In this page, we are providing Improvement in Food Resources Class 9 Extra Questions and Answers Science Chapter 15 pdf download. NCERT Extra Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources with Answers will help to score more marks in your CBSE Board Exams. https://ncertmcq.com/extra-questions-for-class-9-science/
Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Extra Questions and Answers Improvement in Food Resources
Extra Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources with Answers Solutions
Improvement in Food Resources Class 9 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Improvement In Food Resources Class 9 Extra Questions And Answers Question 1.
What is the advantage of selecting seeds of crops with wider adaptability for agriculture?
Answer:
Wider adaptability helps in stabilizing crop production under different environmental conditions.
Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Extra Questions And Answers Question 2.
Name the type of nutrient that we get from mustard seeds and linseed.
Answer:
Mustard seeds and linseed are oilseed crops that provide fats.
Improvement In Food Resources Class 9 Notes Extra Questions And Answers Question 3.
Mention any two abiotic factors that affect crop production.
Answer:
Drought, salinity, waterlogging, heat, cold and frost are the abiotic factors that affect crop production.
Improvement In Food Resources Class 9 Important Questions Question 4.
Students were asked to select one that is not a source of starch amongst the following rice, wheat, sunflower seeds, and potato tuber.
Answer:
Sunflower seeds are not a source of starch. They are a source of fats.
Improvement In Food Resources Class 9 Questions And Answers Pdf Question 5.
Improved varieties can be produced in both animals and plants. How?
Answer:
Improved varieties can be produced in both animals and plants by hybridization and genetic modification.
Ch 15 Science Class 9 Extra Questions Question 6.
Name two protein-containing Rabi crops.
Answer:
Protein containing Rabi crops are gram and peas.
Improvement In Food Resources Class 9 Questions And Answers Question 7.
Identify two crops from the following which provide us carbohydrates for energy requirement. Black gram, wheat, lentil, and rice.
Answer:
Wheat and rice provide energy.
Improvement In Food Resources Class 9 Notes Questions And Answers Question 8.
Name two plants which are used as biopesticide in organic farming.
Answer:
Turmeric and leaves of Neem plant are used as biopesticide in organic farming.
Improvement In Food Resources Question Answer Question 9.
Name the two vitamins which are added in the poultry feed.
Answer:
Vitamin A and K are the vitamins that are added in the poultry feed.
Extra Questions From Chapter Improvement In Food Resources Question 10.
Name the major nutrient which we get from fish.
Answer:
The major nutrient which we get from fish is protein.
Class 9 Improvement In Food Resources Extra Questions Question 11.
How does Catla differ from Mrigal?
Answer:
Callas are surface feeders while Mrigals are bottom feeders.
Class 9 Science Ch 15 Extra Questions Question 12.
What is mariculture?
Or
What do you mean by mariculture?
Answer:
Mariculture is a practice in which marine fishes like mullets, bhetki, and pearl spots are cultured in coastal waters on a commercial scale.
Class 9 Chapter 15 Extra Questions Question 13.
Give one example of local variety and foreign variety of bees.
Answer:
Local variety: Apis cerana Indica is commonly known as the Indian bee.
Foreign variety: Apis mellifera is the Italian variety of bee.
Important Questions Of Improvement In Food Resources Question 14.
State one factor which affects the quality of honey produced.
Answer:
The quality of honey depends upon the pasturage or the flowers available to the bees for nectar and pollen collection.
Question 15.
Give two examples of exotic breeds of cows that are selected for a long lactation period.
Answer:
Exotic or foreign breeds like Jersey and Brown Swiss are selected for long lactation periods.
Question 16.
What is meant by beekeeping?
Answer:
Beekeeping is the practice of rearing the honeybees for obtaining honey and bee wax.
Question 17.
Which species of the honeybee is commonly used for commercial honey production throughout the country?
Answer:
Apis mellifera, the Italian variety of bee is commonly used for commercial honey production throughout the country.
Improvement in Food Resources Class 9 Extra Questions Short Answer Type 1
Question 1.
Mention the names of four marine fish of high economic value.
Answer:
Fishes like mullets, bhetki, pearl spots and prawns are of high economic value.
Question 2.
Give two examples of shellfishes.
Answer:
Shellfish include prawns, mussels and oysters.
Question 3.
Name two desirable traits for variety improvement in poultry farming.
Answer:
The two desirable traits for variety improvement in poultry farming are:
- number and quality of chicks;
- dwarf broiler parent for commercial chick production.
Question 4.
Which method is commonly used for improving cattle breeds and why?
Answer:
Crossbreeding between the indigenous and exotic breeds is commonly used for improving cattle breeds. This is done as it helps to incorporate the desirable qualities like a long lactation period of exotic breeds with the disease resistance of indigenous breeds in the progeny.
Question 5.
What are ‘Sahiwal’ and ‘Jersey’ breeds?
Answer:
Sahiwal is an indigenous breed of cow whereas Jersey is the exotic breed of cow.
Question 6.
State the food requirements of dairy animals.
Answer:
The food requirements of dairy animals are of two types:
- Maintenance requirement, which is the food required to support the animal to live a healthy life.
- Milk producing a requirement, which is the type of food required during the lactation period.
Question 7.
What is mixed cropping? How does it help a farmer?
Answer:
Mixed cropping is the practice of growing two or more crops simultaneously on the same piece of land. For example, wheat and gram, or wheat and mustard, or groundnut and sunflower. It helps the farmer as it reduces the risk and gives some insurance against the failure of one of the crops.
Question 8.
State two advantages of fertilizers over manure.
Answer:
Fertilizers are more advantageous than manure as:
- Fertilizers are nutrient specific and provide the specific nutrients like N, P, K to the soil.
- They are not bulky, so are easier to transport.
Question 9.
What do you mean by vermicompost?
Answer:
The compost prepared by using earthworms to hasten the process of decomposition of plant and animal refuse is called vermicompost.
Question 10.
What are the advantages of fish farming?
Answer:
The advantages of fish farming are:
- It helps to get a large amount of desired fishes from a small area.
- It enables a variety of improvement in a better way.
Question 11.
What is a GM crop? Name anyone such crop which is grown in India.
Answer:
GM crops are the crops obtained by introducing a gene that would provide the desired characteristic to the crop plant. Bt Cotton is a genetically modified (GM) crop which has been made insect-resistant by introducing a gene from bacteria.
Question 12.
Give any two differences between macronutrients and micronutrients.
Answer:
Macronutrient:
- Macronutrients are generally present and utilized by plant tissues in large amounts.
- Apart from carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, the macronutrients include six elements- nitrogen, phosphorous, sulfur, potassium, calcium, and magnesium.
Micronutrient
- The nutrients which are needed by plant tissues in small amounts are called micronutrients.
- These include seven elements: iron, manganese, copper, zinc, molybdenum, boron, and chlorine.
Question 13.
What is a green revolution?
Answer:
An increase in crop production (especially wheat and rice) due to the use of plant breeding techniques and better farming practices, is called the green revolution.
Question 14.
What are the weeds? How do they harm crop plants?
Or
How do they prevent the growth of crops?
Answer:
The unwanted plants which grow along with the crop in the cultivated field are called weeds. Weeds compete for food, space, and light with the crop plant and reduce the growth of the crop.
Question 15.
- What are many animals?
- Give two examples of such animals.
Answer:
- Milk: producing females of cattle are called many animals (dairy animals).
- Examples of such animals are: cows, buffaloes, goats etc.
Question 16.
Mention two advantages of animal husbandry.
Answer:
Animal husbandry is advantageous to get
- Higher milk production from cattle and higher egg production from poultry.
- Utilization of animal wastes in a beneficial way.
Question 17.
State two characteristics of a healthy animal.
Answer:
The two characteristics of a healthy animal are:
- A healthy animal feeds regularly.
- Healthy animals have a normal posture.
Question 18.
Why would a cattle breeder choose to cross-breed a Jersey cow with a Red Sindhi? State two reasons.
Answer:
Jersey cows have a longer lactation period while Red Sindhi are resistant to diseases. So, the two are cross-bred to get animals with
- Long lactation period
- Resistance to diseases.
Question 19.
How are new varieties of poultry birds with desired traits produced?
Answer:
Poultry birds with desired traits are produced by crossbreeding the indigenous variety like Aseel with the exotic variety like Leghorn.
Question 20.
What desirable traits are focussed to develop by cross-breeding indigenous and exotic breeds of fowl?
Or
Mention any four desirable traits for which new varieties are produced?
Answer:
Desirable traits of poultry are:
- number and quality of chicks;
- dwarf broiler parent for commercial chick production;
- summer adaptation capacity/tolerance to high temperature;
- low maintenance requirements;
- reduction in the size of the egg-laying bird with the ability to utilize more fibrous cheaper diets formulated using agricultural by-products.
Question 21.
1. State one demerit with a composite fish culture system.
2. How can this problem be overcome?
Answer:
1. The demerit of composite fish culture system is:
(a) Many of the fishes used in the composite culture system breed only during monsoon.
(b) Lack of availability of good quality seed.
2. The problem is overcome by breeding these fish in ponds using hormonal stimulation. This ensures the supply of pure fish seed in desired quantities.
Improvement in Food Resources Class 9 Extra Questions Short Answer Type 2
Question 1.
(a) Suppose you are in charge of a grain store. How will you find out the presence of pests? Mention any two indicators.
(b) Which method is most effective for destroying insects in stored food grains, spraying or fumigation?
Answer:
(a) The indicators for the presence of pests in grain store are:
(i) Damaged or broken grains having perforations or holes.
(ii) Discoloration of grains, degraded quality of food grains.
(b) Fumigation is a better method than spraying of chemicals as the fumigants completely fill the area with gaseous particles that suffocate the pests and kill them.
Question 2.
Write a short note on marine fisheries.
Answer:
Marine fishery resources include 7500 km coastline and the deep seas beyond it. Some marine fish varieties are pomfret, mackerel, tuna, sardines, and Bombay duck. Fishes like mullets, bhetki, and pearl spots; shellfish such as prawns, mussels, and oysters as well as seaweed are of high economic value.
Question 3.
Differentiate between:
1. Inland fishery and marine fishery
2. Apiculture and aquaculture
Or
Distinguish between
1. Inland fishery and marine fishery
2. Culture fishery and capture fishery
3. Apiculture and aquaculture
Answer:
Inland Fishery:
- Inland fishery resources include canals, ponds, reservoirs, rivers and brackish water resources like estuaries and lagoons.
- Most fish production from these resources is through aquaculture.
Marine Fishery:
- Marine fishery resources include 7500 km coastline and the deep seas beyond it.
- Most fish production from these resources is through mariculture.
Apiculture:
The practice of rearing and maintenance of honeybees for obtaining honey and bee wax is called as apiculture.
Aquaculture:
The practice of breeding, rearing, and harvesting of plants and animals in all types of water environments including ponds, rivers, lakes, and the ocean.
Capture fishery:
Fish are obtained from natural resources in capture fishery.
Culture fishery:
Fish farming done in ponds or tanks is called culture fishery.
Question 4.
Differentiate between layers and broilers. What type of food should be given to broilers?
Answer:
Layers:
- The egg-laying birds which are managed for egg production are called layers.
- The layers start laying eggs at the age of 20 weeks. So, they are kept for longer periods of, around 500 days, called laying period.
- They require enough space, proper light, and hygienic conditions.
- Their feed consists of vitamins, minerals, and certain micronutrients that affect the hatchability of the eggs.
Broilers:
- The birds maintained for meat production are called broilers.
- The broilers are raised in poultry farms up to 6-7 weeks and usually weigh around 700 g to 1.5 kg.
- More stress is given to maintain the feathering, carcass quality, and low levels of mortality.
- The requirement of the broilers is protein and fat-rich food. The level of vitamin A and vitamin K is kept high in their feed.
Question 5.
What are the advantages of bee-keeping?
Answer:
The advantages of bee-keeping are:
- It helps to obtain honey and bee wax which are used in medicines and many cosmetic preparations respectively.
- It requires a very low amount of investment.
- It is less labor-intensive.
- It helps to increase the pollination of flowers.
Question 6.
What is honey? What does the quality of honey depend upon?
Answer:
It is a sugary substance produced and stored by insects like bees in the bee-hives. It has a very high nutritional and medicinal value. The value or quality of honey depends upon the pasturage, or the flowers available to the bees for nectar and pollen collection.
Question 7.
Differentiate between the following:
- Capture fishery and culture fishery
- Beekeeping and Poultry farming
Answer:
- Capture fishery: Fish are obtained from natural resources in capture fishery.
Culture fishery: Fish farming is called culture fishery. - Beekeeping is the practice of rearing honeybees for obtaining honey and bee wax.
Poultry farming is undertaken to raise domestic fowl called layers for egg production and the broilers for chicken meat.
Question 8.
Discuss various methods of weed control.
Answer:
The various methods of weed control are:
Mechanical removal, a spray of chemicals called weedicides, and preventive methods like proper seedbed preparation, timely sowing of crops, intercropping, and crop rotation.
question 9.
Discuss the role of hybridization in crop improvement.
Answer:
Hybridization is one of the methods of crop production which ensures high yield. Hybridization refers to crossing between two genetically dissimilar plants each of which possesses a particular desired character. The two varieties are cross-bred during the process to incorporate both the desirable characteristics in a single variety. This method of hybridization improves crops with respect to yield, disease resistance, pest resistance, etc.
Question 10.
What are the macro and micronutrients of plants? Name two of each kind.
Answer:
Macronutrients: The nutrients which are required in large quantities. They are six.
Example: Nitrogen, Phosphorus.
Micronutrients: The nutrients which are required in small quantities. They are seven.
Example: Iron, Copper.
Question 11.
Name any three processes in plants that are affected by deficiency in nutrients.
Answer:
Deficiency of nutrients affects the following things in plants:
- reproduction
- growth
- susceptibility to diseases.
Question 12.
Distinguish between intercropping and mixed cropping. List any two advantages of intercropping over mixed cropping.
Answer:
Mixed cropping Growing two or more crops simultaneously on the same piece of land.
Inter-cropping: Growing two or more crops simultaneously on the same field in a definite pattern.
Intercropping is better than mixed cropping because:
- The application of pesticides to individual crop is easier and done as per the need of the crop.
- Different crops can be separately harvested and threshed.
Question 13.
What is hybridization? How is it done?
Answer:
Hybridization refers to crossing between two genetically dissimilar plants each of which possesses a particular desired character. The two varieties are cross-bred during the process to incorporate both the desirable characteristics in a single variety. This method of hybridization improves crops with respect to yield, disease resistance, pest resistance, etc.
Question 14.
How are cultivation practices and crop yield related to weather?
Answer:
1. Agriculture in India is largely dependent on the monsoon. The success of crops in most areas is dependent on timely monsoons and sufficient rainfall spread through most of the growing season. Hence, poor monsoons cause crop failure.
2. The cultivation of different varieties of crops is dependent on abiotic stresses like droughts and floods situation in an area.
Question 15.
Name any three methods of irrigation and briefly describe them.
Or
(a) Describe any two irrigation systems adopted in India to supply water to agricultural lands.
(b) Write two advantages of building check dams.
Answer:
(a) The three different types of irrigation systems are:
Wells: There are two types of wells: dug wells and tube wells. In a dug well, water is collected from water-bearing strata. Tube wells can tap water from the deeper strata. From these wells, water is lifted by pumps for irrigation.
Canals: In this system canals receive water from one or more reservoirs or from rivers. The main canal is divided into branch canals having further distributaries to irrigate fields.
River Lift Systems: In this system, water is directly drawn from the rivers for supplementing irrigation in areas close to rivers.
The advantage of check dams are-
- Leads to an increase in groundwater levels.
- The check-dams stop the rainwater from flowing away and reduce soil erosion.
Question 16.
What factors may be responsible for losses of grains during storage? Give one example of both. Give one method/preventive measure to control such losses.
Or
What preventive and control measures should be taken before the storage of grains?
Answer:
Factors responsible for losses of grains during storage are:
- Biotic: insects, rodents, fungi, mites, and bacteria
- Abiotic: inappropriate moisture and temperatures in the place of storage.
Ways to reduce loss during storage of grains:
- Proper treatment and systematic management of warehouses.
- They include strict cleaning of the produce before storage.
- Proper drying of the product first in sunlight and then in shade.
- Fumigation using chemicals that can kill pests.
Question 17.
List six facilities that must be provided to cattle to ensure their good health and production of clean milk.
Answer:
Six facilities that must be provided to cattle to ensure their good health and production of clean milk are:
- The cattle should be housed in well-ventilated sheds,
- The floor of the cattle shed needs to be sloping so as to stay dry and to facilitate cleaning.
- The feeding of cattle should be carried out in a scientific manner. The feed should have:
(a) Roughage, which is largely fiber and
(b) Concentrates, which are low in fiber and have high levels of proteins and other nutrients.
- Leads to an increase in groundwater levels.
- The check-dams stop the rainwater from flowing away and reduce soil erosion.
Question 18.
What is the lactation period? Name two breeds of cattle that are selected for their lactation period. Why are they crossed with local breeds?
Answer:
The period of milk production after the birth of a calf is called the lactation period. Milk production can be increased by increasing the lactation period. Exotic or foreign breeds like Jersey and Brown Swiss are selected for long lactation periods. They (exotic breeds) are crossed with local breeds to get animals with the desired qualities of both the animals.
Question 19.
Which variety of honeybee is advantageous – Apis cerana indica or Apis mellifera and why?
Answer:
Apis mellifera, the Italian variety of bee is better than Apis cerana indica. It has the following advantages:
- They have high honey collection capacity.
- They sting somewhat less.
- They stay in a given beehive for long periods and breed very well.
Question 20.
Match the column A with column B

Answer:
(a) (ii) Surface feeders
(b) (iii) Middle-zone feeders
(c) (i) Bottom feeders
(d) (iv) Culture fishery
Question 21.
Fill in the blanks
(a) Pigeon pea is a good source of ………..
(b) Berseem is an important ………… crop.
(c) The crops which are grown in the rainy season are called ………… crops.
(d) ………… are rich in vitamins.
(e) ………… crop grows in the winter season.
Answer:
(a) protein
(b) fodder
(c) Kharif
(d) Vegetables
(e) Rabi
Question 22.
What is a GM crop? Name anyone such crop which is grown in India.
Answer:
GM crops are the crops obtained by introducing a gene that would provide the desired characteristic to the crop plant. Bt Cotton is a genetically modified (GM) crop which has been made insect-resistant by introducing a gene from bacteria.
Question 23.
List out some useful traits in the improved crop.
Answer:
Some useful traits of improved crops are:
(a) higher yield
(b) improved nutritional quality
(c) resistance to biotic and abiotic stresses
(d) change in maturity duration
(e) wide range of adaptability
(f) desired agronomic characteristics.
Question 24.
Why is organic matter important for crop production?
Answer:
Organic matter is important for crops production because:
(a) it helps in improving soil structure.
(b) it helps in increasing water holding capacity of sandy soil.
(c) It helps in drainage and in avoiding water logging in clayey soils.
Question 25.
Why is excess use of fertilizers detrimental for the environment?
Answer:
Excess use of fertilizers is detrimental for the environment as their residual and unused amounts become pollutants for air, water, and soil. The fertilizers get washed away in the nearby water bodies and cause excessive growth of algae and aquatic plants which can adversely affect the aquatic life and drain the oxygen from water bodies.
Question 26.
Give one word for the following:
(a) Farming without the use of chemicals as fertilizers, herbicides and pesticides is known as ……….
(b) Growing of wheat and groundnut on the same field is called as ……….
(c) Planting soybean and maize in alternate rows in the same field is called as ……….
(d) Growing different crops on a piece of land in pre-planned succession is known as ……….
(e) Xanthium and Parthenium are commonly known as ……….
(f) The causal organism of any disease is called as ……….
Answer:
(a) organic farming
(b) mixed cropping
(c) intercropping
(d) crop-rotation
(e) weeds
(f) pathogen
Question 27.
Match the following A and B
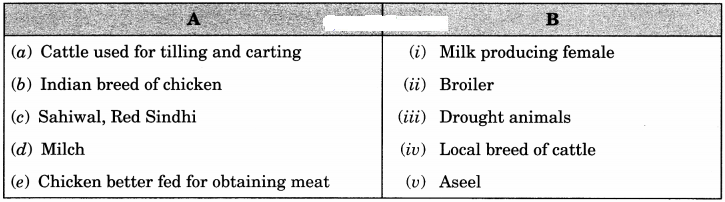
Answer:
(a) → (iii) Drought animals
(b) → (v) Aseel
(c) → (iv) The local breed of cattle
(d) → (i) Milk producing female
(e) → (ii) Broiler
Question 28.
If there is low rainfall in a village throughout the year, what measures will you suggest to the farmers for better cropping?
Answer:
If there is low rainfall in a village throughout the year, then the farmers will be suggested to:
(a) Cultivate crops varieties that are drought resistant and early maturing.
(b) Increase the humus content of the soil in order to increase its water holding capacity.
Question 29.
Group the following and tabulate them as energy-yielding, protein yielding, oil yielding, and fodder crop. Wheat, rice, berseem, maize, gram, oat, pigeon gram, sudangrass, lentil, soybean, groundnut, castor, and mustard.
Answer:
- Energy yielding: wheat, rice, maize
- Protein yielding: gram, pigeon gram, lentil, soybean
- Oil yielding: groundnut, castor, mustard, soybean
- Fodder crops: berseem, oat, sudangrass
Question 30.
Define the term hybridization and photoperiod.
Answer:
Hybridization is one of the methods of crop production which involves crossing between two genetically dissimilar plants each of which possesses a particular desired character. The photoperiod is the duration of sunlight available to the plant. It affects the growth, flowering, and maturation of crops.
Question 31.
Fill in the blanks
(a) Photoperiod affects the ………..
(b) Kharif crops are cultivated from ……….. to ………..
(c) Rabi crops are cultivated from ……….. to ………..
(d) Paddy, maize, green gram and black gram are ……….. crops.
(e) Wheat, gram, pea, mustard are ……….. crops.
Answer:
(a) Flowering of plants
(b) June to October
(c) November to April
(d) Khalil
(e) Rabi
Question 32.
Cultivation practices and crop yield are related to environmental conditions. Explain.
Answer:
Different crops and cultivation practices require different climatic conditions, temperature, photoperiod for their growth and completion of life cycle. Depending upon these conditions some crops called Kharif crops are grown in rainy season while others called as the Rabi crops are grown during winter season.
Question 33.
Fill in the blanks
(a) A total of ……….. nutrients are essential to plants.
(b) ……….. and ……….. are supplied by air to p1ants.
(c) ……….. is supplied by water to plants.
(d) Soil supply ……….. nutrients to plants.
(e) ……….. nutrients are required in large quantity and called.
(f) ……….. nutrients are needed in small quantity for plants and are called.
Answer:
(a) 16 (Sixteen)
(b) Carbon, oxygen
(c) Hydrogen
(d) 13 (Thirteen)
(e) Six, macro
(f) Seven, micro
Question 34.
Differentiate between compost and vermicompost.
Answer:
1. Compost: Compost is prepared by decomposition of the farm waste materials like livestock excreta (cow dung, etc.), vegetable waste, animal refuse, domestic waste, sewage waste, straw, eradicated weeds, etc., in pits.
2. Vermicompost: The compost is called as vermicompost if it is prepared by using earthworms to hasten the process of decomposition of plant and animal refuse.
Question 35.
Arrange these statements in the correct sequence of preparation of green manure.
(a) Green plants are decomposed in soil.
(b) Green plants are cultivated for preparing manure or crop plant parts are used.
(c) Plants are plowed and mixed into the soil.
(d) After decomposition, it becomes green manure.
Answer:
(b)→(c)→(a)→(d)
Question 36.
An Italian bee variety A. mellifera has been introduced in India for honey production. Write about its merits over other varieties.
Answer:
The Italian bee variety A. mellifera has the following advantages:
- They have high honey collection capacity.
- They sting somewhat less.
- They stay in a given beehive for long periods and breed very well.
Question 37.
In agricultural practices, higher input gives a higher yield. Discuss how.
Answer:
The financial conditions of the farmers allow them to take up different farming practices and technologies. The cropping system and production practices of the farmer are decided by the farmer’s purchasing capacity for input. A higher money input helps to raise the yield. So, we can say that in agricultural practices, higher input gives a higher yield.
Improvement in Food Resources Class 9 Extra Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1.
Mention the modern initiatives undertaken in India to supply water to the fields.
Answer:
Indian agriculture is mainly dependent on the monsoons. The irregular or scarcity of rainfall often results in crop failure. To overcome the problem, different types of irrigation systems are in practice in India for the supply of water in agricultural fields. Wells, canals, river lift systems, tanks, etc. are used for irrigation. Some new initiatives like rainwater harvesting and watershed management are being used.
For this small check-dams are constructed to stop the rainwater from flowing and lead to an increase in groundwater levels. The different types of irrigation systems are:
1. Wells: There are two types of wells – dug wells and tube wells. In a dug well, water is collected from water-bearing strata. Tube wells can tap water from the deeper strata. From these wells, water is lifted by pumps for irrigation.
2. Canals: In this system canals receive water from one or more reservoirs or from rivers. The main canal is divided into branch canals having further distributed to irrigate fields.
3. River Lift Systems: In this system, water is directly drawn from the rivers for supplementing irrigation in areas close to rivers.
4. Tanks: These are small storage reservoirs, which intercept and store the run-off of smaller catchment areas.
Question 2.
What do you understand by composite fish culture? Describe in detail with advantages and disadvantages. What are the advantages of composite fish culture?
Answer:
A combination of five or six fish species is used in a single fish pond in the composite fish culture system. The selected species do not compete for food among them as they have different types of food habits.
The types of fishes used are:
Callas are surface feeders, Rohus feed in the middle-zone of the pond, Mrigals, and Common Carps are bottom feeders, and Grass Carps feed on the weeds. As a result, the food available in all the parts of the pond is used.
Advantages of Composite fish culture:
- The species of fishes in the pond utilize all the food available in the pond.
- The species do not compete with each other for food as they have different food habits.
- The yield of fish is increased by such a culture system.
The disadvantage of Composite fish culture:
A major problem in fish farming is the lack of availability of good quality fish seeds.
Question 3.
How do plants get their nutrients?
Or
List the nutrients supplied by air, water, and soil.
Answer:

Question 4.
Define manures. What are its different kinds? State two limitations of manures.
Answer:
Manure is prepared by the decomposition of animal excreta and plant waste and contains a lot of organic matter which helps in enriching the soil with nutrients and increasing soil fertility. Manure is classified on the basis of kind of biological material used as:
1. Compost: Compost is prepared by decomposition of the farm waste materials like livestock excreta (cow dung etc.), vegetable waste, animal refuse, domestic waste, sewage waste, straw, eradicated weeds, etc., in pits.
2. Vermicompost: The compost is called vermicompost if it is prepared by using earthworms to hasten the proœss of decomposition of plant and animal refuse.
3. Green manure: Green plants like sun hemp or guar are grown and then mulched by plowing them into the soil prior to the sowing of the crop seeds to enrich the soil in nitrogen and phosphorus.
The limitations of manure are:
- They do not supply a specific nutrient.
- They are not readily soluble in water so their absorption by plants is slower.
- They are bulky in nature and difficult to be transported.
- Only small amounts of nutrients are supplied by the manure.
Question 5.
Differentiate between manures and fertilizers.
Or
Compare manure and fertilizer in three points.
Manure:
- Manure is prepared by the decomposition of animal excreta and plant waste.
- They are bulky and difficult to be transported.
- They are not nutrient-specific in nature.
- They are not readily soluble in water and thus absorbed slowly by plants.
- Manure contains a lot of organic matter.
- They are environment friendly in nature.
- Difficult to store.
Fertilizer:
- Fertilizers are commercially produced plant nutrients.
- They are not bulky, so easier to transport.
- They are nutrient-specific in nature.
- They are easily absorbed by the plants as they are soluble in water.
- They do not contain organic matter.
- The comparatively less environmentally friendly.
- Easier to store.
Question 6.
Mention the management practices that are common between dairy and poultry farming.
Answer:
Management practices which are common between dairy and poultry fanning are:
- Should be housed in the well-ventilated shelter.
- Proper cleanliness should be maintained.
- Regular visits by a doctor and timely vaccination.
- Balanced food should be provided with additives.
- Regular inspections, with proper record keeping.
Question 7.
What are the differences between broilers and layers with respect to their purpose of breeding and daily requirement? What necessary steps have to be taken to prevent the occurrence of infectious diseases in poultry farms?
Answer:
The meat-producing birds are called broilers and the egg-laying birds are called layers. The housing, nutritional and environmental requirements of the broilers are different from the layers. The broilers are raised in poultry farms up to 6-7 weeks and usually weigh around 700 g to 1.5 kg.
The requirement of the broilers is protein and fat-rich food. The level of vitamin A and vitamin K is kept high in their feed. Care is taken to avoid mortality and to maintain the feathering and carcass quality. The layers start laying eggs at the age of 20 weeks. So, they are kept for longer periods of around 500 days, called laying period. They require enough space, proper light, and hygienic conditions.
heir feed consists of vitamins, minerals, and certain micronutrients that affect the hatchability of the eggs. Necessary steps for prevention of infectious diseases are:
1. Proper cleaning, sanitation, and spraying of disinfectants at regular intervals.
2. Appropriate vaccination to prevent the occurrence of infectious diseases.
Question 8.
Discuss the role of hybridization in crop improvement.
Answer:
Hybridization is one of the methods of crop production which ensures high yield. Hybridization refers to crossing between two genetically dissimilar plants each of which possesses a particular desired character. The two varieties are cross-bred during the process to incorporate both the desirable characteristics in a single variety. This method of hybridization improves crops with respect to yield, disease resistance, pest resistance, etc.
Question 9.
Define
1. Vermicompost
2. Green manure
3. Biofertilizer
Answer:
1. Vermicompost: The compost prepared by using earthworms to hasten the process of decomposition of plant and animal refuse.
2. Green manure: The manure which is prepared by decomposing green plants in field itself is called green manure. For example: sun hemp is grown in fields, mulched by plowing and allowed to
decompose infield for the preparation of green manure. It helps in enriching the soil in nitrogen and phosphorus.
3. Biofertiliser: Living organisms which are used as fertilizer to supply the nutrients to plants, are called as biofertilizers. For example, blue-green algae which fix nitrogen in soil, rice fields, are called biofertilizers.
Question 10.
Discuss various methods of weed control.
Answer:
The various methods of weed control are mechanical removal, a spray of chemicals called weedicides and preventive methods like proper seedbed preparation, timely sowing of crops, intercropping and crop rotation.
Question 11.
Differentiate between the following
- Capture fishery and Culture fishery
- Mixed cropping and Inter-cropping
- Beekeeping and Poultry farming
Answer:
- Capture fishery: Fish are obtained from natural resources in capture fishery. Culture fishery: Fish farming is called culture fishery.
- Mixed cropping: Growing two or more crops simultaneously on the same piece of land. Inter-cropping: Growing two or more crops simultaneously on the same field in a definite pattern.
- Beekeeping is the practice to rear honeybee for obtaining honey. Poultry farming is undertaken to raise domestic fowl called layers for egg production and the broilers for chicken meat.
Question 12.
Give the merits and demerits of fish culture.
Answer:
The merits and demerits of fish culture are:
Merits:
- It helps to get a large amount of desired fishes from a small area.
- It enables a variety of improvements in a better way.
Demerits:
- It is a threat to bio-diversity as only selected varieties are cultured on a large scale.
- It involves the culture of only economically important and valued fishes.
Question 13.
What do you understand by composite fish culture?
Answer:
A combination of five or six fish species is used in a single fish pond in the composite fish culture system. The selected species do not compete for food among them as they have different types of food habits.
The types of fishes used are:
Callas are surface feeders, Rohus feed in the middle-zone of the pond, Mrigals and Common Carps are bottom feeders, and Grass Carps feed on the weeds. As a result, the food available in all the parts of the pond is used.
Question 14.
Why should beekeeping be done in good pasturage?
Answer:
Beekeeping should be done in good pasturage as it:
- Helps in increasing the honey yield.
- Helps in increasing pollination efficiency.
- Provides better quality and quantity of nectar for the honey bees.
Question 15.
Write the modes by which insects affect the crop yield.
Answer:
The modes by which insects affect the crop yield are
- they cut the root, stem and leaf,
- they suck the cell sap from various parts of the plant, and
- they bore into stem and fruits.
Question 16.
Discuss why pesticides are used in very accurate concentration and in a very appropriate manner.
Answer:
Pesticides should be used in very accurate concentration and in a very appropriate manner because it
may have the following adverse effects:
(a) They harm the soil and causes loss of fertility
(b) They act as a check on the replenishment of organic matter
(c) They kill the microorganism of soil and destroy the soil structure
(d) They cause air, water and soil pollution.
Question 17.
Name two types of animal feed and write their functions.
Answer:
The two types of animal feed are:
- Roughage, which is largely fiber.
- Concentrates, which are low in fiber and have high levels of proteins and other nutrients.
Question 18.
What would happen if poultry birds are larger in size and have no summer adaptation capacity? In order to get small sized poultry birds, having summer adaptability, what method will be employed?
Answer:
Maintenance of temperature is needed for better egg production by poultry birds. The egg production is declined due to larger size (increase in surface area of the body) and no adaptability of summer in poultry birds. So, cross-breeding of poultry birds is done to obtain smaller size and higher summer adaptability in them. Small size is ais? needed for better housing and lower feed requirements.
Question 19.
Suggest some preventive measures for the diseases of poultry birds.
Answer:
Some preventive measures of poultry bird diseases are
(a) cleaning of poultry farms
(b) proper sanitation of poultry farms
(c) spraying of disinfectants at regular intervals
(d) appropriate vaccination of birds.
Question 20.
The figure shows the two crop fields [Plots A and BI have been treated by manures and chemical fertilizers respectively, keeping other environmental factors same. Observe the graph and answer the following questions.
- Why does plot B show a sudden increase and then a gradual decrease in yield?
- Why is the highest peak in plot A graph slightly delayed?
- What is the reason for the different patterns of the two graphs?
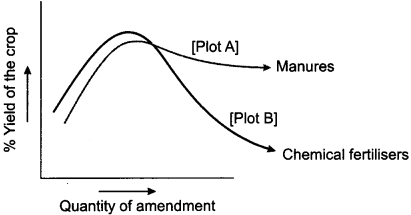
Answer:
1. With the addition of chemical fertilizer, there is a sudden increase in yield due to the release of nutrients Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium (NPK), etc. in high quantity. The gradual decline in the graph may be due to continuous use and a high quantity of chemicals that kill microbes useful for replenishing the organic matter in soil. This decreases soil fertility.
2. Manures supply small quantities of nutrients to the soil slowly as it contains large amounts of organic matter. It enriches soil with nutrients thereby increasing soil fertility continuously.
3. The difference in the two graphs indicates that use of manure is beneficial for a long duration in cropping as the yield tends to remain high when the number of manure increases.
4. In the case of Plot B the chemical fertilizers may cause various problems when used continuously for long time. Loss of microbial activity reduces the decomposition of organic matter and as a result, the soil fertility is lost that affects the yield.
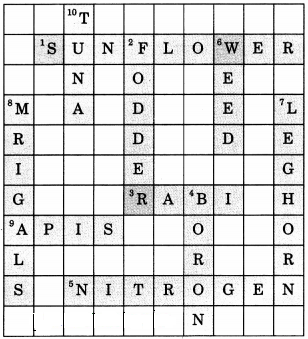
Question 21.
Complete the crossword puzzle
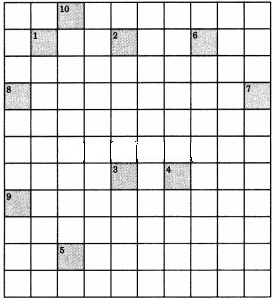
Across:
1. Oil yielding plant (9)
3. Crop grown in winter season (4)
5. Fixed by Rhizobium (8)
9. Common honey bee (4)
Down:
2. Animal feed (6)
4. A micronutrient (5)
6. Unwanted plant in crop fields (4)
7. An exotic breed of chicken(7)
8. Bottom feeders in fish pond(7)
10. A marine fish (4)
Answer:
Improvement in Food Resources Class 9 Extra Questions HOTS
Question 1.
Irrigation systems are in practice in India for the supply of water in agricultural fields. Why?
Answer:
Most agriculture in India is rain-fed and the success of crops in most areas is dependent on timely monsoons and sufficient rainfall. Poor monsoons can cause crop failure. Hence, in order to ensure that the crops get water at the right stages during their growing season, irrigation systems are in practice in India for the supply of water to agricultural fields.
Question 2.
Nitrogenous fertilizers are usually not required by the leguminous crops. Why?
Answer:
The leguminous crops have root nodules that harbor nitrogen-fixing bacteria like Rhizobium in them. These bacteria convert the atmospheric nitrogen to nitrates for their utilization by plants. So, nitrogenous fertilizers are usually not required by the leguminous crops.
Question 3.
Why are crops like guar grown by some farmers before sowing the seeds of a crop?
Answer:
The crops like guar are grown by farmers before sowing the seeds of a crop as the guar crop is mulched by plowing. It turns into green manure which helps in enriching the soil in nitrogen and phosphorus.
Question 4.
Why is the enhancement of food production becoming a major necessity? Which group of activities are required for improving the crop yields?
Answer:
Enhancement of food production has become a major necessity because:
1. The population of the world is increasing at a faster rate, so it is needed to fulfill the food requirements of the population.
2. The land available for cultivation is limited, so the only option available is to increase crop production.
Major groups of activities for improving crop yields:
- Crop variety improvement
- Crop production improvement
- Crop protection management
Question 5.
List some dairy farming practices needed to increase the milk yield potential of cattle.
Answer:
The dairy farming practices needed to increase the milk yield potential of cattle are:
- The cattle should be housed well and have adequate water.
- The cattle should be kept disease-free.
- The feeding of cattle should be carried out in a scientific manner with special emphasis on the quality and quantity of fodder.
- Stringent cleanliness and hygiene should be maintained.
- Regular inspections of cattle should be done with proper record keeping.
- Regular visits by a veterinary doctor should be ensured.
Improvement in Food Resources Class 9 Extra Questions Value Based (VBQs)
Question 1.
Aniket took admission in a dairy research institute and took an active interest in his studies. During the course, he got an opportunity to visit a village. He met the farmers there and advised them about dairy farm practices which can help to increase the milk yield of their cattle. The farmers were able to get an increased yield due to his advice.
- Name two species of cattle in India.
- List two measures that would have been suggested by Aniket to increase milk yield.
- What values are shown by Aniket?
Answer:
1. Indian cattle belong to two different species, Bos indicus, cows, and Bos bubble.s, buffaloes.
2. The measures which would have been suggested by Aniket to increase milk yield are:
(a) The cattle should be housed well and have adequate water.
(b) The cattle should be kept disease-free.
(c) The feeding of cattle should be carried out in a scientific manner with special emphasis on the quality and quantity of fodder.
3. The values shown by Aniket are a concern for others, caring nature, scientific approach, and knowledge.
Question 2.
Sonam got admission in a reputed institute engaged in agricultural research. After the completion of course she decided to go and serve the people of her village. Her village was suffering from a reduction in infertility of the soil and high salinity in soil. She called a meeting of farmers and told them that the use of fertilizers has increased the salinity of the soil. She suggested to them the use of manures and cropping patterns to get better yields.
- What are the different types of manures which can be used?
- Name the different cropping patterns which she would have suggested.
- What values are shown by Sonam?
Answer:
- The types of manures which can be used are: Compost, vermicompost, and green manure.
- The different cropping patterns can be inter-cropping, mixed cropping, and crop rotation.
- The values shown by Sonam are sincerity towards work, scientific aptitude, and concern for others.
