Learninsta presents the core concepts of Biology with high-quality research papers and topical review articles.
Human Neural System Definition and its Function
The human neural system is divided into two, the central neural system (CNS) and the peripheral neural system (PNS). The structural and functional units of the neural system are neurons that transmit nerve impulses. The non-nervous special cells called neuroglia form the supporting cells of the nervous tissue.
There are three functional classes of neurons. They are the afferent neurons that take sensory impulses to the Central Neural system (CNS) from the sensory organs; the efferent neurons that carry motor impulses from the CNS to the effector organs; and interneurons that lie entirely within the CNS between the afferent and efferent neurons.
The central neural system lacks connective tissue, so the interneuron space is filled by neuroglia. They perform several functions such as providing nourishment to the surrounding neurons; involving the memory process; repairing the injured tissues due to their dividing and regenerating capacity; and acting as phagocyte cells to engulf the foreign particles at the time of any injury to the brain.
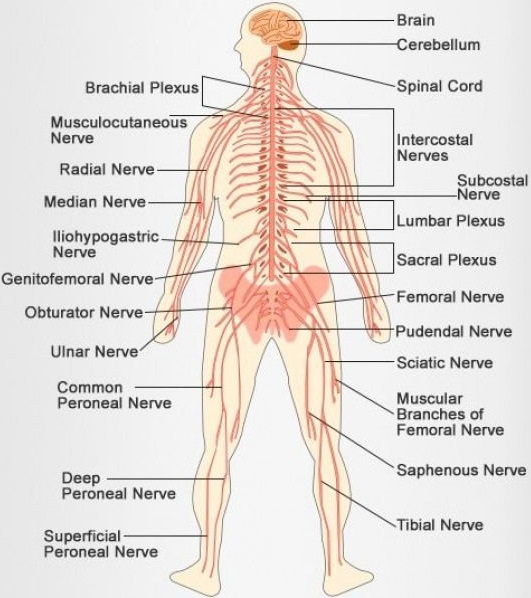
The human nervous system consists of two main parts: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS contains the brain and spinal cord. The PNS consists mainly of nerves, which are long fibers that connect the CNS to every other part of the body.
The central nervous system is made up of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system is made up of the Somatic and the Autonomic nervous systems.
The nervous system of vertebrates (including humans) is divided into the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The (CNS) is the major division, and consists of the brain and the spinal cord. The spinal canal contains the spinal cord, while the cranial cavity contains the brain.
The nervous system is the major controlling, regulatory, and communicating system in the body. It is the center of all mental activity including thought, learning, and memory. Together with the endocrine system, the nervous system is responsible for regulating and maintaining homeostasis.
The Four Main Functions of the Nervous System are:
Control of body’s internal environment to maintain ‘homeostasis’ An example of this is the regulation of body temperature. Programming of spinal cord reflexes. An example of this is the stretch reflex. Memory and learning. Voluntary control of movement.
The Nervous System has two main Parts:
The central nervous system is made up of the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system is made up of nerves that branch off from the spinal cord and extend to all parts of the body.
The nervous system includes the brain, nerves and spinal cord. It is the communication center for the body, sending and receiving messages, regulating body functions and serving as the control center for the five senses and for emotions, speech, coordination, balance, and learning.
The 11 organ systems include the integumentary system, skeletal system, muscular system, lymphatic system, respiratory system, digestive system, nervous system, endocrine system, cardiovascular system, urinary system, and reproductive systems.