NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Biology chapter 3 Human Reproduction
These Solutions are part of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Biology. Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Biology chapter 3 Human Reproduction
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Choose the incorrect statement from the following.
(a) In birds and mammals internal fertilisation takes place.
(b) Colostrum contains antibodies and nutrients.
(c) Polyspermy in mammals is prevented by the chemical changes in the egg surface.
(d) In the human female implantation occurs almost seven days after fertilisation.
Answer:
(c) : Polyspermy is the entry of several sperms into the egg during fertilisation. It occurs in animals with yolky eggs (e.g., birds). In humans, although only one sperm nucleus actually fuses with the egg nucleus. Due to acrosomal reaction, plasma membrane of the sperm fuses with the plasma membrane of the secondary oocyte, so that the sperm contents enter the oocyte. Binding of the sperm to the secondary oocyte induces depolarisation of the oocyte plasma membrane. Depolarisation prevents polyspermy.
Question 2.
Identify the correct statement from the following.
(a) High levels of estrogen triggers the ovulatory surge.
(b) Oogonial cells start to proliferate and give rise to functional ova in regular cycles from puberty onwards.
(c) Sperms released from seminiferous tubules are highly motile.
(d) Progesterone level is high during the post ovulatory phase of menstrual cycle.
Answer:
(d)
Question 3.
Spot the odd one out from the following structures with reference to the male reproductive system.
(a) Rete testis
(b) Epididymis
(c) Vasa efferentia
(d) Isthmus
Answer:
(d) : Females have two oviducts (or Fallopian tubes). Each oviduct has three regions, infundibulum, ampulla and isthmus. Isthmus is the narrow part closest to uterus, while infundibulum is the first part of oviduct that is encountered by released ova.
Question 4.
Seminal plasma, the fluid part of semen, is contributed by
(1) seminal vesicle
(2) prostate
(3) urethra
(4) bulbourethral gland
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(c) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Answer:
(b) : Seminal plasma is the fluid part of semen and is contributed by seminal vesicles, prostate gland and bulbourethral glands. Seminal vesicles contribute fructose, citric acid and other nutrients as well as fibrinogen and prostaglandins. Secretions from prostate gland contain calcium ions, phosphate ion etc. and are alkaline in nature. Bulbourethral glands secrete alkaline mucus which is important for the lubrication of penis.
Question 5.
Spermiation is the process of the release of sperms from
(a) seminiferous tubules
(b) vas deferens
(c) epididymis
(d) prostate gland.
Answer:
(a) : Spermiation is the release of sperm from seminiferous tubules. From here, they will be transported to vasa efferentia and then to epididymis where maturation of sperm occurs.
Question 6.
Mature Graafian follicle is generally present in the ovary of a healthy human female around
(a) 5-8 day of menstrual cycle
(b) 11-17 day of menstrual cycle
(c) 18-23 day of menstrual cycle
(d) 24-28 day of menstrual cycle.
Answer:
(b) : Starting from puberty, monthly changes in ovaries and uterus also starts. The layer of cells surrounding primary oocyte are called granulosa cells and together, they are called primary follicle. The growth of the follicles is under the influence of pituitary hormones FSH and LH. Further growth is also stimulated by estrogen. The mature Graafian follicle is present in the ovary around 11-17 day of menstrual cycle and on rupture of which, ovum is released (because of LH surge, 1-2 days before ovulation).
Question 7.
Acrosomal reaction of the sperm occurs due to
(a) its contact with zona pellucida of the ova
(b) reactions within the uterine environment of the female
(c) reactions within the epididymal environment of the male
(d) androgens produced in the uterus.
Answer:
(a) : When head of sperm binds to zona pellucida (ZP) of ovum the acrosome release its contents by exocytosis. The content inside acrosome includes various hydrolytic enzymes like hyaluronidase, corona penetrating enzymes etc. This is called acrosomal reaction. It helps the sperm to reach the plasma membrane of ovum, by dissolving corona radiata and zona pellucida.
Question 8.
Which one of the following is not a male accessory gland?
(a) Seminal vesicle
(b) Ampulla
(c) Prostate
(d) Bulbourethral gland
Answer:
(b) : Ampulla is the part of oviduct between the infundibulum and isthmus. It is at tfre ampullary-isthmus junction, where fertilisation take place.
Question 9.
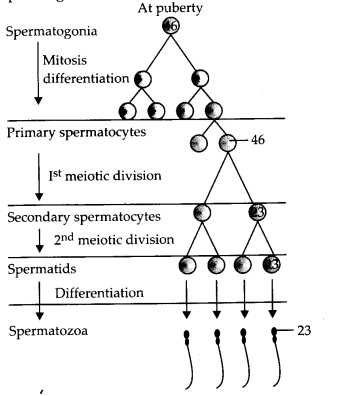
The immature male germ cell undergoes division to produce sperms by the process of spermatogenesis. Choose the correct one with reference to above.
(a) Spermatogonia have 46 chromosomes and always undergo meiotic cell division.
(b) Primary spermatocytes divide by mitotic cell division.
(c) Secondary spermatocytes have 23 chromosomes and undergo second meiotic division.
(d) Spermatozoa are transformed into spermatids.
Answer:
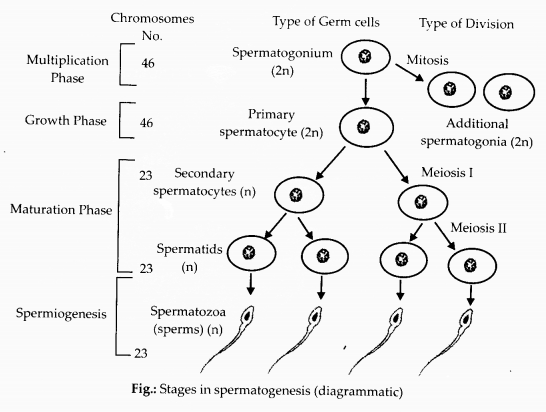
(c) : Spermatogonia are diploid cells on the inside wall of seminiferous tubules that multiply by mitotic divisions. Some of the spermatogonia called primary spermatocyte undergo meiosis-I to give rise to secondary spermatocytes (haploid). Each secondary spermatocyte undergoes meiosis-II to give rise to two haploid spermatids which are transformed to spermatozoa by spermiogenesis.
Question 10.
Match between the following representing parts of the. sperm and their functions and choose the correct option.

(a) A-{ii), B-(iv), C-(i), D-(iii)
(b) A-(iv), B-(iii), C-(i), D-(ii)
(c) A-(iv), B-(i), C-(ii), D-(iii)
(d) A-(ii), B-(i), C-(iii), D-(iv)
Answer:
(b)
Question 11.
Which among the following has 23 chromosomes?
(a) Spermatogonia
(b) Zygote
(c) Secondary oocyte .
(d) Oogonia
Answer:
(c) : Spermatogonia are the cells on the inside wall of seminiferous tubules and consist of 46 chromosomes. Oogonia are also diploid cells and formed in the foetal ovary. Zygote is also diploid and fertilised ovum formed by fusion of male and female gametes. Secondary oocyte has 23 chromosomes and is formed by meiosis-I of primary oocyte.
Question 12.
Match the following and choose the correct option.
(a) A-(ii), B-(i), C-(iii), D-(iv)
(b) A-(iii), B-(iv), C-(ii), D-(i)
(c) A-(iii), B-(i), C-(ii), D-(iv)
(d) A-(ii), B-(iv), C-(iii), D-(i)
Answer:
(b)
Question 13.
Which of the following hormones is not secreted by human placenta?
(a) hCG
(b) Estrogens
(c) Progesterone
(d) LH
Answer:
(d) : LH is the hormone that is not secreted by human placenta. It is secreted by anteribr pituitary. Initially during pregnancy, hCG performs the function of LH of maintaining corpus luteum for the secretion of progesterone. Later (around 16th week) in pregnancy, when placenta itself starts secreting estrogen and progesterone, corpus luteum regresses.
Question 14.
The vas deferens receives duct from the seminal vesicle and opens into urethra as
(a) epididymis
(b) ejaculatory duct
(c) efferent ductule
(d) Ureter
Answer:
(b)
Question 15.
Urethral meatus refers to the
(a) urinogenital duct
(b) opening of vas deferens into urethra
(c) external opening of the urinogenital duct
(d) muscles surrounding the urinogenial duct.
Answer:
(c) : Urethral meatus refers to the external opening of urinogenital duct, through which in males, urine and semen both exits the body.
Question 16.
Morula is a developmental stage
(a) between the zygote and blastocyst
(b) between the blastocyst and gastrula
(c) after the implantation
(d)between implantation and parturition.
Answer:
(a) : After fertilisation, zygote is formed. Zygote undergoes, mitotic divisions, called cleavage, to form 2, 4, 8 and 16 daughter cells called blastomeres. These divisions start when zygote is moving towards uterus. It is called morula at 8-16 cell stage and it continues to divide to form blastocyst. Blastocyst has two type of cells : trophoblast cells and inner cell mass. Around 7 day after fertilisation, implantation through trophoblast cells occurs.
Question 17.
The membranous cover of the ovum at ovulation is
(a) corona radiata
(b) zona radiata
(c) zona pellucida
(d) Chorion
Answer:
(a) : The outermost membranous cover of the ovum at ovulation is corona radiata. It is formed by follicular cells. Inner to corona radiata is zona pel lucid a, which is made up of three different glycoproteins secreted by the ovum itself.
Question 18.
Identify the odd one from the following.
(a) Labia minora
(b) Fimbriae
(c) Infundibulum
(d) Isthmus
Answer:
(a) : Labia minora are paired folds of tissues under labia majora which in turn surrounds the vaginal opening. Fimbriae, infundibulum and isthmus, along with ampulla are parts of oviduct (or Fallopian tube).
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Given below are the events in human reproduction. Write them in correct sequential order. Insemination, gametogenesis, fertilisation, parturition, gestation, implantation
Answer:
Gametogenesis, insemination, fertilisation, implantation, gestation, parturition.
Question 2.
The path of sperm transport is given below. Provide the missing steps in blank boxes.
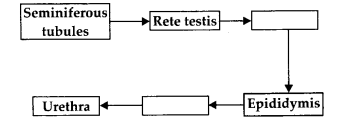
Answer:
Seminiferous tubules —>Rete testis —> Vasa efferentia —> Epididymis —> Vas deferens -> Urethra
Question 3.
What is the role of cervix in the human female reproductive system?
Answer:
Role of cervix in human female reproductive system:
- Cervical canal e., the cavity of cervix and vagina together form birth canal to facilitate parturition.
- It regulates the passage of sperms into the uterus.
Question 4.
Why are menstrual cycles absent during pregnancy?
Answer:
Levels of progesterone and estrogen are high during pregnancy. Their high levels suppress the release of gonadotropin (FSH) responsible for transformation of primary follicles into Graafian follicles, and for ovulation. And, no ovulation means, no menstrual cycle.
Question 5.
Female reproductive organs and associated functions are given below in column A and B. Fill the blank boxes.
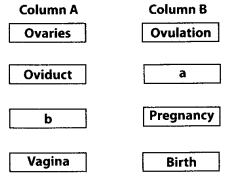
Answer:
a – Fertilisation, b – Uterus
Question 6.
From where the parturition signals arise- mother or foetus? Mention the main hormone involved in parturition.
Answer:
Parturition is induced by complex neuroendocrine mechanism. Signals for parturition originate from fully developed foetus and placenta which induce mild uterine contractions called foetal ejection reflex. Oxytocin from maternal pituitary induces strong uterine contractions of myometrium, which leads to expulsion of baby (parturition) through birth canal.
Question 7.
What is the significance of epididymis in male fertility?
Answer:
Epididymis helps in storage, nutrition and physiological maturation of sperms. It also aids motility to sperms.
Question 8.
Give the names and functions of the hormones involved in the process of spermatogenesis. Write the names of the endocrine glands from where they are released.
Answer:
The name of hormones, its endocrine glands and functions of the hormones involved in the process of spermatogenesis are given in the following table:
| Hormone | Endocrine gland | Function |
| GnRH (Gonado tropin releasing hormone) | Released from hypothalamus | Stimulates the anterior pituitary to release FSH and LH. |
| Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) | Released from anterior pituitary | Stimulates Sertoli cells to secrete certain factors which help in spermatogenesis. |
| Luteinising hormone (LH) | Released from anterior pituitary | Stimulates Leydig’s cells of testes to secrete androgens (testosterone) which regulate |
Question 9.
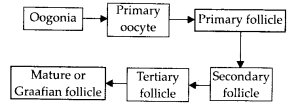
The mother germ cells are transformed into a mature follicle through series of steps. Provide the missing steps in the blank boxes.
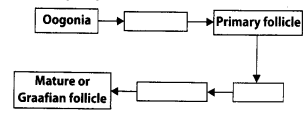
Answer:
Question 10.
During reproduction, the chromosome number (2n) reduces to half (n) in the gametes and again the original number (2n) is restored in the offspring. What are the processes through which these events take place?
Answer:
Chromosome number is reduced to half (n) during the process of gametogenesis, and it is again restored to (2n) as a result of fertilisation.
Question 11.
What is the difference between a primary oocyte and a secondary oocyte?
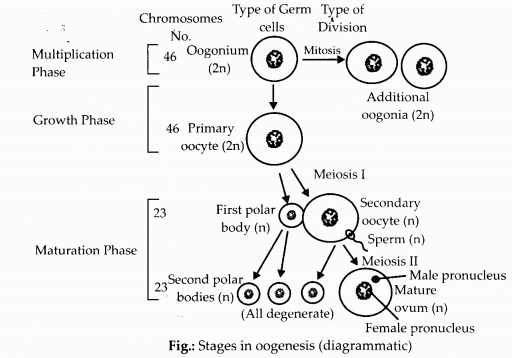
Answer:
Primary oocyte is a diploid structure surrounded by single layer of follicular through mitosis and differentiation. Secondary oocyte is a hapoid structure and is surrounded by a few layer of granular cells and theca. It is formed from primary oocyte after it undergoes first meiotic division.
Question 12.
What is the significance of ampullary-isthmic junction in the female reproductive tract?
Answer:
Ampullary-isthmic junction of oviduct is a site for fertilisation.
Question 13.
How does zona pellucida of ovum help in preventing polyspermy?
Answer:
During fertilisation, a sperm comes in contact with zona pellucida layer of ovum and induces changes in the membrane known as cortical reaction. This blocks the entry of additional sperms (polyspermy) and maintains monospermy.
Question 14.
Mention the importance of LH surge during menstrual cycle.
Answer:
Rapid secretion of LH leading to its maximum level during mid cycle is known as LH surge. It induces rupture of Graafian follicle and release of ovum (ovulation).
Question 15.
Which type of cell division forms spermatids from the secondary spermatocytes?
Answer:
Secondary spermatocytes undergo meiosis II to form spermatids. Secondary spermatocytes and spermatid both are haploid and this meiosis II is known as equational division.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
A human female experiences two major changes, menarche and menopause during her life. Mention the significance of both the events.
Answer:
The first menstrual cycle in females is known as menarche. It indicates the attainment of sexual maturity and puberty stage in females. It signifies the maturation and readiness of the female reproductive system for child bearing. It occurs usually at the age of 10-14 years.Menopause is the period of end of cyclic change in females. It indicates the end of reproductive cycle or fertile period in females. It occurs between 45-55 years of age.
Question 2.
(a) How many spermatozoa are formed from one secondary spermatocyte?
(b) Where does the first cleavage division of zygote take place?
Answer:
(a) A secondary spermatocyte gives rise to two spermatids, which get transformed into two spermatozoa.
(b) First cleavage division of zygote takes place in Fallopian tubes of females.
Question 3.
Corpus luteum in pregnancy has a long life. However, if fertilisation does not take place, it remains active only for 10-12 days. Explain.
Answer:
Zygote formed after fertilisation gets implanted in the inner lining of uterus, called endometrium. Neural signals are conducted to hypothalamus to sustain LH secretion. This helps in maintaining corpus luteum and continue the secretion of progesterone during gestation period. But when fertilisation does not take place, neural signals are not sent to hypothalamus. As a result corpus luteum starts degenerating and can stay alive only for 10-12 days.
Question 4.
What is foetal ejection reflex? Explain how it leads to parturition?
Answer:
Foetal ejection reflex are the uterine contractions induced by fully developed foetus and placenta which signals for parturition.
This stimulates the posterior pituitary of the mother to release oxytocin. Oxytocin causes stronger uterine contractions of smooth muscles of myometrium called labour pains, which further stimulate more secretion of oxytocin. The stimulatory reflex continues resulting in stronger and stronger contractions and leading to expulsion of the baby (parturition) through birth canal.
Question 5.
Except endocrine function, what are the other functions of placenta?
Answer:
Functions of placenta other than endocrine functions are:
- Nutritive organ – Food materials pass from the mother’s blood into the foetal blood through the placenta.
- Digestive organ – The trophoblast of the placenta digests (breaks down) proteins before passing them into the foetal blood.
- Respiratory organ – Oxygen diffuses from the maternal blood into the foetal blood through the placenta. Carbon dioxide diffuses from the foetal blood into the maternal blood also through the placenta for elimination by the mother’s lungs. Foetal haemoglobin has a greater affinity for oxygen than adult haemoglobin.
- Excretory organ – Nitrogenous wastes, such as urea, pass from the foetal blood into the maternal blood via placenta for elimination by mother’s kidneys.
- Storage organ – The placenta stores glycogen for the foetus before liver is formed.
- Barrier – Placenta serves as an efficient barrier and allows those materials to pass into the foetal blood that are necessary.
Question 6.
Why doctors recommend breast feeding during initial period of infant growth?
Answer:
Human milk consists of water, minerals, fats, proteins and sugar necessary for development of the child. The milk produced’ during initial days of lactation is called colostrum. It is rich in proteins (lactalbumin and lactoprotein) and various other nutrients. It also contains certain antibodies (IgA), which provide passive immunity to the baby.
Question 7.
What are the events that take place in the ovary and uterus during follicular phase of the menstrual cycle.
Answer:
(1) Changes inside the ovary during follicular phase :-
- Primary follicle gets transformed into Graafian follicle.
- Increase in level of estrogen
(2) Changes in uterus during follicular phase :-
- Proliferation of endometrium.
- Endometrium becomes highly vascular and glandular.
Question 8.
Given is a flow chart showing ovarian changes during menstrual cycle. Fill in the spaces giving the name of the hormones responsible for events shown.
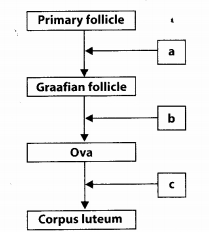
Answer:
a – FSH and LH
b – LH
c – Progesterone
Question 9.
Give a schematic labelled diagram to represent oogenesis (without descriptions).
Answer:
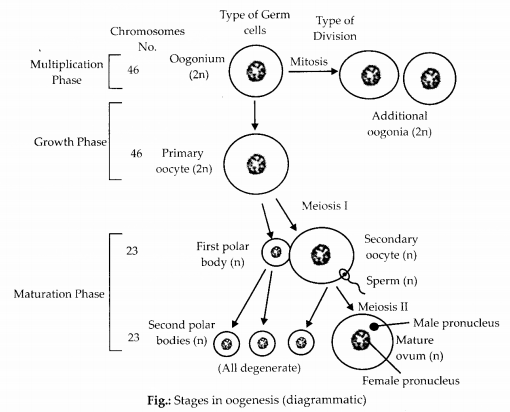
Question 10.
What are the changes in the oogonia during the transition of a primary follicle to Graafian follicle?
Answer:
Oogonia divide by mitosis forming primary oocyte which then gets surrounded by a layer of granulosa cells to form primary follicle. The primary follicles are surrounded by more layers of granulosa cells called secondary follicles.The secondary follicle soon changes into a tertiary follicle which is characterised by a fluid filled cavity called follicular antrum. The tertiary follicle is further converted into mature follicle or Graafian follicle. The formation of Graafian follicle through various stages is called folliculogenesis.
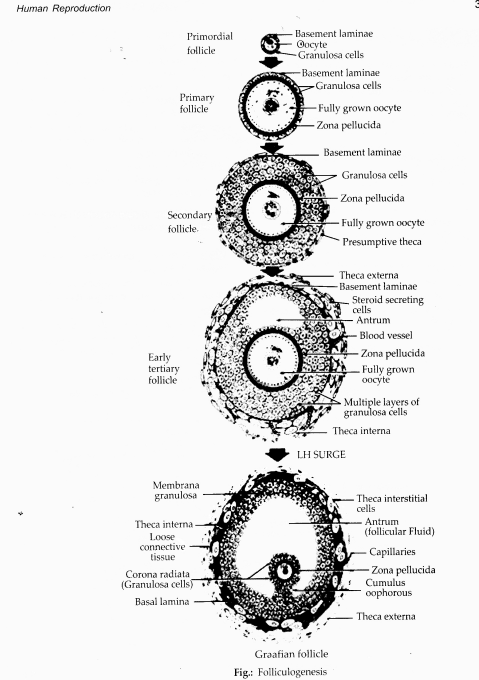
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What role does pituitary gonadotropins play during follicular and ovulatory phases of menstrual cycle? Explain the shifts in steroidal secretions.
Answer:
The menstrual cycle consists of four phases: menstrual phase, follicular phase (proliferative phase), ovulatory phase and secretory phase. Hormonal control during follicular phase:
- FSH from pituitary transforms the primary follicle into Graafian follicle.
- FSH also stimulates Graafian follicular cells to secrete estrogen.
- Estrogen causes proliferation of endometrium of the uterine wall.
Hormonal control during ovulatory phase :
- Pituitary glands are stimulated by estrogen to release LH.
- LH surge (maximum level of LH) causes ovulation from the ovary on 14th day of menstruation cycle. LH also induces transformation of Graafian follicle into corpus luteum, inside the ovary. LH stimulates corpus luteum to secrete progesterone to help implantation,placentation, and maintenance of pregnancy.
- In menstrual phase, there is reduction of progesterone and estrogen. Gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) stimulates the release of FSH and LH. FSH stimulates the ovarian follicles to produce estrogens during proliferative phase. LH stimulates the ovulation in ovulatory phase.
- LH develops corpus luteum which causes increased production of progesterone in secretory phase.
Question 2.
Meiotic division during oogenesis is different from that in spermatogenesis. Explain how and why?
Answer:
Primary spermatocyte divides by meiosis I to form two secondary spermatocytes. Primary oocyte undergoes meiosis I to form one secondary oocyte and one polar body.
Secondary spermatocyte divides by meiosis II to produce two spermatids. Secondary oocyte divides by meiosis II to form one ovum and one polar body.
A spermatocyte forms four spermatozoa. An oocyte forms only one egg or ovum. Unequal cell divisions during oogenesis, makes the ovum much larger than the other three polar bodies. Ovum has more cytoplasm and more organelles, it has a better chances of surviving. The male makes million of tiny sperms while, the female makes one egg per month because the sperms have to search for the eggs and only a few succeed in this task.
Question 3.
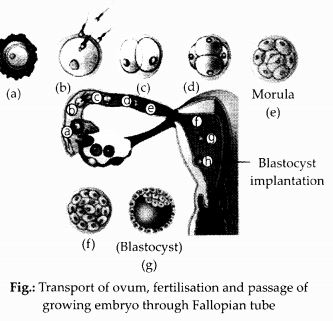
The zygote passes through several developmental stages till implantation. Describe each stage briefly with suitable diagrams.
Answer:
- The zygote moves from isthmus to uterus and undergo mitotic divisions called cleavage divisions.
- It forms 2, 4, 6, 8,16 daughter cells, called blastomeres.
- The embryo with 8-16 blastomeres is called morula.
- The morula continues to get transformed into blastocyst.
- The blastomeres in the blastocyst are arranged into an outer layer called trophoblast, and an inner group of cells attached to trophoblast called inner cell mass.
- The trophoblast layer gets attached to the endometrium and inner cell mass gets differentiated as the embryo.
- After attachment uterine cells divide rapidly and cover the blastocyst.
- As a result the blastocyst becomes embedded in the endometrium of the uterus.
- This is known as implantation, and it leads to pregnancy.
Question 4.
Draw a neat diagram of thefemale reproductive system and label the parts associated with the following (a) production of gamete, (b) site of fertilisation(c) site of implantation and, (d) birth canal.
Answer:
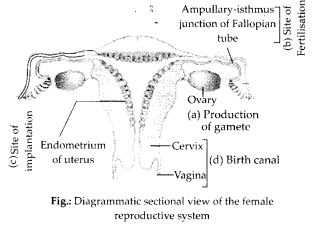
Question 5.
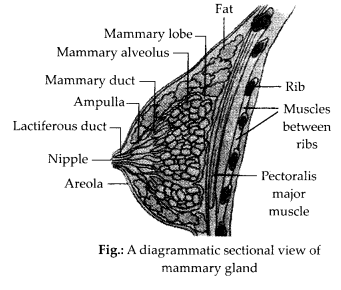
With a suitable diagram, describe the organisation of mammary gland.
Answer:
Mammary glands are paired structures consisting of glandular tissue, the fibrous tissue and variable amount of fat. They are compound tubulo-alveolar modified sweat glands. The glandular tissue of breast consists of about 15-20 lobes of milk glands. Each lobe is formed of many lobules containing cluster of cells called alveoli. The cells of alveoli secrete milk, which is stored in the lumen (cavities) of alveoli. The alveoli open into mammary tubules, the tubules of each lobe join to form a mammary duct. Several mammary ducts join to form a wider mammary ampulla, which is connected to lactiferous duct, through which milk is sucked out. Mammary glands are functional in females and vestigial in males. Breasts in females are small sized upto puberty. The size increases after puberty under stimulation of estrogen. It further increases during pregnancy and after child birth under the stimulation of prolactin and progesterone.
We hope the NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Biology chapter 3 Human Reproduction help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Biology chapter 3 Human Reproduction, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.