
On this page, you will find Light Class 8 Notes Science Chapter 16 Pdf free download. CBSE NCERT Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 16 Light will seemingly help them to revise the important concepts in less time.
CBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 16 Light
Light Class 8 Notes Understanding the Lesson
1. Light is a form of energy.
2. When light reaches our eyes after striking an object, we are able to see an object.
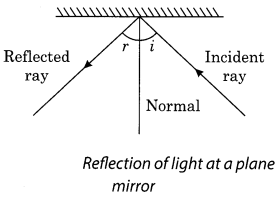
3. The bouncing back of light into the same medium after it falls on a surface is called reflection.
4. The ray of light striking the surface is called an incident ray.
5. The ray of light which is returned back into the same medium is known as the reflected ray.
7. The perpendicular drawn to the reflecting surface at the point where incident ray strikes the mirror is called normal.
8. The angle between the incident ray and the normal is called the angle of incidence.
9. The angle between the reflected ray and the normal is called the angle, of reflection.
10. Laws of reflection:
- The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
- The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal all lie in the same plane.
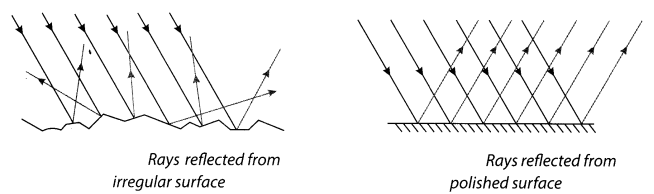
11. When all the parallel rays reflected from a plane surface are not parallel, the reflection is known as irregular reflection.
12. The reflection of light from a smooth and polished surface is known as regular reflection.
13. Two mirrors inclined to each other give multiple images.
14. Kaleidoscope is a device based on the principle of multiple reflections.
15. Sunlight is referred to as white light which consists of seven colours.
16. Splitting of white light into its constituent colours is called dispersion.
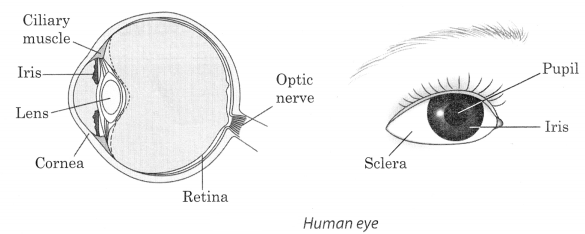
15. The human eye is an important sense organ that enables us to see the world around us. It is nearly spheri¬cal in shape.
16. Important parts of the eye are cornea, iris, pupil, lens, retina and optic nerve.
17. Blind spot is a portion on the retina where the nerve fibres enter the optic nerve. The image falling on the portion can’t be seen.
18. A normal eye can see nearby and distant objects clearly.
19. Long-sightedness or hypermetropia is a defect of the eye where the person cannot clearly see the nearby objects while in short-sightedness or myopia, the far-away objects can not be seen clearly. Visually challenged persons can read and write using the Braille system.
20. Visually challenged persons develop their other senses more sharply to improve their interaction with their environment.
Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Notes Important Terms
Angle of incidence: The angle between the incident ray and the normal is called the angle of incidence.
Angle of reflection: The angle between the reflected ray and the normal is called the angle of reflection.
felind spot: The portion on the retina where the nerve fibres enter the optic nerve is called blind spot. The image falling on this portion can’t be seen.
Braille: The system of representing characters by raised dots which enables the blind person to read is called Braille.
Cones: Visual receptor cells in retina, which are sensitive to bright light and sense colour are called cones.
Cornea: The transparent front part of the eye is called cornea.
Diffused/Irregular reflection: When all the parallel rays reflected from a plane surface are not parallel, the reflection is known as irregular/diffused reflection.
Dispersion: The splitting of light into its constituent colours is known as dispersion.
Incident ray: The ray of light striking the surface is called as incident ray.
Iris: The dark muscular structure behind the cornea is called iris.
Kaleidoscope: A device based on the principle of multiple reflections is called kaleidoscope.
Lateral inversion: The phenomenon of changing side, i.e, left to right and right to left by the mirror while forming an image is called lateral inversion.
Pupil: The small opening in the cornea is called pupil.
Reflected rays: The rays of light which returns back from the surface after reflection is known as refl ected ray.
Reflection: The bouncing back of light into the same medium after it falls on a surfac is called reflection.
Regular reflection: When all the parallel rays reflected from a smooth and polished surface is also parallel is called regular reflection.
Retina: The site where the image is formed in the eye is called retina.
Rods: The nerve cells on retina which are sensitive to dim light are called rods.