Effect of Our Activities on Environment
Since we are an integral part of the environment, our activities also change the environment around us.
Ozone Layer and its Depletion
Ozone (O3) is a deadly poisonous gas that is formed by three atoms of oxygen. It shields the surface of the earth from harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays of the sun, which are known to cause skin cancer in human beings. They also damage the eyes and our immune system.
Formation of Ozone
Ozone is a product of UV radiation acting on oxygen (O2) molecules, which splits apart some molecular oxygen (O2) into free oxygen atoms (O) which combine with the molecular oxygen to form ozone.
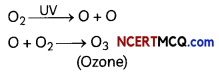
Depletion of Ozone Layer
The amount of ozone in the atmosphere is getting depleted due to the use of synthetic chemicals like chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), which are used as refrigerants and in fire extinguishers. The CFCs released into the air react with the ozone gas present and destroy it gradually due to which the ozone layer is becoming thinner leading to more UV rays entering the earth.
In 1987, the United Nations Environment Programme succeeded in forging an agreement to freeze CFC production at 1986 levels.
Managing the Garbage We Produce
![]()
Example 1.
Case Based:
In the first activity, collect waste material from your homes. This could include all the waste generated during a day, like kitchen waste (spoilt food, vegetable peels, used tea leaves, milk packets and empty cartons), waste paper, empty medicine bottles/ strips/bubble packs, old and tom clothes and broken footwear.
Bury this material in a pit in the school garden or if there is no space available, you can collect the material in an old bucket/flower pot and cover with at least 15 cm of soil.
Keep this material moist and observe at 15-days intervals.
In the second activity, use the library or internet to find out more about biodegradable and non- biodegradable substances. These days, new types of plastics which are said to be biodegradable are available. Find out more about such materials and whether they do or do not harm the environment.
(A) When the waste materials collected from home in the first activity was buried in a pit and kept moist and observed at intervals of 15 days, it is observed that:
(I) Kitchen waste like spoilt food, vegetable peels, used tea leaves changed their form the fastest.
(II) Waste paper remained unchanged over a long time.
(III) Empty medicine bottles and strips changed their form and structure but not as fast as kitchen wastes.
(IV) Milk packets and bubble wraps did not change their form or structure during the period of observation.
The correct observations are:
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (II) and (III)
(c) Both (I) and (IV)
(d) Both (III) and (IV)
Answer:
(c) Both (I) and (IV)
Explanation: Waste materials such as kitchen wastes (vegetable peels, used tea leaves etc), waste paper, cotton clothes are organic substances and hence are easily degraded naturally, whereas wastes such as empty medicine bottles and strips, bubble wrap, milk packets are made up of glass or plastic and are not degraded naturally.
(B) Given below are names of some waste materials that changed and remain unchanged when buried in the soil.
Plastic box, Rubber tyre, Empty Carton, Vegetable peels, Bubble wrap, Waste paper
What materials are correctly classified as biodegradable and non-biodegradable materials?
| Biodegradable | Biodegradable |
| (a) Empty carton, Waste paper, Vegetable peels | Bubble wrap, Plastic box, Rubber tyre |
| (b) Vegetable peels, Bubble wrap, Empty carton | Plastic Box, Rubber tyre, Waste paper |
| (c) Vegetable peels, Rubber tyre, Empty carton | Bubble wrap, Waste paper, Plastic Box |
| (d) Rubber tyre, Empty carton, Waste paper | Vegetable peels, Plastic box |
Answer:
(a) Biodegradable: Empty carton, Waste paper, Vegetable peels;
Non-biodegradable: Bubble wrap, Plastic box, Rubber tyre.
Explanation: The substances such as empty carton, waste paper and vegetable peels which are of plant or animal origin are degraded naturally and are said to be biodegradable materials. Whereas, materials such as plastic box, bubble wrap and rubber tyre are non- biodegradable materials.
(C) How long do you think plastic bottles will last in our environment?
Answer:
As plastic is non-biodegradable, it does not get degraded naturally in our environment but persists in our environment for a very long time. Eventually it gets broken down by physical conditions such as heat and pressure. It takes upto 450 years for plastic to be broken down.
(D) These days, new types of plastics which are said to be biodegradable are available. Do such materials cause any harm to the environment?
Answer:
New types of plastics are made from plastics but some chemicals are added to them so that they break down faster when exposed to physical conditions such as air and light. But they also cause harm to the environment as eventually these plastics are broken down into small pieces which persist in our environment and also cause pollution.
(E) Assertion (A): Man-made materials such as glass persist in the environment for a very long time.
Reason (R): Bacteria and other saprophytes break down the organic matter in our environment.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Answer:
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of the (A).
Explanation: Man made materials such as plastic and glass persist in our environment for a very long time as they are not degraded naturally by the bacteria and other saprophytes present in our environment which act on organic matter only.
![]()
Example 2.
How can you help in reducing the problem of waste disposal? Give any two methods.
Answer:
Problem of waste disposal can be reduced by disposing off of garbage in a scientific manner by first segregating them into bior sgradable and non-biodegradable substances. As far as possible, we should use only biodegradable substances such as cloth and paper bags in place of plastic bags.
Improvement in our life styles and changes in our attitudes have led to greater amounts of waste generation, much of which is non-biodegradable. The disposal of waste should be done in a scientific way.
There are various methods of disposing the garbage.
Biodegradable and Non-biodegradable Wastes
All the waste materials produced by the various activities of man and animals can be sub-divided into the following groups:
- Biodegradable Wastes
- Non-biodegradable Wastes
The waste materials which can be broken down to non-poisonous substances in nature in due course of time by biological processes like the action of micro-organisms are called biodegradable wastes.
Some examples of bio-degradable wastes are cattle dung, compost, animal bones, leather, tea leaves, wool, paper, wheat, wood, hay, cotton, jute, grass, fruit and vegetable peels, leaves, flowers, cake etc. Bio-degradable wastes usually do not pollute the environment.
The waste materials which cannot be broken down into non-poisonous or harmless substances in nature are called non-biodegradable wastes.
Some examples of non-biodegradable wastes are DDT, plastics, polythene bags, synthetic fibres, glass, metal cans, iron nails, silver foils, radioactive wastes etc.
These are the major environmental pollutants as these cannot be decomposed by micro-organisms.
Example 3.
What are the problems caused by the non-biodegradable wastes that we generate?
Answer:
Problems caused by the non-biodegradable wastes that we generate are:
- They will persist in our environment for a very long time and hence make the environment harmful and unfit for survival of living organisms.
- Their presence will block the flow and transfer of energy, minerals and nutrients in the ecosystem.
![]()
Example 4.
Give any two ways in which biodegradable substances would affect the environment.
Answer:
The two ways in which biodegradable substances would affect the environment are:
- Degradation of these substances by the saprophytes and other microorganisms may release foul-smelling gases thus polluting the environment.
- They may become breeding ground for mosquitoes, flies and other pests thus increasing the chances of diseases.
Example 5.
Case Based:
Search the internet or library to find out what hazardous materials have to be dealt with while disposing off electronic items. Find out how these materials affect the environment. Find out how plastics are recycled and whether the recycling process has any impact on the environment.
(A) The hazardous materials to be dealt with while disposing off electronic items are:
(I) cadmium
(II) lead
(III) mercury
(IV) iron
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (III) and (IV)
(c) (I), (II) and (III)
(d) (II), (III) and (IV)
Answer:
(c) (I), (II) and (III)
Explanation: Electronic items contain some hazardous materials such as cadmium, lead, mercury, chromium, some compressed gases, PVCs etc. which can contaminate the environment once released by dumping, melting and burning of electronic wastes.
(B) Which of the following is not correct regarding the effect of hazardous materials present in electronic items on the environment?
(a) They can contaminate the groundwater.
(b) They reLease greenhouse gases.
(c) They are highly toxic and carcinogenic.
(d) Burning of these materials lead to depletion of ozone Layer.
Answer:
(b)They release greenhouse gases.
Explanation: Some of the hazardous materials present in electronic items are cadmium, lead and mercury which are toxic and carcinogenic. They can contaminate the groundwater and also enter the food chain through water or soil. Burning of these materials causes depletion of the ozone layer. However, as burning of these materials does not produce carbon dioxide or methane or any other greenhouse gas, it does not cause global warming.
(C) What is the environmental impact of using single-use packaging materials made of plastic?
Answer:
Single use packaging materials made up of plastic are non-biodegradable and hence cause environmental pollution and they persist in the environment for a very long time.
(D) Does the recycLing of plastic cause any damage to the environment?
Answer:
Yes, recycling of plastic causes environmen¬tal damage as burning plastic and other wastes releases dangerous substances such as heavy metals, persistent organic pollutants (POP), and other toxic chemicals into the air and persist as ash waste residues.
(E) Assertion (A): Disposable pLastic cups are preferred over disposable papercups.
Reason (R): Disposable paper cups are biodegradable.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Answer:
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Explanation: Disposable paper cups are preferred over disposable plastic cups as paper is biodegradable whereas plastic is non-biodegradable and hence persists in our environment for a very long time.