NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants.
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 7 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 12 |
| Chapter Name | Reproduction in Plants |
| Number of Questions Solved | 10 |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks:
(a) Production of new individuals from the vegetative part of the parent is called ……..
(b) A flower may have either male or female reproductive parts. Such a flower is called ………
(c) The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same or of another flower of the same kind is known as ………
(d) The fusion of male and female gametes is termed as ……………..
(e) Seed dispersal takes place by means of …….., ………. and ………..
Answer:
(a) vegetative propagation
(b) unisexual flower
(c) pollination
(d) fertilisation
(e) wind, water, animals.
Question 2.
Describe the different methods of asexual reproduction. Give examples.
Answer:
Various methods of asexual reproduction are:
(i) Vegetative propagation:
It is a type of asexual reproduction in which new plants are produced from roots, stems, leaves, and buds. Since reproduction takes place through the vegetative parts of the plant, it is known as vegetative propagation.
(ii) Budding:
Here, the small bulb-like projection coming out from, the yeast cell is called a bud, gradually grows and gets detached from the parent cell and forms an organism, e.g., yeast. The new yeast grows, matures, and produces more yeasts. If this process continues, a large number of yeasts are produced in a short time.
(iii) Fragmentation:
This type of reproduction is common in algae. These are slimy green patches in ponds, or in other stagnant water bodies. When water and nutrients are available algae grow and multiply rapidly by fragmentation An algae breaks up into two or more fragments. These fragments or pieces grow into new individuals. This process continues and they cover a large area in a short period of time.
(iv) Spore formation:
The fungi on a bread piece grow due to spores which are present in the air. When spores are released, they keep floating in the air. As they are very light, they can travel over long distances. The spores are asexual reproductive bodies. Each spore is covered by a hard protective coat to withstand unfavourable conditions such as high temperature and low humidity. So, they can survive for a long time. Under favourable conditions, a spore germinates and develops into a new individual. Plants such as moss and ferns also reproduce by means of spores.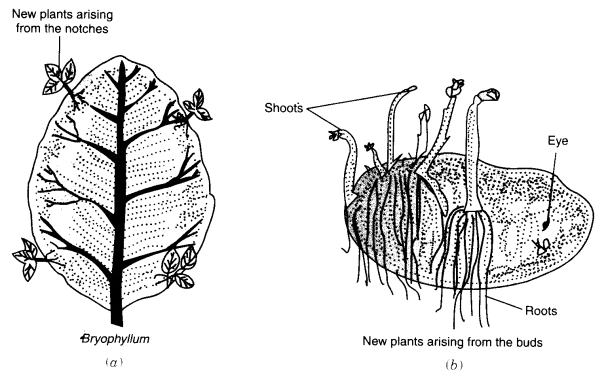
Fig. Vegetative propagation in (a) bryophyllum (by leaf) (b) potato (by the stem)
Question 3.
Explain what do you understand by sexual reproduction?
Answer:
In sexual reproduction, the male and the female gametes fuse to form a zygote. For sexual reproduction, one or two parents are required to produce two different gametes and ultimately after zygote formation, new individual forms.
Question 4.
State the main difference between sexual and asexual reproduction.
Answer:
| Sexual Reproduction | Asexual Reproduction |
| 1. New plants are obtained from seeds. | 1. Plants can give rise to new plants without seeds. |
| 2. Two parents are required to produce an individual. | 2. The new individual comes from a single parent. |
| 3. Takes place with the help of specialized sex cells. | 3. No sex cells are required. |
| 4. New individual has the characters of both the parents. | 4. Characters of the new individual are the same as that of the parent. |
Question 5.
Sketch the reproductive parts of a flower.
Answer:
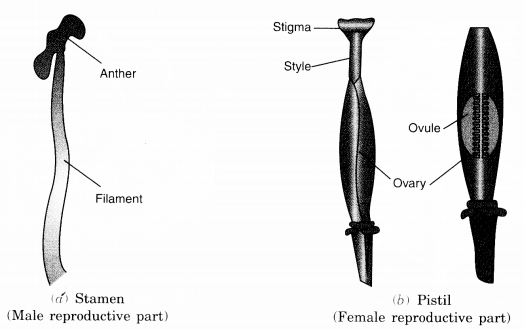
Fig. Reproductive parts of a flower
Question 6.
Explain the difference between self-pollination and cross-pollination.
Answer:
| Self – Pollination | Cross – Pollination |
| 1.In self-pollination, pollen grains of a flower reaches the stigma of the same flower. | 1.In cross-pollination, there is the transfer of pollen grains from the anthers of a flower to the stigma of another flower on a different plant of the same species. |
| 2. No pollinating agent is required. | 2. Pollinating agents like wind, air, or insects are required. |
| 3. Occurs only in bisexual flowers. | 3. Occurs in unisexual flower, under monoecious/dioecious condition. |
| 4. It does not lead to genetic variation in the progeny. | 4. It leads to genetic variation in the progeny. |
Question 7.
How does the process of fertilization take place in flowers?
Answer:
When the pollen grain reaches the stigma of the same species flower, it starts growing out into the pollen tube of the stigma. This tube continues to grow inside the style till it reaches the ovule. Male cells are released into the ovule for fertilization with the female egg cell and thus the zygote is formed. After this process of fertilization, the ovary develops into fruit and ovule into seeds.
Question 8.
Describe the various ways by which the seeds are dispersed.
Answer:
Seeds and fruits of plants are carried away in the following ways:
(i) Dispersion by the wind:
Winged seeds such as those of drumstick and maple, light seeds of grasses, or hairy seeds of aak CMadar) and hairy fruit of sunflower gets blown off with the wind to faraway places.
(ii) Dispersion by water:
Some seeds are dispersed by water. These fruits or seeds usually develop floating ability in the form of the spongy or fibrous outer coat as in coconut.
(iii) Dispersion by animals:
Some seeds are dispersed by animals, especially spiny seeds with hooks which get attached to the bodies of animals and are carried to distant places. Examples are Xanthium and Urena.
(iv) Dispersion by explosion:
Some seeds are dispersed when the fruits burst with sudden jerks. The seeds are scattered far from the parent plant. This happens in the case of castor and balsam.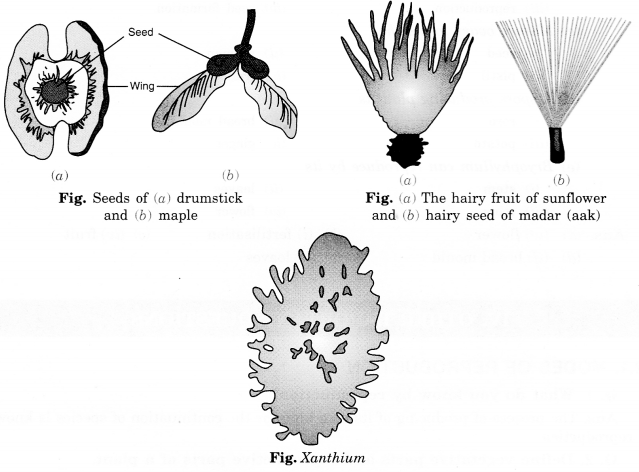
Question 9.
Match items in Column I with those in Column II:
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Bud | (i) Maple |
| (b) Eyes | (ii) Spirogyra |
| (c) Fragmentation | (iii) Yeast |
| (d) Wings | (iv) Bread mould |
| (e) Spores | (v) Potato |
| (vi) Rose |
Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Bud | (iii) Yeast |
| (b) Eyes | (v) Potato |
| (c) Fragmentation | (ii) Spirogyra |
| (d) Wings | (i) Maple |
| (e) Spores | (iv) Bread mould |
Question 10.
Tick (√) the correct answer :
(а) The reproductive part of a plant is the
(i) leaf
(ii) stem
(iii) root
(iv) flower
(b) The process of fusion of the male and the female gametes is called
(i) fertilisation
(ii) pollination
(iii) reproduction
(iv) seed formation
(c) Mature ovary forms the
(i) seed
(ii) stamen
(iii) pistil
(iv) fruit
(d) A spore producing plant is
(i) rose
(ii) bread mould
(iii) potato
(iv) ginger
(e) Bryophyllum can reproduce by its
(i) stem
(ii) leaves
(iii) roots
(iv) flower
Answer:
(a) (iv) flower
(b) (i) fertilisation
(c) (iv) fruit
(d) (ii) bread mould
(e) (ii) leaves
We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.