Here we are providing Class 12 Geography Important Extra Questions and Answers Chapter 6 Spatial Information Technology. Geography Class 12 Important Questions are the best resource for students which helps in class 12 board exams.
Class 12 Geography Chapter 6 Important Extra Questions Spatial Information Technology
Spatial Information Technology Important Extra Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1.
What do you mean by a computer ? What are its characteristics ?
Answer:
Computer. The word ‘Computer’ has been derived from the English word ‘Compute’ meaning measuring. The modern age is computer age. Computer is an electronic device that processes information at high speed with accuracy. The most powerful computers can perform billions of calculations or arithmetic operations per second.
This device is capable of solving problems or manipulating data by accepting the same performing arithmetical operation (using arithmetical instructions, e.g., addition, subtraction, multiplication and division) or logical operations (using logical operators ‘and’, ‘or’, ‘not and’, etc.) of the data, and supplying the results of these operations.
In general, computer can process numbers, words, still pictures, moving pictures and sounds. The computer uses electronic current to carry information. To enable a computer to process information that is not numerical such as words, pictures or sounds, the information is digitised.
Main Characteristics of a Computer
- Speed. A computer can work with high speed.
- Storage capacity. Computer has a large storage capacity. Data can be stored with the help of Discard Tape.
- Accuracy. Computer is important for its accuracy. Computer tries to remove any error if it occurs.
- Variety of jobs. Computer is used for many works like storage of data, designing, games, etc.
- Automation. Computer works like an automatic device and provides a detailed study.
Question 2.
Name the main parts of a computer. Describe the different units of hardware.
Answer:
Parts of Computer System
A computer system consists of two basic components:
1. Hardware
2. Software.
Hardware. It is the physical part of computer system and consists of electronic, magnetic and mechanical devices. A computer system has following main hardware units.
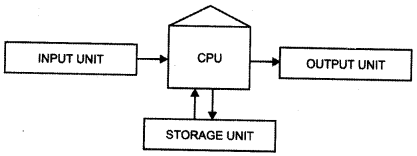
1. Central Processing Unit (CPU). It is the nerve centre of any digital computer system, it coordinates and controls the activities of all other units and performs all the arithmetical and logical processes to be applied to the data. CPU has three separate hardware sections: internal memory, arithmetic unit and a control section.
Chip (thin silicon wafer containing a large amount of integrated electronic circuitry) is the building block of a computer and performs various functions e.g., doing arithmetic operations, serving as the computer’s memory or controlling other chips.
2. Visual Display Unit (VDU) or Terminal. Like Television, display unit consist of a Cathode Ray Tube (CRT), which is used to display characters or graphics representing data read from the main memory of a computer.
3. Input/Output Devices. Input device like keyboard, is used to enter data and programs into the computer memory. Similarly, since all the data and programmes within a computer are stored as electrical impulses in a coded form, output devices like printers, plotters, etc., are employed to transcribe this data into information (e.g. characters, drawings or graphics) that can be used by human beings.
4. Storage Device. A computer consists of a number of storage devices like Hard disk, floppy, tape, Magneto Optical disk, Compact disk (CD), Cartridge, etc; which are used to store both data and program instructions. These devices vary in their capacity of data storage, from megabytes (MB) to gigabytes (GB).
Question 3.
What are the main advantages of using a computer ?
Answer:
(i) Computer is an electronic device that processes information with high speed and accuracy.
(ii) The most powerful computers can perform billions of calculations or arithmetic operations per second.
(iii) This device is capable of solving problems and manipulating data by accepting the same, performing arithmetical operations (using arithmetical instructions, e.g., addition, subtraction, multiplication and division) and supplies the results of these operations
(iv) In general, computer can process numbers, words, still pictures, moving pictures and sounds
(v) The computer uses electronic current to carry information
(vi) To enable a computer to process information that is not numerical—such as words, pictures, or sounds—the information is digitized.
Question 4.
What are the limitations of a computer ?
Answer:
It is necessary for us to know and understand what a computer cannot do.
- A computer cannot do thinking for us.
- Computers can only follow specific, logical steps based on the information we, humans enter
- Thus, a computer can only act on the basis of information we put in it.
- A computer does only what it is told, either by programs (a set of instructions) or by a human operator.
Question 5.
What are the main components of a computer ?
Answer:
A computer system consists of two basic components:
(a) Software
(b) Hardware
(a) Software. Software refers to all programs which can be used on’a particular computer system. It governs the operation of a computer system. It may be classified as:
- Application software
- System software.
(b) Hardware. It is the physical part of computer system and consists of electronic, magnetic and mechanical devices. A computer system has following main hardware units:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU)
- Visual Display Unit (VDU)
- Input-output (I/O) devices
- Storage devices.
Question 6.
Write a note on CPU.
Answer:
Central Processing Unit (CPU). It is the nerve centre of any digital computer system. It coordinates and controls the activities of all other units and performs all the arithmetical and logical process to be applied to the data. CPU has three separate hardware sections:
- internal memory,
- arithmetic unit and
- a control section.
Chip (a thin silicon wafer containing a large amount of integrated electronic circuitry) is the building block of a computer and performs various functions, e.g., doing arithmetic operations, serving as the computer’s memory or controlling other chips.
Question 7.
What is storage device in a computer ?
Answer:
Storage Device. A computer consists of a number of storage devices like Hard disk, floppy, tape, Magneto-Optical disk, Compact disk (CD), Cartridge, etc.; which are used to store both data and program instructions. These devices vary in their capacity of data storage, from megabytes (MB) to gigabytes (GB).
Question 8.
Write a note on application software.
Answer:
Application Software
There are two types of application software :
(i) First type of Application Software relates to database management, business graphics and words processing, covering a broad range of functions used by most business houses and many individuals.
(ii) Second type of application software provides specific professional or technical applications for specific kinds of business. For example, software specifically designed to be used by medical doctors, dentists, architects and engineers performs very special tasks.
The categories of broad-range applications software meant for personal use and business include:
- Accounting — general ledger, payroll, invoicing, etc.
- Communications — electronic mail interaction with central office mainframe computers, connectivity with commercial data banks and other services offered by information utilities.
- Database management – organising data files for central access, retrieval and update, compiling statistics, plot trends and market analysis.
- Educational programs – learning through games, tutorials, simulations, etc.
- Graphics — displaying colour graphics and charts, producing colour slides and other visual aids.
- Programming — translating a problem from its physical environment to a language that a computer can understand and obey.
Question 9.
What is an operating system ?
Answer:
Operating System (OS). Software that controls the executions of computer programs and provides scheduling, debugging, Input / Output control, compilation, data management and related services. Popular types of operating system include DOS (Disk Operating System), UNIX and its variants, VMS (Virtual Memory System), Microsoft Windows, etc.
Question 10.
Write short notes on RAM and ROM.
Answer:
- RAM (Random Access Memory). Memory into which data can be written and from which data can be read.
- ROM (Read Only Memory). Memory containing information which is present and permanent and which cannot be written but can only be read by program routines.
Question 11.
Write a note on Geo-Referencing and Grand Control points.
Answer:
Geo-Coding of Geo-Referencing of Raster Image
Scanned raster images and satellite imageries are corrected for distortions by matching them with Ground Control Points (GCPs) occurring in an image. GCPs are features of known ground location that can be accurately located on the aerial photo or satellite imagery.
GCPs are located both in terms of their image coordinates (column and row numbers) on the distorted image and in terms of their ground coordinates (typically measured from map or established on the ground in terms of latitude and longitude with respect to a particular projection system, say UTM or Polyconic).
A least-square regression analysis is done to interrelate the geometrically correct (map) coordinates and distorted image coordinates. Then, image is wrapped to have correct geometrical relationship with its corresponding ground situation.
Question 12.
Write a note on Digital mapping.
Answer:
Digital fair mapping. Geo-coded raster image is used as a backdrop of draw point, features, line features and aerial features and annotate them with proper symbols and texts. Alternatively, the above features or the raster image may simply be digitized without using symbols to create cartographic database. The digital map may be subjected to automated cartographic processes, like generalisation, classification, etc.
Question 13.
What are the three basic elements of Cartography ?
Answer:
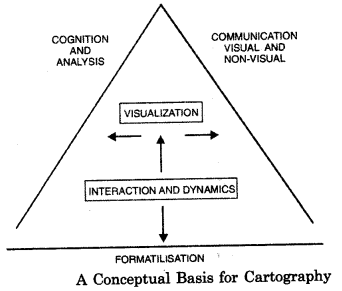
Cartography is undergoing dramatic changes driven primarily by technological developments in both computer and tele- communication fields.
Modern cartography can be represented by a triangle whose arms signify three basic elements which go to give it a new significance.
- Formailisation
- Cognition and analysis, and
- Communication.
‘Formailisation’ forms the base of the triangle; it represents the cartographic production aspects. Cognition and Analysis as well as Communication are the other two sides. Currently, cartography is facing challenges due to fast emerging developments in computer, multimedia and telecommunication fields.
Map designers have greater opportunities to utilise computer and multi-media for spatial data processing. Every year large number of new softwares are developed. Some of the main GIS and mapping software are: Apple, Arc/Info, Auto CAD and Maplnfo, GRAM and so on.
Question 14.
What is the importance of computer in Cartography ?
Answer:
Use of computer in cartography helps in the following ways:
- Maps are made quickly.
- Maps are made according to user’s needs.
- Map construction is possible even if skilled cartographer is unavailable.
- Map making has become less expensive.
- Maps can be made more attractive.
- Map reproduction has become faster.
- Updating of the map can be done if data are in a digital form.
Effect of Space Technology
The space technology has changed mapping in many ways.
- Softcopy images have replaced printed maps for many applications.
- Production time has been reduced drastically.
- For military intelligence and micro-planning for development needs, a timely, high resolution image of a designated site can be obtained in minutes by moving a nearby satellite into a new orbit.
- Automation is also changing the quality as well as variety of spatial information that can be mapped.
- Further, Geographic Information System (GIS) is expanding the role of spatial mapping and analysis in decision making.
Question 15.
Write a note on spatial information technology.
Answer:
Spatial Information Technology
Resource management of a region is performed by two methods:
(i) manual map overlay method
(ii) by computer technology using numerical spatial data sets or geo-based files.
Manual overlaying to transparent maps has its limitations. Only a few maps can be overlaid simultaneously for visual analysis. The computer- assisted technology requires information in digital form. In this approach, interrelation of resource features is performed through numerical transformations.
Thus, cartography gives new impetus to spatial data storage and exchange. Simultaneously, the combined use of Geographic Information System (GIS), and Digital Image Processing (DIP) provide better prospects of geographical monitoring and forecasting over a wider area within limited time-span. It would be easy to develop predictive modelling capabilities for effective public policies in years to come.
Question 16.
What are the elements of data structure ?
Answer:
Elements of Data Structure
Both graphic variable and text help in giving a good aesthetic look to the map. Information about the map is shown through the graphic variable and text.
The following six basic types of graphic variables are popular:
- Size of Typology. Differences in size of the symbols (dots) and lines.
- Lightness or (grey) value. The lighter shades show lower densities and deeper or darker shades show higher densities.
- Grain or texture. In this method, black and white colour are mostly used. Changing the ratio of black and white colours shows the variation intensity of an element.
- Colour Hue. Hue refers to various colours we perceive: red, green, blue and combinations.
- Orientation. Differences in orientation refers to patterns and not to the line elements that form the base map.
- Shape. The various symbols are included for identifying shape differences.
Question 17.
What do you mean by GPS and GIS ?
Answer:
Global Positioning System (GPS)
Global Positioning System (GPS), is an all-weather radio navigation system developed by US military in which individual receivers process data beamed down from satellites. It provides three-dimensional positions, 24-hours-per-day basis around the world.
The space satellite system consists of 24 satellites in a circular orbit and with an orbital period of 12 hours. The orbits are inclined to the equator at 55 degree. The satellites carry an atomic clock moving and generating stable signals. These signals carry information about time and position of satellites.
This provides latitude, longitude and altitude of any spatial unit. Thus, the GPS has been contributing greatly in the field of spatial mapping.
Geographic Information System (GIS)
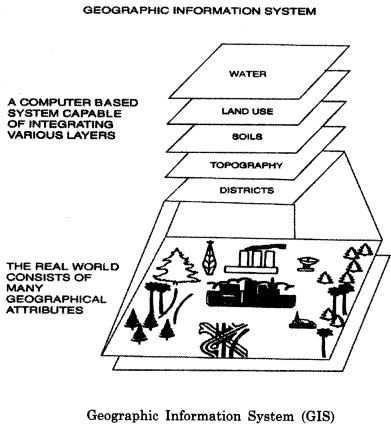
Many scholars defined GIS in various ways. Geographic Information System (GIS) is a database of a particular kind containing spatial information about various levels of observations. GIS can be considered as a tool to analyse resource and environmental information in a spatial context. Development of a GIS requires a clear understanding about its multi-level structure.
GIS can be defined as, “A powerful set of tools for collecting, storing, retrieving at will, transforming and displaying spatial data from the real world”.Thus, GIS is a computer-based system which provides easy access to stored geographical data, customised maps and selective database query. It is easily possible to show forestland, and for reference showing major roads and administrative boundaries in a database of land cover.
Question 18.
What is the application of GIS in Socio-economic planning ?
Answer:
Advantages of GIS
GIS provides an opportunity to interpret various geographical, topographic, socio-economic spatial data in relation to spatial analysis and modelling. The emphasis is on integration of conventional land based and remotely sensed data so as to develop comprehensive databases suitable for various levels of spatial planning. This can be used for development and planning.
In this way, GIS can play an effective role for decision support system of sustainable development and management of the natural resources. The environmental resources are a prime natural capital for human sustenance and development. Thus, development, utilisation and conservation of environment resources are the major priority sectors in the national planning process.
Question 19.
Compare Vector and Raster GIS.
Answer:
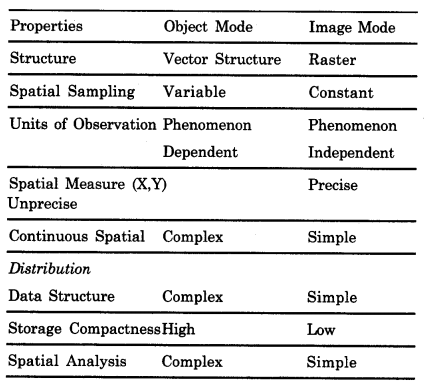
Types of GIS. Vector and Raster
GIS analyses the attributes and their interactions within a region/space. There are two different types of GIS: vector or polygon; and raster or grid structure. Vector structure denotes spatial units of their features to be represented. Such units are of uniform size and shape and relative location within an area.
In the raster (image) data, spatial objects are made of contiguous cells sharing the same attribute within the regions. Attribute dimension is described as a set of grids in which the value assigned to each cell expresses its overall characteristics. The merits and demerits of the two GIS modes are given below:
Question 20.
Write a note on GIS application in Land use change Monitoring and Land suitability analysis.
Answer:
Application of GIS
Using GIS solves many problems such as land and forest cover change, water and air quality assessment, soil erosion risk analysis, natural hazard monitoring, selection of afforestation areas, land capability and suitability analysis, and data directory study. Worldwide experience has shown that remote sensing and GIS are very effective tools for resource management.
GIS can be used as decision support system identifying and integrating, monitoring and predicting natural hazards which are the major environment risks experienced in India. Integrated Watershed Management Plans that consequently result could help reduce the impacts of disasters that continuously threaten us.
(i) Land use Change Monitoring :
Land use is an important input in the geographical monitoring of rural as well as urban resources of a region. The general land cover classification can be derived from past changes in land use in general and forest cover in particular. Deforestation, for example, is a serious ecological problem in the Himalaya.
Forest maps of two time periods can provide information of forest cover changes. Satellite remote sensing can be effectively used for land use mapping and for monitoring forest degradation process in the country. Due to rapid change, the information collected by conventional methods becomes outdated.
(ii) Land Suitability Analysis for Socio-Economic Planning:
Land use suitability analysis helps in taking decision on different land related developments. The GIS analysis integrates various natural, anthropogenic and interactive factors to produce three types of maps:
(1) A map showing what land use will cause the least change in environmental processes.
(2) A map showing qualitative predictions of environmental impacts of proposed development. It also gives certain projects to be carried out and specific environmental actions to be controlled; and
(3) A map showing the best and least suitable locations for those actions. Land use planning in marginal regions like Himalayan region, Rajasthan desert requires such mapping. The analysis of land suitability for agriculture in highlands will produce information and maps related to soil erosion, slope, altitude, water availability and nutrient availability.