NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 15 Communication Systems
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 15 Communication Systems are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics. Here we have given. NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 15 Communication Systems.
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 12 |
| Subject | Physics |
| Chapter | Chapter 15 |
| Chapter Name | Communication Systems |
| Number of Questions Solved | 8 |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
Question 1.
At which of the following frequency/frequencies the communication will not be reliable for a receiver situated beyond the horizon:
(a) 10 kHz
(b) 10 MHz
(c) 1 GHz
(d) 1000 GHz
Answer:
(b) is correct. Here (c) and (d) frequencies have high penetration power so the earth will absorb them. Radiation (a) of 10 kHz will suffer from the problem of the size of the antenna.
Question 2.
Frequencies in the UHF range normally propagate by means of
(a) ground waves
(b) sky waves
(c) surface waves
(d) space waves.
Answer:
(d) space waves.
Question 3.
Digital signals (i) do not provide a continuous set of values, (ii) represent values as discrete steps, (Hi) can utilize the only binary system, and (iv) can utilize decimal as well as a binary system. Which of the following options is true :
(a) Only (i) and (ii).
(b) Only (ii) and (iii).
(c) Only (i), (ii) and (iii), but not (iv).
(d) AH the above (i) to (iv).
Answer:
(c) is correct because the decimal system is concerned with continuous values (i) to (iii).
Question 4.
Is it necessary for a transmitting antenna to be at the same height as that of the receiving antenna for line-of-sight communication? A TV transmitting antenna is 81 m tall. How much service area can it cover if the receiving antenna is at the ground level?
Answer:
For line-of-sight communication, it is necessary that the transmitting antenna and receiving antenna should be eye to eye but it is not necessary that they should be at the same height.

Question 5.
A carrier wave of peak voltage 12 V is used to transmit a message signal. What should be the peak voltage of the modulating signal in order to have a modulation index of 75%?
Answer:
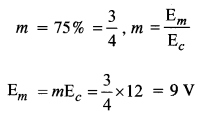
Question 6.
A modulation signal is a square wave as shown in the figure. The carrier wave is given by
C(t) = 2 sin(8πt) V
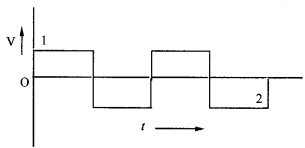
(a) Sketch the amplitude modulated waveform.
(b) What is the modulation index?
Answer:
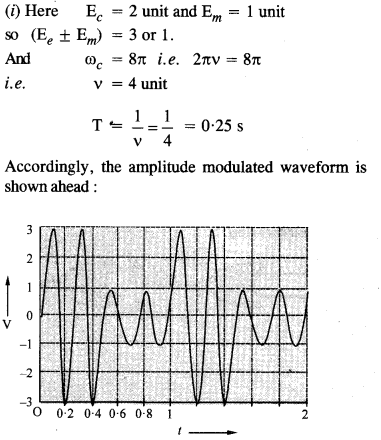
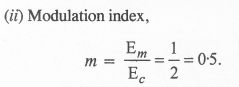
Accordingly, the amplitude modulated waveform is shown ahead:
Question 7.
For an amplitude modulated wave, the maximum amplitude is found to be 10 V while the minimum amplitude is found to be 2 V. Determine the modulation index μ. What would be the value of μ if the minimum amplitude is zero V?
Answer:

Question 8.
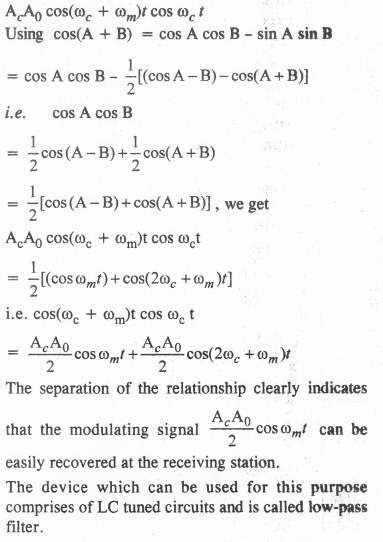
Show that if a device is available which can multiply two signals, then it is possible to recover the modulating signal at the receiver station.
Answer:
Let there be two signals represented by
Ac cos ωct and A0 cos(ωc + ωm)t where Ac is the
amplitude, ωc is the angular frequency of a carrier wave at the receiving end and A0 is the amplitude, (ωc+ ωm) is the angular velocity of the modulated wave.
Multiplying these signals, we get
We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 15 Communication Systems, help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 15 Communication Systems, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.