ML Aggarwal Class 8 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 13 Understanding Quadrilaterals Ex 13.3
Question 1.
Identify all the quadrilaterals that have
(i) four sides of equal length
(ii) four right angles.
Solution:

Question 2.
Explain how a square is
(i) a quadrilateral
(ii) a parallelogram
(iii) a rhombus
(iv) a rectangle.
Solution:

Question 3.
Name the quadrilaterals whose diagonals
(i) bisect each other
(ii) are perpendicular bisectors of each other
(iii) are equal.
Solution:

Question 4.
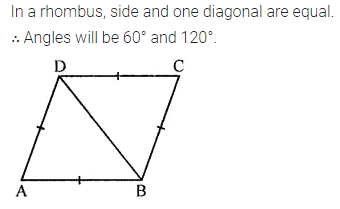
One of the diagonals of a rhombus and its sides are equal. Find the angles of the rhombus.
Solution:
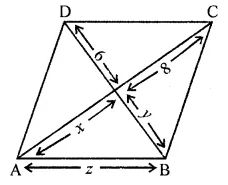
Question 5.
In the given figure, ABCD is a rhombus, find the values of x, y and z.
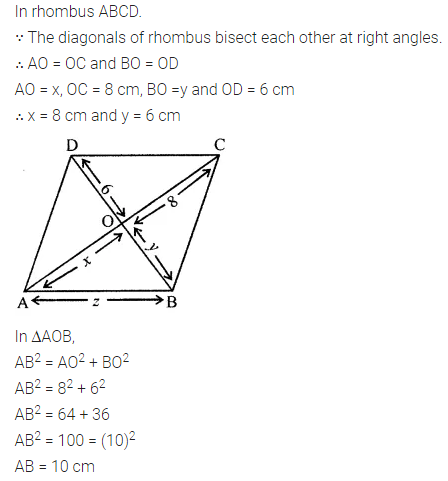
Solution:
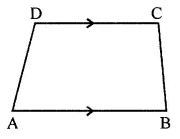
Question 6.
In the given figure, ABCD is a trapezium. If ∠A : ∠D = 5 : 7, ∠B = (3x + 11)° and ZC = (5x – 31)°, then find all the angles of the trapezium.
Solution:


Question 7.
In the given figure, ABCD is a rectangle. If ∠CEB : ∠ECB = 3 : 2 find
(i) ∠CEB,
(ii) ∠DCF
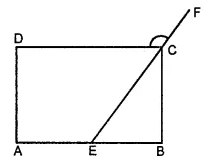
Solution:

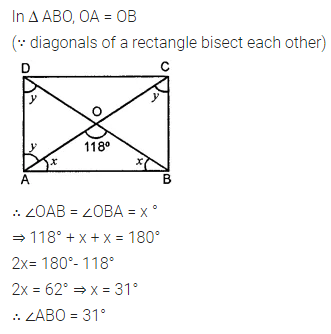
Question 8.
In the given figure, ABCD is a rectangle and diagonals intersect at O. If ∠AOB = 118°, find
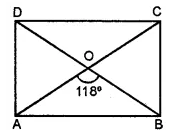
(i) ∠ABO
(ii) ∠ADO
(iii) ∠OCB
Solution:

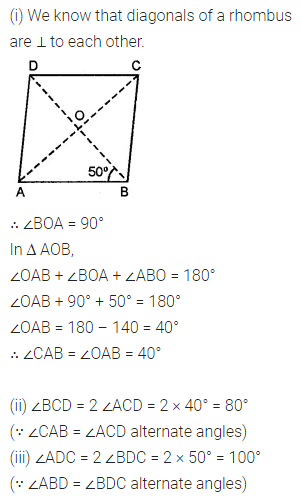
Question 9.
In the given figure, ABCD is a rhombus and ∠ABD = 50°. Find :
(i) ∠CAB
(ii) ∠BCD
(iii) ∠ADC
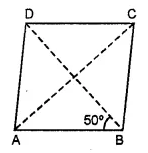
Solution:
Question 10.
In the given isosceles trapezium ABCD, ∠C = 102°. Find all the remaining angles of the trapezium.
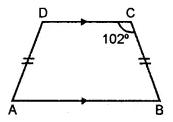
Solution:

Question 11.
In the given figure, PQRS is a kite. Find the values of x and y.
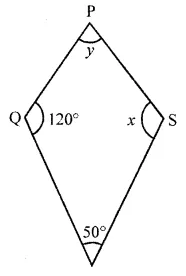
Solution:
