ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 8 Matrices MCQS
These Solutions are part of ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths. Here we have given ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 8 Matrices MCQS
More Exercises
- ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 8 Matrices Ex 8.1
- ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 8 Matrices Ex 8.2
- ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 8 Matrices Ex 8.3
- ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 8 Matrices MCQS
- ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 8 Matrices Chapter Test
Choose the correct answer from the given four options (1 to 14) :
Question 1.
If A = [aij]2×2 where aij = i + j, then A is equal to
(a) \(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 2 \\ 3 & 4 \end{bmatrix} \)
(b) \(\begin{bmatrix} 2 & 3 \\ 3 & 4 \end{bmatrix} \)
(c) \(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 2 \\ 1 & 2 \end{bmatrix} \)
(d) \(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 1 \\ 2 & 2 \end{bmatrix} \)
Solution:
A = [aij]2×2 where aij = i + j, then A is equal to
\(\begin{bmatrix} 2 & 3 \\ 3 & 4 \end{bmatrix} \) (b)
Question 2.
If \(\begin{bmatrix} x+3 & 4 \\ y-4 & x+y \end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix} 5 & 4 \\ 3 & 9 \end{bmatrix} \) then the values of x and y are
(a) x = 2, y = 7
(b) x = 7, y = 2
(c) x = 3, y = 6
(d) x = – 2, y = 7
Solution:
\(\begin{bmatrix} x+3 & 4 \\ y-4 & x+y \end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix} 5 & 4 \\ 3 & 9 \end{bmatrix} \)
Comparing we get
x + 3 = 5
⇒ x = 5 – 3 = 2
and y – 4 = 3
⇒ y = 3 + 4 = 7
x = 2, y = 7 (a)
Question 3.
If \(\begin{bmatrix} x+2y & -y \\ 3x & 7 \end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix} -4 & 3 \\ 6 & 4 \end{bmatrix} \) then the values of x and y are
(a) x = 2, y = 3
(b) x = 2, y = – 3
(c) x = – 2, y = 3
(d) x = 3, y = 2
Solution:
\(\begin{bmatrix} x+2y & -y \\ 3x & 7 \end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix} -4 & 3 \\ 6 & 4 \end{bmatrix} \)
Comparing, we get
3x = 6
⇒ \(x= \frac { 6 }{ 3 } \) = 2
⇒ -y = 3
⇒ y = – 3
x = 2, y = -3 (b)
Question 4.
If \(\begin{bmatrix} x-2y & 5 \\ 3 & y \end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix} 6 & 5 \\ 3 & -2 \end{bmatrix} \) then the value of x is
(a) – 2
(b) 0
(c) 1
(d) 2
Solution:
\(\begin{bmatrix} x-2y & 5 \\ 3 & y \end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix} 6 & 5 \\ 3 & -2 \end{bmatrix} \)
Comparing, we get
y = -2
and x – 2y = 6
⇒ x – 2 x (-2) = 6
⇒ x + 4 = 6
⇒ x = 6 – 4 = 2 (d)
Question 5.
If \(\begin{bmatrix} x+2y & 3y \\ 4x & 2 \end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix} 0 & -3 \\ 8 & 2 \end{bmatrix} \) then the value of x – y is
(a) – 3
(b) 1
(c) 3
(d) 5
Solution:
\(\begin{bmatrix} x+2y & 3y \\ 4x & 2 \end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix} 0 & -3 \\ 8 & 2 \end{bmatrix} \)
Comparing, we get
3y = -3
⇒ \(y= \frac { -3 }{ 3 } \) = -1
4x = 8
⇒ \(x= \frac { 8 }{ 4 } \) = 2
x – y = 2 – (-1) = 2 + 1 = 3 (c)
Question 6.
If \(x\left[ \begin{matrix} 2 \\ 3 \end{matrix} \right] +y\left[ \begin{matrix} -1 \\ 0 \end{matrix} \right] =\left[ \begin{matrix} 10 \\ 6 \end{matrix} \right] \) then the values of x and y are
(a) x = 2, y = 6
(b) x = 2, y = – 6
(c) x = 3, y = – 4
(d) x = 3, y = – 6
Solution:
Given
\(x\left[ \begin{matrix} 2 \\ 3 \end{matrix} \right] +y\left[ \begin{matrix} -1 \\ 0 \end{matrix} \right] =\left[ \begin{matrix} 10 \\ 6 \end{matrix} \right] \)
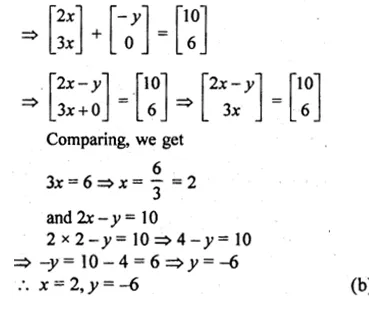
Question 7.
If B = \(\begin{bmatrix} -1 & 5 \\ 0 & 3 \end{bmatrix} \) and A – 2B = \(\begin{bmatrix} 0 & 4 \\ -7 & 5 \end{bmatrix} \)
then the matrix A is equal to
(a) \(\begin{bmatrix} 2 & 14 \\ -7 & 11 \end{bmatrix} \)
(b) \(\begin{bmatrix} -2 & 14 \\ 7 & 11 \end{bmatrix} \)
(c) \(\begin{bmatrix} 2 & -14 \\ 7 & 11 \end{bmatrix} \)
(d) \(\begin{bmatrix} -2 & 14 \\ -7 & 11 \end{bmatrix} \)
Solution:
Given
B = \(\begin{bmatrix} -1 & 5 \\ 0 & 3 \end{bmatrix} \) and
A – 2B = \(\begin{bmatrix} 0 & 4 \\ -7 & 5 \end{bmatrix} \)
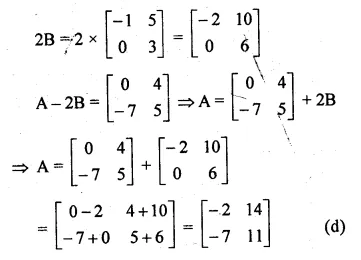
Question 8.
If A + B = \(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ 1 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \) and A – 2B = \(\begin{bmatrix} -1 & 1 \\ 0 & -1 \end{bmatrix} \)
then A is equal to
(a) \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 1 \\ 2 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \)
(b) \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \begin{bmatrix} 2 & 1 \\ 1 & 2 \end{bmatrix} \)
(c) \(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 1 \\ 2 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \)
(d) \(\begin{bmatrix} 2 & 1 \\ 1 & 2 \end{bmatrix} \)
Solution:
A + B = \(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ 1 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \) and
A – 2B = \(\begin{bmatrix} -1 & 1 \\ 0 & -1 \end{bmatrix} \)

Question 9.
A = \(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \) then A² =
(a) \(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 1 \\ 0 & 0 \end{bmatrix} \)
(b) \(\begin{bmatrix} 0 & 0 \\ 1 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \)
(c) \(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \)
(d) \(\begin{bmatrix} 0 & 1 \\ 1 & 0 \end{bmatrix} \)
Solution:
Given
A = \(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \)
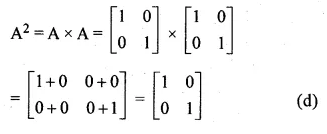
Question 10.
If A = \(\begin{bmatrix} 0 & 1 \\ 1 & 0 \end{bmatrix} \) , then A² =
(a) \(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 1 \\ 0 & 0 \end{bmatrix} \)
(b) \(\begin{bmatrix} 0 & 0 \\ 1 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \)
(c) \(\begin{bmatrix} 0 & 1 \\ 1 & 0 \end{bmatrix} \)
(d) \(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \)
Solution:
Given
A = \(\begin{bmatrix} 0 & 1 \\ 1 & 0 \end{bmatrix} \)
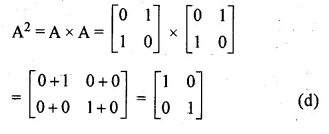
Question 11.
If A = \(\begin{bmatrix} 0 & 0 \\ 1 & 0 \end{bmatrix} \) , then A² =
(a) A
(b) O
(c) I
(d) 2A
Solution:
Given
A = \(\begin{bmatrix} 0 & 0 \\ 1 & 0 \end{bmatrix} \)
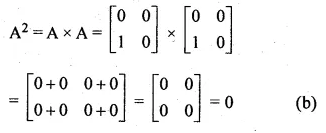
Question 12.
If A = \(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ 1 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \) , then A² =
(a) \(\begin{bmatrix} 2 & 0 \\ 1 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \)
(b) \(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ 1 & 2 \end{bmatrix} \)
(c) \(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ 2 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \)
(d) none of these
Solution:
Given
A = \(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ 1 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \)
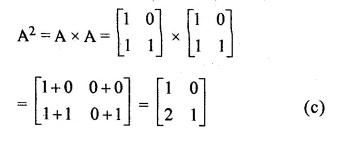
Question 13.
If A = \(\begin{bmatrix} 3 & 1 \\ -1 & 2 \end{bmatrix} \) , then A² =
(a) \(\begin{bmatrix} 8 & 5 \\ -5 & 3 \end{bmatrix} \)
(b) \(\begin{bmatrix} 8 & -5 \\ 5 & 3 \end{bmatrix} \)
(c) \(\begin{bmatrix} 8 & -5 \\ -5 & -3 \end{bmatrix} \)
(d) \(\begin{bmatrix} 8 & -5 \\ -5 & 3 \end{bmatrix} \)
Solution:
A = \(\begin{bmatrix} 3 & 1 \\ -1 & 2 \end{bmatrix} \)
A² = A x A = \(\begin{bmatrix} 3 & 1 \\ -1 & 2 \end{bmatrix} \)\(\begin{bmatrix} 3 & 1 \\ -1 & 2 \end{bmatrix} \)
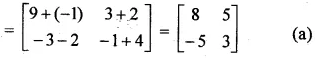
Question 14.
If A = \(\begin{bmatrix} 2 & -2 \\ -2 & 2 \end{bmatrix} \) , then A² = pA, then the value of p is
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) – 2
(d) – 4
Solution:
A = \(\begin{bmatrix} 2 & -2 \\ -2 & 2 \end{bmatrix} \)
and A² = pA
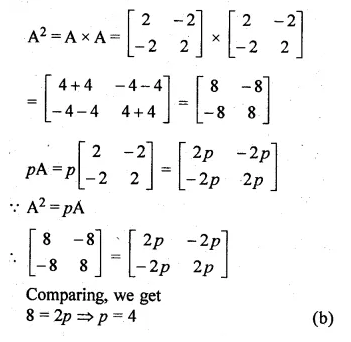
Hope given ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 8 Matrices MCQS are helpful to complete your math homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online math tutoring for you.