NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 16 Digestion and Absorption
These Solutions are part of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 11 Biology. Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 16 Digestion and Absorption.
VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
Question 1.
The food mixes thoroughly with the acidic gastric juice of the stomach by the churning movements of its muscular wall. What do we call the food then?
Solution:
For 4-5 hours, the food is stored in stomach and gets thoroughly mixed with the acidic gastric juice of stomach by the churning movements of its muscular wall. The food at this stage is called as chyme.
Question 2.
Trypsinogen is an inactive enzyme of pancreatic juice. An enzyme, enterokinase, activates it. Which tissue/cells secrete this enzyme?/ How is it activated?
Solution:
Trypsinogen is activated to trypsin in the presence of which enzyme enterkinase is secreted by the intestinal mucosa.
Question 3.
In which part of alimentary, canal does absorption of water, simple sugars and alcohol takes place?
Solution:
The absorption of water, simple sugars, alcohol and some lipid soluble drugs take place by the stomach wall.
Question 4.
Name the enzyme involved in the breakdown of nucleotides into sugars and bases?
Solution:
The enzymes nucleotidases and nucleosidases are involved in the breakdown of nucleotides into sugars and bases.
![]()
Question 5.
What do we call the type of teeth attachment to jaw bones in which each tooth is embedded in a socket of jaws bones?
Solution:
The type of attachment where teeth are embedded in the socket of jaw bone is called thecodont.
Question 6.
Stomach is located in upper left portion of the abdominal cavity and has three major parts. Name these three parts.
Solution:
The three major of stomach are cardio, fundus and pylorus.
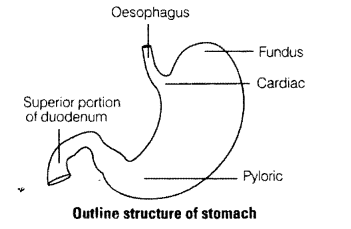
Question 7.
Does gall bladder make bile?
Solution:
Gall bladder is involved in the storage of bile and not associated with the bile formation rather, bile is secreted and from the hepatic cells of the liver.
Question 8.
Correct the following statements by deleting one of entries (given in bold).
(a) Goblet cells are located in the intestinal mucosal epithelium and secrete chymot- rypsin/mucus.
(b) Fats are broken down into di-and monog-lycerides with the help of amylase/lipases.
(c) Gastric glands of stomach mucosa have oxyntic cell/chief which secrete HC1.
(d) Saliva contains enzymes that digest starch/ protein.
Solution:
(a) Goblet cells are located in the intestinal
mucosal epithelium and secrete mucus.
(b) Fats are broken down into di and monoglycerides with the help of lipases. Fats —Llp‘’e’ > Diglycerides —> Monoglycerides.
![]()
(c) Gastric glands of stomach mucosa have oxyntic cells which secrete HCl
(d) Saliva contains enzymes that digest starch
![]()
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
Question 1.
What is pancreas? Mention the major secretions of pancreas that are helpful in digestion.
Solution:
The pancreas is both exocrine and as well as gland endocrine situated between the limbs of ‘U’ shaped duodenum.
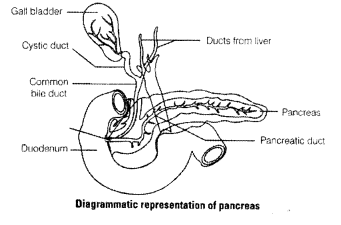
Internal structure of pancreas consist of two parts, i.e., the exocrine and endocrine part.
(i) Exocrine part consists of rounded lobules called acini, that secretes alkaline pancreatic juice of pH 8.4 and is mainly involved in the digestion of starch, proteins, fats and nucleic acids.
(ii) Endocrine part secretes hormones like, insulin and glucagon that regulate glucose metabolism.
Question 2.
Name the part of the alimentary canal where major absorption of digested food takes place. What are the absorbed forms of different kinds of food materials?
Solution:
The principle organ for the absorption of nutrients small intestine is the proces’s of digestion complete here and the final products of digestion are absorbed through the mucosa into the blood stream.
The absorbed form of different food materials are
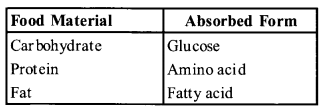
Question 3.
List the organs of human alimentary canal and name the major digestive glands with their location.
Solution:
Humn digestive system consists of two main parts: alimentary canal and digestive glands. The organ of human alimentary canal are mouth, pharynx oesophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum and anus. Major digestive glands with their locations are as follows:
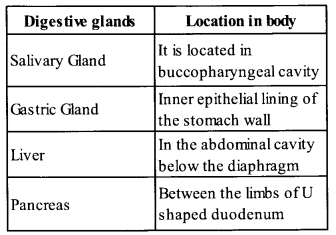
Question 4.
What are three major types of cells found in the gastric glands? Name their secretions.
Solution:
Following are the three major types of cells found in gastric glands. –
(i) Mucous neck cells (Goblet cells) are involved in the secretin of mucus and are present throughout the epithelium of gastrointestinal tract.
(ii) Peptic of Chief cells (Zymogenic cells) are Involved in the secretion of gastric enzymes such as proenzymes pepsinogen and prorenin and usually basal in location.
(iii) Parietal or oxyntic cells are large and most numerous present on the side walls of the gastric glands. They are involved in the secretion of HC1 and Castlis intrinsci Factor (CIF).
Question 5.
How is the intestinal mucosa protected from the acidic food entering from stomach?
Solution:
The intestinal mucosal epithelium has goblet cell which secrete mucus. The mucus along with bicarbonate present in the gastric juice help in lubrication and protection of mucosal epithelium from the acidic food entering from the stomach.
LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
Question 1.
A person had roti and dal for his lunch. Trace the changes in those during its passage through the alimentary canal.
![]()
Solution:
Digestion of Roti (Carbohydrates)
(a) Digestion of Carbohydrates in the Oral Cavity
In oral cavity, the roti get mixed with saliva that contains an enzyme salivary amylase (ptyalin), which converts starch of roti into maltose, isomaltose and small dextrins called a – dextrin. 30% of starch is hydrolysed in the oral cavity.
![]()
(b) Digestion of Carbohydrates in the Small Intestine
The partially digested roti passes from oral cavity to oesophagus and then reaches to stomach by peristalsis. The stomach stores the food for 4-5 hours. The gastric juice does not contain carbohydrate digesting enzyme. The partially digested food is now called as chyme. In intestine, following action occurs.
(i) Action of Pancreatic Juice – Carbohydrates in the chyme are hydrolysed by pancreatic amylase into disaccharides.
Polysaccharides(starch) —Amylas’: > Disaccharides
![]()
(ii) Action of Intestinal Juice – Intestinal Juice contain maltase, isomaltase, sucrase (invertase), lactase and a – dextrinase. hi the presence of these enzymes food is converted into simpler compounds like glucose, fructose, galactose, etc.
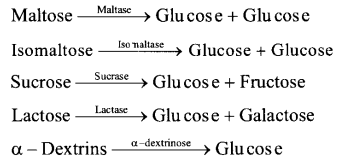
Digestion of Protein
Proteins are made up of amino acids. So proteins are broken down to amino acid during the process of digestion.
Saliva lacks any protein digesting enzyme so, digestion starts further in stomach.
(a) Digestion of Protein in Stomach. The stomach normally stores food for 4-5 hours. The gastric glands of the stomach secrete gastric juice that contains HCI, proenzymes like-pepsinogen and prorennin. Various reactions in stomach are discussed bwlow.
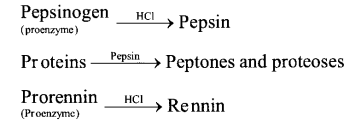
(b) Digestion of Protein in Small Intestine (i) Action of Pancreatic Juice – The enzymes , trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen and procarboxypeptidase in pancreatic juice are all concerned with the protein digestion.
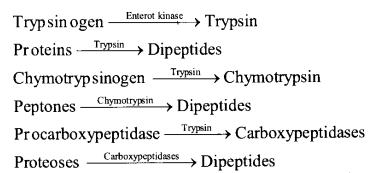
(ii) Action of Intestinal Juice – Intestinal juice contain enzymes enterokinase, amino peptidase and dipeptidase
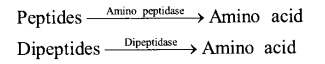
The macromolecules are broken down into simpler components are the products of roti and dal (carbohydrates and proteins) which are further absorbed by the villi in small intestine and the rest undigested food is removed in the form of faeces by large intestine.
Question 2.
Discuss mechanisms of absorption.
Solution:
- Absorption is a process by which the end product of digestion passes through the intestinal mucosa into the blood or lymph.
- It is carried out by passive, active or facilitated transport mechanism. Small amount of monosaccharide like glucose, amino acids and some electrolytes like chloride ions are absorbed by simple diffusion.
- Some of the substance like fructose and some amino acids are absorbed with the help of the carrier ions like Na+ are absorbed by the active transport.
- Fatty acid and glycerol are insoluble, thus they cannot be absorbed by the blood. They are first incorporated into small droplets called micelles which move into the intestinal mucosa.
- They are reformed into very small protein coated fat globules called chylomicrons which are transported into the lacteals of the villi. The lacteals ultimately release the absorbed substance into the blood stream.
- The maximum absorption of food takes place in small intestine.
We hope the NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 11 Biology at Work Chapter 16 Digestion and Absorption, help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 11 Biology at Work Chapter 16 Digestion and Absorption, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.