Learninsta presents the core concepts of Biology with high-quality research papers and topical review articles.
Extra Chromosomal Inheritance – Cytoplasmic Inheritance In Chloroplast
DNA is the universal genetic material. Genes located in nuclear chromosomes follow Mendelian inheritance. But certain traits are governed either by the chloroplast or mitochondrial genes. This phenomenon is known as extra nuclear inheritance.
It is a kind of Non-Mendelian inheritance. Since it involves cytoplasmic organelles such as chloroplast and mitochondrion that act as inheritance vectors, it is also called Cytoplasmic inheritance. It is based on independent, self-replicating extra chromosomal unit called plasmogene located in the cytoplasmic organelles, chloroplast and mitochondrion.
Chloroplast Inheritance
It is found in 4 o’ Clock plant (Mirabilis jalapa). In this, there are two types of variegated leaves namely dark green leaved plants and pale green leaved plants.
When the pollen of dark green leaved plant (male) is transferred to the stigma of pale green leaved plant (female) and pollen of pale green leaved plant is transferred to the stigma of dark green leaved plant, the F1 generation of both the crosses must be identical as per Mendelian inheritance. But in the reciprocal cross the F1 plant differs from each other. In each cross, the F1 plant reveals the character of the plant which is used as female plant.
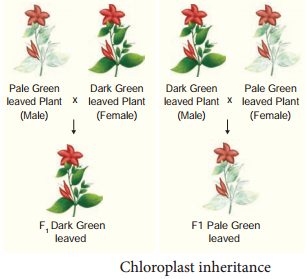
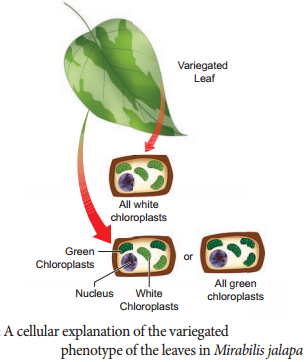
This inheritance is not through nuclear gene. It is due to the chloroplast gene found in the ovum of the female plant which contributes the cytoplasm during fertilization since the male gamete contribute only the nucleus but not cytoplasm.
Recently it has been discovered that cytoplasmic genetic male sterility is common in many plant species. This sterility is maintained by the inflence of both nuclear and cytoplasmic genes. There are commonly two types of cytoplasm N (normal) and S (sterile).
The genes for these are found in mitochondrion. There are also restores of fertility (Rf) genes. Even though these genes are nuclear genes, they are distinct from genetic male sterility genes of other plants. Because the Rf genes do not have any expression of their own, unless the sterile cytoplasm is present. Rf genes are required to restore fertility in S cytoplasm which is responsible for sterility.
So the combination of N cytoplasm with rfrf and S cytoplasm with RfRf produces plants with fertile pollens, while S cytoplasm with rfrf produces only male sterile plants.
Atavism
Atavism is a modifiation of a biological structure whereby an ancestral trait reappears after having been lost through reemergence of sexual reproduction in the flowering plant Hieracium pilosella is the best example for Atavism in plants.