Check the below Online Education NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 9 Geography Chapter 3 Extra Questions and Answers Drainage Pdf free download. https://ncertmcq.com/extra-questions-for-class-9-social-science/
Online Education for Drainage Class 9 Extra Questions Geography Chapter 3
Class 9 Geography Chapter 3 Extra Questions And Answers Question 1.
Where term the Brahmaputra originates?
Answer:
From Tibet.
Drainage Class 9 Extra Questions Question 2.
In which direction does the Brahmaputra flow?
Answer:
The Brahmaputra flows in eastward direction parallel to the Himalayas.
Extra Questions For Class 9 Geography Chapter 3 Drainage Question 3.
Whaf does the Brahmaputra do in Namcha Barwa ?
Answer:
The Brahmaputra reaching Namcha Barwa takes a U-tum and enters India in Arunachal Pradesh.
Class 9 Geography Chapter 3 Extra Questions Question 4.
What is a river basin?
Answer:
A river basin is meant by the area which is drained by a single river system. This a also known as drainage basin.
![]()
Extra Questions For Class 9 Geography Chapter 3 Question 5.
Name two saltwater lakes on the eastern coast of India.
Answer:
- The Chilka – in Orissa.
- The Pulicat – in Tamil Nadu.
Drainage Extra Questions Question 6.
In which states does the Brahmaputra flow in India?
Answer:
- Arunachal Pradesh,
- Assam.
Class 9 Drainage Extra Questions Question 7.
By which name Brahmaputra is known in Tibet?
Answer:
Tsangpo.
Ncert Class 9 Geography Chapter 3 Extra Questions Question 8.
Name the city located on the water divide between the Indus and Ganga.
Answer:
Ambatal.
Class 9 Geography Chapter 3 Short Questions And Answers Question 9.
By which name the mainstream of Ganga is known in Bangladesh?
Answer:
Padma.
Class 9 Geo Ch 3 Extra Questions Question 10.
When is the Ganga known as Tainuna?
Answer:
In Bangladesh where the Brahmaputra joins the Ganga, it is known as Jamuna.
Drainage System Class 11 Extra Questions Question 11.
Where does the Jhelum fall into the Indus?
Answer:
A little over Mithankot.
![]()
Extra Questions Of Drainage Class 9 Question 12.
What is meant by the dendritic pattern of streams?
Answer:
The dendritic pattern of streams indicates the streams resembling like the branches of a tree.
Class 9 Geography Chapter 3 Questions And Answers Question 13.
What is meant by the trellis?
Answer:
Trellis indicates the situation where the tributaries join the mainstream at the right angles.
Class 9 Geography Ch 3 Extra Questions Question 14.
What is meant by a braided stream?
Answer:
The braided stream is channel of a stream that has large island within it.
Geography Class 9 Chapter 3 Extra Questions Question 15.
What is meant by island drainage?
Answer:
Island drainage refers to die rivers not reaching a ocean. Instead, they fall into a sea or lake within the land.
Class 9 Chapter 3 Geography Extra Questions Question 16.
From which glacier does the Yamuna originate?
Answer:
Yamunotri.
Geography Chapter 3 Class 9 Questions And Answers Question 17.
Name the largest peninsular river of India.
Answer:
Godavari.
Chapter 3 Geography Class 9 Extra Questions Question 18.
Name the tributaries of die river Krishana.
Answer:
- The Tungabhadra,
- The Koyna,
- The Ghatprabha,
- The Musi,
- The Bhima.
Ch 3 Drainage Extra Questions And Answers Question 19.
Name the states which fall, into the drainage basin of the Narmada
Answer:
- Maharashtra,
- Karnataka,
- Andhra Pradesh.
![]()
Geography Chapter 3 Class 9 Extra Questions Question 20.
Which river originates from the Brahmagir range of the Western Ghats?
Answer:
The Kaveri.
Question 21.
Why are the peninsular rivers seasonal?
Answer:
They are seasonal because their flow depends on die rainfall.
Question 22.
Point out the prominent features of the Ganga-Brahmaputra delta.
Answer:
- It is the largest delta of die world.
- It is one of the most fertile areas of the world.
- It is a triangular-shaped area.
- It is a well-watered area.
- The lower part of this delta is marshy.
- Mangroves are found only in this place of the whole India.
Question 23.
How Would you differentiate between a glacier and a river?
Answer:
| The Glacier | The River |
| 1. Glaciers are in the solid form. | 1. Rivers are in liquid form. |
| 2. Glaciers look like a mountain of ice. | 2. Rivers may be seen flowing. |
| 3. Glaciers move very slowly. | 3. Rivers move with a greater speed. |
| 4. The movement of a glacier is not discernible. | 4. The movement of a river is easily discernible. |
Question 24.
How the lakes are formed?
Answer:
- Lakes are formed in the mountainous area when the glaciers block the valleys and large amount of water is collected in that place.
- The violent movements of the earth, like the earthquakes, also create lakes when the depressions formed on the crust of the earth are filled with rainwater.
- Human beings also form lakes, for various purposes.
![]()
Question 25.
What is meant by the Indus water treaty?
Answer:
Indus water treaty is a treaty between India and Pakistan. This treaty is about the- sharing of the waters of the Indus system. According to this treaty, India can use only 20% of the total of the water carried by the Indus river system.
Question 26.
Name the states through whicn the river Mahanadi flows.
Answer:
The river Mahanadi flows through three states of India:
- It originates in Chattisgarh
- If falls in the Bay of, Bengal in Orissa.
- Hence it flows through Chattisgarh and Orissa Only.
Question 27.
Why are the rivers considered the lifelines of human civilisation?
Answer:
Rivers are undoubtedly the lifelines of the human civilisation. All the early: civilisations whether in India, Mesopotamia, Egypt or in China, flourished in the river valleys. The Harappan culture of India flourished in the Indus valley. The Egyptian civilization flourished in the Nile valley and the Mesopotamian in the valleys of the Tigris and Euphrates.
It is a well-known fact that the rivers provide us water Without water, one can not imagine life. Hence it is a very natural tendency to stay and live by the sides of the river and their nearby areas. So that water heed for drinking and cultivation etc could be fulfilled easily.
Question 28.
What do you mean by the drainage?
Answer:
Drainage is an outcome of the evolutionary process of the broad relief features of the country. It is meant by the river system of an area.
Question 29.
Answer the following questions:
(i) Three major rivers Originating beyond the Himalayas.
(ii) The source area of these rivers.
(iii) Point out the feature formed by these rivers.
Answer:
(i) Three major rivers originating beyond tire Himalayas are:
- The Indus,
- The Satluj,
- The Brahmputra.
(ii) The source of the above rivers is Mansarovar near the Kailash.
(iii) Gorges, Canyons, U-shaped valleys.
Question 30.
Write a few lines on the Ganga.
Answer:
The Ganga river originates from the Gangotri glacier in the Himalayas. After crossing through India and Bangladesh, it falls in the Bay of Bengal. It is of nearly 2500 km. length. The main tribu taries of Ganga are the Yamuna, Gomut, Ghagra, gandak and Kosi. The southern tributaries of the Ganga are Son. Chambel, Betwa and Kosi.
Question 31.
Which are the important peninsular rivers of India?
Or
Give a brief account of the different peninsular rivers of India.
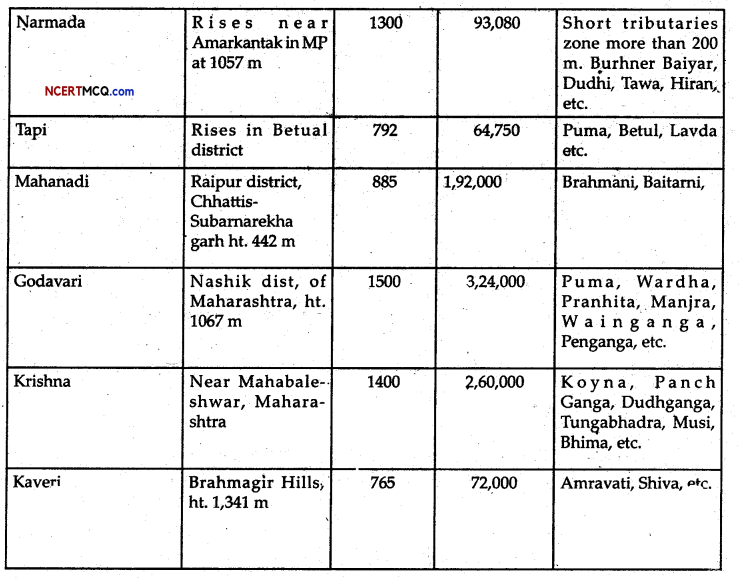
Answer:
The Narmada: If rises from Amarkantak in Madhya Pradesh. It flows west-southward in a trough for a distance about 1300 km. The Narmada gorge in the marble rocks of Madhya Pradesh is very famous for its beauty.
The Tapi: It rises from the Betul district of Madhya Pradesh. It flows in a trough parallel to the Narmada. However, it is smaller in size than that of the Narmada: The Godavari: It is also known as the Dakshin Ganga and Vridha Ganga.
It is the largest among the peninsular rivers of India. It rises in Nashik district of Maharashtra. Its length is about 15000 km. It drains into the Bay of Bengal.
The Mahanadi: It rises ill Chattisgarh and flows through Orissa and reaches the Bay of Bengal.
The Krishna: It rises from the spring near Mahabaleshwar. If flows-for nearly about 1400 km. Its drainage basin is shared by Maharashtra, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh.
The Kaveri: It rises in the Brahmagir ranges of the Western Ghats. If flows over 800 km. Near the Kaveripatnam, it reaches the Bay of Bengal.
Question 32.
What is the reason of the water pollution? How the pollution level can be reduced?
Or
Suggest some measures to reduce the pollution of water.
Answer:
Water pollution indicates that the water is not pure and safe for the health. Today, many factors are causing the water pollution; It is very dangerous for health as well as for tire environment. The large number of the dead fishes found in Yamuna at Agra proved it.
Factories, especially the chemical industries, paper mills, sugar mills, tanneries etc are causing the water to be polluted. The disposal of sewage of urban areas into the rivers also lead to this pollution. As for example, the Najafgarh Nala in Delhi may be taken.
![]()
Question 33.
What is meant by a lake? Introduce some of the important lakes of India.
Or
How are the lakes useful for us?
Or
Point out the importance of lakes.
Answer:
A large low lying depression in the earth filled with water is called a lake. A lake may be natural or artificial that is, human-made Lakes may be in the hill areas as well as in the plain.
Importance of the Lakes
- Lakes help us in drainage.
- These are the beauties attracting the tourists.
- These are important for nature and protecting the natural beauty.
- Lakes are also important for the economy of a country.
- They are used for boating and fishing.
- They provide the opportunities for recreation.
Reduction in water (low due to ever-increasing abstraction of water for irrigation from the river Ganga through canals.
Question 34.
Point out the achievements of the Ganga Action Plan.
Answer:
- Mainly 260 schemes have been launched in the Ganga Action Plan.
- Nearly 45 of them have been completed with positive results.
- Trees have been planted in badly, eroded portions to check the dams repuned in the upper reaches of the river.
- The interception and diversion of several major drains carrying savage and the industrial wastes to the river Ganga have been completed in several cities like Varanasi Kanpur and Patna.
- It has reduced the pollution level substantially.
- Turtles and the Gangetic dolphins which had been disappeared for several years reappeared in Varanasi and the other places.,
- All of the above points indicate the recovery of the health of the Ganga.
Hence though the Ganga Action Plan has miles to go it have no doubt achieved several landmark achievements.
Question 35.
Give an account of the drainage of the surface water of India.
Answer:
- Two-third of the total surface water of India drains into the Bay of Bengal.
- About 20% of the surface water drains into the Arabian Sea.
- A little less than 10% drain to form part of the inland drainage of Rajasthan desert and Aksai Chain.
- Nearly 1% drains to the Andaman Sea through the tributaries of the Irrawaddy in Myanmar.
Question 36.
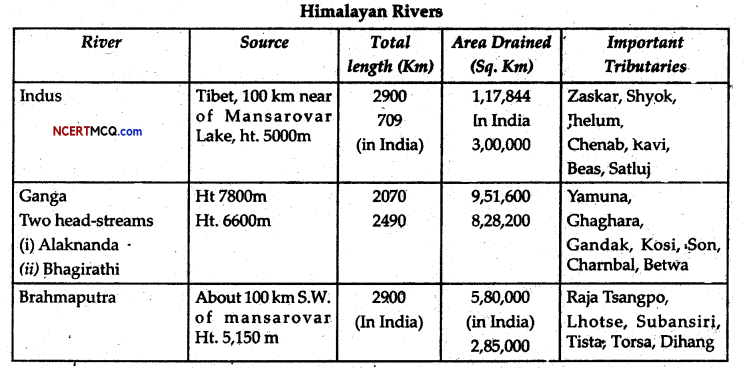
Write a detailed note on the Indus River System.
Answer:
The river Indus rises in Tibet, near Lake Mansarovar. Flowing west, it enters India in the Ladakh district of Jammu and Kashmir through a picturesque gorge. Several tributaries, the Zaskar, the Shyok and the Huzana, join it in this region. It flows through Baltistan and Gilgit and emerges from the mountains at Attack.
The famous five rivers of Punjab-the Satluj; the Beas, the Ravi, the Chenab and the Jhelum-enter.the Indus is a little above Mithankol in Pakistan. Beyond this, the Indus flows southwards eventually reaching the Arabian Sea, east of Karachi. The total length of the river is about 2900Jem, ranking it amongst the longest rivers of the world. A little over a third of the Indus basin is located in India in the states of Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh and the Punjab and the rest is in Pakistan.
Question 37.
What do you know about the Brahmaputra rivers System?
Answer:
The Brahmaputra rises in Tibet east of Mansarovar lake very close to the sources of the Indus and the Satluj. In Tibet, it is called the Tscmgpo. It is slightly longer than the Indus, and most of its course lies outside India. It flows eastwards parallel to the Himalayas to its south.
On reaching the mountain peak the Namcha Barwa (7757 m), it takes a ‘U’ turn and enters India in Arunachal Pradesh through a gorge. Here it is called the Dihang and it is joined by the Dibang, the Lohit the Kenula and many other tributaries to form the Brahmaputra in Assam.
In Tibet the river carries a smaller volume of water and less silt as if is a comparatively dry area. In India, it passes through a region, which receives a huge amount of rainfall. As a result, the river carries a large volume of water and considerable amount of silt. The Brahmaputra has a braided channel in its entire length in Assam, with many riverine islands.
![]()
Objective Type Questions
1. Put (✓) before the correct sentences and (✗) before the incorrect sentences.
(i) Of the 260 schemes of the Ganga Action plan, 45 have been completed with positive result
Answer:
(✓)
(ii) The Kaveri raises from Amarkantak,
Answer:
(✗)
(iii) India has comparatively a few natural lakes.
Answer:
(✓)
(iv) Over two-thirds of the surface water of India drains into the Bay of Bengal.
Answer:
(✓)
![]()
(v) Aksai Chin is in Uttaranchal.
Answer:
(✗)
(vi) The Krishana is famous as the Vridha Ganga.
Answer:
(✗)
(vii) The Chilka lake is a large lagoon.
Answer:
(✓)
(viii) The rising pollution of Ganga became a cause of concern during 1970 and 1980s.
Answer:
(✓).
2. Fill in the blanks with suitable words.
(i) The Mahanadi rises from ………………… .
Answer:
Chattisgarh
(ii) The Krisha flows for about ……………….. Km.
Answer:
1400
(iii) Where the sweet water mixes with the saltwater of ocean is known as ………………… .
Answer:
estuaries
(iv) The ………………… basin is shared by Kerala, Karnataka and Tamilnadu.
Answer:
Kaveri,
(v) Aksai chin is in ………………… .
Answer:
Jammu and Kashmir.
3. Match the following two lists.
| List I | List II |
| (i) Bhima | Farakka |
| (ii) Godavari | Krishna, |
| (iii) Rajasthan | Nashik |
| (iv) Kaveri | 800 Km. |
| (v) Loktak Inland | drainage |
| (vi) Ganga | Manipur. |
Answer:
| List I | List II |
| (i) Bhima | Krishna |
| (ii) Godavari | Nashik |
| (iii) Rajasthan Inland | drainage |
| (iv) Kaveri | 800 Km. |
| (v) Loktak | Manipur |
| (vi) Ganga | Farakka. |
![]()
4. Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below:
(i) The river Indus rise from the following:
(a) Mansarovar
(b) Gangotri
(c) Nasik
(d) Mahabaleswar.
Answer:
(a) Mansarovar
(ii) The Ganga is also known as:
(a) Krishana
(b) Bhagirathi
(c) Narmada
(d) Kaveri.
Answer:
(b) Bhagirathi
(iii) The following is a peninsular rivers
(a) The Ganga
(b) The Tapi
(c) The Indus
(d) TheBrahmpaputra
Answer:
(b) The Tapi
(iv) The following is the largest peninsular river:
(a) Mahanadi
(b) Krishna
(c) Godawari
(d) Narmada.
Answer:
(c) Godawari
(v) The following is the range from where the river Tapi rises:
(a) Satpura
(b) Aravalli
(c) Vindhya
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Satpura.
