Learninsta presents the core concepts of Biology with high-quality research papers and topical review articles.
Photorespiration or Cycle or Photosynthetic Carbon Oxidation (PCO) Cycle
Respiration is a continuous process for all living organisms including plants. Decker (1959) observed that rate of respiration is more in light than in dark. Photorespiration is the excess respiration taking place in photosynthetic cells due to absence of CO2 and increases of O2 (Table 13.5). This condition changes the carboxylase role of RUBISCO into oxygenase.
|
Photorespiration |
Dark respiration |
| 1. It takes place in photosynthetic green cells | 1. It takes place in all living cells |
| 2. It takes place only in the presence of light | 2. It takes place all the time |
| 3. It involves chloroplast, peroxisome and mitochondria |
3. It involves only mitochondria |
| 4. It does not involve Glycolysis, Kreb’s Cycle, and ETS | 4. It involves glycolysis, Kreb’s Cycle and ETS |
| 5. Substrate is glycolic acid | 5. Substrate is carbohydrates, protein or fats |
| 6. It is not essential for survival | 6. Essential for survival |
| 7. No phosphorylation and yield of ATP | 7. Phosphorylation produces ATP energy |
| 8. NADH2 is oxidised to NAD+ | 8. NAD+ is reduced to NADH2 |
| 9. Hydrogen peroxide is produced | 9. Hydrogen peroxide is not produced |
| 10. End products are CO2 and PGA | 10. End products are CO2 and water |
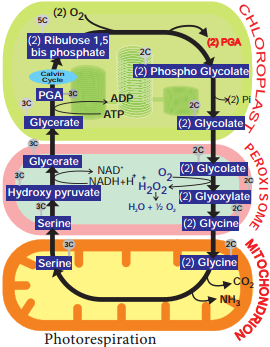
C2 Cycle takes place in chloroplast, peroxisome and mitochondria. RUBP is converted into PGA and a 2C-compound phosphoglycolate by Rubisco enzyme in chloroplast. Since the first product is a 2C-compound, this cycle is known as C2 Cycle. Phosphoglycolate by loss of phosphate becomes glycolate. Glycolate formed in chloroplast enters into peroxisome to form glyoxylate and hydrogen peroxide.
Glyoxylate is converted into glycine and transferred into mitochondria. In mitochondria, two molecules of glycine combine to form serine. Serine enters into peroxisome to form hydroxy pyruvate. Hydroxy pyruvate with help of NADH + H+ becomes glyceric acid.
Glyceric acid is cycled back to chloroplast util ising ATP and becomes Phosphoglyceric acid (PGA) and enters into the Calvin cycle (PCR cycle). Photorespiration does not yield any free energy in the form of ATP. Under certain conditions 50% of the photosynthetic potential is lost because of Photorespiration (Figure 13.20).
Significance of Photorespiration
- Glycine and Serine synthesised during this process are precursors of many biomolecules like chlorophyll, proteins, nucleotides.
- It consumes excess NADH + H+ generated.
- Glycolate protects cells from Photo oxidation.
Carbon Dioxide Compensation Point
When the rate of photosynthesis equals the rate of respiration, there is no exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide and this is called as carbon dioxide compensation point. This will happen at particular light intensity when exchange of gases becomes zero. When light is not a limiting factor and atmospheric CO2 concentration is between 50 to 100 ppm the net exchange is zero.