Find free online Chemistry Topics covering a broad range of concepts from research institutes around the world.
General Methods of Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones
A. Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones
1. Oxidation and Catalytic Dehydrogenation of Alcohols
We have already learnt that the oxidation of primary alcohol gives aldehydes and secondary alcohol gives a ketone. Oxidising agents such as acidified Na2Cr2O7, KMnO4, PCC are used for oxidation. Oxidation using PCC yield aldehydes. Other oxidising agents further oxidise the aldhydes / ketones in to carboxylic acids.
When vapours of alcohols are passed over heavy metal catalyst such as Cu, Ag, alcohols give aldehydes and ketons.
Catalytic Dehydrogenation of Alcohols
2. Ozonolysis of Alkenes
We have already learnt in XIth standard that the reductive ozonolysis of alkenes gives aldehydes and ketones. Alkenes react with ozone to form ozonide which on subsequent cleavage with zinc and water gives aldehydes and ketones. Zinc dust removes H2O2 formed, which otherwise can oxidise aldehydes/ketones.
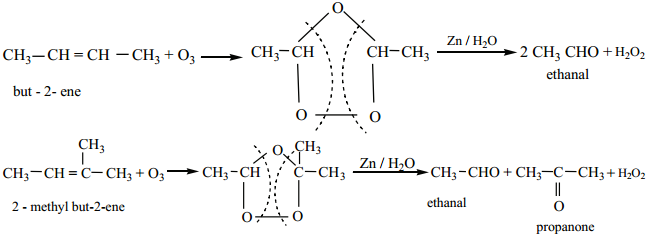
Terminal olefies give formaldehyde as one of the product.
3. Hydration of Alkynes
We have already learnt in XI standard that the hydration of alkynes in presence of 40% dilute sulphuric acid and 1% HgSO4 to give the corresponding aldehydes/ketones.
(a) Hydration of acetylene yields acetaldehyde
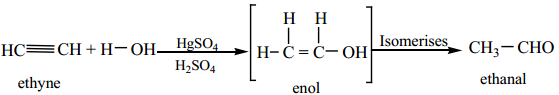
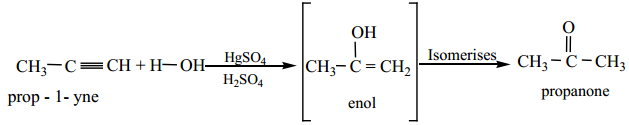
(b) Hydration of alkynes, other than acetylene gives ketones
4. From Calcium Salts of Carboxylic Acids
Aldehydes and ketones may be prepared by the dry distillation of calcium salts of carboxylic acids.
(a) Aldehydes are obtained when the mixture of calcium salt of carboxylic acid and calcium formate is subjected to dry distillation.
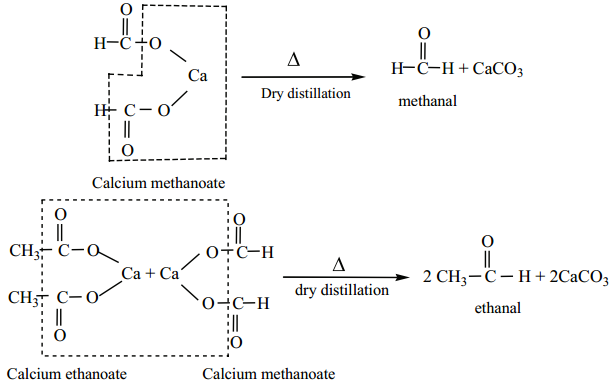
(b) Symmetrical ketones can be obtained by dry distillation of the calcium salt of carboxylic acid (except formic acid)
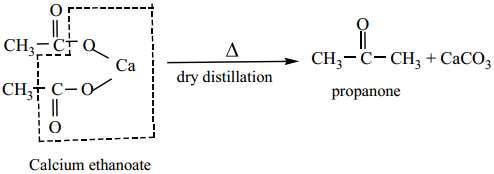
B. Preparation of Aldehydes
1. Rosenmund Reduction
(a) Aldehydes can be prepared by the hydrogenation of acid chloride, in the presence of palladium supported by barium sulphate. This reaction is called Rosenmund reduction.
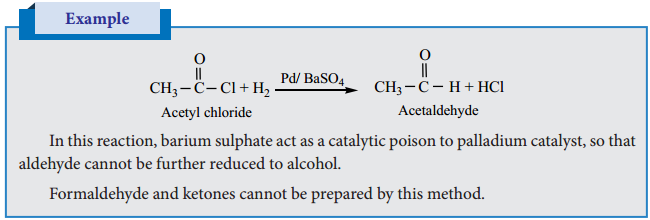
2. Stephen’s Reaction
When alkylcyanides are reduced using SnCl2/HCl, imines are formed, which on hydrolysis gives corresponding aldehyde.
![]()
3. Selective Reduction of Cyanides
Diisobutyl aluminium hydride (DIBAL -H) selectively reduces the alkyl cyanides to form imines which on hydrolysis gives aldehydes.
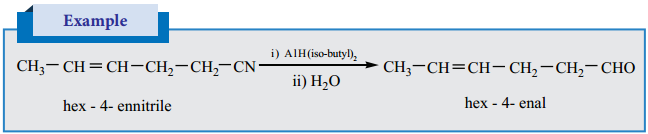
(c) Preparation of Benzaldehyde
1. Side chain oxidation of toluene and its derivatives by strong oxidising agents such as KMnO4 gives benzoic acid. When chromylchloride is used as an oxidising agent, toluene gives benzaldehyde. This reaction is called Etard reaction. Acetic anhydride and CrO3 can also be used for this reaction.
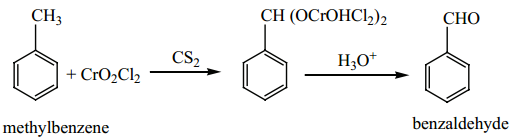
Oxidation of toluene by chromic oxide gives benzylidine diacetate which on hydrolysis gives benzaldehyde.
2. Gattermann – Koch Reaction
This reaction is a variant of Friedel – Crafts acylation reaction. In this method, reaction of carbon monoxide and HCl generate an intermediate which reacts like formyl chloride.
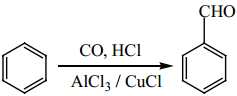
3. Manufacture of Benzaldehyde from Toluene
Side chain chlorination of toluene gives benzal chloride, which on hydrolysis gives benzaldehyde.
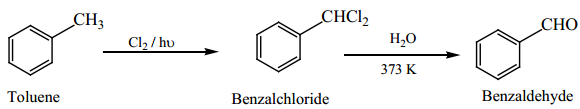
This is the commercial method for the manufacture of benzaldehye.
(d) Preparation of Ketones
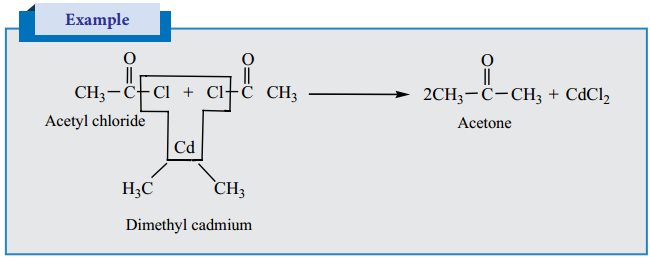
1. Ketones can be prepared by the action of acid chloride with dialkyl cadmium.
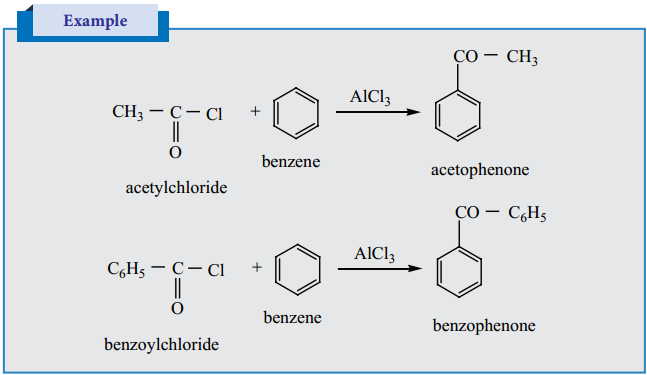
2. Preparation of Phenyl Ketones
Friedel – Craft Acylation
It is the best method for preparing alkyl aryl ketones or diaryl ketones. This reaction succeeds only with benzene and activated benzene derivatives.