Find free online Chemistry Topics covering a broad range of concepts from research institutes around the world.
Nitro Compounds
Nitro compounds are considered as the derivaties of hydrocarbons. If one of the hydrogen atom of hydrocarbon is replaced by the – NO2 group, the resultant organic compound is called a nitrocompound.
Classification of Nitrocompounds
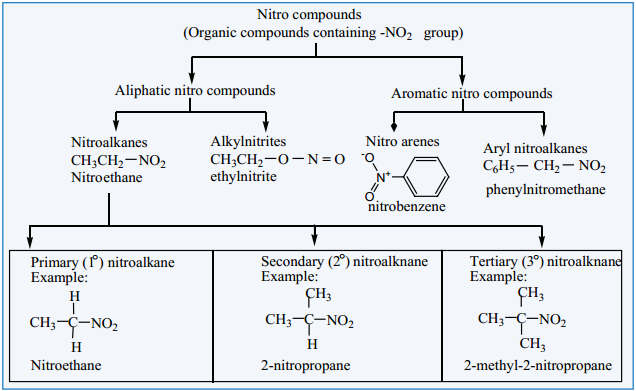
Nitroalkanes are represented by the formula, R-NO2 where R is an alkyl group (CnH2n+1-). Nitroalkanes are further classified into primary, secondary, tertiary nitroalkanes on the basis of type of carbon atom to which the nitro (-NO2) group is attached.
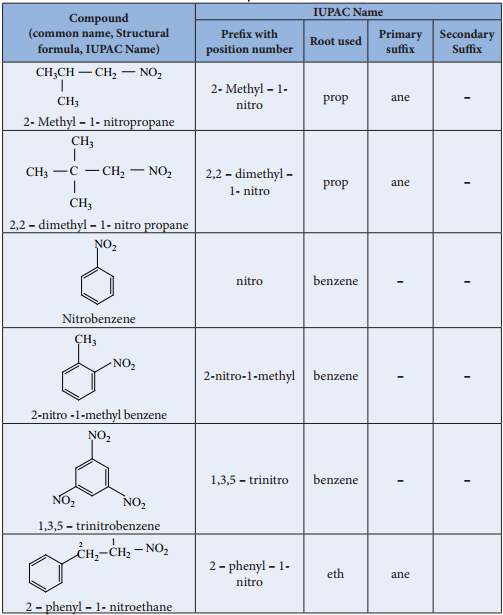
Nomenclature of Nitroalkanes
In the IUPAC nomenclature, the nitroalkanes are named by adding prefi nitro before the name of alkane, the position of the nitro group is indicated by number.
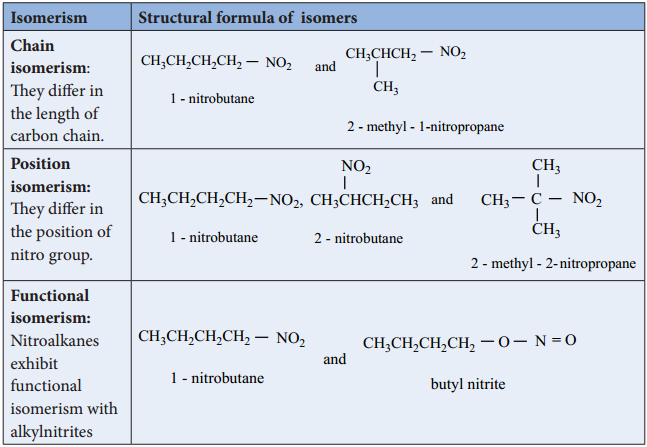
ISOMERISM
Nitroalkanes exhibit chain and position isomerism among their own class and functional isomerism with alkyl nitrites and special type tautomerism can also exist in nitro alkanes having an α – H atom. For example, nitro compounds having the molecular formula C4H9NO2 exhibit the following isomerisms.
Tautomerism:
Primary and secondary nitroalkanes, having α-H, also show an equilibrium mixture of two tautomers namely nitro – and aci – form.
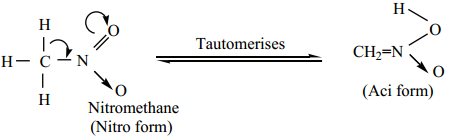
Tertiary nitro alkanes do not exhibit tautomerism due to absence of α – H atom.
|
Nitro Form |
Aci-Form |
| 1. Less Acidic | 1. More Acidic |
| 2. Dissolves in NaOH slowly | 2. Dissolves in NaOH instantly |
| 3. Decolourises FeCl3 solution | 3. With FeCl3 gives reddish brown colour |
| 4. Electrical conductivity is low | 4. Electrical conductivity is high |
Acidic Nature of Nitro Alkanes
Th α – H atom of 1° & 2° nitroalkanes show acidic character because of the electron with drawing effect of NO2 group. These are more acidic than aldehydes, ketones, ester and cyanides. Nitroalkanes dissolve in NaOH solution to form a salt. Aci – nitro derivatives are more acidic than nitro form. When the number of alkyl group attached to α carbon increases, acidity decreases. due to +I effect of alkyl groups.
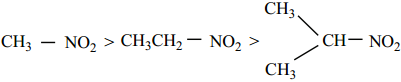
Preparation of Nitroalkanes
1. From Alkyl Halides: (Laboratory Method)
(a) Alkyl bromides (or) iodides on heating with ethanolic solution of potassium nitrite gives nitroethane.
![]()
The reaction follows SN2 mechanism.
This method is not suitable for preparing nitrobenzene because the bromine directly attached to the benzene ring cannot be cleaved easily.
2. Vapour Phase Nitration of Alkanes: (Industrial Method)
Gaseous mixture of methane and nitric acid passed through a red hot metal tube to give nitromethane.
![]()
Except methane, other alkanes (upto n – hexane) give a mixture of nitroalkanes due to C-C cleavage. The individual nitro alkanes can be separated by fractional distillation.
![]()
3. From α – Halocarboxylic Acid
α – choloroacetic acid when boiled with aqueous solution of sodium nitrite gives nitromethane.
![]()
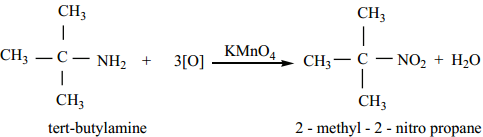
4. Oxidation of Tert – Alkyl Amines
tert – butyl amine is oxidised with aqueous KMnO4 to give tert – nitro alkanes.
5. Oxidation of Oximes
Oxidation of acetaldoxime and acetoneoxime with trifloroperoxy acetic acid gives nitroethane (1°) and 2 – nitropropane (2°) respectively.
![]()
Preparation of Nitroarenes
1. By Direct Nitration
When benzene is heated at 330K with a nitrating mixture (Con.HNO3 + Con.H2SO4), electrophilic
substitution takes place to form nitro benzene. (Oil of mirbane)
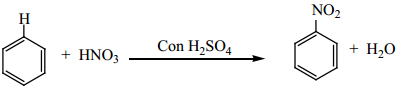
On direct nitration of nitrobenzene m – dinitrobenzene is obtained
2. Indirect Method
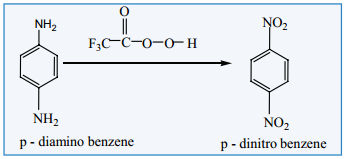
Nitration of nitro benzene gives m-dinitrobenzene. The following method is adopted for the preparation of p-dinitrobenzene.
For example
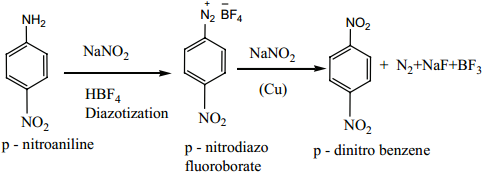
Amino group can be directly converted into nitro group, using caro’s acid (H2SO5) (or) persulphuric acid
(H2S2O8) (or) peroxytrifluro acetic acid (F3C.CO3H) as oxidising agent.
Physical Properties of Nitro Alkane
The lower nitroalkanes are colourless pleasant smelling liquids, sparingly soluble in water, but readily soluble in organic solvents like benzene, acetone etc… They have high boiling points because of their highly polar nature. Alkylnitrites have lower boiling points than nitro alkanes.
Chemical Properties of Nitroalkanes
Nitroalkanes undergo the following common reactions.
- Reduction
- Hydrolysis
- Halogenations
1. Reduction of Nitroalkanes
Reduction of nitroalkanes has important synthetic applications. The various reduction stages of nitro group are given below.
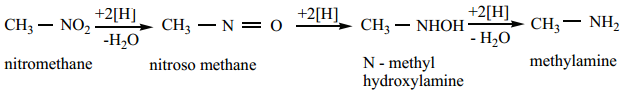
The final product depends upon the nature of reducing agent as well as the pH of the medium.
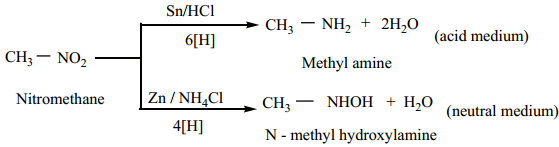
Reduction of Alkyl Nitrites
Ethylnitrite on reduction with Sn / HCl gives ethanol
![]()
2. Hydrolysis of Nitroalkanes
Hydrolysis can be effected using conc. HCl or conc. H2SO4. Primary nitroalkanes on hydrolysis gives carboxylic acid, and the secondary nitroalkanes give ketones. The tertiary nitroalkanes have no reaction.
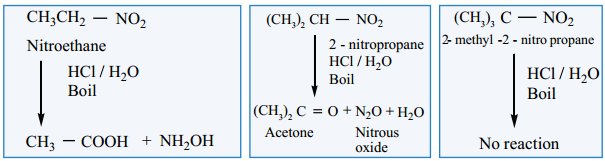
On the other hand, the acid or base hydrolysis of ethyl nitrite gives ethanol.
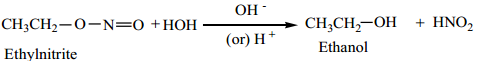
3. Halogenation of Nitroalkanes
Primary and secondary nitroalkanes on treatement with Cl2 or Br2 in the presence of NaOH give halonitroalkanes. The α – H atom of nitroalkanes are successively replaced by halogen atoms.
![]()
Toxicity
Nitroethane is suspected to cause genetic damage and be harmful to the nervous system.
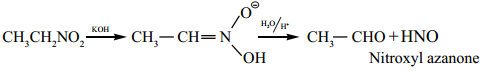
Nef Carbonyl Synthesis:
Chemical Properties of Nitrobenzene
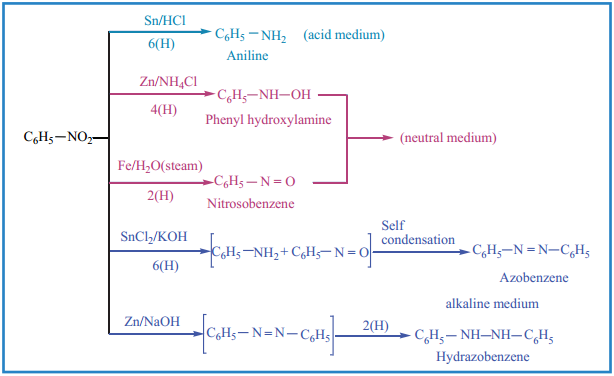
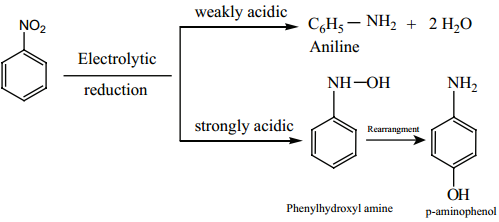
Electrolytic Reduction:
Reduction of Catalytic and Metal Hydrides
Nitrobenzene reduction with Ni (or) Pt, (or) LiAlH4 to give aniline
![]()
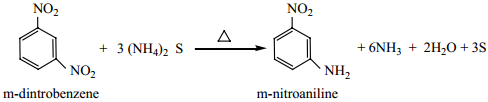
Selective Reduction of Polynitro Compounds
Electrophilic Substitution Reaction
The electrophilic substitution reactions of nitrobenzene are usually very slow and vigorous reaction condition have to be employed (-NO2 group is strongly deactivating and m – directing).
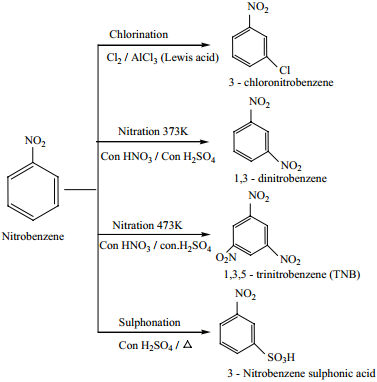
Nitrobenzene does not undergo Friedel – Craft reactions due to the strong deactivating nature of -NO2 group.