By going through these CBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 14 Ecosystem, students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Ecosystem Notes Class 12 Biology Chapter 14
→ An ecosystem is a structural and functional unit of the biosphere which consists of a community of living beings and the physical environment, both of them interacting and exchanging materials between them. In short, the ecosystem is a self-supporting, stable ecological unit that results from an interaction between the biotic community and its abiotic’ environment.
→ The ecosystem has two main components: an abiotic component that includes all plants, animals, and microorganisms, and an abiotic component that includes soil, water, minerals, CO2, and oxygen. It receives energy in the form of sunlight.
→ The biotic component of the ecosystem contains all the living members. These are connected to each Other by food and energy. They are divided into producers (autotrophs) and consumers (herbivores and carnivores) and decomposers.
→ Food is manufactured from inorganic raw materials by autotrophs only so they are called producers. They are mainly photosynthetic plants that contain chlorophyll. Consumers are animals that feed on plants (herbivores) directly, are called primary consumers, and animals that feed on other organisms or their parts are called secondary or tertiary consumers (carnivores).
Microorganisms break the dead organic matter into simple substances which are returned to the environment for reuse, they are called decomposers. Based on the source of nutrition every organism occupies a place in an ecosystem. This place is called a trophic level of the organism.
→ Productivity, decomposition, energy flow, and nutrient cycling are the main functions of an ecosystem. The nutrients are used again and again in a cyclic manner but energy trapped from sunlight is lost as heat.
→ A food chain consists of various trophic levels which include a producer, various levels of consumers, and a decomposer.
→ Food chains are of three kinds viz. predator, parasitic and saprophytic chain. The food chains are interlinked to each other. The various food chains in a community form a food web.
→ Primary productivity is the rate of capture of solar energy or biomass production of the producers. It can be, gross primary productivity (GPP) and net primary productivity (NPP). GPP is the rate of capture of solar energy or total production of organic matter. NPP is the remaining biomass or the energy left after the utilization of producers. Secondary productivity is the rate of assimilation of food energy by the consumers. Decomposition is the breakdown of complex organic compounds of detritus into CO2, water, and inorganic nutrients. It involves three processes: fragmentation of detritus, leaching, and catabolism.
→ Energy flow is unidirectional. The number of materials and energy transferred as food through successive higher trophic levels progressively decreases.
→ The graphic representation of the relationship of food and energy between organisms at different trophic levels is called pyramids. The base of each pyramid represents the producers and the apex represents the tertiary consumer.
The ecological pyramids are of three types:
- pyramid of number,
- pyramid of biomass and
- pyramid of energy.
Mostly the pyramid of number and biomass are upright but sometimes the pyramid of biomass may be of the inverted type, e.g. in a sea. The pyramid of energy is always upright.
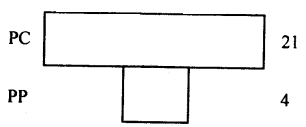
The inverted pyramid of biomass. A small standing crop of phytoplankton supports a large standing crop of zooplankton.
→ Biosphere or ecosphere is the part of the earth inhabited by organisms and their living and non-living environment. The earth is a closed system regarding materials. The substances vital for life are limited and must be recycled to sustain life. The earth is an open system regarding energy. It receives energy from the Sun in the form of solar energy, a part of it is trapped by living organisms and the major part is radiated back to outer space. The biosphere consists of the atmosphere, lithosphere, and hydrosphere.
→ The storage and movement of nutrient elements through the various components of the ecosystem is called nutrient cycling or Biogeochemical cycle, bio: living organisms, geo: rocks, air, water.
Nutrient cycles are of two types:
- Gaseous cycle: It has carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen as a reservoir and exists in the atmosphere and
- Sedimentary cycle: It has phosphorus, sulfur, calcium, potassium, etc. as a reservoir and is located in the earth’s crust.
The gaseous cycles are more balanced than the sedimentary cycles. The reservoir compensates for the deficit which occurs due to an imbalance in the rate of influx and efflux.
→ Biomes are regional, integrated, natural biotic units, which can be identified by the forum of life of the climax vegetation. Biomes may also include developing and modified communities, within the same climatic region like forest biomes will include young successional forests and open grass-dominated tracts.
The three major biomes are:
- forest biome,
- grassland biome, and
- desert biome.
Each biome has a characteristic array of plants and animal life. Climatic and edaphic factors, latitude, and barriers determine the extent of a biome.
→ Ecotones are the zones present between adjacent biomes, these support some organisms from each adjoining biome and some typical characters of their own.
→ Abiotic components: Consists of environmental factors. These are inorganic substances, organic substances, and climatic factors.
→ Biotic components: These comprise various kinds of organisms which are producers. consumers and decomposers.
→ Biome: Biomes are regional, integrated, natural biotic units, which are identified by the life form of the climax vegetation.
→ Biotics: Study of the functions of life.
→ Boreal forest: Another name of the taiga.
→ Biodegradation: Breakdown of organic and inorganic material by bacteria and fungi.
→ Consumers: Organisms that depend upon producers for food. These are herbivores and carnivores.
→ Canopy: Part of a woodland or forest community that ¡s formed by the trees.
→ Community retrogression: The reversal of ecological succession due to a disturbance in some serai stage like the destruction of grass by overgrazing.
→ Decom posers: Heterotrophic organisms like bacteria and fungi. They recycle the nutrients in the ecosýstem.
→ Epilimnion: tipper layer of warm water in a stratified lake.
→ Eutrophic: Water body rich in nutrients.
→ Edge effect: Tendency of ecotone to have a greater number of species and higher population density as compared to adjacent communities.
→ Forb: Any herbaceous plant other than grass.
→ Ecotone: Transitional zone between two vegetation regions.
→ Ecotype: The climate and edaphic factors of a place constitute ecotype.
→ Hygrometer: Instrument to measure the humidity of air or gas.
→ Incomplete ecosystem: Lacks one or more basic components e.g. deep sea, due to absence of light lacks producers.
→ Limnology: Study of freshwater bodies like lakes.
→ Meteorology: Study of atmospheric phenomena like forecasting weather.
→ Nutrient cycle: The movement of nutrient elements through the various components oían ecosystem.
→ Oiigatrohic: Water body poor in nutrients.
→ Productivity: The rate of biomass production.
→ Phenology: Study of periodic phenomena of plant and animal life like breeding, migration in relation to seasonal changes.
→ Rain gauge: Instrument for measuring rainfall.
→ Root detritus: Detritus formed by dead, underground roots of plants.
→ Photosynthetic active radiation (PAR): Visible light which carries about 50% of the energy of total incident solar radiation and iš available to producers for absorption.
→ Standing biomass: The biomass present in an ecosystem at a given time.
→ Standing crop: Amount of living material in a component population of a specific trophic level at a given time.
→ Stratification: Vertical distribution of different species occupying different levels.
→ Species composition: Identification and enumeration of plant and animal species of an ecosystem.