Learninsta presents the core concepts of Biology with high-quality research papers and topical review articles.
Hypo and Hyper Activity of Endocrine Glands and Related Disorders
The hyper secretion and hypo secretion of hormones leads to several disorders. Dwarfism is due to hyposecretion of growth hormone (GH) in children, skeletal growth and sexual maturity is arrested. They attain a maximum height of 4 feet only (Figure 11.8).

Gigantism is due to hypersecretion of growth hormone (GH) in children. Overgrowth of skeletal structure occurs (up to 8 feet) and the visceral growth is not appropriate with that of limbs. Figure 11.9.

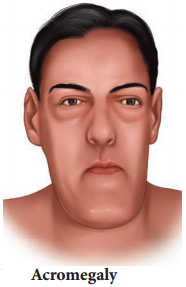
Acromegaly is due to excessive secretion of growth hormone in adults. Over growth of hand bones, feet bones, jaw bones, malfunctioning of gonads, enlargement of viscera, tongue, lungs, heart, liver, spleen and endocrine gland like thyroid, adrenal etc., are the symptoms of acromegaly. (Figure 11.10)
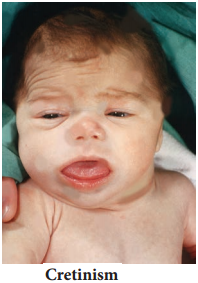
In infants, hypothyroidism causes cretinism. A cretin shows retarded skeletal growth, absence of sexual maturity, retarded mental ability, thick wrinkled skin, protruded enlarged tongue, bloated face, thick and short limbs occurs. The other symptoms are low BMR, slow pulse rate, subnormal body temperature and elevated blood cholesterol levels. (Figure 11.11)
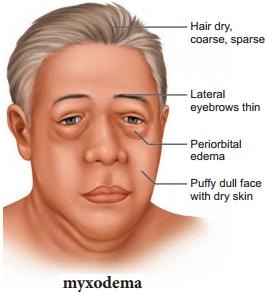
Hyposecretion of thyroid in adults causes myxodema. It is otherwise called Gull’s disease. This disease is characterised by decreased mental activity, memory loss, slowness of movement, speech, and general weakness of body, dry coarse skin, scarce hair, puffy appearance, disturbed sexual function, low BMR, poor appetite, and subnormal body temperature. (Figure 11.12)
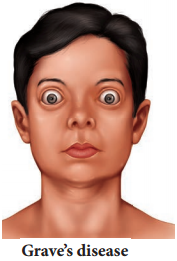
Grave’s disease also called as thyrotoxicosis or exophthalmic goitre. This disease is caused due to hyper secretion of thyroid. It is characterised by enlargement of thyroid gland, increased BMR (50% – 100%), elevated respiratory and excretory rates, increased heart beat, high BP, increased body temperature, protrusion of eyeball and weakness of eye muscles and weight loss. (Figure 11.13)
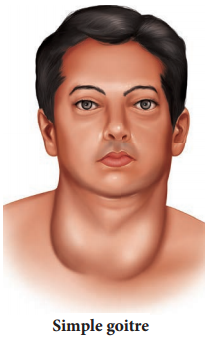
Simple goitre is also known asEndemic goitre. It is caused due to hyposecretion of thyroxine. The symptoms includes enlargement of thyroid gland, fall in serum thyroxine level, increased TSH secretion. (Figure 11.14)
Tetany is caused due to the hyposecretion of parathyroid hormone (PTH). Due to hyposecretion of PTH serum calcium level decreases (Hypocalcemia), as a result serum phosphate level increases. Calcium and phosphate excretion level decreases. Generalized convulsion, locking of jaws increased heart beat rate, increased body temperature, muscular spasm are the major symptoms of tetany.
Hyperparathyroidism is caused due to excess PTH in blood. Demineralisation of bone, cyst formation, softening of bone, loss of muscle tone, general weakness, renal disorders are the symptoms of hyperparathyroidism.
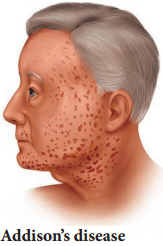
Addison’s disease is caused due to hyposecretion of glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids from the adrenal cortex. Muscular weakness, low BP., loss of appetite, vomiting, hyper pigmentation of skin, low metabolic rate, subnormal temperature, reduced blood volume, weight loss are the symptoms that occur in Addison’s disease (Figure 11.15). Reduced aldosterone secretion increases urinary excretion of NaCl and water and decreases potassium excretion leading to dehydration.
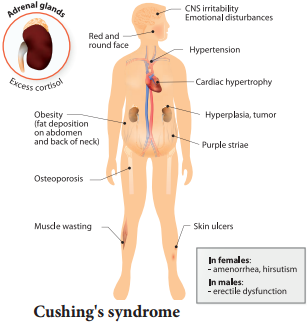
Cushing’s syndrome is caused due to excess secretion of cortisol. Obesity of the face and trunk, redness of face, hand, feet, thin skin, excessive hair growth, loss of minerals from bone (osteoporosis) systolic hypertension are features of Cushing’s syndrome. Suppression of sexual function like atrophy of gonads are the other symptoms of Cushing’s syndrome. (Figure 11.16)
Hypoglycaemia is due to increased secretion of insulin thereby blood glucose level decreases. In this disorder blood glucose level lowers than normal fasting index. Increased heartbeat, weakness, nervousness, headache, confusion, lack of co-ordination, slurred speech, serious brain defects like epilepsy and coma occurs.
Hyperglycaemia is otherwise known as Diabetes mellitus. It is caused due to reduced secretion of insulin. As the result, blood glucose level is elevated. Diabetes mellitus is of two types, Type I Diabetes and Type II Diabetes. Type I diabetes is also known Insulin dependent diabetes, caused by the lack of insulin secretion due to illness or viral infections.
Type II diabetes is also known as Non – Insulin dependent diabetes, caused due to reduced sensitivity to insulin, often called as insulin resistance. Symptoms of diabetes includes, polyurea (excessive urination), polyphagia (excessive intake of food), polydipsia (excessive consumption liquids due to thirst), ketosis (breakdown of fat into glucose results in accumulation of ketone bodies) in blood. Gluconeogenesis (Conversion of non – carbohydrate form like amino acids and fat into glucose) also occur in diabetes.
Diabates insipidus is caused due to hyposecretion of vasopressin (ADH) from neurohypophysis. The symptom includes frequent urination (polyurea) and excessive consumption of liquids due to thirst (polydipsia).