By going through these CBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 4 Reproductive Health, students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Reproductive Health Notes Class 12 Biology Chapter 4
→ According to World Health Organisation (WHO), reproductive health means total well-being in all aspects of reproduction. It includes physical, emotional, behavioral, and social health. A reproductively healthy society has people with normal emotional and behavioral interactions as well as physically and functionally normal reproductive organs.
India has greater proportions of young individuals who belong to different age groups such as adolescents, early childhood, and puberty. Health and education of the younger generation, age of marriage, and childbearing capacity of women are some important areas of concern for the overall reproductive health of the human population.
Reports have revealed that enrolments for secondary school education are low especially for girls, complications during pregnancy, childbirth, and abortions are major reasons for female deaths, the chances of infection of sexually transmitted diseases are maximum between 15 – 24 years.
→ In the world, India was the first country to start action plans and programs to attain total reproductive health at the national level. These programs are called family planning and were started in 1951. Reproductive and Child Health Care (RCH) programs are creating awareness about various reproduction-related areas, providing facilities and support for building a reproductively healthy society.
→ The health centers provide information, guidance, and assistance to mothers before and after delivery. Pregnant women need more nutritious food especially calcium, iron, and vitamins. They should avoid the use of alcohol, drugs, and tobacco because they may cause abnormalities in the developing baby. Women should avoid taking medicines as some may be teratogenic (abnormality causing).
→ These centers also provide safe delivery of the infant and postnatal care. Delivery by untrained midwives may be dangerous so women should prefer delivery in hospitals with trained physicians.
→ The health centers also take care of infant immunization and prophylaxis against anemia and deficiency of vitamins. They should be provided with the following vaccines:
Table: National Immunisation Schedule
| Age | Vaccination |
| 3 – 12 Months | DPT – 3 doses at intervals of 4-6 weeks. Polio (oral) – 3 doses at intervals of 4-6 weeks. BCG (intradermal). |
| 9 – 15 Months | The measles vaccine – one dose. |
| 18 – 24 Months | DPT – booster dose. Polio (oral) – booster dose. |
| 5 – 6 Years | DT (bivalent vaccine) against diphtheria and tetanus – booster dose. Typhoid vaccine – 2 doses at an interval of 1-2 months. |
| 10 Years | Tetanus toxoid – booster dose. Typhoid vaccine – booster dose. |
| 16 Years | Tetanus toxoid – booster dose. Typhoid vaccine – booster dose. |
| Mother during pregnancy | (a) Previously immunized One booster dose of tetanus toxoid 4 weeks before the expected delivery date.(b) Nonimmunised Two doses of tetanus toxoid: 1st between 16-24 weeks and 2nd between 24-32 weeks of pregnancy. |
→ These centers train midwives to handle the safe delivery of infants. They also arrange for milk feeding programs. The infants do not have antibodies of their own, they get it from the mother’s milk. Such infants are less prone to allergies than bottle-fed ones.
→ The health centers educate the couples about the importance of small families and proper spacing between successive birth. Too young women are likely to produce underweight and weak babies. To start with pregnancy the reproductive system should be fully mature, physically and functionally as well.
→ Government and non-governmental agencies are working together, using various audio-visual aids to aware people about various programs, infrastructure facilities and to find out new improved methods and to implement them properly.
→ Increased health facilities and better living conditions have increased the population at an alarming level. A rapid decline in death rate, the maternal mortality rate (MMR) and infant mortality rate (IMR), and an increase in the number of people in reproducible age are the main reasons for this. This could lead to a scarcity of basic amenities so serious efforts to check this population growth rate are required.
→ One step to control the population rate is to control the birth rate of the population. To educate and motivate the fertile couples to have smaller families.
→ The regulation of conception by preventive methods or devices to limit the number of off-springs is called birth control. A variety of methods are used for birth control.
→ The birth control methods which prevent fertilization are known as contraception. A contraceptive should be user-friendly, easily available, effective, and reversible with no side effects.
These contraceptive methods are of two main types:
1. Temporary methods: As clear from the name these are temporary measures that are effective for a limited period.
(a) Safe period or Rhythm method: Generally one week before and one week after the menstrual cycle is considered a safe period. This is also called natural family planning. In it, the couples avoid coitus from 10 to 17 days of the menstrual cycle.
It is termed Periodic abstinence. It is based on the observations that ovulation occurs on about the 14th day of the menstrual cycle. An ovum survives for about 1-2 days, sperms remain active for about 3 days. This method reduces the chances of fertilization to 80%.
(b) Coitus Interruptus: This is the oldest method of birth control. It involves the withdrawal of the penis from the vagina by the male before ejaculation so as to avoid insemination. The drawbacks of this method are that the male produces some lubricating fluid from Cowper’s glands which contains many sperms. A lapse of timing may result in late withdrawal and therefore pregnancy.
(c) Lactational Amenorrhea: This means the absence of menstruation. It is based on the fact that ovulation does not occur during intense lactation after parturition, so there is no menstrual! cycle. The chances of conception are nil. This method does not have any side effects. It can only be effective for a maximum of six months after parturition.
(d) Chemical methods: These include jellies, foam tablets, pastes, or creams that contain spermicides (agents to kill sperms) such as lactic acid, boric acid, citric acid, zinc sulfate, or potassium permanganate. Before intercourse, if these are introduced into the vagina, they adhere to the mucous membrane and kill the sperms.
(e) Mechanical means: These are barrier methods that prevent the sperms and ovum to come closer.
They are of three types:
1. Condom (Nirodh) is made up of a thin rubber/latex sheath meant to cover the penis so that semen would not enter into the female reproductive system. The female condom covers the vagina and cervix, just before coitus. These should be discarded after a single-use. Their use is simple and has no side effects. These are very useful against STDs and AIDS.
2. Diaphragm and cervical cap: These are the rubber plastic covers that are fitted on the cervix in a female’s vagina and blocks the entry of sperms through the cervix. These are reusable and must be kept fit for at least six hours after intercourse. Every time these are smeared with spermicidal jelly, creams, or foams to increase their contraceptive efficiency.
3. Intrauterine Devices (IUDs): These are metal or plastic objects inserted inside the uterus of the female. These may be non-medicated lUD’s such as Lippes Loop, Copper releasing IUDs e.g. CuT, Cu7, Multiload 375, and the hormone-releasing ones e.g. Progestasert. LNG-20.
They prevent the fertilization of egg or embryo implantation. IUDs increase phagocytosis of sperms within the uterus, Cu2+ ions released by some of them suppress sperm motility and their fertilizing capacity. The hormone-releasing IUDs make the uterus unsuitable for implantation and cervix, hostile to the sperms. These should be used with the help of a physician. Their presence may act as a minor irritant.
Their drawbacks are spontaneous expulsion, occasional hemorrhage, perforation of the uterus, or tubal pregnancy.
1. Physiological (Oral) devices: These are birth control pills that check ovulation by inhibiting the secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone. A combined pill is widely used, it contains progesterone and estrogen in high doses to prevent ovulation.
→ Pill Mala D is taken daily, and pill Saheli is taken weekly, it contains a non-steroidal preparation called ‘Centchroman’. These have side effects like nausea, breast tenderness, weight gain, slight bleeding, and high blood pressure. They also reduce certain types of cancer.
→ Progestagen along with estrogen is used by females as injections or implants under the skin. Their action is similar to pills and is for a longer duration (3 to 4 years).
→ Progestagens if taken within 72 hours of coitus are very effective and can avoid pregnancy due to some accidents.
2. Permanent Method: These are surgical methods or sterilization, which provides a permanent or terminal method for birth control. In males, it is called vasectomy and in females, it is called tubectomy. Surgical methods block gamete transport and thus prevent pregnancy. In a vasectomy, a small part of the vas deferens is removed or tied up by a small incision on the scrotum.
In tubectomy, a small part of the fallopian tube is removed or tied up through a small incision in the abdomen or through the vagina. This is done under local anesthesia and does not affect the normal sex life. These techniques are highly effective and widely used but they have poor reversibility.
→ Laparoscopy: A small laparoscope (telescopic instrument) is used in tubal ligation. It blocks the fallopian tubes. Thus the eggs fail to pass the fallopian tube and sperms fail to reach the eggs.
→ Sterilization is the most effective measure for birth control. All these methods should be used under the guidance of a medical practitioner.
→ Voluntary Termination of Pregnancy or Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) is known as abortion. The pregnancy is terminated before the fetus becomes viable. It is a method of fertility control used all over the world. Certain pills induce menstruation which acts as abortions and checks the implantation of a zygote or detaches the implanted egg. MTPs if done during the first 12 weeks of pregnancy is safe. It becomes riskier during the second trimester. Only a certified practitioner should be contacted for MTP.
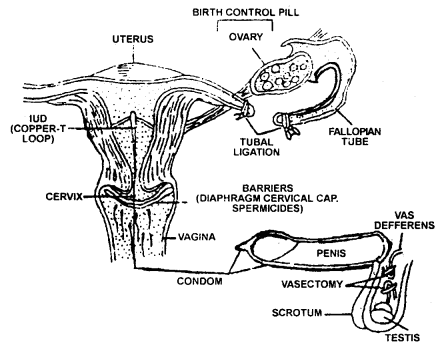
Contraception methods
→ RU – 486 is an analog of progesterone that terminates pregnancy within the first few weeks. It acts by blocking the receptors in the uterus thus preventing progesterone from maintaining pregnancy.
→ Infections or diseases that transmit through unsafe sexual intercourse are called sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) or reproductive tract infections (RTI) or Venereal diseases (VD) Gonorrhoea and syphilis are the most common. Another is AIDS. Adolescents are more vulnerable to these because of a lack of proper knowledge.
Table: Common STDs and their causative agents
| Infection/Disease | Causative agent |
| Gonorrhea | Neisseria gonorrhoeae |
| Syphilis | Treponema pallidum |
| Chlamydiosis | Chiarnydia trachomatis |
| Genital Herpes | Herpes Simplex Virus. Human Papilloma Virus |
| Hepatitis-B | Hepatitis Virus |
| HIV-AIDS | Human Immunodeficiency virus |
| Trichomoniasis | Trichomonas vaginal is/Protozoan |
→ To avoid these one should avoid having sex with unknown partners or multiple partners, always use condoms during coitus and seek medical help as soon as possible.
→ Early symptoms of most of these infections are minor. It includes slight itching, fluid discharge, slight pain or swelling in the genital region. If not paid proper attention these may become complicated ones as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), abortions, ectopic pregnancy, stillbirth, infertility, or even cancer of the reproductive tract.
→ Infertility is the condition when couples are unable to produce children in spite of unprotected sexual cohabitation. Infertility may be physical, congenital, diseases, drugs, immunological, or even psychological. These problems can be cured by assisted reproductive technologies (ART). In vitro fertilization (IVF) is done followed by Embryo transfer (ET)is one of such practices done to cure infertility.
In IVF, ova from the donor female and sperms from the donor male are collected and induced to form a zygote, which is then transferred into the fallopian tube known as ZIFT-zygote intrafallopian transfer. For ZIFT the embryos are up to 8 blastomeres. Embryos with more than 8 blastomeres are transferred into the uterus called JUT (intrauterine transfer) for further complete development.
GIFT: gamete intrafallopian transfer, is the transfer of ovum from a donor to the receiver female who cannot produce one. Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) is a product where embryos are produced in the laboratory. The artificial insemination (AI) technique is used in case of male’s sperm count is low. In IUT: intrauterine insemination, semen is collected from donors and artificially introduced into the vagina or uterus.
→ Polyovulation: Discharge of several ova in one ovulatory cycle.
→ Hygienist: A person well versed in the principles of hygiene.
→ Laparoscopy: Examination of the peritoneal cavity through an incision in the abdominal wall.
→ Abortion: Giving birth to an embryo or fetus prior to the stage of viability at about 20 weeks of gestation.
→ Premature birth: Birth after the age of fetal viability but before full term.
→ Fetus: Developing young one from the end of the eight weeks to the moment of birth.
→ Foeticide: Destruction of embryo or fetus in the uterus.
→ RCH programs: Reproductive and Child Health Care program.
→ IUDs: Intra-Uterine Devices.
→ MTP: Medical termination of pregnancy.
→ VD: Venereal diseases.
→ RTI: Reproductive tract infections.
→ PID: Pelvic inflammatory diseases.
→ ART: Assisted reproductive technologies.
→ IVF: Invitro fertilization.
→ ET: Embryo transfer.
→ ZIFT: Zygote intrafallopian transfer.
→ IUT: Intra uterine transfer. .
→ GIFT: Gamete intrafallopian transfer.
→ ICSI: Intracytoplasmic sperm injection.
→ AI: Artificial insemination.
→ IUI: Intra-uterine insemination.