Find free online Chemistry Topics covering a broad range of concepts from research institutes around the world.
Ionisation of Water
We have learnt that when an acidic or a basic substance is dissolved in water, depending upon its nature, it can either donate (or) accept a proton. In addition to that the pure water itself has a little tendency to dissociate. i.e, one water molecule donates a proton to an another water molecule. This is known as auto ionisation of water and it is represented as below.
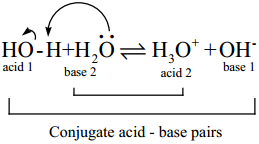
In the above ionisation, one water molecule acts as an acid while the another water molecule acts as a base. The dissociation constant for the above ionisation is given by the following expression
![]() …………… (8.3)
…………… (8.3)
The concentration of pure liquid water is one. i.e, [H2O]2 = 1
∵ Kw = [H3O+][OH–] …………. (8.4)
Here, Kw represents the ionic product (ionic product constant) of water.
It was experimentally found that the concentration of H3O+ in pure water is 1 × 10-7 at 25°C. Since the dissociation of water produces equal number of H3O+ and OH–, the concentration of OH– is also equal to 1 × 10-7 at 25°C.
Therefore, the ionic product of water at 25°C is
KW = [H3O]+[OH–] …………. (8.4)
KW = (1 × 10-7)(1 × 10-7)
= 1 × 10-14.
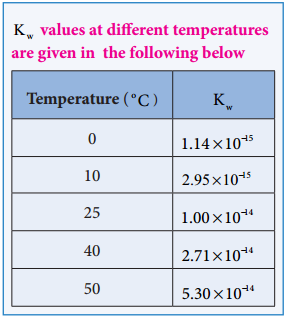
Like all equilibrium constants, Kw is also a constant at a particular temperature. The dissociation of water is an endothermic reaction. With the increase in temperature, the concentration of H3O+ and OH– also increases, and hence the ionic product also increases.
In neutral aqueous solution like NaCl solution, the concentration of H3O+ is always equal to the concentration of OH– whereas in case of an aqueous solution of a substance which may behave as an acid (or) a base, the concentration of H3O+ will not equal to
[OH–].
We can understand this by considering the aqueous HCl as an example. In addition to the auto ionisation of water, the following equilibrium due to the dissociation of HCl can also exist.
HCl + H2O ⇄ H3O+ + Cl–
In this case, in addition to the auto ionisation of water, HCl molecules also produces H3O+ ion by donating
a proton to water and hence [H3O+]>[OH–]. It means that the aqueous HCl solution is acidic. Similarly, in basic solution such as aqueous NH3, NaOH etc…. [OH–]>[H3O+].