Find free online Chemistry Topics covering a broad range of concepts from research institutes around the world.
Empirical Formula and Molecular Formula
Elemental analysis of a compound gives the mass percentage of atoms present in the compound. Using the mass percentage, we can determine the empirical formula of the compound. Molecular formula of the compound can be arrived at from the empirical formula using the molar mass of the compound.
Empirical formula of a compound is the formula written with the simplest ratio of the number of different atoms present in one molecule of the compound as subscript to the atomic symbol. Molecular formula of a compound is the formula written with the actual number of different atoms present in one molecule as a subscript to the atomic symbol.
Let us understand the empirical formula by considering acetic acid as an example.
The molecular formula of acetic acid is C2H4O2
The ratio of C : H : O is 1 : 2 : 1 and hence the empirical formula is CH2O.
Determination of Empirical Formula from Elemental Analysis Data:
Step 1:
Since the composition is expressed in percentage, we can consider the total mass of the compound as 100 g and the percentage values of individual elements as mass in grams.
Step 2:
Divide the mass of each element by its atomic mass. This gives the relative number of moles of various elements in the compound.
Step 3:
Divide the value of relative number of moles obtained in the step 2 by the smallest number of them to get the simplest ratio.
Step 4:
(only if necessary) in case the simplest ratios obtained in the step 3 are not whole numbers then they may be converted into whole number by multiplying by a suitable smallest number.
Example:
1. An acid found in Tamarind on analysis shows the following percentage composition: 32 % Carbon; 4 % Hydrogen; 64 % Oxygen. Find the empirical formula of the compound.
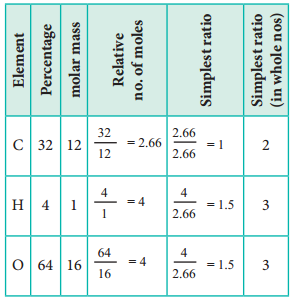
The empirical formula is C2H3O3
2. An organic compound present in vinegar has 40 % carbon, 6.6 % hydrogen and 53.4 % oxygen. Find the empirical formula of the compound.
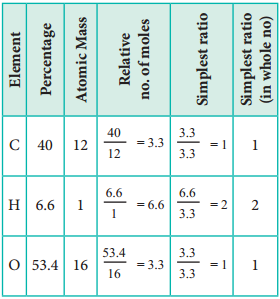
The empirical formula is CH2O
Molecular formula of a compound is a whole number multiple of the empirical formula. The whole number can be calculated from the molar mass of the compound using the following expression
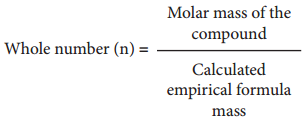
Calculation of Molecular Formula from Empirical Formula:
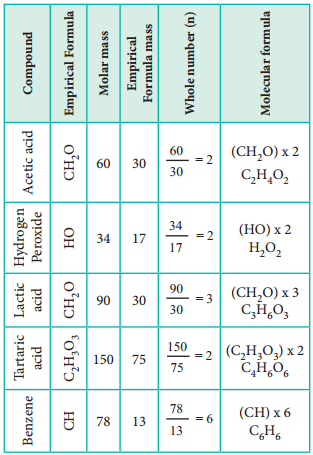
Let us understand the calculations of molecular formula from the following example.
Two organic compounds, one present in vinegar (molar mass: 60 g mol-1), another one present in sour milk (molar mass: 90 g mol-1) have the following mass percentage composition. C-40%, H-6.6%; O-53.4%. Find their molecular formula.
Since both compounds have same mass percentage composition, their empirical formula are the same as worked out in the example problem no 2. Empirical formula is CH2O. Calculated empirical formula mass (CH2O) = 12 + (2×1) + 16 = 30 g mol-1.
Formula for the compound present in vinegar
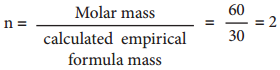
∴ Molecular formula = (CH2O)2
= C2H4O2 (acitic acid)
Caluculation of molecular formula for the compound present in sour milk.
![]()
Molecular formula = (CH2O)3
= C3H6O3 (lactic acid)