NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 18 Wastewater Story are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 18 Wastewater Story.
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 7 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 18 |
| Chapter Name | Wastewater Story |
| Number of Questions Solved | 12 |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 18 Wastewater Story
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks:
- Cleaning of water is a process of removing ……….
- Wastewater released by houses is called ……….
- Dried …….. is used as manure.
- Drains get blocked by …….. and ……
Answer:
- pollutants
- sewage
- sludge
- cooking oils and fats
Question 2.
What is sewage? Explain why it is harmful to discharge untreated sewage into rivers or seas?
Answer:
Sewage is wastewater released by homes, industries, hospitals, offices, and other users. It also includes rainwater that has run down the street during a storm or heavy rain. The water that washes off roads and rooftops carries harmful substances with it. Sewage is a liquid waste. Mostly, sewage contains water, which has dissolved and suspended impurities which are called contaminants. That is why it is harmful to discharge untreated sewage into rivers or seas.
Question 3.
Why should oils and fats be not released in the drain? Explain.
Answer:
Oils and fats should not be thrown down the drain. They get hard and block the pipes. In an open drain, the fats clog the soil pores reducing their effectiveness in filtering water.
Question 4.
Describe the steps involved in getting clarified water from wastewater.
Answer:
Following steps are involved in getting clarified water from wastewater:
(i) Firstly, wastewater is passed through bar screens. Large objects like rags, sticks, cans, plastic packets, napkins are removed.
(ii) Water then, goes to a grit and sand removal tank. The speed of the incoming wastewater is decreased to allow sand, grit, and pebbles to settle down
(iii) The water is then allowed to settle in a large tank which is sloped towards the middle. Solids like faeces settle at the bottom and are removed with a scraper. This is the sludge. A skimmer removes the floatable solids like oil and grease. Water so cleared is called clarified water. The sludge is transferred to a separate tank where it is decomposed by the anaerobic bacteria. The biogas produced in the process can be used as fuel or can be used to produce electricity.
(iv) Air is pumped into the clarified water to help aerobic bacteria to grow. Bacteria consume human waste, food waste, soaps, and other unwanted matter still remaining in clarified water. After several hours, the suspended microbes settle at the bottom of the tank as activated sludge. The water is then removed from the top. The activated sludge is about 97% water. The water is removed by sand drying beds or machines. Dried sludge is used as manure, returning organic matter and nutrients to the soil.
The treated water has a very low level of organic material and suspended matter. It is discharged into a sea, a river or into the ground. Nature cleans it up further. Sometimes it may be necessary to disinfect water with chemicals like chlorine and ozone before releasing it into the distribution system.
Question 5.
What is sludge? Explain how it is treated.
Answer:
Solids like faeces which settle at the bottom of the tank and are removed with a scraper are called sludge. The sludge is transferred to a separate tank where it is decomposed by the anaerobic bacteria. The biogas produced in the process can be used as fuel or can be used to produce electricity.
Question 6.
Untreated human excreta is a health hazard. Explain.
Answer:
Untreated human excreta is a health hazard. It may cause water pollution and soil pollution. Both the surface water and groundwater get polluted. Groundwater is a source of water for wells, tube-wells, springs, and many rivers. Thus, it becomes the most common route for water-borne diseases. They include cholera, typhoid, polio, hepatitis, and dysentery.
Question 7.
Name two chemicals used to disinfect water.
Answer:
- Chlorine
- Ozone
Question 8.
Explain the function of bar screens in a wastewater treatment plant.
Answer:
Wastewater is passed through bar screens for removal of large objects such as rags, sticks, cans, plastic packets, napkins, etc.
Question 9.
Explain the relationship between sanitation and disease.
Answer:
Sanitation is the hygienic means of promoting health through the prevention of hazards of wastes as well as the treatment and proper disposal of sewage wastewater.
Poor sanitation is a major cause of diseases worldwide and improving sanitation is known to have a significant beneficial impact on households and across communities. So poor sanitation and contaminated water is the cause of a large number of diseases.
Question 10.
Outline your role as an active citizen in relation to sanitation.
Answer:
We all have a role to play in keeping our environment clean and healthy. We must realize our responsibility in maintaining the water sources in a healthy state. Through good sanitation practices, we keep our environment clean and healthy. We should make people aware of the benefits of sanitation and help municipal corporations to cover all the open drains and remove disease-causing substances thrown in open.
Question 11.
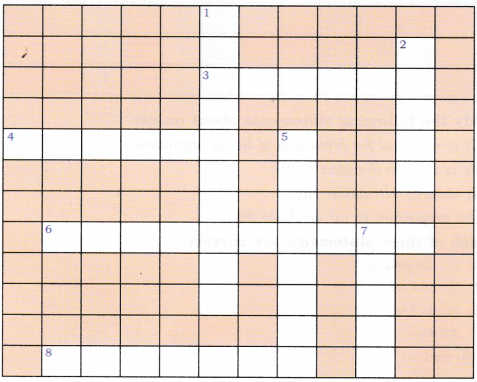
Here is a crossword puzzle. Good luck!
Across:
3. Liquid waste products
4. Solid waste extracted in sewage treatment fi. A word related to hygiene
8. Waste matter discharged from the human body.
Down:
1. Used water
2. A pipe carrying sewage
5. Microorganisms which cause cholera
7. A chemical to disinfect water
Answer:
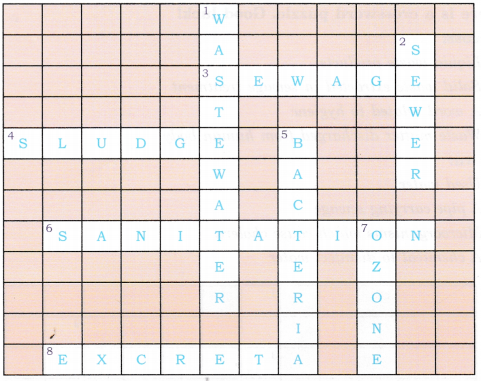
Across:
3. Sewage
4. Sludge
6. Sanitation
8. Excreta
Down:
1. Wastewater
2. Sewer
5. Bacteria
7. Ozone
Question 12.
Study the following statements about ozone:
(a) It is essential for the breathing of living organisms.
(b) It is used to disinfect water.
(c) It absorbs ultraviolet rays.
(d) Its proportion in the air is about 3%.
Which of these statements are correct?
(i) (a), (b) and (c)
(ii) (b) and (c)
(iii) (a) and (d)
(iv) All four
Answer:
(ii) (b) and (c)
We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 18 Wastewater Story help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 18 Wastewater Story, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.