NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts
These Solutions are part of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science. Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts
NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
What happens when a solution of an acid is mixed with a solution of a base in a test tube ?
(i) The temperature of the solution increases
(ii) The temperature of the solution decreases
(iii) The temperature of the solution remains the same
(iv) Salt formation takes place
(a) (i) only
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Answer:
(d). Salt formation takes place in the neutralisation reaction. It is always exothermic and temperature increases.
More Resources
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
- Value Based Questions in Science for Class 10
- HOTS Questions for Class 10 Science
- Previous Year Question Papers for CBSE Class 10 Science
Question 2.
An aqueous solution turns red litmus solution blue. Excess addition of which of the following solutions would reverse the change ?
(a) Baking powder
(b) Lime
(c) Ammonium hydroxide solution
(d) Hydrochloric acid
Answer:
(d). The aqueous solution is of basic nature since red litmus changes to blue. The reaction can be reversed (acidic solution) by adding excess of hydrochloric acid.
Question 3.
During the preparation of hydrogen chloride gas on a humid day, the gas is usually passed through the guard tube containing anhydrous calcium chloride. The role of anhydrous calcium chloride taken in the guard tube is to
(a) absorb the evolved gas
(b) moisten the gas
(c) absorb moisture from the gas
(d) absorb Cl– ions from the evolved gas
Answer:
(c). Anhydrous CaCl2 absorbs moisture to keep the gas in dry state. Otherwise, it will dissolve in moisture to form hydrochloric acid.
Question 4.
Which of the following salts does not contain any water of crystallisation ?
(a) Blue vitriol
(b) Baking soda
(c) Washing soda
(d) Gypsum
Answer:
(b). Baking soda (NaHCO3) does not contain any water of crystallisation.
Question 5.
Sodium carbonate is a basic salt because it is a salt of
(a) strong acid and strong base
(b) weak acid and weak base
(c) strong acid and weak base
(d) weak acid and strong base
Answer:
(d). Na2CO3 is a salt of weak acid (H2CO3) and strong base (NaOH).
Question 6.
Calcium phosphate is present in tooth enamel. Its nature is
(a) basic
(b) acidic
(c) neutral
(d) amphoteric
Answer:
(a). Ca3(PO4)2 is a salt of strong base Ca(OH)2 and weak acid H3PO4.
Question 7.
A sample of soil is mixed with water and allowed to settle. The clear supernatant solution turns the pH paper yellowish-orange. Which of the following would change the colour of this pH paper to greenish-blue ?
(a) Lemon juice
(b) Vinegar
(c) Common salt
(d) An antacid
Answer:
(d). The colour of the pH paper signifies that the solution is somewhat acidic. In order to change it to greenish-blue, we need an antacid.
Question 8.
Which of the following gives the correct increasing order of acidic strength ?
(a) Water
(b) Water
(c) Acetic acid
(d) Hydrochloric acid Water Acetic acid
Answer:
(a).
Question 9.
If a few drops of a concentrated acid accidentally spill over the hand of a student, what should be done ?
(a) Wash the hand with saline solution
(b) Wash the hand immediately with plenty of water and apply a paste of sodium hydrogen carbonate
(c) After washing hand with plenty of water, apply solution of sodium hydroxide on the hand
(d) Neutralise the acid with a strong alkali
Answer:
(b). Washing the hand initially with plenty of water gives partial relief from burning sensation. The paste of sodium hydrogen carbonate completely neutralises the effect of the acid.
Question 10.
Sodium hydrogen carbonate when added to acetic acid evolves a gas. Which of the following statements are true about the gas evolved ?
(i) It turns lime water milky
(ii) It extinguishes a burning splinter
(iii) It dissolves in a solution of sodium hydroxide
(iv) It has a pungent odour
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(c) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Answer:
(b). The gas evolved is carbon dioxide (CO2). The statements (i), (ii) and (iii) are true about the gas.
Question 11.
Common salt besides being used in kitchen can also be used as the raw material for making
(i) washing soda
(ii) bleaching powder
(iii) baking soda
(iv) slaked lime
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (i), (iii) and (iv)
Answer:
(c).
Question 12.
One of the constituents of baking powder is sodium hydrogen carbonate. The other constituent is :
(a) hydrochloric acid
(b) tartaric acid
(c) acetic acid
(d) sulphuric acid
Answer:
(b). Tartaric acid is the other consument.
Question 13.
To protect tooth decay, we are advised to brush our teeth regularly. The nature of the tooth paste commonly used is
(a) acidic
(b) neutral
(c) basic
(d) corrosive
Answer:
(c). The basic ingredient in the paste will neutralise any acid released from the sugary’ items which we eat.
Question 14.
Which of the following statements is correct about an aqueous solution of an acid and of a base ?
(i) Higher the pH, stronger the acid
(ii) Higher the pH, weaker the acid
(iii) Lower the pH, stronger the base
(iv) Lower the pH, weaker the base
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Answer:
(d). Statements (ii) and (iv) are correct.
Question 15.
The pH of the gastric juices released during digestion is
(a) less than 7
(b) more than 7
(c) equal to 7
(d) equal to 0
Answer:
(a). Gastric juices generally release hydrochloric acid during digestion. Therefore the pH is less than 7.
Question 16.
Which of the following phenomena occur when a small amount of acid is added to water ?
(i) Ionisation
(ii) Neutralisation
(iii) Dilution
(iv) Salt formation
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Answer:
(b). Water helps in the ionisation of acid and also in its dilution.
Question 17.
Which one of the following can be used as an acid- base indicator by a visually impared student ?
(a) Litmus
(b) Turmeric
(c) Vanilla essence
(d) Petunia leaves
Answer:
(c). Vanilla essence is an olfactory inidicator.
Question 18.
Which of the following substances will not give carbon dioxide on treatment with dilute acid ?
(a) Marble
(b) Lime stone
(c) Baking soda
(d) Lime
Answer:
(d). Since lime (CaO) does not contain carbon, it will not give any carbon dioxide gas.
Question 19.
Which of the following is acidic in nature ?
(a) Lime juice
(b) Human blood
(c) Lime water
(d) Antacid
Answer:
(a). Lime juice is of acidic nature. It contains citric acid.
Question 20.
In an attempt to demonstrate electrical conductivity through an electrolyte, the apparatus set up is given. Which among the following statement(s) is(are) correct ?
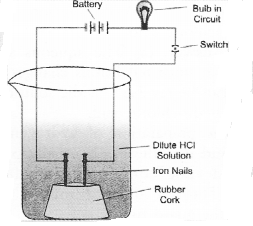
(i) Bulb will not glow because electrolyte is not acidic
(ii) Bulb will glow because HCl is a strong acid and furnishes ions for conduction.
(iii) Bulb will not glow because circuit is incomplete
(iv) Bulb will not glow because it depends upon the type of electrolytic solution
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (ii) only
(d) (iv) only
Answer:
(c). Bulb will glow because the acid will furnish ions which conduct electricity.
Question 21.
Which of the following is used for dissolution of gold ?
(a) Hydrochloric acid
(b) Sulphuric acid
(c) Nitric acid
(d) Aqua regia.
Answer:
(d). For the details of aqua regia.
Question 22.
Which of the following is not a mineral acid ?
(a) Hydrochloric acid
(b) Citric acid
(c) Sulphuric acid
(d) Nitric acid.
Answer:
(b). Citric acid is an organic acid present in citrus fruits. It is not a mineral acid.
Question 23.
Which of the following is not a base ?
(a) NaOH
(b) KOH
(c) NH4OH
(d) C2H5OH.
Answer:
(d). Ethyl alcohol (C2H5OH) is not a base. It is an alcohol and is very weakly acidic in nature.
Question 24.
Which of the following statements is not correct ?
(a) All metal carbonates react with acid to give a salt, water and carbon dioxide
(b) All metal oxides react with water to give salt and acid
(c) Some metals react with acids to give salt and hydrogen
(d) Some non metal oxides react with water to form an acid
Answer:
(b). The statement is not correct as the metal oxide reacts with water to form metal hydroxide.
Question 25.
Match the chemical substances given in Column (A) with their appropriate application given in Column (B)
|
Column (A) |
Column (B) |
|
(1) Bleaching powder |
(i) Constituent of glass |
|
(2) Baking soda |
(ii) Production of H2 and Cl? |
| (3) Borax |
(iii) Decolourisation |
| (4) Sodium chloride |
(iv) Antacid |
(a) 1—(ii), 2—(i), 3—(iv), 4—(iii)
(b) 1—(iii), 2—(ii), 3—(iv), 4—(i)
(c) 1—(iii), 2—(iv), 3—(i), 4—(ii)
(d) 1—(ii), 2—(iv), 3—(i), 4—(iii)
Answer:
(c).
Question 26.
Equal volumes of hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide solutions of same concentration are mixed and the pH of the resulting solution is checked with a pH paper. What would be the colour obtained ?
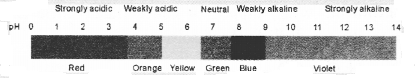
(a) Red
(b) Yellow
(c) Green
(d) Blue
Answer:
(c). pH paper will acqure green colour which indicates that the solution is of neutral nature.
Question 27.
Which of the following is(are) true when HCl (g) is passed through water ?
(i) It does not ionise in the solution as it is a covalent compound.
(ii) It ionises in the solution
(iii) It gives both hydrogen and hydroxyl ions in the solution
(iv) It forms hydronium ion in the solution due to the combination of hydrogen ion with water molecule
(a) (i) only
(b) (iii) only
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Answer:
(c). Both are true.
Question 28.
Which of the following statements is true for acids ?
(a) Bitter and change red litmus to blue
(b) Sour and change red litmus to blue
(c) Sour and change blue litmus to red
(d) Bitter and change blue litmus to red
Answer:
(c). Both are the characteristics of acids.
Question 29.
Which of the following are present in a dilute aqueous solution of hydrochloric acid ?
(a) H3O+ + Cl–
(b) H3O+ + OH–
(c) Cl– + OH–
(d) unionised HCl
Answer:
(a). HCl will react with water as follows :
HCl (l) + H2O(l) ———> H3O+(aq) + Cl–(aq)
Question 30.
Identify the correct representation of reaction occurring during chloralkali process
(а) 2NaCl(l) + 2H2O(l) ———–>2NaOH(s) + Cl2(g) + H2(g)
(b) 2NaCI(aq) + 2H2O (aq) ———–> 2NaOH(aq) + Cl2(g) + H2 (aq)
(c) 2NaCl(aq) + 2H2O(l) ———–> 2NaOH(aq) + Cl2(aq) + H2(g)
(d) 2NaCl (aq) + 2H2O (l) ———–> 2NaOH (aq) + Cl2(g) + H2(g)
Answer:
(d). It is the correct answer since the physical states of all the species involved are correct.
NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Short Answer Questions
Question 31.
Match the acids given in column (A) with their correct sources given in column (B)
|
Column (A) |
Column (B) |
|
(a) Lactic acid |
(i) Tamarind |
|
(b) Acetic acid |
(ii) Lemon |
| (c) Citric acid |
(iii) Vinegar |
| (d) Tartaric acid |
(iv) Curd |
Answer:
(a)-(iv)
(b)-(iii)
(c)-(ii)
(d)-(i)
Question 32.
Match the important chemicals given in Column (A) with the chemical formulae given in Column (B)
|
Column (A) |
Column (B) |
|
(a) Plaster of Paris |
(i) Ca(OH)2 |
|
(b) Gypsum |
(ii) CaSO4.½ H2O |
| (c) Bleaching Powder |
(iii) CaS04.2H7O |
| (d) Tartaric acid |
(iv) CaOCl2 |
Answer:
(a)-(ii) ;
(b)-(iii) ;
(c)-(iv) ;
(d)-(i)
Question 33.
What will be the action of the following substances on blue litmus paper ?
Answer:
Dry HCl gas, Moistened NH3 gas, Lemon juice, Carbonated soft drink, Curd, Soap solution.
It will become red, will remain blue, will become red, will become red, will become red, will remain blue.
Question 34.
Name the acid present in ant sting and give its chemical formula. Also give the common method to get relief from the discomfort caused by the ant sting.
Answer:
The acid present in ant sting is methanoic acid or formic acid. Its chemical formula is HCOOH. Being poisonous in nature, it causes pain and irritation. Even blisters may appear on the stung area. One should immediately rub the stung area with a mild base like baking soda (NaHCO3). It will react with formic acid to form salt and water. Its poisonous effect will be completely neutralised.
Remember : We should never apply sodium hydroxide pellets or solution directly or the affected portion. Being strongly corrosive in nature, it will aggrievate pain by forming more blisters. However, sodium hydrogen carbonate can be applied.
Question 35.
What happens when egg shell is placed in concentrated nitric acid taken in a beaker ?
Answer:
Egg shell contains calcium carbonate as its main constituent. When dipped in concentrated nitric acid, calcium carbonate reacts to evolve carbon dioxide. As a result, egg shell slowly dissolves.
![]()
Question 36.
A student prepares solutions of (i) an acid and (ii) a base in two separate beakers. She forgets to label the solutions and litmus paper is not available in the laboratory. Since both the solutions are colourless, how will she distinguish between the two ?
Answer:
Phenolphthalein and methyl orange are also acid-base indicators. They can be used in place of litmus.
Procedure : Transfer a portion of the colourless solutions to two glass tubes. Add one or two drops of henolphthalein indicator to these. An acid solution will remain colourless while the solution of base will ecome pink. Now, repeat the experiment with methyl orange indicator. In acid solution, the indicator will become reddish while in base, it will be yellowish.
Question 37.
How would you distinguish between baking soda and washing soda upon heating ?
Answer:
Baking soda is sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3). Upon heating, it will evolve CO2 gas which upon passing through lime water, will make it milky.
![]()
Washing soda is sodium carbonate decahydrate (Na2CO3.10H2O). Upon heating, it will not evolve any gas.
![]()
Question 38.
Salt ‘A’ commonly used in bakery products on heating gets converted into another salt ‘B which itself is used for the removal of hardness of water and a gas ‘C’ is evolved. The gas ‘C’ when passed through lime water, turns it milky. Identify A, B and C.
Answer:
The salt ‘A’ is sodium hydrogen carbonate (baking soda) and is commonly used in bakeries as a constitutent of baking power. Upon heating, it changes to sodium carbonate ‘B’ and evolves carbon dioxide gas ‘C’.
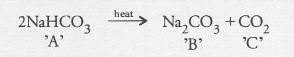
Sodium carbonate removes hardness from water while CO2 gas turns lime water milky.
Question 39.
In one of the industrial processes used for the manufacture of sodium hydroxide, a gas ‘X’ is formed as by-product. The gas ‘X’ reacts with lime water to give a compound ‘Y’ which is used as a bleaching agent in chemical industry. Identify ‘X’ and ‘Y’ giving the chemical equation of the reactions involved.
Answer:
Sodium hydroxide is manufactured by the electrolysis of a strong solution of sodium chloride (called brine). As a result, chlorine (X) is evolved at anode while hydrogen at cathode. Chlorine reacts with lime water containing slaked lime to form bleaching power (Y)
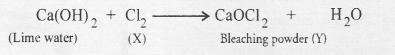
Question 40.
Fill in the missing data in the following table

Answer:

Question 41.
What are strong and weak acids ? In the following list of acids, separate strong acids from weak acids.
Hydrochloric acid, citric acid, acetic acid, nitric acid, formic acid, sulphuric acid.
Answer:
For the definitions of strong and weak acids and bases,
An acid may be defined as a substance which releases one or more H+ ions in aqueous solution. These ions exist as hydronium (H2O+) ions.
A base may be defined as a substance capable of releasing one or more OH– ions in aqueous solution.
In general, mineral acids are strong acids while organic acids are weak. From the available list :
Strong acids : Hydrochloric acid, nitric acid, sulphuric acid.
Weak acids : Citric acid, acetic acid, formic acid.
Question 42.
When zinc metal is treated with a dilute solution of a strong acid, a gas is evolved which is utilised in the hydrogenation of oils. Name the gas evolved. Write the chemical equation of the reaction involved and also write a test to detect the gas formed.
Answer:
The gas evoloved is hydrogen. The gas burns brightly with a pop sound when a burning splinter is brought in its contact. This causes the hydrogenation of edible liquid oils to form solid fats also called Vanaspati ghee.
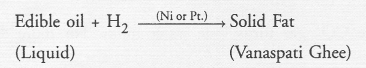
NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Long Answer Questions
Question 43.
In the following schematic diagram for the preparation of hydrogen gas as shown in the figure, what would happen if following changes are made ?
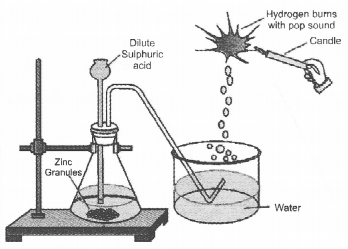
(a) In place of zinc granules, same amount of zinc dust is taken in the test tube
(b) Instead of dilute sulphuric acid, dilute hydrochloric acid is taken
(c) In place of zinc, copper turnings are taken
(d) Sodium hydroxide is taken in place of dilute sulphuric acid and the tube is heated.
Answer:
(a) Hydrogen gas would evolve at a greater speed because zinc dust provides more surface area as compared to zinc granules.
(b) Both would react in the same way. There would be no effect on the volume of the gas evolved.
(c) Copper does not react with either dilute HCl or dilute H2SO4. No gas would evolve in both the cases.
(d) Hydrogen gas would evolve in this case also.
Question 44.
For making cake, baking powder is taken. If at home your mother uses baking soda instead of baking powder in cake,
(a) how will it affect the taste of the cake and why ?
(b) how can baking soda be converted into baking powder ?
(c) what is the role of tartaric acid added to baking soda ?
Answer:
Baking powder is a mixture of baking soda and tartaric acid. Out of the two, only baking soda is actually used for making bread or cake fluffy. The role of tartaric acid is to neutralise sodium carbonate formed in the reaction.
(a) If baking soda is used for making cake in place of baking powder, then cake will taste bitter since there is no tartaric acid available to neutralise sodium carbonate formed.
![]()
(b) Baking soda can be converted to baking powder by adding appropriate amount of tartaric acid.
(c) Tartaric acid as pointed above will react with sodium carbonate which makes cake bitter. This means that the cake will not taste bitter.
Question 45.
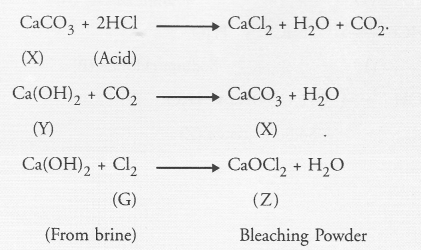
A metal carbonate (X) on reacting with an acid gives a gas which when passed through a solution (Y) gives the carbonate back. On the other hand, a gas (G) that is obtained at anode during electrolysis of brine is passed on dry substance (Y). It gives a compound (Z), used for disinfecting drinking water. Identity X, Y, G and Z.
Answer:
The gas (G) obtained at anode during the electrolysis of brine is chlorine. The compound (Z) used for disinfecting drinking water is bleaching powder. It is formed on reacting chlorine with dry slaked lime i.e., Ca(OH)2. It is denoted as ‘Y’ This means that the metal carbonate ‘X’ is calcium carbonate. Upon heating, it evolves CO2 gas which gives back ‘X’ on reacting with calcium hydroxide. The chemical reactions involved are listed :
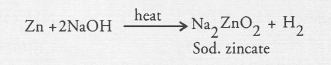
Question 46.
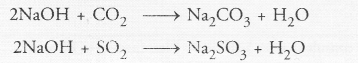
A dry pellet of a common base ‘B’, when kept in open absorbs moisture and turns sticky. The compound is also formed by chloralkali process. Identify ‘B’. What type of reaction occurs when B is treated with an acidic oxide ? Write a balanced chemical equation for one such solution.
Answer:
The available information suggests that the base ‘B’ is sodium hydroxide (NaOH). It is a deliquescent substance and becomes sticky on absorbing moisture from atmosphere. It is commercially formed by the electrolysis of a strong solution of sodium chloride (brine).
It reacts with an acidic oxide such as CO2 or SO, gas to form corresponding salt and water. For example,
Question 47.
A sulphate salt of Group 2 element of the Periodic Table is a white, soft substance which can be moulded into different shapes by making its dough. When this compound is left in open for some time, it becomes a solid mass and cannot be used for moulding purposes. Identify the sulphate salt. Why does it show such a behaviour ? Give the reaction involved.
Answer:
The available information suggests that the element present in group 2 of the Periodic Table* is calcium (Ca) and the sulphate salt (white in colour) is Plaster of Paris. It can be moulded into different shapes by making its dough with water. When left in the open, Plaster of Paris changes into Gypsum which is a solid mass quite hard in nature and can no longer be used for moulding.
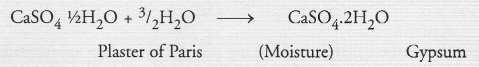
Question 48.
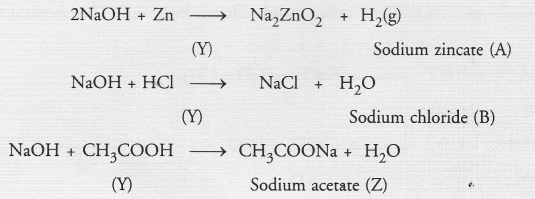
Identify the compound ‘Y’ on the basis of the reactions given below. Also write the name and chemical formulae of A, B and C.
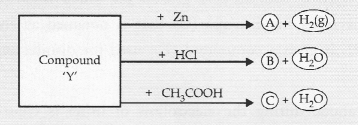
Answer:
The compound ‘Y’ is sodium hydroxide. It forms A, B and C as follows :
Hope given NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts are helpful to complete your science homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online science tutoring for you.