ML Aggarwal Class 6 Solutions Chapter 13 Practical Geometry Ex 13.1 for ICSE Understanding Mathematics acts as the best resource during your learning and helps you score well in your exams.
ML Aggarwal Class 6 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 13 Practical Geometry Ex 13.1
Question 1.
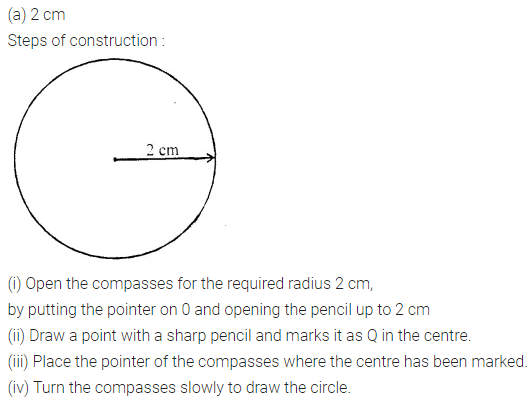
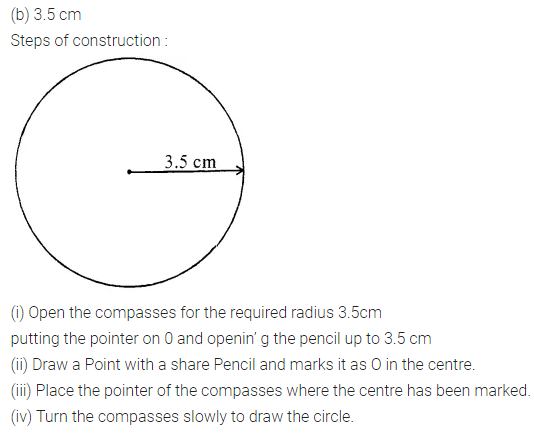
Construct a circle of radius:
(i) 2 cm
(ii) 3.5 cm
Solution:
Question 2.
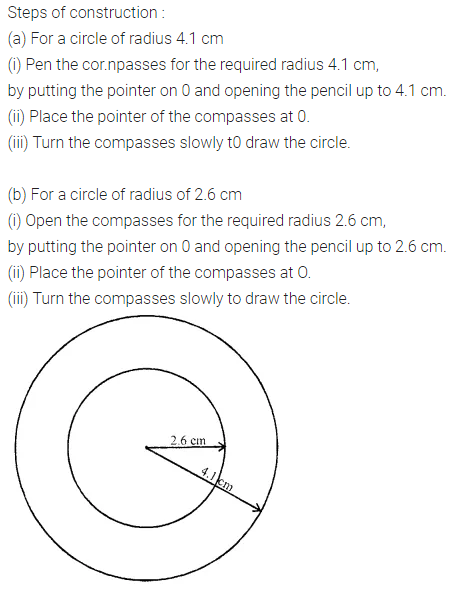
With the same centre O, draw two circles of radii 2.6 cm and 4.1 cm.
Solution:
Question 3.
Draw any circle and mark points A, B and C such that
(i) A is on the circle.
(ii) B is in the interior of the circle.
(iii) C is in the exterior of the circle.
Solution:
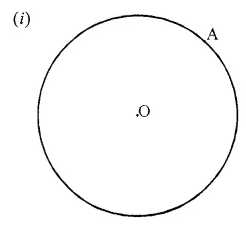
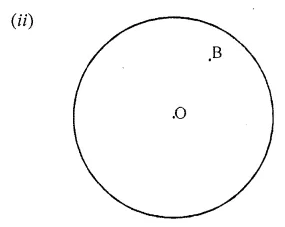
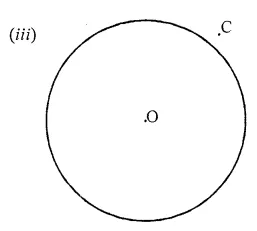
Question 4.
Draw a circle and any two of its (non-perpendicular) diameters. If you join the ends of these diameters, what is the figure obtained? What figure is obtained if the diameters are perpendicular to each other? How do you check your answer?
Solution:
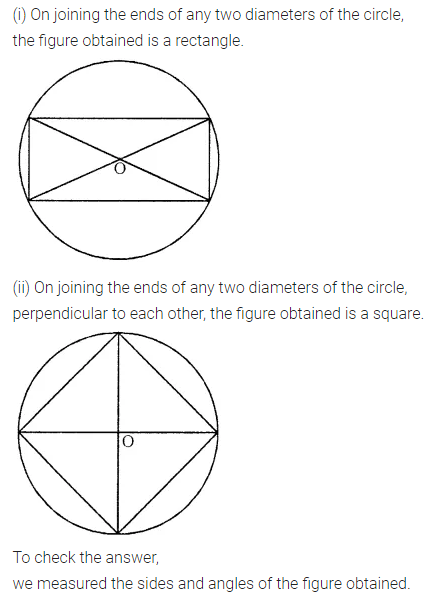
Question 5.
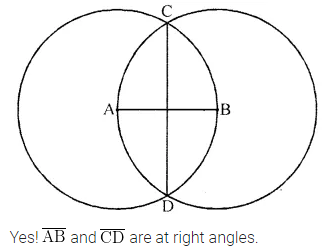
Let A, B be the centres of two circles of equal radii; draw them so that each one of them passes through the centre of the other. Let them intersect at C and D.
Examine whether \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\) and \(\overline{\mathrm{CD}}\) are at right angles.
Solution:
Question 6.
Construct a line segment of the length of 6.3 cm using ruler and compass.
Solution:

Question 7.
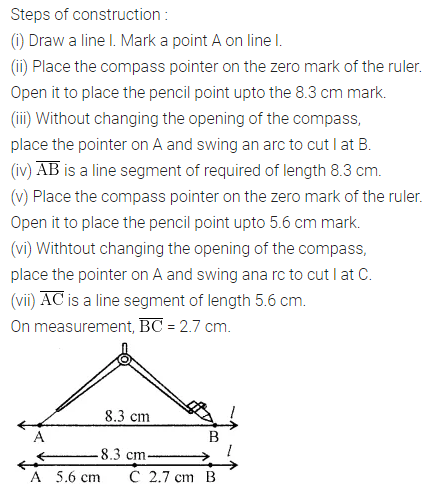
Construct \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\) of length 8.3 cm. From this cut off \(\overline{\mathrm{AC}}\) of length 5.6 cm. Measure the length of BC . .
Solution:
Question 8.
Draw any line segment \(\overline{\mathrm{PQ}}\). Without measure \(\overline{\mathrm{PQ}}\), construct a copy of \(\overline{\mathrm{PQ}}\).
Solution:

Question 9.
Given some line segment \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\), whose length you do not know, construct \(\overline{\mathrm{PQ}}\) such that the length of \(\overline{\mathrm{PQ}}\) is twice that of \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\).
Solution:

Question 10.
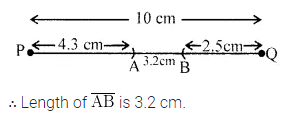
Take a line segment \(\overline{\mathrm{PQ}}\) of length 10 cm. From \(\overline{\mathrm{PQ}}\), cut of \(\overline{\mathrm{PA}}\) of length 4.3 cm and \(\overline{\mathrm{BQ}}\) of length 2.5 cm. Measure the length of segment \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\).
Solution:
Question 11.
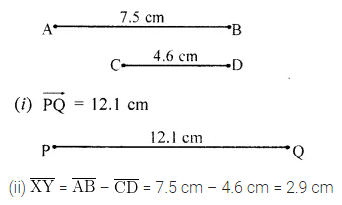
Given two line segments \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\) and \(\overline{\mathrm{CD}}\) of length 7.5 cm and 4.6 respectively. Construct line segments.
(i) \(\overrightarrow { PQ } \) of length equal to the sum of the lengths of \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\) and \(\overline{\mathrm{CD}}\).
(ii) \(\overline{\mathrm{XY}}\) of length equal to the difference of the lengths of \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\) and \(\overline{\mathrm{CD}}\). Verify these lengths by measurements.
Solution: