Learninsta presents the core concepts of Biology with high-quality research papers and topical review articles.
Nuclear Divisions – Definition and its Difference
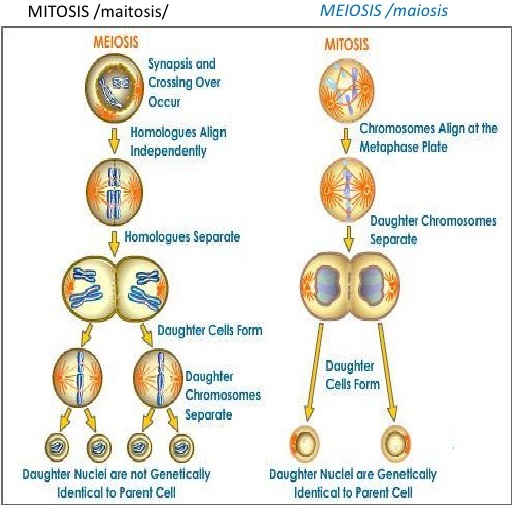
There are two types of nuclear division, as mitosis and meiosis. In mitosis, the daughter cells formed will have the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell, typically diploid (2n) state. Mitosis is the nuclear division that occurs when cells grow or when cells need to be replaced and when organism reproduces asexually.
In meiosis, the daughter cells contain half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell and is known as haploid state (n). Whichever division takes place, it is normally followed by division of the cytoplasm to form separate cells, called as cytokinesis.
The process by which a nucleus divides, resulting in the segregation of the genome to opposite poles of a dividing cell. Supplement, Nuclear divisions occur in both mitosis and meiosis. In mitosis, the result is the division of duplicated copies of genome into two.
There are two kinds of nuclear division-mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis divides the nucleus so that both daughter cells are genetically identical. In contrast, meiosis is a reduction division, producing daughter cells that contain half the genetic information of the parent cell.
Mitosis is a process of nuclear division in eukaryotic cells that occurs when a parent cell divides to produce two identical daughter cells. Mitosis is conventionally divided into five stages known as prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Mitosis is a single nuclear division that results in two nuclei, usually partitioned into two new cells. The nuclei resulting from a mitotic division are genetically identical to the original. They have the same number of sets of chromosomes: one in the case of haploid cells, and two in the case of diploid cells. Mitosis is a single nuclear division that results in two nuclei that are usually partitioned into two new daughter cells.
The process by which a nucleus divides, resulting in the segregation of the genome to opposite poles of a dividing cell. Nuclear divisions occur in both mitosis and meiosis. In mitosis, the result is the division of duplicated copies of genome into two.
Cytokinesis is the physical process of cell division, which divides the cytoplasm of a parental cell into two daughter cells. It occurs concurrently with two types of nuclear division called mitosis and meiosis, which occur in animal cells.
Meiosis I, the first meiotic division, begins with prophase I. During prophase I, the complex of DNA and protein known as chromatin condenses to form chromosomes. The pairs of replicated chromosomes are known as sister chromatids, and they remain joined at a central point called the centromere.
Under the microscope, you will now see the chromosomes lined up in the middle of the cell. You will probably also see thin-stranded structures that appear to radiate outward from the chromosomes to the outer poles of the cell.
Nuclear division occures twice during meiosis as four haploid gametes are produced; each of which are genetically different from each other. In both processes the nuclear envelope is fragmented and completley broken down into small vesicles during prophase, to allow the chromosomes to segregate. Cell division occurs during phase, which consists of nuclear division (mitosis) followed by cytoplasmic division (cytokinesis).
They are also genetically identical to the parental cell. Mitosis has five different stages: interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. The process of cell division is only complete after cytokinesis, which takes place during anaphase and telophase.