Learninsta presents the core concepts of Biology with high-quality research papers and topical review articles.
Organism and Its Environment
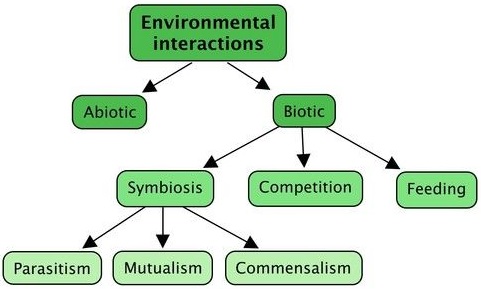
Every living organism has its own specific surrounding, medium or environment with which it continuously interacts and develops suitable adaptations for survival there. Environment is a collective term which includes the different conditions in which an organism lives or is present. The common and infulencing factors in any environment are light, temperature, pressure, water, salinity. These are collectively referred to as Abiotic components.
Environments are variable and dynamic, in which temperature changes and light changes are diurnal and seasonal. These inflence the organisms inhabiting them. An organism’s growth, distribution, number, behaviour and reproduction is determined by the different factors present in the environment.
Ecology is the study of how living organisms interact with each other and with their environment. Abiotic factors are the parts of the environment that have never been alive, while biotic factors are the parts of the environment that are alive, or were alive and then died.
Ecology is the study of the interaction of organisms in an area with the surrounding environment. This interaction constitutes an overall adaptation of the organisms to their environment which also includes the continuity of species.
Ecology is the study of organisms and how they interact with the environment around them. An ecologist studies the relationship between living things and their habitats.
Environment is the living and non living things surrounding the living organism. An organism’s habitat refers to an ecological or environmental area inhabited by particular species of plants, animals, fungi, etc. It refers to an organism’s natural environment. Life has to adapt to specific environmental conditions.
Ecology is the study of how organisms interact with one another and with their physical environment. The distribution and abundance of organisms on Earth is shaped by both biotic, living-organism-related, and abiotic, nonliving or physical, factors.
7 Ecological Principles
The seven principles are:-
- Maintain diversity and Redundancy
- Manage connectivity
- Manage slow variables and feedbacks
- Foster complex adaptive systems thinking
- Encourage learning
- Broaden participation and
- Promote polycentric governance systems.