NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 11 Transport in Plants
These Solutions are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 11 Transport in Plants.
Question 1.
What are the factors affecting the rate of diffusion?
Solution:
Diffusion rates are affected by the gradient of concentration, the permeability of the membrane separating them, temperature, and pressure.
Question 2.
What are porins? What role do they play in diffusion?
Solution:
Porins are proteins that form huge pores in outer membranes of plastids, mitochondria and some bacteria, allowing molecules upto the size of small proteins to pass through. Thus porins facilitate diffusion.
Question 3.
Describe the role played by protein pumps during active transport in plants.
Solution:
Active transport uses energy to pump molecules against a concentration gradient. Active transport is carried out by membrane-proteins. Hence different proteins in the membrane play a major role in both active as well as passive transport. Pumps are proteins that use energy to carry substances across the cell membrane.
This pump can transport substances from a low concentration to a high concentration. The transport rate reaches a maximum when all the protein transporters are being used or are saturated. Like enzymes, the carrier protein is very specific in what it carries across the membrane. These proteins are sensitive to inhibitors that react with protein side chains.
Question 4.
Explain why pure water has maximum water potential?
Solution:
Water molecules possess kinetic energy. In liquid and gaseous form they are in random motion that is both rapid and constant. The greater the concentration of water in a system, the greater is its kinetic energy or water potential. Hence, it is obvious that pure water will have the greatest water potential.
Question 5.
Differentiate between the following:
(a) Diffusion and Osmosis
(b) Transpiration and Evaporation
(c) Osmotic Pressure and Osmotic Potential
(d) Imbibition and Diffusion
(e) Apoplast and Symplast pathways of movement of water in plants
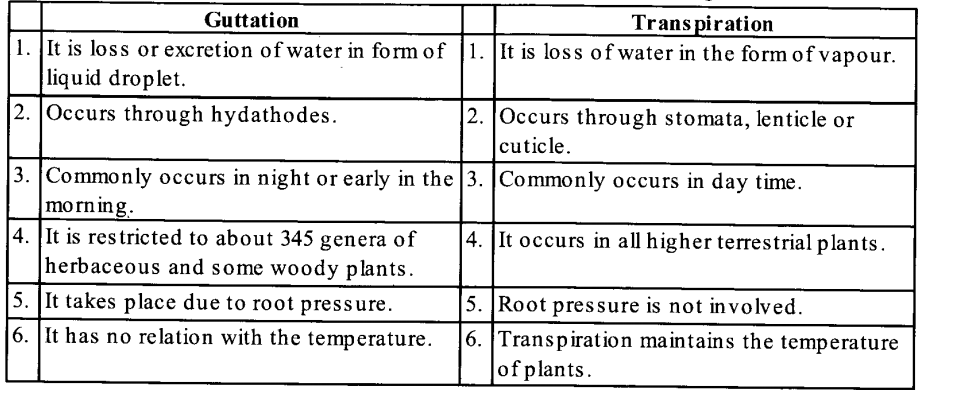
(f) Guttation and Transpiration
Solution:
(a) The differences between diffusion and osmosis are as following:
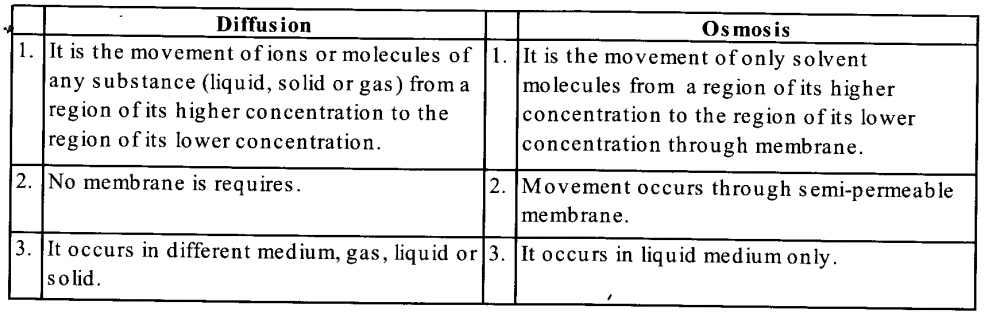
(b) The differences between transpiration and evaporation are as following:
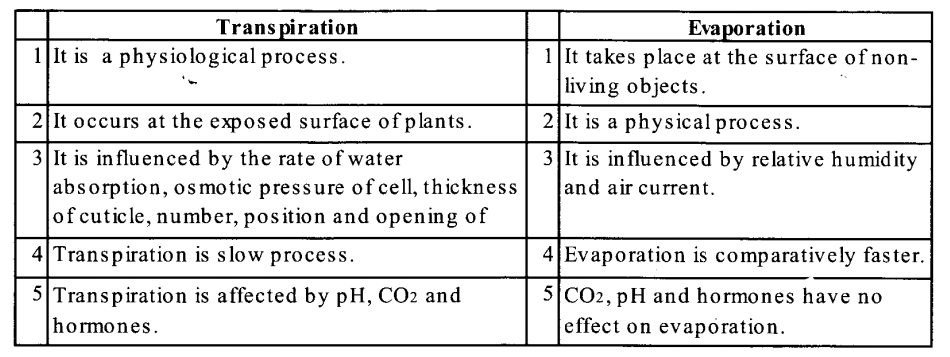
(c) The main differences between osmotic pressure and osmotic potential are as following:
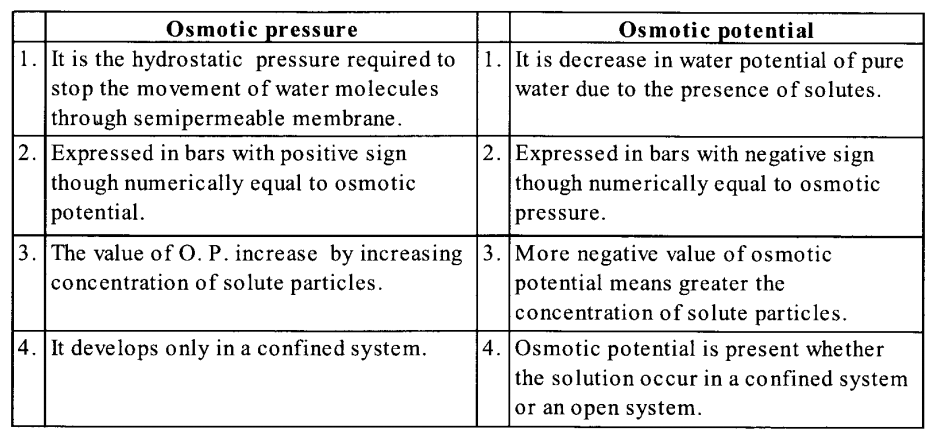
(d) The main differences between imbibition and diffusion are as following:
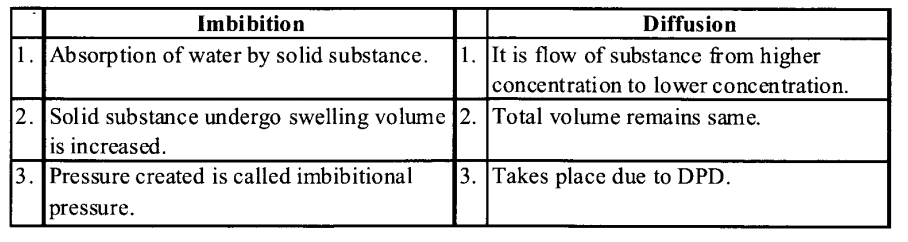
(e) The main differences between apoplast and symplast pathways of movement of water in plants are as following :

(f) The main differences between guttation and transpiration are as following :
Question 6.
Briefly describe water potential. What are the factors affecting it?
Solution:
Water potential: Free energy per mole of water molecule is called water potential. It is represented by Greek letter ‘φ’ (Psi). Water potential of pure water is zero and addition of solute, decreases its free energy or water “‘potential.
Factors affecting water potential are as following:
(i) Matric potential (φm) causes by adsorbent or colloidal particles (always negative and almost negligible).
(ii) Solute potential (φs) caused by presence of solute particles (decreases the water potential).
(iii) Pressure potential (φp) caused by entry or exit of water (increases the water potential).
φw= φp + φs + φm
Question 7.
What happens when a pressure greater than the atmospheric pressure is applied to pure water or a solution?
Solution:
If a pressure greater than atmospheric pressure is applied to pure water or a solution, its water potential increases. It is equivalent to pumping water from one place to another.
Question 8.
(a) With the help of well-labelled diagrams, describe the process of plasmolysis in plants, giving appropriate examples.
(b) Explain what will happen to a plant cell if it is kept in a solution having higher water potential.
Solution:
(a) Plasmolysis is the shrinkage of the protoplast of a cell from its cell wall under the influence of a hypertonic solution (solution of higher concentration).
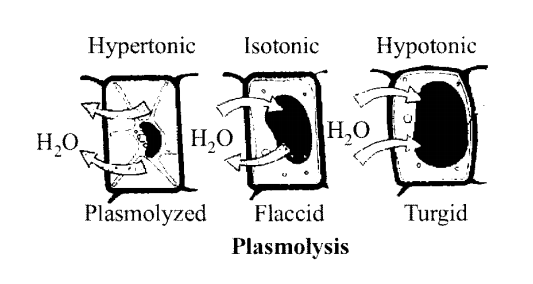
(b) The process of plasmolysis is usually reversible. When the cells are placed in hypotonic solution (solution with low concentration), water diffuses into the cell causing the cytoplasm to swell up. The swelling of shrunken protoplast is called as deplasmolysis.
Question 9.
How is the mycorrhizal association helpful in the absorption of water and mineral in plants?
Solution:
Some plants have additional structures associated with them that help in water (and mineral) absorption. A mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association of a fungus with a root system. The fungal filaments form a network around the young root or they penetrate the root cells. The hyphae have a very large surface area that absorbs mineral ions and water from the soil from a much larger volume of soil that perhaps a root cannot do.
The fungus provides minerals and water to the roots, in turn, the roots provide sugars and N-containing compounds to the mycorrhizae. Some plants have an obligate association with the mycorrhizae. For example, Pinus seeds cannot germinate and establish without the presence of mycorrhizae.
Question 10.
What role does root pressure play in water movement in plants?
Solution:
As various ions from the soil are actively transported into the vascular tissues of the roots, water flows and increases the pressure inside the xylem. This positive pressure is called root pressure and can be responsible for pushing up water to small heights in the stem.
Root pressure can only provide a modest push in the overall process of water transport. The greatest contribution is to re-establish the continuous chains of water molecules in the xylem which often break under the enormous tensions created by transpiration.
Question 11.
Describe the transpiration pull model of water transport in plants. What are the factors influencing transpiration? How is it useful to plants?
Solution:
Transpiration pull theory: The theory was put forward by Dixon and Jolly.
The main features of the theory are :
(i) There is a continuous column of water (present in the tracheary element) from the root through the stem and into the leaves.
(ii) Water molecules attached to one another, by cohesion force, adhesion force (between their walls and water molecules), and surface tension.
(iii) The water in the tracheary element would come under tension, due to transpiration also called transpiration pull.
Factor affecting transpiration: External factors e.g. atmospheric pressure, temperature, humidity, CO2, sunlight, wind velocity, etc. The thickness of cuticle, number, position and closing and opening of stomata, pH, and hormones are internal factors which affect transpiration. Significance of transpiration:
- Ascent of sap
- Removal of the excess water
- Cooling effect
- Distribution of minerals.
- Transpiration supplies water for photosynthesis.
Question 12.
Discuss the factors responsible for the ascent of xylem sap in plants.
Solution:
The ascent of xylem sap is supported by the following factors.
(i) Root pressure (positive pressure that develops in the xylem sap of root).
(ii) Cohesion (adhesion of water molecules due to hydrogen bonding).
(iii) Adhesion (force between tracheary wall and water molecule).
(iv) Transpiration pull (tension develops due to transpiration) is the main cause of ascent of xylem sap.
Question 13.
What essential role does the root endodermis play during mineral absorption in plants?
Solution:
Water flowing through apoplast contains minerals useful to plants and also toxins. Endodermal cells have many transport proteins embedded in their plasma membrane; they let some solutes cross the membrane, but not others. Transport proteins of endodermal cells are control points, where a plant adjusts the quantity and types of solutes that reach the xylem.
Question 14.
Explain why xylem transport is unidirectional and phloem transport bidirectional.
Solution:
- The plant part which synthesise the food, i.e. leaf known as source and part that needs or stores the food called as sink.
- Food, primarily sucrose, is transported by vasculai tissue phloem, from a source to a sink. But depending on season or plants need, the source sink may be reversed.
- Sugar stored in roots may be mobilised to become a source of food source in early spring when buds of trees require energy for their growth and development and act as sink.
- Since the source – sink relationship is bidirection in phloem while in xylem it is unidirection.
Question 15.
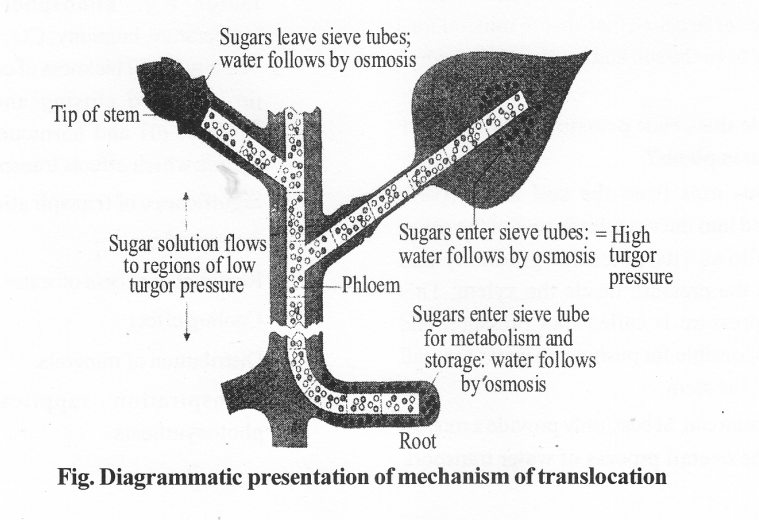
Explain pressure flow hypothesis of translocation of sugars in plants.
Solution:
Mass flow or Pressure Flow Flypothesis : It was put forward by Munch (1927,1930).
- According to this hypothesis organic substance move from region of high osmotic pressure to low osmotic pressure due to turgor pressure.
- A high osmotic concentration is present in source e.g. mesophyll cells (due to photosynthesis).
- Sugar present in them passed into sieve tube therefore high osmotic concentration develops and it absorbs water from xylem and develop a high turgor pressure. It causes flow of sugar towards area of low turgor pressure or sink.
Question 16.
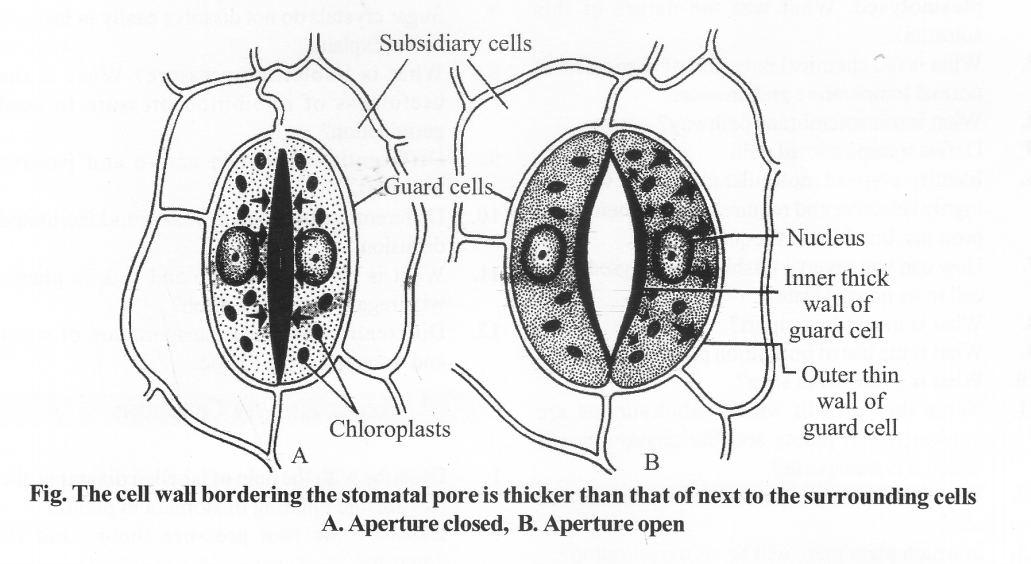
What causes the opening and closing of guard cells of stomata during transpiration?
Solution:
- The opening and closing of stomata depend upon the turgid or flaccid state of the guard cells.
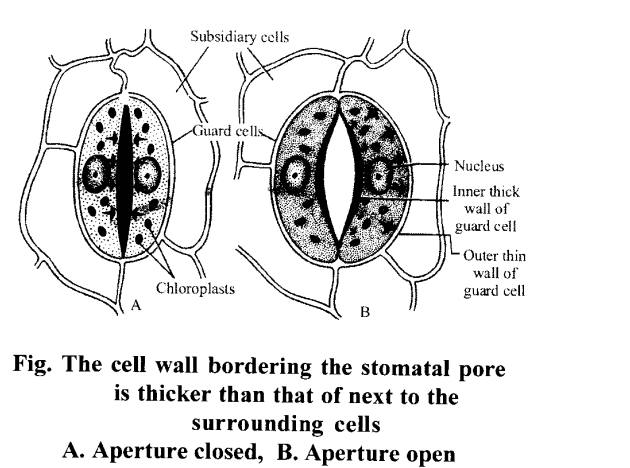
- The inner wall of guard cells (towards pore) is thick and outer wall (towards other epidermal cells) is thin.
- When the turgor pressure of the guard cells in increased the outer thinner wall of the guard cell is pushed out (towards the periphery) thus pulling the inner thicker wall leading to the opening of stomatal pore.
- When the guard cells are in a flaccid state the outer thinner wall of guard cells returns to original position (moves towards pore) due to which tension on the inner wall is released and stomatal aperture gets closed.
VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
Question 1.
What fraction of soil water is readily available to plants?
Solution:
Capillary water.
Question 2.
What is a hypertonic solution? (Oct. 87, M.Q.P., Apr. 2000)
Solution:
The external solution which has a concentration higher than that of the cell sap is called a Hypertonic solution.
Question 3.
What is the chemical potential of pure water at normal temperature and pressure?
Solution:
Zero.
Question 4.
What is transmembrane pathway?
Solution:
The movement of water through the cell membrane is called transmembrane pathway or symplast pathway.
Question 5.
What happens to the plant cell when it is plasmolyzed? (Apr. 95)
Solution:
becomes flaccid
Question 6.
Identify a type of molecular movement which is highly selective and requires special membrane proteins, but does not require energy.
Solution:
Facilitated diffusion.
Question 7.
How can you revert a freshly plasmolysed plant cell to its normal state?
Solution:
By placing it in aqueous solution.
Question 8.
What is meant by uniport?
Solution:
A molecule moves across the membrane independent of other molecule called as uniport.
Question 9.
What is the use of imbibition pressure to plants?
Solution:
Responsible for the seedling to emerge out of the soil.
Question 10.
What is a casparian strip?
Solution:
Casparian strip is band of suberin on the tangential and radial walls of endodermal cells.
Question 11.
Name the form in which cabohydrates are transported in plants and the tissue through which it is transported.
Solution:
Sucrose, phloem.
Question 12.
What is the pressure potential of a plasmolysed cell?
Solution:
Pressure potential of a plasmolysed cell is negative.
Question 13.
Give reason:
Excessive use of chemical fertilizers results in wilting of plants. (June 2009)
Solution:
Excessive use of fertilizers increases the solute concentration of the soil solution causing exosmosis resulting in the wilting of plants.
Question 14.
If water enters a cell what is the pressure exerted by its swollen protoplasts?
Solution:
The pressure exerted will be turgor pressure.
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
Question 1.
List any four mechanisms that contribute to the ascent of sap in tall trees.
Solution:
Mechanisms that contribute to the ascent of sap in tall trees are :
- Adhesion
- Cohesion
- Transpirational pull
- Root pressure.
Question 2.
Mention two advantage of transpiration.
Solution:
Advantages of transpiration:
(1) It helps in mineral absorption and ascent of sap.
(2) Transpiration, by evaporating of water causes a cooling effect of plant body.
Question 3.
How do rise in temperature and wind velocity affect transpiration? Write any three adaptations shown by plants to reduce transpiration.
Solution:
Rise in temperature, wind velocity increases the rate of transpiration.
Three adaptations shown by plants to reduce transpiration are:
(a) leaves with thick cuticle
(b) sunken stomata
(c) modification of leaves into scales or spines and stem into phylloclades.
Question 4.
What is meant by apoplast pathway? Why does it occur in cortex and not in endodermis?
Solution:
The movement of water exclusively through cell wall without crossing cell membrane, is called apoplast pathway. It occurs in cortex due to the absence of casparian strip and presence of loosely packed cells. It does not occur in endodermis due to the presence of suberin in casparian strip.
Question 5.
What is the significance of osmosis?
Solution:
Significance of osmosis:
(1) Osmosis is important in the absorption of water by plants.
(2) Helps in cell to cell movement of water.
(3) Provides rigidity to the plant organs.
(4) Helps in opening and closing of stomata.
Question 6.
Describe the apoplastic and symplastic movements of water in plants.
Solution:
Apoplastic movement of water occurs exclusively through the non-living cell wall without crossing any membrane. Symplastic movement of water occurs from one cell to the other through plasmodesmata it passes across membrane and i.e. living components.
Question 7.
Sugar crystals do not dissolve easily in ice cold water. Explain.
Solution:
Rate of diffusion is increased when temperature increase. So, sugar crystal do not dissolve easily in ice cold water.etrads of homo logous chromosomes and crossing as the genetic material exchange takes place. Thus this stage is marked with genetic recombination.
Question 8.
What is imbibition pressure? What is the usefulness of imbibition pressure to seed germination?
Solution:
Imbibition pressure is the pressure developed in an adsorbent due to diffusion of water into it.
This pressure makes the seedlings to emerge above the ground during seed germination.
Question 9.
Differentiate between active and passive transport.
Solution:
The main difference between active transport and passive transport are :
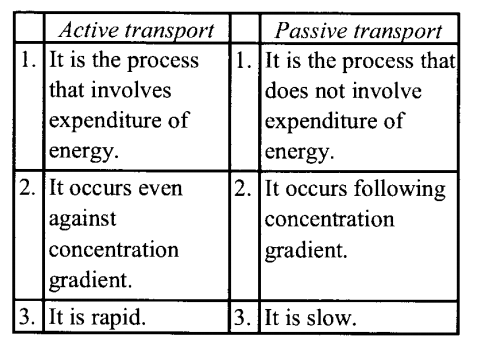
Question 10.
Differentiate between diffusion and facilitated diffusion.
Solution:
The main difference between diffusion and facilitated diffusion are :
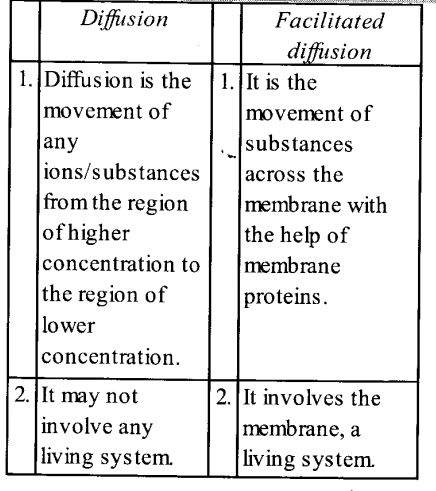
Question 11.
What is meant by source and sink in plants, with regard to translocation?
Solution:
Source : Source is the part of the plant which synthesises the food, they are the leaves.
Sink: Sink is the part of the plant that needs or stores the food like roots, tubers, any storage organ etc.
Question 12.
Differentiate between transportation of water and translocation of Food.
Solution:
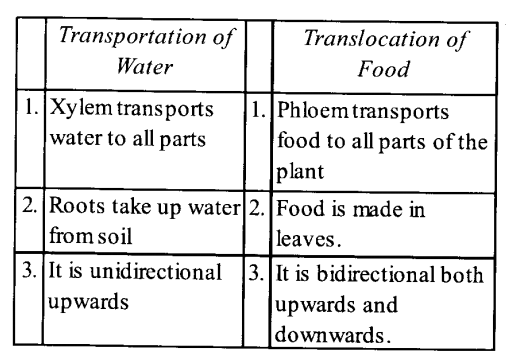
LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
Question 1.
Describe with the help of labelled diagrams, the closing and opening of stomata in plants.
Solution:
- Stomata are minute openings formed in the epidermis of leaves, stem and in (some cases) even flowers.
- Each stomata contains pore surrounded by two guard cells. The guard cells are joined at both ends but separate in the mid-region of their length.
- Stomata are mostly present on the lower epidermis of the leaf. The open stomata account for diffusion of water vapour through them.
- During the day, the cell- sap concentration becomes high due to accumulation of sugar as a result of photosynthesis.
- This results into endosmosis and tl\e water is withdrawn into guard cells from the neighboring cells.
- This makes the guard cells turgid and stomata open. If the availability of water is reduced, the guard cells lose their turgidity and they become flaccid by exosmosis of water from guard cells.
- This leads to the closing of stomata and transpiration stops.
Question 2.
Describe the root pressure theory and its demerits.
Solution:
Root pressure theory : The theory was put forward by Priestley (1916). Root pressure refers to positive hydrostatic pressure which is develops in xylem sap, when rate of water absorption is more than the rate of transpiration and as a result of which water is pushed up in tracheary element of root.
Demerits of root pressure concept :
(1) Magnitude of root pressure is maximum upto 2 atmosphere which can raise water upto 64ft. only. It can’t drive water in tall trees (300-400 feet) there is need of 20 atmosphere root pressure.
(2) No root pressure in conifers.
(3) Root pressure is low in summer when transpiration is high and high in spring when transpiration is low
(4) Root pressure is not seen in rapidly transpiring plants.
Question 3.
Discuss the factor affecting the water absorption.
Solution:
The factor affecting the water absorption are :
(1) Temperature : Optimum temperature for
absorption is 20-30°C. Absorption decrease at low temperature by decreasing permeability, retarding in growth of root and availability of water and by increasing viscosity of water.
(2) Concentration of soil solution: Absorption decreases with increase in concentration of soil solution, e.g. Halophytes (Rhizophora) are able to grow in swamps with high salt cont-entration because their cell sap concentration is also high.
(3) Soil aeration : Flooding of fields reduces soil air (02). Hence metabolic processes and absorption are also reduced.
(4) Increase in C02 : High C02 concentration lowers the rate of respiration and thus influence metabolic processes. These result low water absorption.
(5) Available soil water : Maximum absorption occurs when the available soil water is in the range of field capacity and permanent wilting coefficient.
(6) Root growth : Deep rooted plant absorb more water. Older roots are suberized and absorb slowly.
Question 4.
Differentiate the following
(a) Simple diffusion and active transport
(b) Turgid cell and flaccid cell
(c) Isotonic solution and hypotonic solution
Solution:
(a) The main difference between simple diffusion and active transport are :
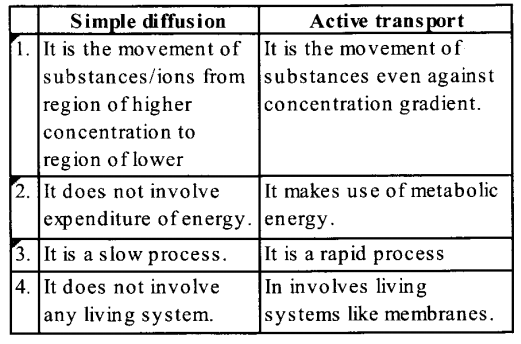
(b) The main difference between the turgid cell and flaccid cell are :
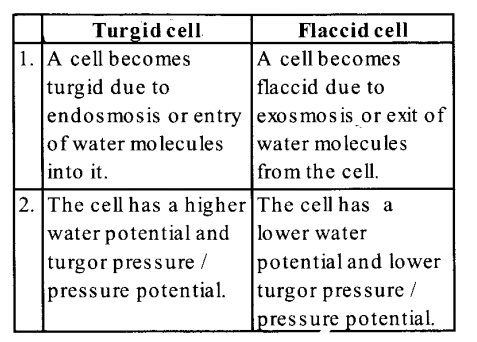
(c) The main difference between isotonic solution and hypotonic solution are :
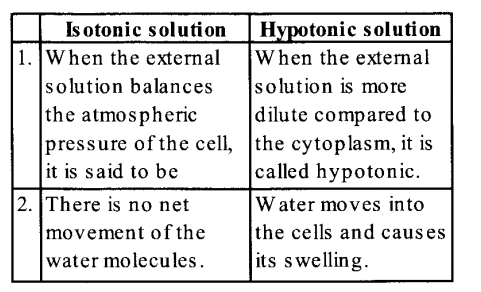
Question 5.
What are the properties that favours the upward movement water through xylem?
Solution:
The properties are:
(1) Cohesion : mutual attraction between water molecules
(2) Adhesion : attraction of water molecules to polar surfaces
(3)Surface Tension : water molecules are attracted to each other and give water high tensile strength i.e., an ability to resist a pulling force
(4) Capillarity : ability to rise in their tubes. These are also related to the transpiration pull. With this pull water comes to leaves for photosynthesis as well.
We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology at Work Chapter 11 Transport in Plants, help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology at Work Chapter 11 Transport in Plants, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.