NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 Respiration in Plants
These Solutions are part of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 11 Biology. Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 Respiration in Plants.
VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
Question 1.
Energy is released during the oxidation of 3. compounds in respiration. How is this energy stored and released as and when it is needed?
Solution:
The energy currency of every living cell Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP).
Complex organic food molecules such as sugars, fats and proteins are rich sources of energy for cell because much of the energy used to form these molecules is stored within the chemical bonds that hold them together. So, the cells release the stored energy through a series of oxidation reactions.
During oxidation of food, the product of reaction has a lower energy content than the donor molecule. At the same time, electron acceptor molecules capture some of the energy lost during oxidation and store it for later use.
Cells convert the energy from oxidation reactions to energy-rich molecules such as ATP that can be used through the cell for metabolism and construct new cellular components.
Question 2.
How does Respiratory Quotient 5. (RQ) indicate which type of substrate, i.e., carbohydrate, fat or protein is getting oxidised?
R.Q=A/B
What do A and B stand for?
What type of substrates have R.Q. of 1,< 1 or > 1?
Solution:
The ratio of C02 evolved and 02 consumed in respiration is called the Respiratory Quotient (RQ) or respiratory ratio.

Example:
(i) During aerobic respiration carbohydrates have RQ = 1
(ii) During germination of seeds proteins and fats have RQ of < 1. (iii) Under aerobic conditions substrates like organic acids have RQ of > 1
Question 3.
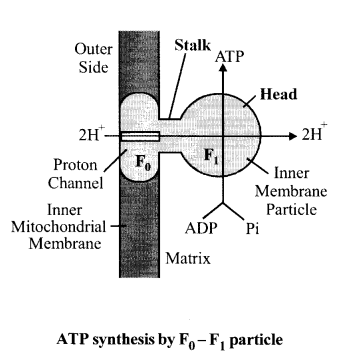
F0 – F1 particles participate in the synthesis of …… .
Solution:
F0 – F1 particles present in the inner mitochondrial membrane are involved in the Adenosine Triphosphate synthesis. It is known as the energy currency of the cell.
Question 4.
When does anaerobic respiration occur in man and yeast?
Solution:
In animals anaerobic respiration occurs in the situation of oxygen deficiency during heavy exercise, when pyruvic acid is reduced to lactic acid by the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase.
In yeast, the incomplete oxidation of glucose occurs in anaerobic conditions, during which pyruvic acid is converted to COz and ethanol by the action of enzyme pyruvic acid decarboxylase and alcohol dehydrogenase.
Question 5.
Which of the following will release more energy on oxidation? Arrange them in ascending order.
(a) 1 gm of fat
(b) 1 gm of protein
(c) 1 gm of glucose
(d) 0.5 gm of protein + 0.5 gm glucose
Solution:
The ascending order of substrate that will release more energy on oxidation will be as follows
1 gm protein < 0.5 gm in protein < 1 gm glucose < 1 gm fat + 0.5 gm glucose
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
Question 1.
If a person is feeling dizzy, glucose or fruit juice is given immediately but not a cheese sandwich, which might have more energy. Explain.
Solution:
The glucose is absorbed and reaches blood quickly and gives instant energy. Whereas, cheese sandwich require time for digestion, and absorption. Sick person needs immediate energy supply, so glucose or fruit juices containing glucose are given to them.
Question 2.
Pyruvic acid is the end product of glycolysis. What are the three metabolic fats of pyruvic acid under aerobic and anaerobic conditions? Write in the space provided in the diagram.
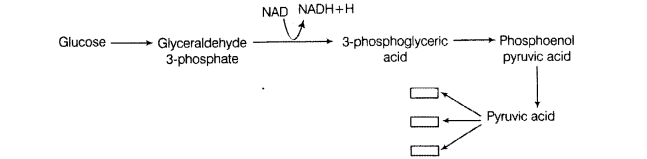
Solution:
The three metabolic products formed under 3. aerobic and anaerobic conditions are Lactic acid, Ethanol and Acetyl Co-A Lactic acid is formed under anaerobic condition in skeletal muscles by the oxidation of pyruvic acid.
Ethanol is formed under anaerobic condition by the oxidation of pyruvic acid in yeast.
Acetyl Co-A is formed by the oxidation of pyruvic acid that take place within the mitochondria under aerobic condition.
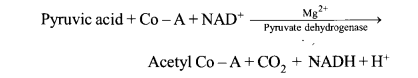
Question 3.
Oxygen is an essential requirement for aerobic respiration by it enters the respiratory process at the end? Discuss.
Solution:
Aerobic respiration needs oxygen in order to generate ATP. Oxygen acts as final acceptor in respiratory process.
In pulse e (electrons) that energy from the electron transport chain ETC and take up protons from medium to form water.
It plays a vital role in respiration. 02 enters in the respiratory process at the end. It drives the process of aerobic respiration by removing hydrogen from the system. Thus, acting as final hydrogen acceptor.
By the process of oxidative phosphorylation the energy is produced, utilising the energy of oxidation reduction reactions.
Question 4.
The figure given below shows the steps in glycolysis. Fill in the missing steps A, B, C, D and also indicate whether ATP is being used up or released at step E?
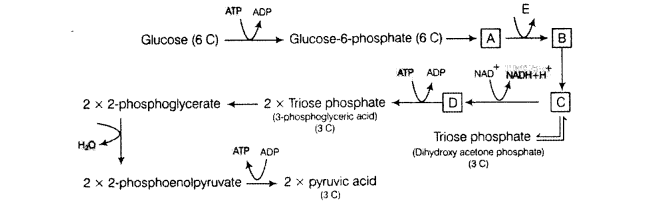
Solution:
Process ofglycolysis is summarised as follow
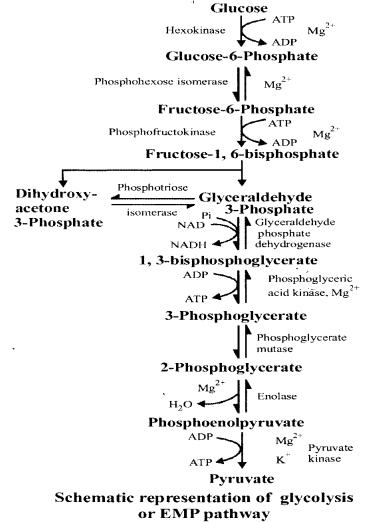
Question 5.
Do you know any step in the TCA cycle where there is substrate level phosphorylation.
Which one?
Solution:
In an intermediate reaction TCA cycle,
succinyl Co-A is converted succinic acid and one GTP molecule is synthesised through substrate level
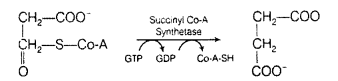
GTP formed in this reaction gives rise to ATP as follows
GTP+ADP GDP + ATP
Question 6.
In a way green plants and cyanobacteria have synthesised all the food on the earth. Comment.
Solution:
Cyanobacteria are unicellular prokaryotic organisms. Besides, some primitive cellular cell organelles, they have photosynthetic lamellae where photosynthetic pigments like chlorophyll-a c, phycocyanin and phycoerythrin, are present.
These coloured pigments confer typical blue green colour to the bacteria and enable them to manufacture food for themselves and aquatic animals.
Green plants are multicellular are organisms, which is capable of making food by using C02, H20 and light energy in specialized cell organelles called chlorcplast. So bacteria and green plants make food for living organisms on earth.
Question 7.
When a substrate is being metabolised, why does not all the energy that is produced get released in one step. It is released in multiple steps. What is the advantage of step-wise release?
Solution:
This is an enzyme that has dual nature. When C02 concentration is good enough in atmosphere. It acts as carboxylase. But if concentration of O2 increase, its nature changes and it binds with O2 and acts as oxygenase enzyme that forces CO2 to enter in C2 cycle that leads to photorespiration and loss of CO2.
Question 8.
Respiration requires 02. How did the first cells on the earth manage to survive in an atmosphere that lacked O2?
Solution:
Respiration always does not require O2. There are some organisms which respire in anaerobic condition i.e. in the absence of O2.
The first cells of earth i.g., chemosynthetic bacteria, which are the primitive organisms found earlier on earth. They obtain energy by breaking down inorganic molecules like H2S, NO2 – etc.
12H4S + 6 CO2 -> C6H12O6 + 6H2O + 12S
Question 9.
It is known that red muscle fibres in animals can work for longer periods of time continuously. How is this possible?
Solution:
There are basically two kinds of muscle fibres red muscles and white muscles
Red muscles work continuously for a longer time because
(i) These muscle fibres are dark red, due to the presence of red haemoprotein called myoglobin. It binds and stores oxygen as oxymyoglobin in the red fibres. Oxymyoglobin liberates oxygen for utilisation during muscle contraction.
(ii) Mitochondria are more in numbers, hence they work for long periods of time.
(iii) Red muscles possesses less sarcoplasmic reticulum.
(iv) They carry out considerable aerobic oxidation without accumulating much lactic acid. Thus without fatigue red muscle fibres can contract for a longer period.
(v) These muscle fibre have slow rate of contraction for long periods, e.g., extensor muscles of the human back.
Question 10.
RuBP carboxylase, PEPcase, pyruvate dehydrogenase, ATPase, cytochrome oxidase, hexokinase, lactate dehydrogenase, Select/ choose enzymes from the list above which are involved in
(a) Photosynthesis
(b) Respiration
(c) Both in photosynthesis and respiration
Solution:
RuBP Carboxylase is an enzyme that takes part in dark reaction of photosynthesis. It catalyses the fixing of C02 in C3 cycle
PEPcase an enzymes that takes part in photosynthesis of C4 plants. It catalyses the reaction of fixing of C02 to form first stable product oxaloacetate. 4 carbon compound.
Pyruvate dehydrogenase is an enzyme involved in aerobic respiration and catalyses the reaction ( of formation of acetyle Co-A from pyruvic acid.
It requires the participation of NAD and Co- enzyme-A.
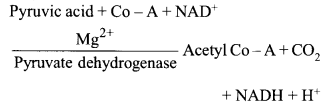
ATPase is a part of both respiration and photosynthesis. Both these processes uses etc, associated proton pump and ATP synthase.
These all play a key part in the process is used by ETC pump hydrogen ions across a membrane.
The protons flows back through ATP synthase, driving the production of ATP.
Cytochrome Oxidase is involved in both respiration and photosynthesis. It acts as electron carrier in the electron transport chain. Hexokinase is an enzymes which is also involved in, respiration. In glycolysis, it catalyses the first reaction, i.e., formation of glucose -6- phosphate from glucose molecule.
It uses one ATP molecule which transfers P04 group to glucose molecules.
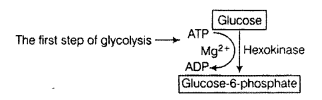
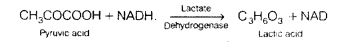
Lactate Dehydrogenase is an enzyme which is involved in anaerobic respiration in bacteria Lactobacillus.
Pyruvic acid formed at the end of glycolysis is converted to lactic acid by the help of homo- fermentative lactic acid bacteria. Hydrogen from NADH molecule is transferred to pyruvate is then transferred to pyruvate molecule lactic acid molecule leading to the formation of acid.
Question 11.
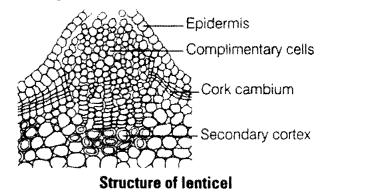
How does a tree trunk exchange gases with the environment although it lacks stomata?
Solution:
The old tree trunk is covered by dead woody tissue called cork. The epidermal layers of such tree get ruptured and outer cortical cells are loosely arranged. These structures are called as lenticels.
These are the sites of gaseous exchange and transpiration.
Question 12.
Mention the important series of events of aerobic respiration that occur in the matrix of the mitochondrion as well as one that take place in inner membrane of the mitochondrion.
Solution:
Kreb ’ s cycle occurs in the matrix of mitochondria. It is given in the following series of reactions
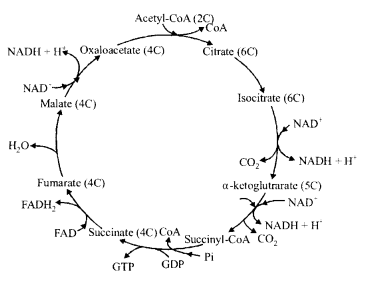
Electron transport chain is carried out in the inner mitochondria membrane
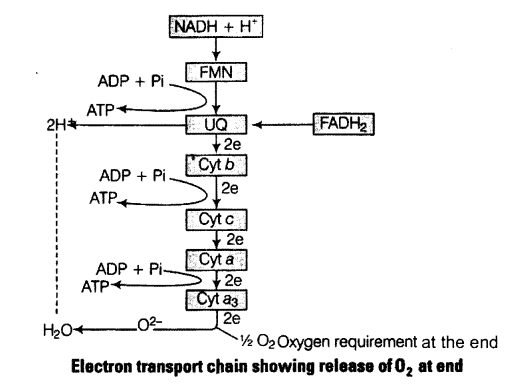
The inner mitochondrial membrane is specific about possessing proton (H+) and electron (e ) acceptors in a particular sequence called electron transport chain. It consists four enzyme complexes.
The electrons either follow the pathway of complexes I, III and IV or II, III and IV that depends that upon the substrates from Kreb’s cycle.
Following are the ways through which the transfer of electrons and hydrogen atoms takes place.
Complex I It consists of flavoproteins of NADH dehydrogenase (FPN), of which FMN is the prosthetic group. It is combined with the flavoprotein is non-heme iron of NADH dehydrogenase. This complex spans inner mitochondrial membrane and is also able to translocate protons across it form matrix side to outer side.
Complex II It consists of flavoprotein of succinate dehydrogenase, of which FAD is the prosthetic group. It is combined with the flavoprotein is non-heme iron of succinate dehydrogenase.
Between complexes II and in the mobile carrier coenzyme-Q (Co-Q) or ubiquinone (UQ) is present
Complex III It consists of cytochrome-/) and cytochrome-c that is associated with cytochrome-h is non-heme iron of complex III. Between complexes III and IV is the mobile carrier cytochrome-c.
Complex IV It consists of cytochrome-a and cytochrome-a3, and bound copper that are required for this complex reaction to occur. This cytochrome also called cytochrome oxidase. It is the only electron carrier in which the heme iron has a free ligand that can react directly with molecular oxygen.
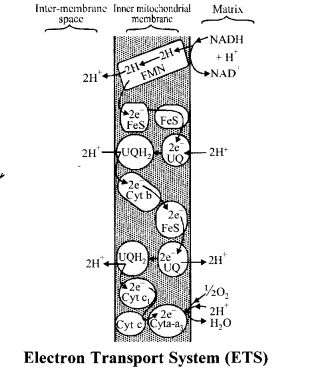
- Thus, hydride ions are transferred from the substance to be oxidised to NAD+. From NAD+ the hydrogen atoms are transferred to FMN of flavor protein 1 (Fp’N). After FMN the hydrogen atom splits into an electron and a proton.
- In further stages transfer of e~s occur but there is no longer a transfer of hydrogens. The electron passes to co-enzyme-Q, and from co-enzyme Q to cytochromes- b, cp c, a and ay The proton is released free.
- As the hydrogen atom or electron passes down by F0 – F1 particle at the same time oxidation of one coenzyme and reduction occurs at another steps. Oxygen is able to diffuse inside the mitochondria.
- It is converted to anionic form 02-, combines with 2H+ and forms metabolic water reduced co-enzyme NADH + H+ that helps in pushing out three pairs of H+ to outer chamber while FADH2 sends two pairs of H+ to outer chamber.
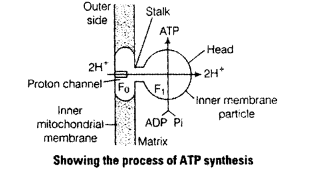
- Oxidative phosphorylation is the synthesis of ATP molecules, with the help of energy liberated during oxidation of reduced co-enzyme (NADH2, FADH2) produced in respiration.
- The enzyme required for this synthesis is called ATP synthase present in inner mitochondria membrane.
The following figures shows this process
LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
Question 1.
Oxygen is critical for aerobic respiration. Explain its role with respect to ETS.
Solution:
The oxidation of glucose starts with glycolysis in cytoplasm which followed by Krebs’ cycle and finally Electron transport Chain (ETC) in inner mitochondrial membrane. The end of ETC 02 is required.
Where, it acts as final hydrogen acceptor. 02 is responsible for removing electrons from the system. In the absence of oxygen, electrons could not be passed through the co-enzymes, intum proton pump will not be established and ATP will not be produced via oxidative phosphorylation. Thus oxygen plays an important role in aerobic respiration in mitochondrial matrix.
Question 2.
Enumerate the assumptions that we undertake in making the respiratory balance sheet. Are these assumptions valid for a living system? Compare fermentation and aerobic respiration in this context.
Solution:
The assumption that we undertake is making the respiratory balance sheet one as follows:
(i) Respiratory substrate is glucose
(ii) There is sequential pathway i.e., glycolysis in cytoplasm, TCA cycle in mitochondrial matrix and ETS in inner mitochondriol membrane.
(iii) NADH synthesised in glycolysis enters into ETC for phosphorylation.
(iv) None of the intermediates in the pathway are utilised to synthesise any other compound.
These assumptions are not valid for a living system because of following reasons:
(i) Glycolysis, TCA and ETC work simultaneously and do not take place one after the other.
(ii) ATP is uutilised when needed.
(iii) Rate of enzyme actions are controlled by multiple means.
Comparison between fermentation and aerobic respiration in this context is as follows:
(i) Fermentation is partial breakdown of glucose whereas aerobic respiration is complete breakdown of glucose.
(ii) Net gain of only 2 ATP in fermentation whereas in aerobic respiration 38 ATP is produced.
We hope the NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 11 Biology at Work Chapter 14 Respiration in Plants, help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 11 Biology at Work Chapter 14 Respiration in Plants, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.