Mineral and Power Resources Class 8 Extra Questions Geography Chapter 3
Question 1.
Mention the physical properties of minerals.
Answer:
Colour, density and hardness.
Question 2.
Write any one chemical property of minerals.
Answer:
Solubility.
Question 3.
Classify the minerals on the basis of composition.
Answer:
Metallic and non-metallic.
Question 4.
Into which two types can metallic minerals be divided.
Answer:
- Ferrous
- Non-ferrous.
Question 5.
How are minerals extracted?
Answer:
Minerals are extracted by mining, drilling or quarrying.
![]()
Question 6.
Which continent produces more than half of the world’s tin?
Answer:
Asia.
Question 7.
Which countries are the leading producers of tin in the world?
Answer:
China, Malaysia and Indonesia.
Question 8.
Which country is the largest producer of high-grade iron-ore?
Answer:
Brazil.
Question 9.
Which countries of South America are the leading producers of copper 7
Answer:
Chile and Peru.
Question 10.
Which countries of South America are the world’s largest producers of tin?
Answer:
Brazil and Bolivia.
Question 11.
Which two areas of Australia are rich in gold deposits?
Answer:
Kalgoorlie and Coolgardie.
Question 12.
Which country is the largest producer and exporter of mica in the world?
Answer:
India.
Question 13.
In which part of India deposits of gold are found?
Answer:
Kolar in Karnataka.
![]()
Question 14.
Which minerals are obtained from quartz and bauxite?
Answer:
Mineral obtained from quartz is silicon and aluminium from bauxite.
Question 15.
Into which two categories can power resources be classified?
Answer:
Conventional and non-conventional resources.
Question 16.
Name two main conventional energy sources.
Answer:
Firewood and fossil fuels.
Question 17.
Give two examples of fossil fuels.
Answer:
Coal, petroleum.
Question 18.
How is wind energy generated?
Answer:
The high-speed winds rotate the windmill which is connected to a generator to produce electricity.
Question 19.
Name the greatest producers of nuclear power in the world.
Answer:
USA and Europe.
Question 20.
Where do geothermal plants are located in India?
Answer:
- Manikaran in Himachal Pradesh
- Puga Valley in Ladakh.
Question 21.
Which type of resources are coal and petroleum?
Answer:
Non-renewable.
![]()
Question 22.
What are minerals? How do they form?
Answer:
A naturally occurring substance that has a definite chemical composition is a mineral. They are formed in different types of geological environments under varying conditions.
Question 23.
Write two characteristics of metals.
Answer:
- Metals are hard substances that conduct heat and electricity.
- They have a characteristic lustre or shine. For example, iron, aluminium, copper, etc.
Question 24.
Distinguish between open-cast mining and shaft mining.
Answer:
Open-cast mining – When minerals lie at shallow depths, they are taken out by removing the surface layer. This is called open-cast mining.
Shaft mining – When minerals lie at the great depth deep bores are made to extract. This is called shaft mining.
Question 25.
Certain minerals are found in igneous and metamorphic rocks. Give three such examples.
Answer:
- Iron-ore in north Sweden.
- Copper and nickel in Ontario, Canada.
- Iron, nickel, chromites and platinum in South Africa.
Question 26.
Name the minerals found in sedimentary rocks along with their location.
Answer:
- Limestone in Caucasus region of France.
- Manganese deposits of Georgia and Ukraine.
- Phosphate beds of Algeria.
Question 27.
Name the minerals found in Europe.
Answer:
- Iron ore is found in Russia, Ukraine, Sweden and France.
- Copper, lead, zinc, manganese and nickel are found in eastern Europe and European Russia.
![]()
Question 28.
Mention the three zones of North America where mineral deposits are located.
Answer:
- The Canadian region north of the Great Lakes.
- The Appalachian region.
- The mountain ranges of the West.
Question 29.
Name the four countries of South America where mineral oil is found.
Answer:
- Venezuela,
- Argentina,
- Chile,
- Peru,
- Columbia.
Question 30.
Write the minerals which have been predicted to be found in Antarctica.
Answer:
- Deposits of coal in the Trans-Antarctic Mountains.
- Iron near the Prince Charles Mountains of East Antarctica.
- Iron-ore, gold, silver and oil are also present.
Question 31.
Where is iron found in India?
Answer:
Jharkhand, Orissa, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Goa, Maharashtra and Karnataka.
Question 32.
In which states of India is bauxite found?
Answer:
Jharkhand, Orissa, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu.
![]()
Question 33.
Write two advantages and disadvantages of petroleum.
Answer:
Advantages of petroleum –
- It is easier to transport.
- It is the basis of petrochemical industry.
Disadvantages of petroleum –
- Oxygen gets depleted due to oil spillage and gas leakage.
- Pollutants released while burning, cause acid rain.
Question 34.
Write two advantages and disadvantages of firewood.
Answer:
Advantages of firewood –
- It is easily accessible.
- It provides energy to a large number of people.
Disadvantages of firewood –
- Collection of firewood is time-consuming.
- It causes air pollution.
Question 35.
Write two merits and demerits of coal.
Answer:
Advantages of coal –
- It is extensively available.
- It can efficiently be converted into electricity.
Disadvantages of coal –
- It pollutes the environment.
- It is bulky to transport.
Question 36.
How are fossil fuels formed?
Answer:
Remains of plants and animals which are buried under the earth for millions of years get converted by the heat and pressure into the fossil fuels.
![]()
Question 37.
Write four uses of coal.
Answer:
- It is used as a domestic fuel.
- It is used in industries such as iron and steel industry, brick industry etc.
- Coal is used to run steam engines.
- It is used to generate electricity.
Question 38.
Why is coal referred to as Buried Sunshine?
Answer:
The coal was formed millions of years ago when giant ferns and swamps got buried under the layer of the earth. Therefore, coal is referred to as Buried Sunshine.
Question 39.
Name four coal producing countries of the world.
Answer:
- China,
- USA,
- Germany,
- Russia,
- South Africa,
- France.
Question 49.
Name the major coal-producing areas of India.
Answer:
Raniganj, Jharia, Dhanbad and Bokaro.
Question 41.
Name the products produced from crude oil.
Answer:
Diesel, petrol, kerosene, wax, plastics and lubricants.
Question 42.
Name the chief petroleum-producing countries.
Answer:
Iran, Iraq, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, USA, Russia, Venezuela and Algeria.
Question 43.
Name the leading oil producer states of India.
Answer:
- Digboi in Assam.
- Bombay High in Mumbai.
- Deltas of Krishna and Godavari rivers.
Question 44.
Where is natural gas found in India?
Answer:
- Jaisalmer
- Krishna-Godavari .delta
- Tripura
- Offshore in Mumbai.
Question 45.
Name the leading producers of hydel power in the world.
Answer:
Paraguay, Norway, Brazil and China.
![]()
Question 46.
Write the advantages and disadvantages of solar energy.
Answer:
Advantages of solar energy
- It is inexhaustible.
- It does not cause pollution.
Disadvantage of solar energy:
The method of extracting solar energy is costly.
Question 47.
Write one advantage and disadvantage of each tidal and nuclear energy.
Answer:
Tidal energy – Advantage – It is non-polluting and inexhaustible.
Disadvantage – It destroys wildlife habitat. It is also difficult to harness tidal energy.
Nuclear energy – Advantage- It emits large amount of energy.
Disadvantage – It generates radioactive wastes.
Question 48.
Write the uses of solar energy.
Answer:
- Solar energy is used in solar heaters, solar cookers, solar dryers.
- It is also used for community lighting and traffic signals.
Question 49.
Name the countries which are noted for their wind energy production.
Answer:
Netherlands, Germany, Denmark, UK, USA and Spain are noted for their wind energy production.
Question 50.
How is nuclear power generated?
Answer:
Nuclear power is obtained from energy stored in the nuclei of atoms of radioactive elements like uranium and thorium. These fuels undergo nuclear fission in nuclear reactors and emit power.
Question 51.
In which states of India are deposits of uranium and thorium found?
Answer:
Uranium is found in Rajasthan and Jharkhand. Thorium is found in the monazite sands of Kerala.
Question 52.
Name four hydel power stations of India.
Answer:
- Bhakra Nangal
- Gandhi Sagar
- Nagarjuna Sagar
- Damodar Valley.
Question 53.
Mention the major nuclear power stations of India.
Answer:
- Kalpakkam in Tamil Nadu
- Tarapur in Maharashtra
- Rana Pratap Sagar near Kota in Rajasthan
- Narora in Uttar Pradesh
- Kaiga in Karnataka.
Question 54.
Write the uses of geothermal energy.
Answer:
Geothermal energy in the form of hot springs is used for cooking, heating and bathing.
![]()
Question 55.
Name the countries where geothermal plants are located.
Answer:
- USA has the world’s largest geothermal power plant.
- New Zealand
- Iceland
- Philippines
- Central America.
Question 56.
Locate on the outline map of the world.
(a) Mineral oils in India
(b) Coal mines in USA
(c) Coal mines in China
Answer:
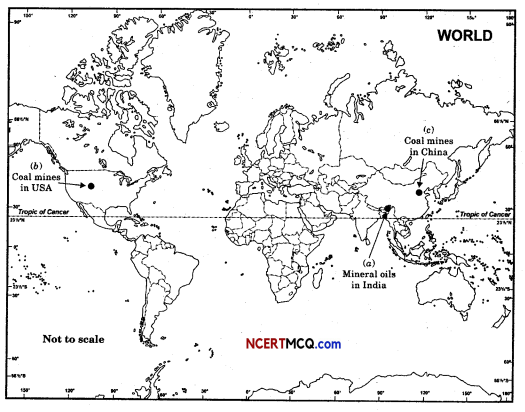
Question 57.
Show the following on the outline map of the world.
(i) South Africa
(ii) China
(iii) India
(iv) USA
(v) Australia
Answer:
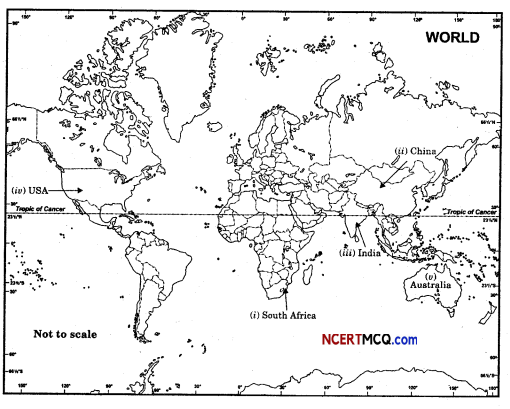
Question 58.
Describe the distribution of minerals in North America.
Answer:
In North America, mineral deposits are found in three zones –
- The Canadian Shield- Iron-ore, nickel, gold, uranium and copper are found.
- Appalachian region – Coal
- Western Cordilleras – Copper, lead, zinc, gold and silver.
Question 59.
Africa is rich in mineral resources. Justify.
Answer:
- Africa is the world’s largest producer of diamonds, gold and platinum.
- South Africa, Zimbabwe and Zaire produce a large portion of the world’s gold.
- Copper, iron ore, chromium, uranium, cobalt and bauxite are the other minerals found in Africa.
- Oil is found in Nigeria, Libya and Angola.
Question 60.
Give a brief account of minerals found in Australia.
Answer:
- Australia is the largest producer of bauxite in the world.
- It is a leading producer of gold, diamond, iron ore, tin and nickel.
- Rich deposits of copper, lead, zinc and manganese are also found.
- Large deposits of gold are found in Kalgoorlie and Coolgardie.
Question 61.
Name two metallic and non-metallic minerals found in India. Also, mention the areas where they are found.
Answer:
Two metallic minerals of India are –
- Copper-It is found in Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Jharkhand, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh.
- Manganese – It is found in Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Orissa, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh.
Two non-metallic minerals of India are –
- Limestone – Major limestone producing states are Bihar, Jharkhand, Orissa, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Rajasthan, Gujarat and Tamil Nadu.
- Salt – It is obtained from seas, lakes and rocks. Salt is extracted in Rajasthan and Gujarat.
Question 62.
Why is conservation of minerals necessary? Mention two ways by which minerals can be conserved.
Answer:
Conservation of minerals is important because:
- It takes thousands of years for the formation and concentration of minerals.
- The rate of formation of minerals is much slow in comparison to their consumption.
Two ways by which minerals can be conserved are –
- To reduce the wastage in the process of mining.
- Recycling of metals.
Question 63.
Write the advantages and disadvantages of hydel power.
Answer:
Advantages ;
- It does not cause environmental pollution.
- It promotes irrigation and fishing.
- It is cheap.
Disadvantages :
- It leads to the displacement of local community.
- It is expensive to set up a hydel power project.
- It affects the natural flow of the rivers. It also causes excessive sedimentation at the bottom of the reservoir.
![]()
Question 64.
Where are the reserves of natural gas found? Mention its uses. Also mention the major natural gas producing countries.
Answer:
- Natural gas is found with petroleum deposits and is released when crude oil is brought to the surface.
- It can be used as a domestic and industrial fuel.
- The major natural gas producing countries are Russia, Norway, UK and Netherlands.
Question 65.
How is the hydel power produced?
Answer:
Water stored in the dams is made to fall from heights. The falling water flows through pipes inside the dam over turbine blades placed at the bottom of the dam. The moving blades then turn the generator to produce electricity.
Question 66.
Why is there need for using non-conventional sources of energy?
Answer:
- The sharp increase in the consumption of fossil fuels has led to their depletion at an alarming rate.
- The toxic pollutants released from burning the fuels cause environmental pollution.
- The conventional sources are non-renewable.
- It takes millions of years for the formation of fossil fuels.
Therefore, there is need for using non-conventional sources such as solar energy, wind energy. These sources are renewable.
Question 67.
Write the advantages and disadvantages of wind energy.
Answer:
Advantages :
- It does not cause environmental pollution.
- Once the windmill is set up, the cost of production of electricity is less.
- It is safe and does not leave any waste.
Disadvantages :
- It causes noise pollution.
- Windmills are costly to set-up.
- Windmills disturb radio and TV reception.
- Windmills are harmful to birds.
Question 68.
What is biogas? How is it obtained? Write its two uses.
Answer:
- Organic wastes such as dead plant and animal material, animal dung and kitchen waste can be converted into a gaseous fuel called biogas.
- The organic waste is decomposed by bacteria in biogas digesters to emit biogas which is essentially a mixture of methane and carbon dioxide.
Uses of biogas :
(a) Biogas is used for cooking and lighting.
(b) It produces huge amount of organic manure.
![]()
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
1. Which one of the following is not a correct statement?
(a) The metallic minerals contain metal in raw form.
(b) Minerals occur in different types of rocks.
(c) Minerals that lie near the surface are simply dugout, by the process known as mining.
(d) Africa is the world’s largest producer of diamonds.
Answer:
(c) Minerals that lie near the surface are simply dugout, by the process known as mining.
2. Which one of the following is not a ferrous mineral?
(a) Lead
(b) Manganese
(c) Chromites
(d) Iron ore.
Answer:
(a) Lead.
3. Tick the odd ‘miniral-use’ pair in the following.
(a) Silicon – Computer
(b) Aluminium-Steel
(c) Copper – Coins
(d) Minerals – Gems.
Answer:
(b) Aluminium-Steel.
4. Jharkhand is a major producer of many minerals but it lacks :
(a) iron ore
(b) coal
(c) mica
(d) gold
Answer:
(d) gold.
![]()
5. Which of the following statements is not correct?
(а) Coal is referred to as ‘Buried Sunshine’.
(b) Petroleum and its derivatives (or products) are called ‘Black Gold’.
(c) Minerals are a renewable resource.
(d) Firewood and fossil fuels are conventional energy resources.
Answer:
(c) Minerals are a renewable resource.
Glossary:
→ Mineral – A naturally occurring substance that has a definite chemical composition is a mineral.
→ Metallic minerals – The minerals which contain metal are called metallic minerals.
→ Non-metallic minerals – The minerals which do not contain metals are called non-metallic minerals.
→ Mining- The process of taking out minerals from rocks buried under the earth’s surface is called mining.
→ Open-cast mining – When minerals are extracted by removing the surface layer is called open-cast mining.
→ Shaft-mining- It is done to extract minerals found in great depths.
→ Drilling – When deep wells are bored to take out minerals is called drilling.
→ Quarrying – Minerals that lie near the surface are dug out by the process of quarrying.
→ Rock – A rock is an aggregate of one or more minerals but without definite composition of mineral’s constituent.
→ Ores – Rocks from which minerals are mined are known as ores.
→ Conventional sources – Those sources of energy which have been in common use for a long time.
→ Thermal power – Electricity generated from coal is called thermal power.
→ Hydel power-The energy generated by falling water over the turbine blades.
→ Nuclear power – The energy obtained from energy stored in the nuclei of atoms of naturally occurring radioactive elements like uranium and thorium.
→ Geothermal energy- Heat energy obtained from the earth is called geothermal energy.
→ Tidal energy – Energy generated from tides is called tidal energy.
→ Biogas- Organic waste such as dead plant and animal material, animal dung and kitchen waste can be converted into gaseous fuel called biogas.
