ML Aggarwal Class 8 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 13 Understanding Quadrilaterals Ex 13.2
Question 1.
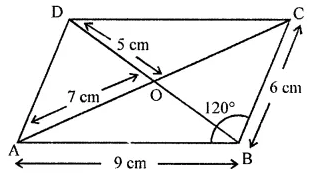
In the given figure, ABCD is a parallelogram. Complete each statement along with the definition or property used.
(i) AD = ………..
(ii) DC = ………..
(iii) ∠DCB = ………..
(iv) ∠ADC = ………..
(v) ∠DAB = ………..
(vi) OC = ………..
(vii) OB = ………..
(viii) m∠DAB + m∠CDA = ………..
Solution:
Question 2.
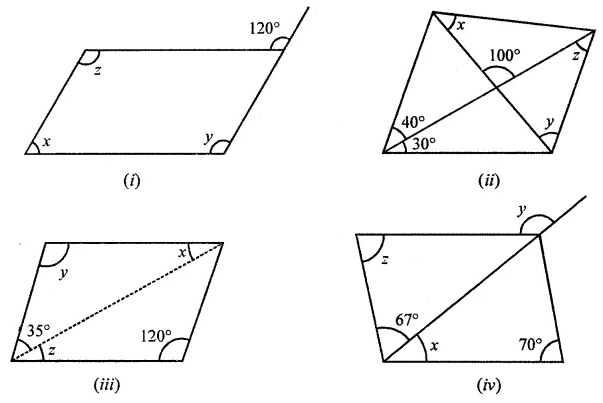
Consider the following parallelograms. Find the values of x, y, z in each.
Solution:
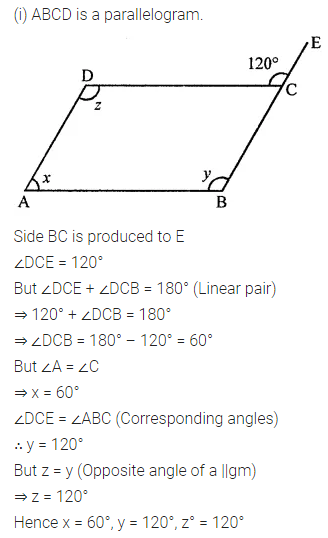
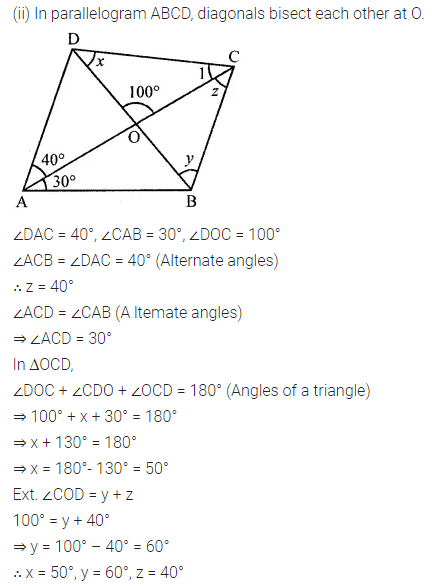
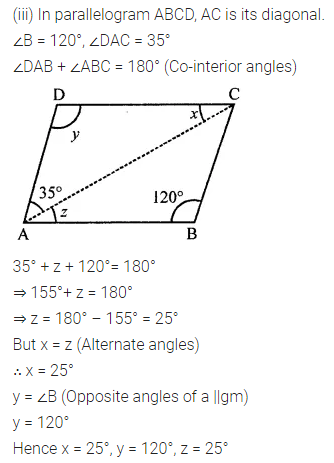
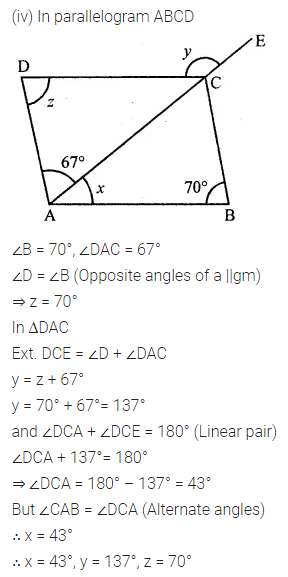
Question 3.
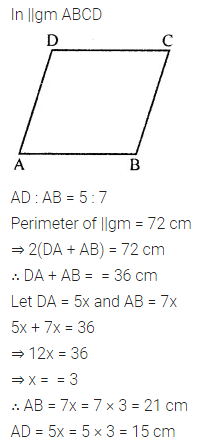
Two adjacent sides of a parallelogram are in the ratio 5 : 7. If the perimeter of a parallelogram is 72 cm, find the length of its sides.
Solution:
Question 4.
The measure of two adjacent angles of a parallelogram is in the ratio 4 : 5. Find the measure of each angle of the parallelogram.
Solution:
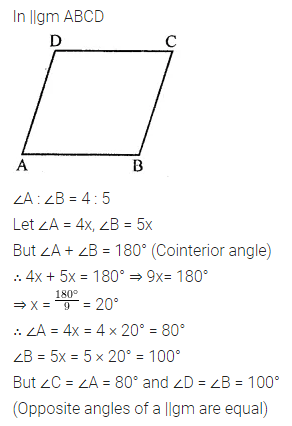
Question 5.
Can a quadrilateral ABCD be a parallelogram, give reasons in support of your answer.
(i) ∠A + ∠C= 180°?
(ii) AD = BC = 6 cm, AB = 5 cm, DC = 4.5 cm?
(iii) ∠B = 80°, ∠D = 70°?
(iv) ∠B + ∠C= 180°?
Solution:

Question 6.
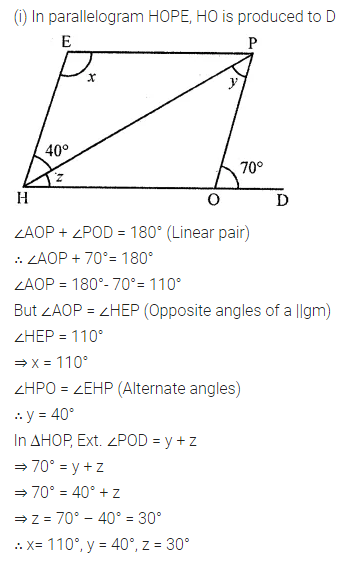
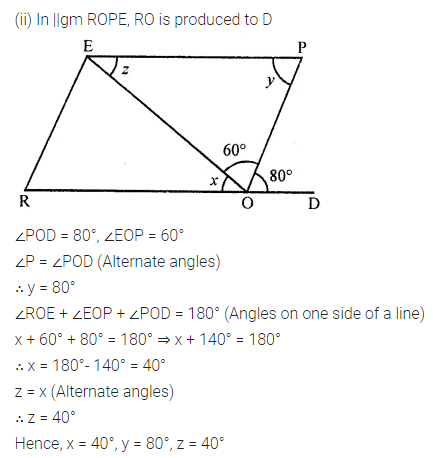
In the following figures, HOPE and ROPE are parallelograms. Find the measures of angles x, y and z. State the properties you use to find them.
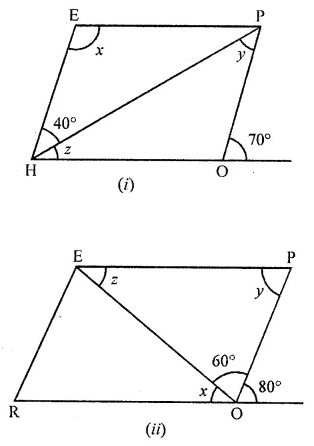
Solution:
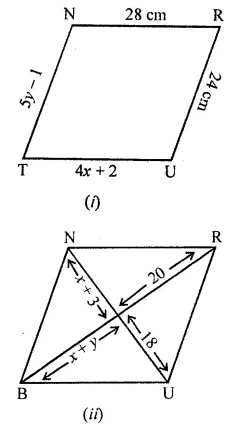
Question 7.
In the given figure TURN and BURN are parallelograms. Find the measures of x and y (lengths are in cm).
Solution:
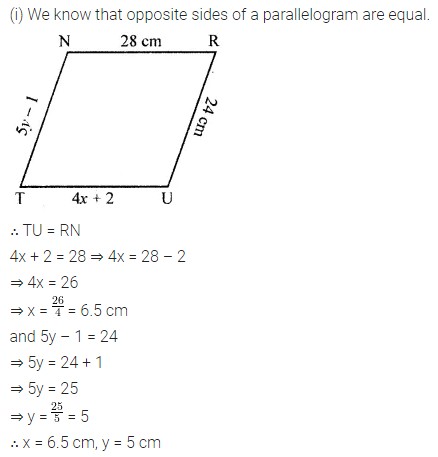
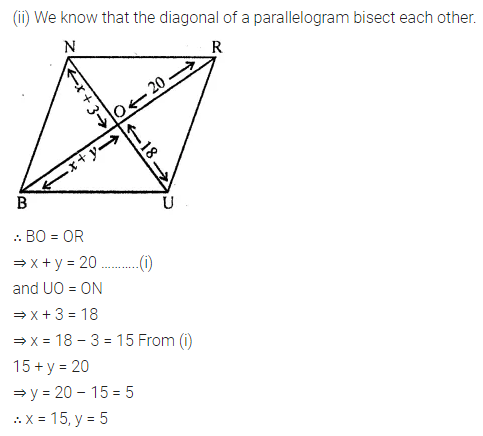
Question 8.
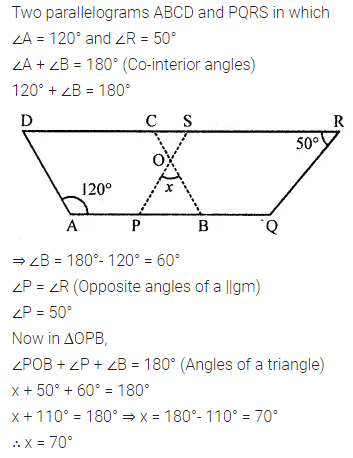
In the following figure, both ABCD and PQRS are parallelograms. Find the value of x.
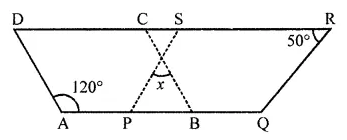
Solution:
Question 9.
In the given figure, ABCD, is a parallelogram and diagonals intersect at O. Find :
(i) ∠CAD
(ii) ∠ACD
(iii) ∠ADC
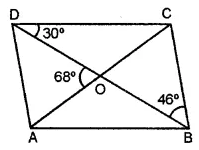
Solution:

Question 10.
In the given figure, ABCD is a parallelogram. Perpendiculars DN and BP are drawn on diagonal AC. Prove that:
(i) ∆DCN ≅ ∆BAP
(ii) AN = CP
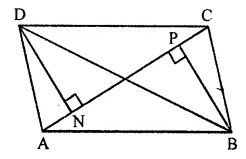
Solution:

Question 11.
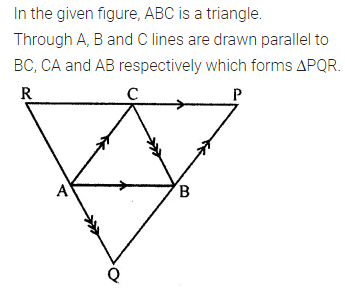
In the given figure, ABC is a triangle. Through A, B and C lines are drawn parallel to BC, CA and AB respectively, which forms a ∆PQR. Show that 2(AB + BC + CA) = PQ + QR + RP.
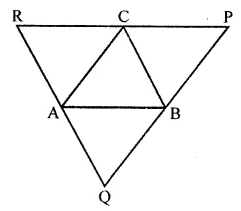
Solution: