Learninsta presents the core concepts of Biology with high-quality research papers and topical review articles.
The Physiology of Micturition Definition and its Uses
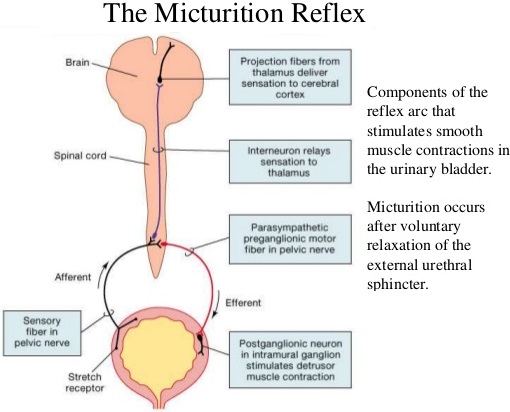
The process of release of urine from the bladder is called micturition or urination. Urine formed by the nephrons is ultimately carried to the urinary bladder where it is stored till it receives a voluntary signal from the central nervous system. The stretch receptors present in the urinary bladder are stimulated when it gets filled with urine.
Stretching of the urinary bladder stimulates the CNS via the sensory neurons of the parasympathetic nervous system and brings about contraction of the bladder. Simultaneously, somatic motor neurons induce the sphincters to close. Smooth muscles contracts resulting in the opening of the internal sphincters passively and relaxing the external sphincter.
When the stimulatory and inhibitory controls exceed the threshold, the sphincter opens and the urine is expelled out. An adult human on an average excretes 1 to 1.5 L of urine per day. The urine formed is a yellow coloured watery fluid which is slightly acidic in nature (pH 6.0), Changes in diet may cause pH to vary between 4.5 to 8.0 and has a characteristic odour. The yellow colour of the urine is due to the presence of a pigment, urochrome.
On an average, 25-30 gms of urea is excreted per day. Various metabolic disorders can affect the composition of urine. Analysis of urine helps in clinical diagnosis of various metabolic disorders and the malfunctioning of the kidneys. For example the presence of glucose (glucosuria) and ketone bodies (ketonuria) in the urine are indications of diabetes mellitus.
The exact cause of micturition syncope isn’t fully understood. But it may be related to opening (vasodilation) of the blood vessels that occurs when getting up and standing at the toilet or that occurs at the rapid emptying of a full bladder. This is thought to result in a sudden drop in blood pressure.
Micturition involves the simultaneous coordinated contraction of the bladder detrusor muscle, which is controlled by parasympathetic (cholinergic) nerves, and the relaxation of the bladder neck and sphincter, which are controlled by sympathetic (α-adrenergic) nerves.
Micturition syncope causes more than 8 percent of all episodes of fainting. People who experience it are more prone to fainting under other circumstances, too. Micturition syncope occurs more often in men. It often happens after using the bathroom in the middle of the night or first thing in the morning.
The pons is a major relay center between the brain and the bladder. The mechanical process of urination is coordinated by the pons in the area known as the pontine micturition center (PMC). The conscious sensations associated with bladder activity are transmitted to the pons from the cerebral cortex.
Introduction. Micturition is the process of eliminating water and electrolytes from the urinary system, commonly known as urinating. It has two discrete phases: the storage/continence phase, when urine is stored in the bladder; and the voiding phase, where urine is released through the urethra.
Micturition is the process by which the urine from the urinary bladder is excreted. This reflex stimulates the urge to pass out urine. To discharge urine, the urethral sphincter relaxes and the smooth muscles of the bladder contract. This forces the urine out from the bladder.