol (1% solution).
(iii) Cationic detergents: The substances which have a long hydrocarbon chain with a positive charge on the nitrogen atom (cationic part) which is involved in cleaning action are called cationic detergents. These are quaternary ammonium salts of amines with acetates, chlorides, or bromides as anions, for example, cetyltrimethylammonium bromide.
Question 2.
What is the following substance? Give one example of it:
Antacids (CBSE2011, CBSE Delhi 2012)
Answer:
Antacids: These are the chemical substances that neutralize excess acid in the gastric juices and give relief from acid indigestion, acidity, heartburns, and gastric ulcers. Until 1970, the antacids such as sodium bicarbonate or a mixture of aluminum and magnesium hydroxide have been commonly used for the treatment of acidity.
However, excessive bicarbonate can make the stomach alkaline and trigger the production of even more acid. Nowadays, acidity is cured by drugs such as cimetidine (Tagamet), ranitidine (Zantac), omeprazole, lansoprazole, etc.
Question 3.
(i) Which one of the following is a food preservative?
Equanil, Morphine, Sodium benzoate
Answer:
Sodium benzoate
(ii) Why is bithional added to soap?
Answer:
Bithional acts as an antiseptic agent and reduces the odors produced by the bacterial decomposition of organic matter on the skin.
(iii) Which class of drugs is used in sleeping pills? (CBSE Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Tranquilizers.
Question 4.
(i) What class of drug is Ranitidine?
Answer:
Antacid
(ii) If the water contains dissolved Ca2+ ions, out of soaps and synthetic detergent, which will you use for cleaning clothes?
Answer:
Synthetic detergent
(iii) Which of the following is an antiseptic:
0. 2% phenol, 1% phenol? (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
0.2% phenol: antiseptic; 1% phenol: disinfectant
Question 5.
(i) Give two examples of macromolecules that are chosen as drug targets.
Answer:
Carbohydrates, proteins.
(ii) What are antiseptics? Give an example.
Answer:
The chemical substances which are used to either kill or prevent the growth of micro-organisms are called antiseptics. These are not harmful to live tissues and can be safely applied on wounds, cuts, ulcers, diseased skin surfaces, etc.
For example, Dettol.
(iii) Why is the use of aspartame limited to cold foods and soft drinks? (CBSE Delhi 2014)
Answer:
Aspartame is unstable at cooking temperatures and therefore, it is used as sugar substitute for cold foods and
soft drinks.
Question 6.
(i) Name the sweetening agent used in the preparation of sweets for a diabetic patient.
Answer:
Saccharin
(ii) What are antibiotics? Give an example.
Answer:
Antibiotics are chemical substances that are produced by micro-organisms (bacteria, fungi, moulds) and can inhibit the growth or even destroy other micro-organisms. For example, Penicillin.
(iii) Give two examples of macromolecules that are chosen as drug targets. (CBSE Delhi 2014)
Answer:
Proteins, lipids.
Question 7.
(a) Differentiate between antiseptic and disinfectant. Give one example of each.
(b) Why do we require artificial sweetening agents?
OR
Define the following terms:
(a) Tranquilizers
(b) Antacids
(c) Analgesics (CBSE2019C)
Answer:
(a) Antiseptics: Antiseptics are the chemical substances that are used to either kill or prevent the growth of micro-organisms. These are not harmful to live tissues and can be safely applied on wounds, cuts, diseased skin surfaces. For example, Dettol, Savlon, furnace, tobramycin, etc.
Disinfectants: Disinfectants are chemical substances that kill micro-organisms but cannot be applied to living tissues. In other words, they also kill micro-organisms like antiseptics but are not safe for living tissues. These are commonly applied to inanimate objects such as the floor, drainage systems, instruments, etc. Some common examples of disinfectants are phenol (1% solution), chlorine (0.2 to 0.4 ppm), etc.
(b) Artificial sweetening agents are used to reduce calorie intake. These also protect teeth from decay.
OR
(a) The chemical substances used for the treatment of stress, fatigue, mild and severe mental diseases are called tranquilizers.
Tranquilizers are neurologically active drugs that affect the message transfer mechanism from nerve to receptor. These are used to relieve or reduce mental tension, irritability, excitement, and anxiety leading to calmness. These form an essential component of sleeping pills.
(b) Acidic stomach is necessary for good health, but excessive acidity in the stomach can cause discomforts such as acid indigestion, heartburn, irritation, or pain of gastric ulcers. The chemical substances which neutralize excess acid in the gastric juices and give relief from add indigestion, acidity, heartburns, and gastric ulcers are called antacids.
(c) The chemical substances which are used to relieve pains without causing impairment of consciousness, mental confusion, incoordination or paralysis, or some other disturbances of the nervous system are called analgesics.
These are of two types:
- Non-narcotic (non-addictive) drugs
- Narcotic drugs
Question 8.
Explain the following terms with one suitable example for each:
(i) A sweetening agent for diabetic patients
Answer:
A sweetening agent for diabetic patients: The chemical substances which give a sweetening effect to food but do not add any calorie to our body are called artificial sweetening agents. The sweetening agent for diabetic patients is saccharin.
(ii) Enzymes
Answer:
Enzymes: Enzymes are biological catalysts produced by living cells that catalyze the biochemical reaction in living organisms. Chemically enzymes are naturally occurring simple or conjugated proteins and some enzymes are non-proteins also. These increase the rates of biochemical reactions by providing alternative paths of lower energy. For example, maltase, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of maltose to glucose.

(iii) Analgesics (CBSE AI 2011)
Answer:
Analgesics: These are medicines used to relieve pains. Aspirin and some other antipyretics are also used as analgesics. Certain narcotics (which produce sleep and unconsciousness) are also used as analgesics. For example, morphine, codeine, heroin, marijuana. These are known to be habit-forming.
Question 9.
Define and write an example for the following:
(a) Broad-spectrum antibiotics.
Answer:
Broad-spectrum antibiotics: These are the antibiotics that are effective against several types of harmful micro-organisms. Therefore, these are used for curing a variety of diseases. The common examples are tetracycline, Chloromycetin, and chloramphenicol which are effective against a variety of diseases.
Other important broad-spectrum antibiotics used are vancomycin and ofloxacin. The antibiotic dysidazirine is found to be toxic to certain strains of cancer cells.
(b) Analgesics (CBSE Sample Paper 2019)
Answer:
Analgesics: The chemical substances which are used to relieve pains without causing impairment of consciousness, mental confusion, incoordination or paralysis, or some other disturbances of the nervous system are called analgesics.
These are of two types:
- Non-narcotic (non-addictive) drugs
- Narcotic drugs
1. Non-narcotic drugs: The common non-addictive analgesics are aspirin and paracetamol. Aspirin (2-acetoxy benzoic acid) is the most familiar example. It inhibits the synthesis of compounds known as prostaglandins which stimulate inflammation in the tissues and cause pain. These drugs are effective in relieving skeletal pain such as that due to arthritis.
Aspirin has also been very popular because it has antipyretic (temperature lowering) properties. Now, aspirin also finds use in the prevention of heart attack because it has anti-blood-clotting action. In addition, many other potential applications of aspirin, presently under investigation, include pregnancy-related complications, viral inflammation in AIDS patients, Alzheimer’s disease, dementia, cancer, etc.
Because of the shortcomings of aspirin, other analgesics like naproxen, ibuprofen, and diclofenac sodium or potassium find use as alternatives.
2. Narcotic drugs: Certain narcotics (which produce sleep and unconsciousness) are also used as analgesics. For example, morphine and its derivatives codeine, heroin, and marijuana are used in severe pain as analgesics. These are known to be habit-forming. When used in medicinal doses, these relieve pain and produce sleep. However, in excessive (poisonous) doses these produce stupor coma, convulsions and ultimately leading to death.
These analgesics are mainly used for relief in postoperative pains, cardiac pain, and pains related to childbirth and terminal cancer.
Question 10.
(a) Why are metal hydroxides better alternatives than sodium hydrogen carbonate in antacids?
(b) Why is aspirin used in the prevention of heart attacks?
(c) Why antihistamines do not affect the secretion of acid in the stomach?
OR
Define the following terms with a suitable example of each:
(a) Tranquilizers
(b) Antibiotics
(c) Non-ionic detergents (CBSE AI 2019)
Answer:
(a) Metal hydroxides are better alternatives than sodium hydrogen carbonates because of being insoluble. These do not increase the pH above neutrality. However, excessive hydrogen carbonates can make the stomach alkaline and may trigger the production of even more acid.
(b) Aspirin is a blood thinner and has anti-blood-clotting action and therefore, used in the prevention of heart attacks.
(c) Antihistamines do not affect the secretion of acid in the stomach because anti-allergic and antacid drugs work on different receptors. The receptors present in the stomach do not react with antihistamines.
OR
(a) Tranquilizers: These are substances used to relieve mental diseases. They reduce tension and anxiety. They act on higher centers of the nervous system. These are the constituents of sleeping pills. The common examples are Derivatives of barbituric acid, Equanil, luminal, diazepam, methedrine, etc.
(b) Antibiotics: Antibiotics are chemical substances that are produced by micro-organisms (bacteria, fungi, molds) and can inhibit the growth or even destroy other micro-organisms. For example, penicillin.
(c) Non-ionic detergents: These detergents do not contain any iron in their constitution and therefore, are non-ionic like the esters of high molecular mass. However, these contain polar groups which can form hydrogen bonds with water. For example, polyethylene glycol stearate.
Question 11.
(i) Why bithional is added in soap?
(ii) Why magnesium hydroxide is a better antacid than sodium bicarbonate?
(iii) Why soaps are biodegradable whereas detergents are non-biodegradable?
OR
Define the following terms with a suitable example in each:
(i) Antibiotics
(ii) Artificial sweeteners
(iii) Analgesics (CBSE Delhi 2019)
Answer:
(i) Bithional is added to soap because it acts as an antiseptic agent and reduces the odors produced by the bacterial decomposition of organic matter on the skin.
(ii) Magnesium hydroxide is insoluble and does not increase the pH above neutrality. But excess sodium bicarbonate can make the stomach alkaline and may trigger the production of even more acid.
(iii) The synthetic detergents have hydrocarbon chains that are highly branched. Bacteria cannot degrade them easily. Therefore, detergents are non-biodegradable. On the other hand, soaps have unbranched chains which can be biodegraded more easily. Hence, soaps are biodegradable.
OR
(i) Antibiotics: Antibiotics are chemical substances that are produced by microorganisms (bacteria, fungi, and molds) and can inhibit the growth or even destroy other micro-organisms, for example, penicillin, ampicillin, Amoxycillin, etc.
(ii) Artificial sweeteners: These are the chemical compounds that give a sweetening effect to the food and enhance its odor and flavor, for example, saccharin, aspartame, alitame, etc.
(iii) Analgesics: These are neurologically active pain-killing drugs that reduce or abolish pain without causing impairment of consciousness, incoordination, mental confusion, paralysis, or some other disturbances of the nervous system, for example, aspirin, paracetamol, naproxen, ibuprofen, etc.
Question 12.
Give reasons for the following:
(i) Use of aspartame as an artificial sweetener is limited to cold foods.
Answer:
It is unstable at cooking temperature.
(ii) Metal hydroxides are better alternatives than sodium hydrogen carbonate for the treatment of acidity.
Answer:
Excessive hydrogen carbonate can make the stomach alkaline and trigger the production of even more acid. Metal hydroxides being insoluble do not increase the pH above neutrality,
(iii) Aspirin is used in the prevention of heart attacks. (CBSE Sample Paper 2018, 2019)
Answer:
Aspirin has anti-blood-clotting action.
Question 13.
(i) Why is bithional added to soap?
Answer:
To impart antiseptic properties
(ii) What is the tincture of iodine? Write its one use.
Answer:
2-3% solution of iodine in the alcohol-water mixture is the tincture of iodine. Iodine dissolved in alcohol, used as an antiseptic, and applied on wounds.
(iii) Among the following, which one acts as a food preservative?
Sodium benzoate, Aspartame (CBSE 2016)
Answer:
Sodium benzoate
Question 14.
(a) Which one of the following is a disinfectant?
0-2% solution of phenol or 1% solution of phenol
(b) What is the difference between agonists and antagonists?
(c) Write one example of each of
(i) Artificial sweetener
(ii) Antacids
OR
Define the following terms with a suitable example of each:
(a) Antiseptics
(b) Bactericidal antibiotics
(c) Cationic detergents (CBSE Al 2019)
Answer:
(a) 1% solution of phenol
(b) Agonists are substances that bind the receptor and produce a biological response.
Antagonists are the substances that bind to the receptor but inhibit its natural biological response.
(c) (i) Saccharin
(ii) Ranitidine
OR
(a) Antiseptics: The chemicals which either kill or prevent the growth of microorganisms when applied on living tissues are called antiseptics, for example, tobramycin.
(b) Bactericidal antibiotics: The chemicals which have a killing effect on microbes are called bactericidal antibiotics, for example, penicillin.
(c) Cationic detergents: The molecules which have long hydrocarbon chains with a positive charge on the nitrogen atom (cationic part) which is involved in cleansing action are called cationic detergents. These are quaternary ammonium salts of amines with acetates, chlorides, or bromides as anions. The cationic part of the molecule is involved in the cleansing action, for example, cetyltrimethylammonium bromide.
Question 15.
(i) How are synthetic detergents better than soaps?
Answer:
The detergents are better than soaps because of the following reasons:
(a) Detergents can be used for washing even in hard water. On the other hand, soaps cannot be used in hard water.
(b) Detergents can be used in acidic solutions because they are not readily decomposed in an acidic medium. On the other hand, soaps cannot be used in an acidic medium because they are decomposed into carboxylic acids in an acidic medium.
(c) Detergents have a stronger cleansing action than soap.
(ii) Can you use soaps and synthetic detergents to check the hardness of water? (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
Soaps give an insoluble precipitate of calcium and magnesium in hard water whereas detergents do not give a precipitate. Therefore, soaps but not detergents can be used to check the hardness of the water.
Question 16.
Explain the role of the allosteric site in enzyme inhibition?
Answer:
Some drugs do not bind to the enzyme’s active site. These bind to a different site of enzyme which is called the allosteric site. This bonding of inhibitor at the allosteric site changes the shape of the active site in such a way that the substrate cannot recognize it. As a result, the affinity of the substrate for the active site is reduced.
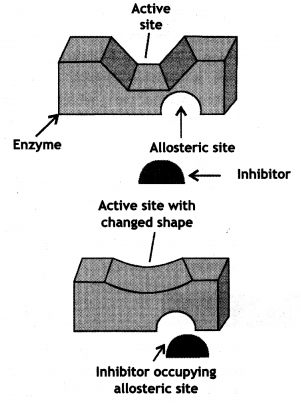
It may be noted that if the bond formed between enzyme and inhibitor is a strong covalent bond and therefore cannot be broken easily, then the enzyme gets blocked permanently. The body then degrades the enzyme-inhibitor complex and synthesizes a new enzyme.
Question 17.
What are food additives? Describe the following with suitable examples:
(i) Preservatives
(ii) Artificial sweetening agents
Answer:
Food additives are the chemicals that are added to food for their preservation and enhancing their appeal. Some common food additives are:
(a) Flavours and sweeteners
(b) Food colors (dyes)
(c) Stabilising agents
(d) Antioxidants
(e) Preservatives
(f) Nutritional supplements such as vitamins, minerals, and amino acids.
(i) Preservatives: These are the chemical substances that are added to the food materials to prevent their spoilage and to retain their nutritive value for long periods. These preservatives prevent the rancidity of food and inhibit the growth or kill the micro-organisms.
The common salt is generally added to resist the activity of micro-organisms in food. The preservation of food by adding a sufficient amount of salt to it is called salting. It is used for the preservation of raw mango, amla, beans, tamarind, fish, meat, etc. The salt prevents the water from being available for microbial growth.
Sugar syrup is also used for preserving many fruits such as apples, mango, strawberry, carrot, etc. Besides these vinegar, oils, spices, citric acid is also used as food preservatives, which are used for pickles, ketchup, jams, squashes, etc.
The growth of microbes in food material can also be prevented by adding certain chemical substances. The most common preservative used is sodium benzoate (C6H5COONa), salts of propanoic acid, sorbic acid, and potassium metabisulphite (source of sulfur dioxide). Certain food preservatives such as butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA) and butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) for edible oils also act as antioxidants.
(ii) Artificial sweetening agents. These are the chemical compounds that give a sweetening effect to the food and enhance its odor and flavor. Ortho- sulphobenzimide known as saccharin is the most popular sweetening agent and has been used for many articles of food. It has a very sweet taste and is about 550 times sweeter than sucrose.
Other artificial sweeteners commercially used in food articles are aspartame (methyl ester), alitame, dulcin (urea sweetener), dihydrochalcones (DHC), sucralose, etc.