In this page, we are providing Natural Resources Class 9 Extra Questions and Answers Science Chapter 14 pdf download. NCERT Extra Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources with Answers will help to score more marks in your CBSE Board Exams. https://ncertmcq.com/extra-questions-for-class-9-science/
Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Extra Questions and Answers Natural Resources
Extra Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources with Answers Solutions
Natural Resources Class 9 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Natural Resources Class 9 Extra Questions Question 1.
What are the resources available on Earth for life to exist?
Answer:
Air, water and land are the resources available on the Earth which help life to exist.
Natural Resources Class 9 Important Questions Question 2.
Name the compound of carbon responsible for the ozone hole in the atmosphere.
Answer:
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFC’s) are responsible for the ozone hole in the atmosphere.
Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Extra Questions And Answers Question 3.
State the temperature range on the surface of the moon.
Answer:
The temperature ranges from -190°C to 110°C on the moon
Natural Resources Class 9 Extra Questions And Answers Question 4.
State any one difference between oxygen and ozone.
Answer:
Oxygen is a diatomic molecule with formula 02 whereas ozone is a triatomic molecule-with formula 03.
Extra Questions For Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources Question 5.
Name the stage in the life cycle of aquatic animals which is affected by a change in temperature.
Answer:
The stage of animals which is affected by the change in the temperature is – the eggs at the hatching stage, the larvae and the young ones of the animals.
Extra Questions Of Natural Resources Class 9 Question 6.
Along with the natural resources available on the Earth, what else is required to meet the basic requirements of all life forms on the Earth?
Answer:
Solar energy is required to meet the basic requirements of all life forms on Earth.
Natural Resources Class 9 Questions And Answers Question 7.
How is biosphere a dynamic and stable system?
Answer:
There is a constant interaction between the biotic and the abiotic components of the global ecosystem (biosphere) which makes it a stable system. The basic composition and the structure of the system do not change while carrying out the various processes. So, it is a stable system.
Natural Resources Extra Questions Question 8.
How do forests play a major role in maintaining the water cycle?
Answer:
The amount of water vapour in the atmosphere is dependent on the transpiration of water from the leaves of the plants present in a forest. Also, the storage of water in watershed is influenced by the forests. So, forests play a major role in maintaining the water cycle.
Ch 14 Science Class 9 Extra Questions Question 9.
Why is step farming done in hills?
Answer:
Step farming is done in hills to prevent soil erosion by slowing down the speed of the water running down the slopes.
Class 9 Natural Resources Extra Questions Question 10.
Why are root nodules useful for plants?
Answer:
The root nodules of leguminous plants contain nitrogen-fixing bacteria like the Rhizobium which help to increase the fertility of the soil by fixing atmospheric nitrogen.
Class 9 Science Ch 14 Extra Questions Question 11.
What are the biotic and the abiotic components of the biosphere?
Answer:
- Biotic component: comprises of living things.
- Abiotic component: comprises of non-living things like temperature, rainfall, air, water and soil.
Questions On Natural Resources Class 9 Question 12.
What percentage of oxygen and nitrogen are present in the atmosphere?
Answer:
The approximate percentage of oxygen and nitrogen in the atmosphere are:
Oxygen: 21%, Nitrogen: 78%
Extra Questions On Natural Resources Class 9 Question 13.
Give the major source of minerals in the soil.
Answer:
The minerals in the soil depend upon the rocks from which the soil is formed. So, the rocks are the major source of minerals in the soil.
Natural Resources Class 9 Important Questions With Answers Question 14.
Name the two gases given out during the burning of fossil fuels which dissolve in rain to form acid rain.
Answer:
Sulphur dioxide and oxides of nitrogen.
Extra Questions Of Chapter Natural Resources Class 9 Question 15.
Name the group of compounds responsible for ozone layer depletion.
Answer:
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) are responsible for ozone layer depletion.
Natural Resources Class 9 Extra Questions Short Answer Type 1
Question 1.
What are the sources of oxygen in the atmosphere?
Answer:
The sources of oxygen in the atmosphere are:
- Oxygen released during photosynthesis by plants
- The dissociation of oxides from their compounds
- The disintegration of ozone in presence of UV rays
- As the water in combined form
Question 2.
- What causes winds?
- List any two methods of preventing soil erosion.
Answer:
1. Due to the unequal heating of land and water, the land get heated up faster during the day, the air on land rises up and creates a region of low pressure. As a result, the air over the sea moves towards the region of low pressure formed on the land. This causes winds to flow.
2. (a) Overgrazing by cattle should be avoided.
(b) Large scale afforestation should be done as roots of plants prevent the soil from getting carried away.
(c) Increasing the vegetation cover on the ground reduces the impact of flowing water on soil and prevents it from getting washed away.
(d) Contour farming can be done by ploughing the land in furrows across the natural slope of the land to trap water flowing down.
(e) Step farming is practised in hilly regions which reduce the flow of water and give it more time to percolate into the soil.
Question 3.
List the importance of oxygen gas and ozone gas in the atmosphere.
Answer:
Role of Oxygen gas: It helps in the process of combustion, respiration and formation of many organic compounds.
Role of Ozone: It absorbs the harmful UV rays of the Sun which can cause skin diseases and cancer on reaching the Earth’s surface.
Question 4.
Mention one method by which living organisms influence the formation of soil.
Answer:
The living organisms like lichens and mosses are the initial colonisers of rocks which secrete certain chemical substances that dissolve the minerals of rock and cause the gradual weathering of rocks. The rocks get broken down into small, fine particles of soil. So, living organisms play an important role in the formation of soil.
Question 5.
Explain the occurrence of land breeze in coastal areas.
Answer:
During the day, in coastal regions, the air above land gets heated faster and warm air being lighter rises up thereby creating a region of low pressure. The air over the sea then moves towards the area of low pressure. The movement of air from one region to the other creates winds. At night, water cools down slower than the land, so the air above water would be warmer than the air above land. This causes air over the land to move towards the region of low pressure over water.
Question 6.
What are the two ways in which carbon dioxide is fixed in the environment?
Answer:
Carbon dioxide is fixed in the atmosphere when:
- Green plants utilise the carbon dioxide and convert it into glucose during photosynthesis.
- Carbon dioxide dissolved in seawater in the form of carbonates gets used up by the marine animals for the formation of their shells.
Question 7.
- Why do terrestrial forms require freshwater?
- Give two examples where freshwater can be found in the frozen form on the Earth.
Answer:
- The terrestrial organisms require freshwater as they face osmotic problems if kept in marine water because they have low osmotic concentration. In order to maintain the balance of the salts present in their body, freshwater organisms require a medium having less salt concentration i.e., freshwater.
- Freshwater can be found in a frozen form at polar ice-caps and the glaciers.
Question 8.
What is the role of the atmosphere in climate control?
Answer:
The atmosphere acts as a buffer which checks excessive rise in temperature during the day and prevents excessive cooling of the Earth during the night. The atmosphere helps to keep the average temperature of the Earth steady.
Question 9.
State any two harmful effects of air pollution.
Answer:
The two harmful effects of air pollution are:
- Respiratory problems and difficulty in breathing
- Acid rains
Question 10.
1. Define the term ‘smog’.
2. Name any two types of disease caused by regularly breathing polluted air.
Answer:
1. Smog is a kind of air pollution, named for the mixture of smoke and fog in the air. The thick cloud of water droplets having smoke particles suspended in the atmosphere which restricts visibility is called smog.
2. Diseases caused by breathing polluted air are:
(a) Allergy
(b) Respiratory disorders
(c) Heart-related problems
Question 11.
Mention a cause and a consequence of acid rain.
Answer:
Cause of acid rain: The oxides of nitrogen and sulphur like nitrogen dioxide and sulphur dioxide released from the burning of fossil fuels gets mixed with water vapour present in the atmosphere to form acids. These acids dissolve in the rainwater and fall as acid rain on the Earth.
A consequence of acid rain:
- The fertility of soil gets reduced due to the acidity created in the soil by the acid rains.
- Acid rain corrodes the historic monuments and structures made of marble, metals, painted surfaces, etc.
- The aquatic life is also harmed due to excess amount of acids which gets dissolved in water by acid rains.
Question 12.
What is meant by biogeochemical cycle? Name the two essentials which are transferred between different components of the biosphere.
Answer:
The movement of nutrient elements through the various components of an ecosystem i.e., biotic and the abiotic components, is called a biogeochemical cycle.
The two essentials which are transferred between different components of the biosphere are: Matter and energy,
Question 13.
What is the difference between nitrification and denitrification?
Answer:
Nitrification:
The process by which ammonia or ammonium compounds is converted into nitrites by Nitrosomonas and nitrites into nitrates by the Nitrobacter is called nitrification.
Denitrification:
The process by which the nitrites or nitrates are broken down into elemental nitrogen (N2) by Pseudomonas or Thiobacillus is called denitrification.
Question 14.
Draw a well-labelled diagram to show the carbon cycle in nature.
Answer:
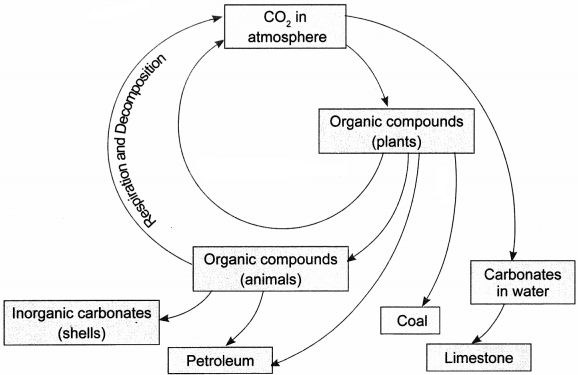
Question 15.
State the role of photosynthesis and respiration in the carbon cycle.
Answer:
Photosynthesis: Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is fixed by green plants during the process of photosynthesis and converted into glucose.
Respiration: Glucose is oxidised during respiration to obtain energy. Carbon dioxide gets released during the process and is returned to the atmosphere. In this way photosynthesis and respiration help in maintaining the carbon cycle in nature.
Question 16.
Draw a neat labelled diagram to show the nitrogen cycle.
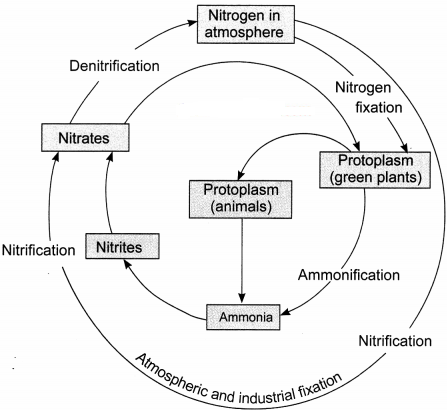
Question 17.
Name any four carbon-containing molecules which are essential for human beings.
Answer:
The carbon-containing molecules essential for human beings are:
- Deoxyribonucleic acid-DNA
- Proteins
- Carbohydrates
- Fats
Question 18.
Draw a well-labelled diagram to show the oxygen cycle in nature.
Answer:
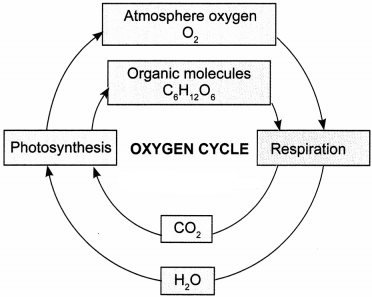
Question 19.
(a) Why do terrestrial forms require freshwater?
(b) Mention any two processes involved in the water cycle.
Answer:
(a) Terrestrial forms require water for carrying out the various cellular and metabolic process which occur in their body.
(b) Two processes involved in the water cycle are: Evaporation of water from water bodies and precipitation of water in the form of rain, hail or snow.
Question 20.
What is the importance of greenhouse gases present in the atmosphere?
Answer:
The greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane prevent the escape of heat from the Earth. Thus, these gases play an important role of keeping the average temperature of the Earth constant.
Question 21.
What is the greenhouse effect? What will happen if the concentration of greenhouse gases increase in the air?
Answer:
The phenomenon in which the incoming sunlight is allowed to pass through the atmosphere but heat radiated back from the planet’s surface is trapped by the gases like carbon dioxide, water vapour and methane present in the atmosphere is called the greenhouse effect.
Increase in concentration of greenhouse gases would prevent the escape of heat from the Earth, increase the average temperature worldwide and result in global warming. Global warming will cause a rise in sea and odd climatic changes due to faster melting of glaciers and polar ice caps.
Natural Resources Class 9 Extra Questions Short Answer Type 2
Question 1.
1. The circulation of carbon is important in nature. Give reasons for your answer.
2. Explain any two processes involved in the cycling of nitrogen in the environment.
Answer:
1. The circulation of carbon dioxide is important in nature as it helps in maintaining the balance of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide is taken up by plants for photosynthesis and oxygen released during photosynthesis is utilised by the plants and animals for respiration.
Hence, it is necessary to maintain the balance of these gases. Carbon dioxide gas gets cycled between the atmosphere and the living organisms. An excess of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere causes global warming due to the greenhouse effect.
2. The two-process involved in the cycling of nitrogen in the environment are nitrogen fixation and ammonification.
(a) Nitrogen fixation in which the atmospheric nitrogen is converted into nitrites and nitrates which are water-soluble and are easily taken up the roots.
(b) Ammonification: Formation of ammonia due to the decomposition of dead organic matter is called as Ammonification.
Question 2.
State the reason for the following:
1. Excess burning of coal causes the greenhouse effect.
2. Soil is a mixture.
3. Temperature ranges from (-190°C -110°C) on the surface of the moon.
Answer:
1. Carbon dioxide gas is released during the burning of fuel like coal and petroleum. Carbon dioxide has a property due to which it allows rays of the Sun to pass through and reach the surface of the Earth but stops the long-wave infra-red radiations to pass through on being re-radiated from the surface of the Earth. Thus, carbon dioxide traps the heat rays of the Sun and causes the greenhouse effect.
2. Soil is a mixture of minerals, organic matter, gases, liquids, and the various organisms that together support life on Earth.
3. The moon does not have an atmosphere like that on the Earth which traps the heat rays of the Sun and keeps its warm. The atmosphere helps in checking rise in temperature during the day and the fall in temperature during night. So, in spite of being at the same distance from the Sun as the Earth, the temperature on moon ranges from (-190°C-110° C).
Question 3.
With the help of the diagram shows the carbon cycle in nature. What are the two ways in which carbon dioxide is fixed in the environment?
Answer:
The carbon cycle in nature can be depicted by the following diagram:
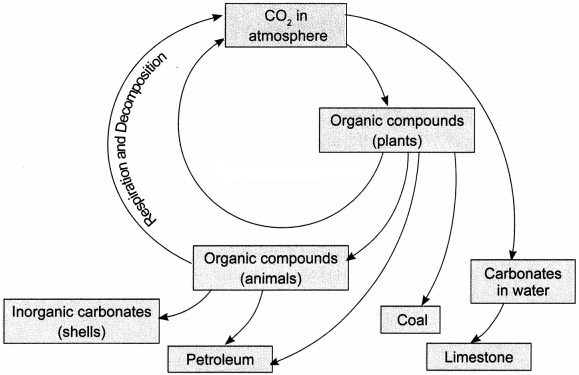
Carbon dioxide is fixed in the atmosphere by the following two ways:
1. Green plants utilise the carbon dioxide and convert it into glucose during photosynthesis.
2. Carbon dioxide dissolved in seawater in the form of carbonates gets used up by marine animals for the formation of their shells.
Question 4.
Sun as a natural factor helps in the formation of soil. Explain.
Answer:
The Sun helps in soil formation in the following ways:
Rocks expand when they get heated by the Sun during the day. During the night, the rocks cool down and contract. This results in the formation of cracks in the rocks as the rate of expansion and contraction are different. The rocks split and break into smaller pieces.
Question 5.
What is the percentage of oxygen in the atmosphere? Name any two compounds of oxygen found in nature. Name any three processes by which oxygen is used up in the atmosphere.
Answer:
The percentage of oxygen in the atmosphere is approximately 21%.
The diatomic form oxygen (O2) and the triatomic form ozone (O3) are the two forms in which oxygen is found in nature.
The three processes by which oxygen is used up in the atmosphere are:
- Combustion of fossil fuels.
- Respiration by living organisms.
- Decomposition of organic matter.
- Formation of oxides during fixation and other chemical reactions.
Question 6.
How is the greenhouse effect related to global warming? Explain.
Answer:
The phenomenon in which the incoming sunlight is allowed to pass through the atmosphere but heat radiated back from the planet’s surface is trapped by the gases like carbon dioxide, water vapour and methane present in the atmosphere is called the greenhouse effect.
An increase in the percentage of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane prevents the escape of heat from the Earth. So, the greenhouse effect is responsible for the increase in average temperature worldwide and is causing global warming. Global warming leads to melting of glaciers and polar ice caps at a faster rate which causes a rise of the sea and other odd climatic changes.
Question 7.
Why is water necessary for the living organisms?
Answer:
Water is necessary for living organisms because:
- All cellular metabolic processes occur in the water medium.
- The transportation of various substances from one part of the body to another occurs in dissolved form in water.
- All the reactions taking place in the cells or in our body occur between substances which are dissolved in water.
Question 8.
How are various biological factors needed for soil formation?
Or
Which symbiotic life forms can grow on stones and help in the formation of soil? Write the model of their action for making soil from rocks.
Answer:
Lichens are the symbiotic association of algae and fungi. Lichens help in the formation of soil. The living organisms like lichens and mosses are the initial colonisers of the rocks which secrete certain chemical substances which dissolve the minerals of rock and cause the gradual weathering of rocks. The rocks get broken down into small, fine particles of soil. So, biological factors play an important role in the formation of soil.
Question 9.
What is topsoil? Mention two factors that decide which plants will thrive on that soil.
Answer:
Topsoil refers to the topmost layer of the soil which contains humus, soil particles and living organisms.
The two factors that decide which plants will thrive on that soil are:
- The humus content and the type of microbes present in the soil.
- The size and texture of soil particles along with the composition of the soil.
Question 10.
What are the causes of soil erosion?
Answer:
The causes of soil erosion are:
- Large scale deforestation
- Large scale overgrazing
- Industrialisation
- Urbanisation
- The land left uncultivated for a long time
- Mining and other human activities which lead to loss of topsoil
Question 11.
Rivers from land, add minerals to seawater. Discuss how.
Answer:
Yes, it is true because water has the ability to dissolve a large number of substances. When the river water flows over the rocks containing soluble minerals, some of the minerals from the rocks get dissolved in the water. These minerals are carried away by the river water into the sea. Thus, the nutrients from the land are carried away by the river into the sea.
Question12.
How can we prevent the loss of topsoil?
Answer:
The loss of the topsoil can be prevented by the following ways:
- Overgrazing by cattle should be avoided.
- Large scale afforestation should be done as roots of the plants prevent the soil from getting carried away.
- Increasing the vegetation cover on the ground reduces the impact of flowing water on soil and prevents it from getting washed away.
- Contour farming can be done by ploughing the land in furrows across the natural slope of the land to trap water flowing down.
- Step farming is practised in hilly regions which reduces the flow of water and gives it more time to percolate into the soil.
Question 13.
How is the life of organisms living in water affected when water gets polluted?
Answer:
When the water gets polluted, the life of organisms living in water gets affected in the following ways:
- The domestic wastewater contains detergents and nutrients which increase the growth of aquatic plants, algae, etc., and reduces the amount of dissolved oxygen in the water body. This adversely affects the aquatic animals as they die due to scarcity of oxygen.
- The fertilisers, pesticides, etc., which get washed into the water body from the agricultural fields also harm the aquatic organisms.
- Many disease-causing organisms are also released in the domestic wastewater which acts as a source of many water-borne diseases like cholera.
- The heated water released directly into the water bodies by some industries can cause the death of aquatic organisms which are not able to tolerate the sudden change in temperature.
- The heavy metals dissolved in polluted water is also harmful to the living organisms.
Question 14.
During summer, if you go near the lake, you feel relief from the heat, why?
Answer:
We feel relief from the heat when we go near a lake during summer because:
1. The Sunrays heat the land near the lakes more quickly than the water of the lake. The hot air rises up to create a region of low pressure on the land. Evaporation of the water causes cooling of the air above the lake and this cool air flows from the lake towards the region of low pressure on the land. The cool air gives relief to us from the heat.
Question 15.
In the coastal area, wind current moves from the sea towards the land during the day; but during the night
Answer:
During the day, in the coastal regions, the air above the land gets heated faster and the warm air being lighter rises up thereby creating a region of low pressure. The air over the sea then moves towards the area of low pressure. The movement of air from one region to the other creates winds. At night, water cools down slower than the land, so the air above the water would be warmer than the air above land. This causes air over the land to move towards the region of low pressure over water.
Question 16.
Following are a few organisms
(a) lichen
(b) mosses
(c) mango tree
(d) cactus.
Which among the above can grow on stones; and also help in the formation of soil? Write the model of their action for making soil.
Answer:
Lichens and the mosses can grow on stones and help in the formation of soil. The chemical substances secreted by the living organisms like lichens and mosses degrade the rocks and convert them into fine particles of soil. They also cause crevices and cracks in the rocks which help in the colonisation of rocks by bigger plants. The roots of these plants widen the cracks and cause the breakdown of large rocks.
Question 17.
Soil formation is done by both abiotic and biotic factors. List the names of these factors by classifying them as abiotic and biotic?
Answer:
The abiotic factors involved in soil formation are: Sun, water, wind.
The biotic factors involved in soil formation are: lichens, mosses and trees, microorganisms, etc.
Question 18.
All the living organisms are basically made up of C, N, S, P, H and O. How do they enter the living forms? Discuss.
Answer:
Elements like C, N, S, P, H and O enter the living forms through the process of photosynthesis and on getting absorbed from soil by the plants and living organisms.
Question 19.
Why does the percentage of gases like oxygen, nitrogen and carbon dioxide remain almost the same in the atmosphere?
Answer:
The biotic and the abiotic components of the biosphere interact with each other and continuously cycle the elements like nitrogen, oxygen and carbon through their respective cycles called as biogeochemical cycles. This helps to maintain the percentage of these gases almost constant in the atmosphere.
Question 20.
Why does the moon have very cold and very hot temperature variations e.g., from -190°C to 110°C even though it is at the same distance from the Sun as the Earth is?
Answer:
The moon does not have an atmosphere due to which very cold and very hot temperature variations from -190°C to 110°C occur on its surface. The atmosphere helps in maintaining the temperature as it prevents the excessive rise in temperature during daytime and prevents excessive cooling during the night by trapping heat energy of the Sun.
Question 21.
Why do people love to fly kites near the seashore?
Answer:
The wind blows from the sea towards the land during the daytime which helps in flying the kite higher. Also, the wind coming from the sea is cooler which makes the kite flyers feel comfortable. So, people love to fly kites near the seashore.
Question 22.
Why does Mathura refinery pose problems to the Taj Mahal?
Answer:
The harmful gases like sulphur dioxide released from the Mathura oil refinery get mixed with the water vapour present in the air and form acids like sulphuric acid. This acid falls along with the rains in the form of acid rain. The acid present in the acid rain is causing the corrosion of the marble used in the Taj Mahal. The colour (yellowing of marble was caused), as well as the quality of the marble, was getting degraded due to the acid rains. Thus, Mathura refinery posed a problem to the Taj Mahal.
Question 23.
Why do lichens not occur in Delhi whereas they commonly grow in Manali or Darjeeling?
Answer:
Lichens are bio-indicators as they help in assessing the level of pollution in the environment. They are highly sensitive to the gaseous pollutants like sulphur dioxide released from the vehicles and other sources. Delhi has a large number of vehicles and the industries which emit these gases compared to Manali or Darjeeling. So, lichens are unable to grow in Delhi.
Question 24.
Why does water need conservation even though large oceans surround the landmasses?
Answer:
The freshwater resources like river, ponds, lake, etc., are not evenly distributed on the Earth. Most part of the Earth is covered by the oceans and seas which have marine water (salty water) which is not fit for human consumption. So, there is a need to conserve the freshwater resources and the water available to us.
Question 25.
There is a mass mortality of fishes in a pond. What may be the reasons?
Answer:
The mass mortality of fishes in a pond can be the result of one or more of the following factors:
- Thermal pollution due to the heated water directly released into the water body which harms the organisms that are not able to withstand the sudden change in temperature.
- The release of heavy metals, poisonous substances like mercury or other harmful chemicals into the waterbody.
- Blockage of the gills of the fishes by the pollutants or the suspended particles released into the waterbody.
- Harmful pesticides or chemicals washed into the waterbody from the agricultural fields.
- Toxic wastes released into the water by the industries.
Question 26.
Lichens are called pioneer colonisers of bare rock. How can they help in the formation of soil?
Answer:
The chemicals released by the lichen cause the gradual weathering of the large particles of rock into smaller fine particles of soil. Thus, they help in the formation of soil.
Question 27.
“Soil is formed by water.” If you agree to this statement then give reasons.
Answer:
Yes, water helps in the formation of soil as it helps in the breakdown of large rocks into fine particles of soil by the following two ways:
- The water enters the cracks and crevices in the rocks, gets unevenly heated by the Sun and when it expands during freezing in the winter season, the rocks break down in smaller pieces.
- Also, the fast running water over the surface of the rocks causes weathering of rocks to form soil.
Question 28.
Fertile soil has lots of humus. Why?
Answer:
Fertile soil has a lot of hummus because
- Soil particles are bound in the form of crumbs by the humus which helps the soil in aeration as well as hydration.
- Humus contains many kinds of minerals dissolved in it.
- Growth of the plants is enhanced by the various chemicals present in humus.
- Soil becomes porous due to humus which facilitates the penetration of roots into the soil.
Question 29.
Why is step farming common in hills?
Answer:
Step farming is practised in hilly regions which reduce the flow of water or the rainwater and gives it more time to percolate into the soil.
Question 30.
Why are root nodules useful for the plants?
Answer:
The plants called legumes to harbour the nitrogen-fixing bacteria like Rhizobium in their roots in the form of root nodules. These bacteria convert the atmospheric nitrogen into nitrites or nitrates which can be assimilated by plants.
Natural Resources Class 9 Extra Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1.
1. Make a neat and labelled sketch of the nitrogen cycle in nature.
2. Describe in brief the role of nitrogen-fixing bacteria and lightning in fixing nitrogen.
Answer:
1. The nitrogen cycle is:
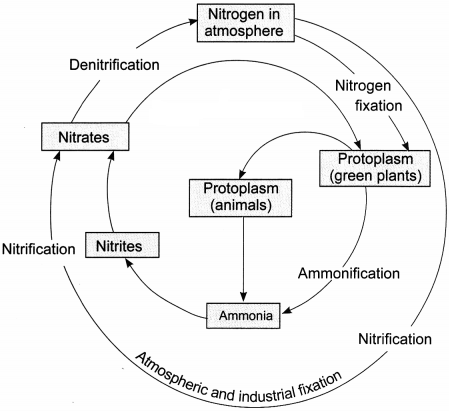
2. The atmospheric nitrogen can be fixed in the following ways:
By nitrogen-fixing bacteria: The nitrogen-fixing bacteria live either in a symbiotic association like the Rhizobium in the root nodules of the legumes or live freely like Azotobacter. The bacteria fix the atmospheric nitrogen into nitrates which are absorbed by the plants in soluble form and assimilated in their body.
By lightning: Lightning has enormous energy which breaks nitrogen molecules and enables their atoms to combine with oxygen present in the air to form nitrogen oxides. These oxides dissolve in rain, form nitrates and are carried to the Earth with the rains.
Question 2.
Explain the role of the atmosphere as a blanket. List the factors deciding the rainfall patterns.
Answer:
The atmosphere is a blanket of air around the Earth which acts as a buffer to prevent the excessive or
sudden rise of temperature during the day and also prevents excessive cooling of the Earth during the night. It slows down the escape of heat into the outer space during the night.
Thus, the atmosphere helps to keep the average temperature of the Earth fairly steady during the day and also during the whole year. The prevailing wind patterns decide the rainfall patterns. The South-West monsoon and the North-East monsoon cause rains in large parts of India.
Question 3.
1. Many municipal corporations are trying water harvesting to improve the availability of water. Give reason.
2. Rainwater sometimes contains traces of acid. Why? Explain in brief.
Answer:
1. The Municipal Corporations are trying water harvesting in order to recharge the underground water reservoirs and the underground water level. This ensures the availability of water during the scarcity of rainfall or water. Rainwater harvesting involves the collection of water from surfaces on which rain falls and stores this water for later use. Generally, the water is collected from the roofs of buildings and stored in rainwater tanks.
2. Combustion of fossil fuels releases oxides of nitrogen (NO2) and sulphur (SO2) which dissolve in rainwater to form their respective acids. These acids then fall along with rains and such rain is called acid rain. Due to the presence of such acids, the rainwater sometimes contains traces of acids.
Question 4.
How does the addition of undesirable substances and change in temperature affect water life?
Answer:
Addition of undesirable substances affects the water life in the following ways:
- Addition of harmful chemicals or metals like mercury, lead, etc., cause poisoning of water bodies and harm aquatic organisms.
- The pathogens released into the water bodies are the cause of many human diseases like cholera, typhoid, etc.
- Aquatic organisms are harmed and even killed due to deficiency of oxygen which occurs when the addition of sewage, fertilisers and nutrients in the water body resulting in excessive growth of algae. The algae drain out the oxygen from the water body.
The change in temperature can also affect water life because:
- The variation in temperature affects the breeding patterns of aquatic animals.
- The hatching of the eggs is adversely affected due to the changes in the temperature of the water.
Question 5.
What are the various factors or the processes that make soil?
Answer:
Soil is formed due to various physical, chemical and biological processes which result in the breakdown of rocks into fine particles of soil over millions of years. The formation of soil occurs due to factors and processes like Sun, water, wind, living organisms and lichens.
1. Sun: Rocks expand when they get heated by the Sun during the day. During the night, the rocks cool down and contract. This result in the formation of cracks in the rocks as the rate of expansion and contraction are different. The rocks split and break into smaller pieces.
2. Water: Water acts in two ways to break the large rocks into small pieces. Water enters the cracks and crevices in the rocks, gets unevenly heated by the Sun and when it expands during freezing in the winter season, the rocks break down into smaller pieces. Also, the fast running water over the surface of the rocks causes weathering of rocks to form soil.
3. Wind: The winds carry small rocks and sand from one place to another and these strong winds rub against the large rocks to erode them.
4. Living organisms (Lichens): The chemical substances secreted by the living organisms like lichens degrade the rocks and convert them into fine particles of soil.
Question 6.
How do fossil fuels cause air pollution?
Answer:
Fossil fuels like coal and petroleum produce oxides of nitrogen and sulphur on combustion. These gases react with water vapour present in the air to form acids which fall down along with rains on the Earth. Acid rain is very harmful to the plants, animals and the microorganisms present in the soil. Also, the suspended particulate matter released on the burning of fossil fuels cause respiratory problems to human beings and reduces visibility when it forms smog.
Question 7.
What are the causes of water pollution? Discuss how you can contribute in reducing water pollution. Ans. Addition of undesirable and harmful substances in water or the removal of useful substances from water
is referred to as water pollution. It is caused due to:
- Addition of fertilisers and pesticides washed away from the agricultural field into the nearby water bodies.
- Disposal of domestic sewage into the waterbody like rivers.
- The death of many aquatic organisms occurs when hot water from the industries is directly released into the water body. This also reduces the amount of dissolved oxygen in the waterbody.
- Washing of the clothes in the waterbody using detergents.
- Many harmful radioactive substances released from the industries dumped into the waterbody.
Water pollution can be reduced by the following measures:
- The sewer lines should not be directly connected to the waterbody.
- Disposal of garbage and wastes into the waterbody should not be allowed.
- Toxic compounds released from the industries should not be dumped in the water bodies.
- Detergents increase the nutrient content of water which is harmful to aquatic organisms as the amount of dissolved oxygen gets reduced in water due to excessive algal growth. Therefore water containing detergents should not be allowed to run off into water bodies.
- Trees should be planted near the banks of the river to prevent soil erosion which leads to siltation in the water bodies.
Question 8.
A motor car, with its glass totally closed, is parked directly under the Sun. The inside temperature of the car rises very high. Explain why.
Answer:
Glass has a property due to which it allows the radiations of the Sun to pass through and enter the car. Infrared radiations also enter the car along with other radiations. Glass is transparent to infrared. radiation from the Sun having smaller wavelength but opaque to longer wavelength radiations that are emitted by the interior of the car.
The infrared radiations get re-radiated by upholstery and other inner parts of the car but cannot pass out of the glass like the other radiations. So, the heat trapped inside raises the temperature inside the car.
Question 9.
Justify “Dust is a pollutant”.
Answer:
Dust can be considered as a pollutant because:
- Suspended particles are present in the dust which can enter the respiratory systems of the organisms and can cause asthma, bronchitis, allergies or other respiratory diseases.
- When dust falls on the leaf surface, it can cause blocking of the stomata which adversely affects the process of photosynthesis and plant growth.
- Many heavy metals and toxic compounds are present in the dust which can harm living organisms.
- Dust can be harmful to the eyes of the organism as irritation and reddening of eyes can be caused due to it.
Question 10.
Explain the role of the Sun in the formation of soil.
Answer:
The Sun helps in soil formation in the following ways:
Rocks expand when they get heated by the Sun during the day. During the night, the rocks cool down and contract. This result in the formation of cracks in the rocks as the rate of expansion and contraction are different. The rocks split and break into smaller pieces.
Question 11.
Carbon dioxide is necessary for plants. Why do we consider it as a pollutant?
Answer:
Carbon dioxide is necessary for the plants, as it is utilised during the process of photosynthesis. It acts as a raw material for photosynthesis and helps in maintaining the temperature on the Earth. If the concentration of carbon dioxide increases in the atmosphere above a certain level, it traps more heat of the Sun because it is a greenhouse gas.
This ultimately results in an increase in the average temperature on Earth and causes global warming. Due to higher temperatures, the polar ice caps, glaciers and the snow of mountains melt faster. This can lead to floods and an increase in seawater level. So, carbon dioxide is considered a pollutant.
Natural Resources Class 9 Extra Questions HOTS
Question 1.
What is the fate of the glucose molecules formed in photosynthesis?
Answer:
The glucose molecules formed during photosynthesis are either stored in the form of starch in the green plants or get transported in the form of sucrose to the various parts of the plant. Glucose is also utilised by the plants during respiration to obtain energy.
Question 2.
What is the likely outcome if all the oxygen in the environment gets converted into ozone?
Answer:
If all the oxygen in the environment gets converted into ozone it will be harmful to the living organisms as ozone adversely affects the living organisms and would eventually kill them.
Question 3.
We are lucky that ozone is not stable near the Earth’s surface. Why?
Answer:
The ozone present in the lower atmosphere is called ‘bad ozone’ as it adversely affects the living organisms, corrodes metals, acts as a greenhouse gas and creates respiratory problems in animals. So, we are lucky that ozone is not stable near the Earth’s surface as it gets converted into oxygen or the various oxides.
Question 4.
1. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria are usually found only in the root nodules of leguminous plants. Why?
2. Name a non-leguminous plant which has nitrogen-fixing bacteria in root nodules and the microbe present in it.
Answer:
1. The nitrogen-fixing bacteria are usually found only in the leguminous plants as the roots of the leguminous plants provide shelter and the specific conditions required for such bacteria. The bacteria like Rhizobium live in symbiotic association with the roots of leguminous plants.
2. Alnus is a non-leguminous plant which has a nitrogen-fixing bacteria called Frankia in its root nodules.
Question 5.
What will be the consequences if all the decomposers are removed from the Earth?
Answer:
Decomposers play a vital role in the recycling of various nutrients. The recycling of the nutrients would be hindered in the absence of decomposers. They also help in the decomposition of dead plants, animals and organic matter. In the absence of decomposers, the Earth would get covered by the remains of such organisms and it would become difficult for the organisms to survive on Earth.
Question 6.
Excessive use of pesticides in the fields can adversely affect the fishes living in the nearby ponds. How?
Answer:
- The pesticides used in the fields can get washed into the nearby water bodies by the rains and flowing water.
- These pesticides cause a phenomenon called biological magnification which adversely affects the fishes of the pond.
Question 7.
Excess use of fertilisers in the field is not advisable to the farmers. Give reasons.
Answer:
Excess use of fertilisers increases the food production for a short term but in the long term, it is not advisable to the farmers because
1. Excess use of fertilisers increases the salinity of the soil and reduces its fertility.
2. The fertilisers can get washed away into the nearby ponds where they cause excessive growth of algae due to nutrient enrichment. This depletes the dissolved oxygen from the water body and harms the other aquatic organisms.
Question 8.
The public transport like buses and the autos have shifted to CNG instead of petrol or diesel in Delhi. Why?
Answer:
The public transport like the buses and the autos have shifted to CNG instead of petrol or diesel in Delhi because the gases released from these vehicles cause a lot of pollution and harms the environment in following ways:
- The oxides of nitrogen and sulphur released from the vehicles result in acid rains which is harmful to the living organisms.
- The harmful gases from the exhaust result in several problems like asthma, respiratory disorders, cancer, etc.
Question 9.
Discharge of sewage into the water body decreases the amount of oxygen dissolved in water. How?
Answer:
The sewage water consists of a lot of organic matter which is decomposed by the microorganisms present in the water body. The microorganisms multiply at a rapid rate and consume a lot of dissolved oxygen in order to decompose the organic matter. This reduces the amount of dissolved oxygen in the water.
Question 10.
What will be the result if all the plants get eliminated from the Earth?
Answer:
Plants perform photosynthesis and release oxygen during the process which is used by the other organisms for survival. If all the plants become extinct, eventually all the oxygen requiring living organisms including us will get eliminated from the Earth.
Natural Resources Class 9 Extra Questions Value Based (VBQs)
Question 1.
Vijay is the son of a rich businessman. He lives in a very big house. He always insists and reminds the family members to switch off lights, fans, TVs, etc., of rooms when there is no one in the room, so that use of electricity is minimum. He realises that power generation on a large scale in thermal power plants produces a lot of carbon dioxide and fly ash.
Read the given passage and answer the following questions:
- How is carbon dioxide responsible for global warming?
- What measures will you take to reduce levels of carbon dioxide?
- What values are displayed by Vijay in his action and thoughts?
Answer:
1. Carbon dioxide has a property due to which it allows rays of Sun to pass through and reach the surface of the Earth but stops the rays from being re-radiated from the surface of Earth. The heat of the Sun rays gets trapped by carbon dioxide in this way and causes global warming.
2. The levels of carbon dioxide can be reduced in the atmosphere by increasing the efficiency of engines of vehicles, large scale afforestation, reducing the emission of carbon dioxide from the industries and using alternative sources of energy in place of fossil fuels.
3. The values shown by Vijay are a concern for the environment, intelligence, awareness and scientific attitude.
Question 2.
Due to the establishment of a petroleum refinery near the city, many people started suffering from respiratory problems and the marble used in their houses turned yellow. A survey carried out by Arpit and his colleagues attributed this to the gases released from the refinery. They consulted the Government agencies and suggested to shift the refinery away from the city.
Based on the above, answer the following questions:
- What can be the reason behind the yellowing of marble?
- What are the various harmful effects of air pollution?
- What values are depicted by the efforts of Arpit and his colleagues?
Answer:
- The oxides of nitrogen and sulphur released from the petroleum refinery dissolve in rainwater to form acids and fall on the Earth. When this acid rain falls on marble it causes yellowing of the marble.
- The other harmful effects of air pollution are:
(a) Formation of smog which harms living organisms.
(b) Respiratory problems, bronchitis, asthma, cancer, etc. - The values depicted by Arpit and his colleagues are scientific aptitude, care for the environment and a responsible citizen.
Question 3.
Amrita saw that the farmers of her village use excessive fertilisers and pesticides on their crop. She searched the internet for the effect of such action on the environment. She came to know that their excessive use is harmful to the environment. She talked to the Head of the village and the farmers were motivated to use fertilisers and pesticides judiciously. They were also motivated to practice organic farming for better crop yield.
Based on the above, answer the following questions:
1. How is excessive use of fertilisers and pesticides harmful to the environment?
2. What is organic farming?
3. What values are shown by Amrita in solving the problem?
Answer:
1. The fertilisers and the pesticides get washed away into the nearby water bodies with rainwater or the flowing water.
Excess use of fertilisers causes uncontrolled growth of algae in water bodies which depletes the dissolved oxygen in the water and causes death other aquatic organisms. Excess use of pesticides causes biological magnification which leads to death of many fishes in the water bodies.
2. Organic farming is a method of crop production in which no chemical pesticides or fertilisers are used during the cultivation of crops.
3. The values shown by Amrita are curiosity, inquisitive nature, care for the environment and scientific attitude.
Question 4.
Zeenat and her sister were very happy when their father brought home a new refrigerator. She saw a sticker pasted on the refrigerator which read ‘CFC free’. She asked her father about it. Her father told her that the compounds called CFC are the cause of the ozone hole and so they are not used in the refrigerators to save our environment.
Read the above passage and answer the following:
- What is ozone and why is it important?
- What are CFCs and why are they harmful?
- What values are shown by Zeenat and her father?
Answer:
- Ozone is a triatomic molecule of oxygen with formula 03. It traps the harmful rays of the Sun and protects the living organisms.
- The CFCs are the carbon compounds having both fluorine and chlorine which are very stable and not degraded by any biological process. They persist in the atmosphere and degrade the ozone layer.
- The quality shown by Zeenat is a curious nature. Her father shows the values of concern for the environment, patience and imparting right knowledge to children.
Question 5.
A farmer came for a consultation with Rajni who worked as ‘Kisan Mitra’ in the village. He told her that he was growing leguminous crop in the field, so what will by the right amount of nitrogenous fertilisers required in his field? Rajni told him that since he was growing leguminous crops in the field, he does not require adding more nitrogenous fertilisers in the field. She further suggested him to grow the leguminous crop alternately with maize or wheat.
Based on the above, answer the following questions:
1. Why did Rajni advise the farmer not to add more nitrogenous fertilisers in his field?
2. Why did she suggest him to grow leguminous crop alternately with maize or wheat?
3. What values are shown by Rajni?
Answer:
1. Rajni advised the farmer not to add more nitrogenous fertilisers as the leguminous plants which the farmer had sown in the field have root nodules which contain nitrogen-fixing bacteria. These nitrogen-fixing bacteria fix the atmospheric nitrogen and give it to the plant, so no additional nitrogen-containing fertilisers are required in the field.
2. Rajni advised the farmer to grow leguminous crop alternately with maize or wheat as the nutrients are taken up by the wheat or maize from the soil will be restored by the nitrogen-fixing bacteria present in the root nodules of the leguminous crop. In this way, the fertility of the soil will be restored and enriched again by the leguminous crop. The process is called crop rotation.
3. The values shown by Rajni are patience, knowledge, proper decision making, scientific aptitude, concern for the environment
