Learninsta presents the core concepts of Biology with high-quality research papers and topical review articles.
Nutritional and Digestive Disorders
Intestinal tract is more prone to bacterial, viral and parasitic worm infections. This infection may cause inflammation of the inner lining of colon called colitis. The most common symptoms of colitis are rectal bleeding, abdominal cramps, and diarrhoea.
Protein Energy Malnutrition: (PEM)
Growing children require more amount of protein for their growth and development. Protein deficient diet during early stage of children may lead to protein energy malnutrition such as Marasmus and Kwashiorkor. Symptoms are dry skin, pot-belly, oedema in the legs and face, stunted growth, changes in hair colour, weakness and irritability.
Marasmus is an acute form of protein malnutrition. This condition is due to a diet with inadequate carbohydrate and protein. Such children are suffer from diarrhoea, body becomes lean and weak (emaciated) with reduced fat and muscle tissue with thin and folded skin.
Indigestion:
It is a digestive disorder in which the food is not properly digested leading to a feeling of fullness of stomach. It may be due to inadequate enzyme secretion, anxiety, food poisoning, over eating, and spicy food.
Constipation:
In this condition, the faeces are retained within the rectum because of irregular bowel movement due to poor intake of fire in the diet and lack of physical activities.
Vomiting:
It is reverse peristalsis. Harmful substances and contaminated food from stomach are ejected through the mouth. This action is controlled by the vomit centre located in the medulla oblongata. A feeling of nausea precedes vomiting.
Jaundice:
It is the condition in which liver is affected and the defective liver fails to break down haemoglobin and to remove bile pigments from the blood. Deposition of these pigments changes the colour of eye and skin yellow. Sometimes, jaundice is caused due to hepatitis viral infections.
Liver Cirrhosis:
Chronic disease of liver results in degeneration and destruction of liver cells resulting in abnormal blood vessel and bile duct leading to the formation of fibrosis. It is also called deserted liver or scarred liver. It is caused due to infection, consumption of poison, malnutrition and alcoholism.
Gall Stones:
Any alteration in the composition of the bile can cause the formation of stones in the gall bladder. The stones are mostly formed of crystallized cholesterol in the bile. The gall stone causes obstruction in the cystic duct, hepatic duct and also hepato-pancreatic duct causing pain, jaundice and pancreatitis.
Appendicitis:
It is the inflammation of the vermiform appendix, leading to severe abdominal pain. The treatment involves the removal of appendix by surgery. If treatment is delayed the appendix may rupture and results in infection of the abdomen, called peritonitis.
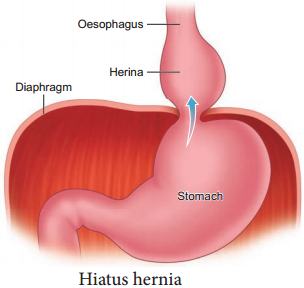
Hiatus Hernia (Diaphragmatic hernia):
It is a structural abnormality in which superior part of the stomach protrudes slightly above the diaphragm. The exact cause of hiatus hernias is not known. In some people, injury or other damage may weaken muscle tissue, by applying too much pressure (repeatedly) on the muscles around the stomach while coughing, vomiting, and straining during bowel movement and lifting heavy object.
Heart burn is also common in those with a hiatus hernia. In this condition, stomach contents travel back into the oesophagus or even into oral cavity and causes pain in the centre of the chest due to the eroding nature of acidity (Figure 5.10).
Diarrhoea:
It is the most common gastrointestinal disorder worldwide. It is sometimes caused by bacteria or viral infections through food or water. When the colon is infected, the lining of the intestine is damaged by the pathogens, thereby the colon is unable to absorb fluid.
The abnormal frequency of bowel movement and increased liquidity of the faecal discharge is known as diarrhoea. Unless the condition is treated, dehydration can occur. Treatment is known as oral hydration therapy. This involves drinking plenty of fluids – sipping small amounts of water at a time to rehydrate the body.
Peptic Ulcer:
It refers to an eroded area of the tissue lining (mucosa) in the stomach or duodenum. Duodenal ulcer occurs in people in the age group of 25 – 45 years. Gastric ulcer is more common in persons above the age of 50 years.
Ulcer is mostly due to infections caused by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. It may also be caused due to uncontrolled usage of aspirin or certain antiinflammatory drugs. Ulcer may also be caused due to smoking, alcohol, caffine and psychological stress.
Obesity:
It is caused due to the storage of excess of body fat in adipose tissue. It may induce hypertension, atherosclerotic heart disease and diabetes. Obesity may be genetic or due to excess intake of food, endocrine and metabolic disorders.
Degree of obesity is assessed by body mass index (BMI). A normal BMI range for adult is 19-25 above 25 is considered as obese. BMI is calculated as body weight in Kg, divided by the square of body height in meters. For example, a 50 Kg person with a height of 160 cms would have a BMI of 19.5. That is BMI = 50/(1.6)2 = 19.5