Here we are providing Class 12 Political Science Important Extra Questions and Answers Chapter 4 Alternative Centres of Power. Political Science Class 12 Important Questions are the best resource for students which helps in class 12 board exams.
Class 12 Political Science Chapter 4 Important Extra Questions Alternative Centres of Power
Alternative Centres of Power Important Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
When was the ASEAN Regional Forum established? What was its main objective? (Imp.) C.B.S.E. 2013)
Answer:
ASEAN Regional Forum was established in 1967 by five countries of South-East Asia.
The objective of ASEAN:
- The main objective of ASEAN was to accelerate economic growth and through that social progress and cultural development.
- To promote regional peace and stability based on the rule of law and the principles of the United Nations Charter.
Question 2.
Write two achievements of ASEAN.
Answer:
- ASEAN economy is the fastest growing economy in the world.
- Scope of activities of ASEAN is very wide. It wants its members to excel and develop in all fields.
Question 3.
Mention any two steps taken by China to improve its economy. (C.B.S.E. 2010)
Answer:
- In 1978, China adopted the ‘Open Door’ policy in its economy.
- In 2001 China became a member of the World Trade Organisation and opened her economy to other countries of the world.
Question 4.
State any two features of j the European Union that make it an influential organisation: (Imp.) (C.B.S.E. 2014)
Answer:
There are two features of the European Union that make it an influential organisation:
- The European Union has economic, political, diplomatic and military influence.
- Britain and France hold permanent seats in the UN Security Council.
Question 5.
What do ASEAN and FTA stand for? (C.B.S.E. 2008)
Answer:
- ASEAN stands for Association of South-East Asian Nations.
- FTA stands for Free Trade Agreement.
Question 6.
Explain any two causes that led to the formation of the European Union. (Sample Paper)
Or
What led to the formation of the European Union? (C.B.S.E. 2009)
Answer:
- Under the Marshall Plan, an organisation of European Economic Cooperation was established in 1948 to channelise aid to the West European states.
- The disintegration of the Soviet Union in December 1991 encouraged Western European countries to move further for regional cooperation.
Alternative Centres of Power Important Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type (2 Marks)
Question 1.
Name any two founder member states of ASEAN. (C.B.S.E. 2014)
Answer:
- Indonesia
- Malaysia.
Question 2.
Why was ASEAN established (C.B.S.E. 2016)
Answer:
ASEAN was established to accelerate economic growth and through that social progress and cultural development.
Question 3.
What does the logo on the ASEAN flag symbolise? (C.B.S.E. 2016)
Answer:
The Logo on the ASEAN flag symbolises the ten Southeast Asian Countries bound together in friendship and solidarity. The circle symbolises the unity of ASEAN.
Question 4.
What is meant by ‘ASEAN Way’? (C.B.S.E. 2012 Outside Delhi)
Answer:
‘ASEAN Way’ is a form of interaction among ASEAN members that is informal and cooperative.
Question 5.
Under which plan did the U.S.A. extend financial support for reviving Europe’s economy after the Second World War? (Imp.)(C.B.S.E. 2014)
Answer:
Under the Marshall Plan, the USA extended financial support for reviving Europe’s economy after the Second World War.
Question 6.
What were the objectives of founding the European Union? (C.B.S.E. 2012)
Answer:
The main objective of founding the European Union was to establish an economic and political organisation of the European States.
Question 7.
Since the end of the Cold War, there have been significant changes in India-China relations. Identify anyone such change. (C.B.S.E. 2019)
Answer:
Since the end of the Cold War, India-China relations now have a strategic as well as an economic dimension.
Question 8.
Britain’s former Prime-minister, Margaret Thatcher kept the U.K. out of the European market. Highlight the reason behind this decision. (C.B.S.E. 2019)
Answer:
There is a deep-seated Euroskepticism in some parts of Europe about the European Union’s integrationist agenda. Therefor Margaret Thatcher kept the U.K. out of European Market.
Choose the correct answer:
Question 9.
The Council of Europe was established in:
(a) 1948 (b) 1949
(c) 1970 (d) 1994.
Answer:
(b) 1949
Question 10.
In January 2007 which of the following countries joined E.U.?
(a) Finland and Sweden
(b) Denmark and Ireland
(c) Bulgaria and Romania
(d) Germany and England.
Answer:
(c) Bulgaria and Romania
Question 11.
In which year Unification of Germany took place?
(a) October 1990 (b) January 1990
(c) October 2000 (d) January 1995.
Answer:
(a) October 1990
Question 12.
Informal, non-confrontationist and cooperative interaction among members of South East Asian Nations is also called (Sample Paper 2019-20)
Answer:
Informal, non-confrontationist and cooperative interaction among members of South East Asian Nations is also called ASEAN WAY’.
Alternative Centres of Power Important Extra Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Mention any four common features of the European Union. (C.B.S.E. 2008)
Answer:
Following are the main features of the European Union:
- The European Union is the world’s largest economy with a GDP of more than $12 trillion in 2005.
- The European Union has its own flag, anthem, founding date and currency.
- Its currency, the Euro, can pose a threat to the dominance of the U.S. Dollar.
- The European Union has economic, political and diplomatic and military influence.
- Its economic power influences its closest neighbours as well as Asia and Africa.
Question 2.
In which four ways did the new economic policy of China benefit its: economy? (Imp.) C.B.S.E. 2016, 2017)
Answer:
- The Chinese economy, including both industry and agriculture, grew at a faster rate.
- China became a member of W.T.O. in 2001.
- China emerged as an economic superpower in Asia.
- China has become the most important destination for foreign direct investment anywhere in the world.
Question 3.
What was the main objective behind China’s adoption of the Soviet model of the economy? In which two ways was China benefitted by it? (C.B.S.E. 2017)
Answer:
Objective:
- The economic development of the country.
- To give a boost to employment.
Benefit:
- The Chinese economy, including both industry and agriculture, grew at a faster rate.
- China became a member of W.T.O. in 2001.
- China emerged as an economic superpower in Asia.
- China has become the most important destination for foreign direct investment anywhere in the world.
Question 4.
Mention any four significant: changes in Indo-China relations that j have taken place after the Cold War. • (Imp.) C.B.S.E. 2016)
Answer:
After the end of Cold-War there were following significant changes which took place in Indo-China relations:
- Both countries have improved their relation not only in politics but also in the economic field also. Their relations now have a strategic as well as economic dimension. India and China have adopted international economic institution like the “World Trade Organisation’.
- Both governments have agreed to contain conflicts and maintain ‘peace and tranquillity’ on borders.
- China and India have also signed agreements on cultural exchange and co-operation in science and technology. They mutually opened four border posts for trade.
- Since 1999, Indo-China trade is growing 30% per year.
Question 5.
What is meant by the ASEAN: Way? Mention any two of its objectives. (C.B.S.E. 2014)
Answer:
Meaning of ASEAN Way: The ASEAN Way is a form of interaction among ASEAN members that is informal and cooperative.
Objectives of ASEAN:
- To accelerate the economic growth of the member countries.
- To promote the social and cultural development of the region through co-operative programmes.
Question 6.
How has the European Union evolved over time from an economic union to an increasingly political one? (C.B.S.E. 20IS)
Answer:
European Union is a very strong organisation of European countries. European Union is also called the European Common Market or European Common Community. The European Union is the world’s largest economy with a GDP of more than $12 trillion in 2005. Within a short period of time, it became a very powerful economic and political organisation. It has its own parliament, own flag, anthem and its own currency. The E.U. also exercises political and diplomatic influence.
Question 7.
Describe the four major objectives of the ASEAN economic community. (C.B.S.E. 2017)
Answer:
Following are the major objectives of the ASEAN economic community.
- To encourage common production and common and collective Bazar (market) for the ASEAN countries.
- To help in the social and economic development of ASEAN economic community.
- To improve the present situation by solving the disputes of ASEAN countries.
- Encourage the free trade market for ASEAN countries.
Question 8.
Describe any four long-term implication of the conflict of 1962 between India and China. (C.B.S.E. 2017)
Answer:
Following are the long term implications of the conflict of 1962 between India and China.
- By waging war in 1962, China was able to capture thousands of miles of Indian territory, which is still under its possession.
- It ended the diplomatic relations between India and China from 1962-1976.
- No Indian Prime-minister made any tour to China till 1988.
- China too adopted a hostile attitude during the Indo Pak war, but relations started improving since the time of Indira Gandhi.
Question 9.
Explain any four steps taken by China that led to the rise of its economy. (C.B.S.E. 2018)
Or
What were the two major policy decisions taken by the Chinese leadership in the 1970s? (C.B.S.E. 2010)
Answer:
- China ended her political isolation and started making friendly relations with the capitalist countries. China was made a member of the U.N. with the support of U.S.A. In 1972, China established a relationship with the U.S.A.
- Prime Minister of China, Zhou Enlai proposed ‘four modernisation’ (agriculture, industry, science and technology and military) in 1973. The four modernisations era was associated with the rise to prominence of Deng Xiaoping.
- Deng Xiaoping announced the ‘Open Door’ policy and economic reforms in China.
- China followed the ‘Open Door’ policy rather than choosing the way of Shock Therapy.
Question 10.
Explain the New Economic Policy of China since 1978. (C.B.S.E. 2013)
Or
“China followed its own path in j introducing a market economy”. Justify this statement with four suitable arguments? (C.B.S.E. Sample paper 2018)
Answer
- In 1978, Deng Xiaoping adopted the ‘Open Door’ policy and economic reforms in China.
- China started privatisation in the agricultural sector in 1982.
- China started privatisation in the industrial sector in 1998.
- Trade barriers were removed from the Special Economic Zone where foreign investors could set up their enterprises.
Question 11.
Why does ASEAN still remain principally an economic association? (C.B.S.E. 2015)
Or
How far is it correct to describe ASEAN as an alternative Centre of power in the world? (C.B.S.E. Sample paper 2018)
Answer:
ASEAN still remain principally an economic association. ASEAN was established in 1967 by five countries of this region. This region is much smaller than other associations like EU, the US and Japan. The main objective of ASEAN was to accelerate economic growth. ASEAN is rapidly growing into a very important regional organisation. It is the basis of creating a common market and production within the region and boost social and economic development in the region.
It has created a Free-Trade Area for investment, labour and services. Its vision 2020 has defined an outward-looking role for ASEAN in the international community. In its vision 2020 ASEAN has hoped that it will become very strong in an economy that it will be able to play an important role in international affairs.
Question 12.
While the Chinese economy has improved dramatically, why has every Chinese not received the benefit of the reform? Give any four reasons. (C.B.S.E. 2016)
Or
Mention any four negative consequences on the people of China in spite of the improvement in the Chinese economy. (C.B.S.E. 2017)
Answer:
- Privatisation of industry and agriculture and the new economic policies helped the Chinese economy to break from stagnation but unemployment has risen in China. Nearly 100 million people are in search of jobs.
- Women employment and conditions of work are miserable.
- Privatisation of agriculture and industry have increased corruption and environmental degradation.
- It also increased economic inequality between rural and urban residents and coastal and inland provinces.
Question 13.
Describe India-China relations from 1947 to 1962. (C.B.S.E. 2016, 2017)
Answer:
India’s Policy of Contentment crossed limits when India gave its extra-territorial rights enjoyed in Tibet, to China by signing a trade-agreement on 29th April 1954. Both the countries at the time of agreement expressed their faith in the principles of Panchsheel. These principles were elaborated in 1953 at the Bandung Conference. The Chinese Prime Minister Chou-En-Lai visited India in 1954 and Pt. Nehru also went to China.
Chinese invasion over India: China attacked both the Western and Eastern sectors of the Indian Border on 20th Oct. 1962. The Chinese soldiers overpowered the military posts till Indian forces balanced themselves after this sudden attack China declared a unilateral ceasefire on 21st Nov. By waging a war. China was able to capture thousands of miles of Indian area which is still in its possession.
Question 14.
“China has been fastest growing economy since the reform first began there” justify. (C.B.S.E. 2017)
Answer:
In 1970 the Chinese leadership took major policy decisions i.e., China ended its political and economic isolation with the establishment of relations with the United States in 1972. Premier Zhou Enlai proposed the four modernization i.e., agriculture, industry, science and technology and military in 1973. By 1978, then-leader Deng Xiaoping adopted ‘Open Door Policy’ and economic reforms in China. China’s economic success since 1978 has been linked to its rise as a great power.
China followed its own path in introducing a market economy. The privatisation of agriculture in 1982 was followed by the privatisation of industry in 1998. Trade barriers were removed in Special Economic Zones (SEZs) where foreign investors could set up enterprises. Past-Mao China established an all-time global record in doubling per capita output between 1977 and 1987. According to the World Bank’s purchasing power parity (PPP) estimated, china with 1994 GDP of just under 8.3 trillion has become the second-largest economy in the world, after the United States.
Now China is growing as great power. In the economic sphere, China’s economy is growing very fast. It is projected to overtake the U.S. as the world’s largest economy by 2040.
Alternative Centres of Power Important Extra Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1.
‘The European Union has economic, political and diplomatic, and military influence’. Substantiate the statement. (C.B.S.E. Sample Q.P. 2017)
Or
Analyse any three factors responsible for the European Union to be a highly influential regional organisation. (C.B.S.E. 2015)
Answer:
European Union (EU) is a very strong regional organisation of European countries. It plays an important role in world politics. European Union is also called the European Common Market or European Common Community. Within a short period, it became a very powerful economic and political regional organisation. In fact, it has become a supranational organisation. European Union has its own parliament, own flag, anthem and its own currency. Headquarter of the European Union is in Brussels (Belgium). E.U.’s official languages include Bulgarian, Danish, Dutch, Italian, Romanian, Spanish, Polish, Swedish, etc. (total 23).
1. The E.U. as the biggest Economy. The E.U. is the world’s biggest economy with a GDP of more than $12 trillion in 2003, slightly larger than that of the United States. Its currency, the Euro is now in a position to pose a threat to the dominance of the U.S. dollar. Its share of world trade is three times larger than that of the United States allowing it to be more assertive in trade disputes with the U.S. and China. Due to its economic power, it exercises a great influence over its neighbours as well as over Asia and Africa. It also functions as an important bloc in the international economic organisation such as WTO.
2. The E.U. as Political and Diplomatic Influence. The E.U. also exercises political and diplomatic influence. France is permanent members of the Security Council of U.N. Several members of E.U. are non-permanent members of the Security Council. Thus, E.U. exercises a great influence on the policies of the U.N. as well as on the U.S.
3. The E.U. Military Influence. The E.U. combined armed forces are the second largest in the world.
Thus, E.U. is a supernational organisation and can intervene in the economic, political and social matters of the world.
Limitations of E.U:
However, there are certain limitations of E.U.
(a) European Union has failed to adopt a common constitution. Prime Minister Churchill’s dream of the United States of Europe could not become a reality.
(b) Common currency of E.U. is not adopted by all the member states.
(c) The member states also have their own foreign and defence policies which are sometimes at odds with each other. For example, Germany and France opposed the United States decision to invade Iraq.
On Dec. 13, 2007 head of states and government of the European Union member states signed the Lisbass Treaty which they hope can make decision-making more efficient. The Lisbass Treaty has provided far-reaching changes in E.U. institutions and decision-making mechanisms. It created the post of a long-term president of the European Council. E.U. member states had one year to ratify the treaty. It came into force as planned in January 2009.
Question 2.
Analyse the basis of the projection of China to overtake the U.S. as the world’s largest economy by 2040. (C.B.S.E. 2008 Delhi Set-I)
Or
Explain any six reasons for the rise of the Chinese economy. (C.B.S.E. 2019)
Answer:
After the disintegration of the Soviet Union in 1990, it looked, as if, the world has become unipolar. But in reality, it is not so. China is growing as a great power. In the economic sphere, China’s economy is growing very fast. It is projected to overtake the U.S. as the world’s largest economy by 2040.
After the inception of the People’s Republic of China in 1949, the Soviet model of planned and State-controlled economy was followed. But in 1970, the Chinese leadership took major policy decisions i.e., China ended its political and economic isolation with the establishment of relations with the United States. In 1972, Premier Zhou Enlai proposed the four modernisation i.e., agriculture, industry, science and technology and military in 1973. By 1978, then-leader Deng Xiaoping adopted the ‘Open Door Policy’ and economic reforms in China. China’s economic success since 1978 has been linked to its rise as a great power.
China followed its own path in introducing a market economy. The privatisation of agriculture in 1982 was followed by the privatisation of industry in 1998. Trade barriers were removed in Special Economic Zones (SEZs) where foreign investors could set up enterprises. Past-Mao China established an all-time global record in doubling per capita output between 1977 and 1987. According to the World Bank’s purchasing power parity (PPP) estimated, China with 1994, GDP of just under $ 8.3 trillion has become the second-largest economy in the world, after the United States.
According to a Rand study, China’s GDP will reach $11.3 trillion by the year 2010 as compared to $10.7 trillion for the United States. China has large foreign exchange reserves and in a position to make big investments in other countries. China is a member of the World Trade Organisation. The country plans to deepen its integration into the world economy and shape the future world economic order.
It is estimated that China’s economy would become the largest economy in the world by the end of 2040.
Question 3.
Evaluate any three major factors responsible for making the European Union a political force from; being an economic force. (C.B.S.E. 2016)
Or
Analyse any three major factors responsible for evolving the European V V Union from an economic union to a • political one. (C.B.S.E. 2017)
Or
How has the European Union evolved over time from an economic union to an increasingly political one? Explain. (C.B.S.E. 2019)
Answer:
European Union (EU) is a very strong regional organisation of European countries. It plays an important role in world politics. European Union is also called. European Common Market or European Common Community.
The two World Wars within a very short duration inflicted very heavy losses upon European countries. During six years of the Second World War, European countries suffered heavy economic, material and manpower losses. The Second World War shattered many of the assumptions and structures on which the European states had based their relations.
After the Second World War majority of the European leaders were convinced that their relations should be reconstructed. They were compelled to find out solutions from the European perspective and ultimately formed an organisation known as the European Union.
European Union is a very strong organisation of European countries. European Union is also called the European Common Market or European Common Community. The European Union is the world’s largest economy with a GDP of more than $12 trillion in 2005. Within a short period of time, it became a very powerful economic and political organisation. It has its own parliament, own flag, anthem and its own currency. The E.U. also exercises political and diplomatic influence.
Question 4.
Describe the aims and achievements of the Association of South East-Asian Nations (ASEAN).
Or
Assess the role of ASEAN as an Economic Association. (C.B.S.E. 2016)
Answer:
The Association of South-East Asian Nations (ASEAN) was established on August 8, 1967, in Bangkok. The Bangkok (Thailand) Declaration was signed by five original member countries of this region: Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore and Thailand. Brunei Darussalam joined the Association on January 8, 1984. On July 28, 1995, Vietnam became the seventh member of ASEAN. Laos and Myanmar were admitted into ASEAN on July 20, 1997.
Aims of ASEAN: Main aims of ASEAN are as follows:
- To accelerate the economic growth of the member countries.
- To promote the social and cultural development of the region through co-operative programmes.
- To safeguard the political and economic stability of the region against big power rivalry.
- To promote and strengthen collective self-reliance among the countries of South Asia.
- To strengthen co-operation with other developing countries.
Activities and Achievements of ASEAN: ASEAN was established as an economic Association of South East Asian Region in 1967 and even now it is an economic association. ASEAN summits were not held regularly. But the meetings of the ministers of member countries are held annually. ASEAN is not a military alliance. The communique issued at the end of the second summit held in 1977 declared that ASEAN was neither a military bloc nor did it have any desire to become one in future. At the second summit, the leaders stressed the desire to have peaceful and mutually beneficial relations with all countries of the region. They stressed in particular that they do not want to take a side in the Indo-China conflict.
The ASEAN includes about 8% of the world’s population and in 2003 it had a combined G.D.P. of about $8,700 billion. By 2003, ASEAN had several agreements and by these agreements, member countries promised to uphold peace, neutrality, cooperation, non-interference and respect for sovereign rights.
The ASEAN has focused on creating a Free Trade Area (F.T.A.) for investment, labour and service. The U.S. and China have already moved fast to negotiate FTAs with ASEAN. After joining of India and China as dialogue partners to ASEAN, the ASEAN had successfully challenged the economic and political power centres of the world.
On December 20, 2012, India and the 10 Asian nations resolved to strengthen bilateral cooperation to ensure maritime security and freedom of navigation in the disputed sea in accordance with the international law. India and ASEAN also finalised free trade agreement in services and investment.
At present, ASEAN is developing as an important and useful agency of regional co-operation for development among the member countries.
Question 5.
Examine the changing Indo-China relations. (Imp.) (C.B.S.E. 2009)
Answer:
India and China had cordial relations earlier, but China attacked India in 1962 and became hostile to India. China still occupies some territory of India. India is inclined to improve relations with China but the Chinese attitude remains inimical.
Indo-China relations during Nehru Era. (1947 to May 1965)
The policy of friendship towards China. India, since the beginning, adopted the policy of friendship towards Communist China. India first recognised China and then supported its induction in U.N.O.
India’s Policy of Contentment crossed limits when India gave its extra-territorial rights enjoyed in Tibet, to China by signing a trade-agreement on 29th April 1954. Both the countries at the time of agreement expressed their faith in the principles of Panchsheel. These principles were elaborated in 1953 at the Bandung Conference. The Chinese Prime Minister Chou-En-Lai visited India in 1954 and Pt. J.L. Nehru also went to China.
Chinese invasion over India. China attacked both the Western and Eastern sectors of the Indian Border on 20th Oct. 1962. The Chinese soldiers overpowered the military posts till Indian forces balanced themselves after this sudden attack. China declared a unilateral ceasefire on 21st November. By waging a war, China was able to capture thousands of miles of Indian area which is still in its possession.
Colombo Resolution and attitude of China. Ceylon, Burma, Cambodia, Indonesia, Egypt organised the Colombo Conference in December 1962 to facilitate Indo-China talks. Mrs Bhandarnaike brought this resolution to Delhi and Peking. This resolution was published on 19th January 1963.
Sino-Indian relations during Shastri Period. (May 1964 to January 1966). After the death of Pt. Nehru, Shri Lai Bahadur Shastri remained the PrimeMinister of India till 10th January 1966. Sino-Indian relations did not improve during this period. China adopted a hostile attitude during the Indo-Pak war in 1965. China fully supported Pakistan and declared India as an invader.
Problems of Bangladesh and Chinese attitude towards Indo-Pak war. The year 1971 was replete with problems for India. China disliked India’s co-operation in Bangladesh movement and it fully supported the dictators of Pakistan. China favoured Pakistan in the meetings of the Security Council during the Indo-Pak war and held India responsible for the invasion. China again threatened India but these threats proved hollow.
Indo-China relations remained tense till April 1976.
Indo-China relations from May 1976 to 1979: With the deaths of Chou-En-Lai, Chu Teh and Mao in 1976, Indo-China relations slightly improved. On 15 April 1976 Shri K.R. Narayanan was sent to Peking as an ambassador to China. China, too, sent its ambassador to India.
The external affairs minister, Mr A.B. Vajpayee reached Peking on February 12, 1979. India raised the border question at the first-ever ministerial dialogue with China since 1960. India and China agreed to maintain the existing tranquillity along their common borders.
Indo-China Relations from January 1980 to 1991: The Chinese Prime Minister Mr Hua Kuofeng told Prime Minister Indira Gandhi at Belgrade (Yugoslavia) on May 9, 1980, that his country was more than ready to improve its relations with India.
The three rounds of talks with China-First in Beijing in December 1981, second in Delhi in May,
1982 and third in January 1983-on the border dispute failed to make any progress. Two more rounds of talks took place between India and China between
1983 and 1985.
Indian Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi visited China in 1988 and many misunderstandings were removed. A joint working group was formed.
The joint working groups have held six rounds of talk.
Visit of the Chinese President to India: On 28th Nov. 1996 Chinese President, Mr Jiang Zemin visited India on a four day State visit. Mr Jiang was the first Chinese head of the State who had visited India. Chinese President, Mr Jiang Zemin said, “My visit will further promote friendship between the two countries.” On 29th Nov. 1996 India and China signed a historic agreement pledging themselves not to attack each other or cross the Line of Control and reduce troops and armaments along the common border.
Post-Pokhran Sino-Indian Relation. India’s underground nuclear test, at Pokhran on May 11, 1998—after 24 years of its maiden nuclear test. On 14th June 1999 Indian External Affairs Minister Mr Jaswant Singh visited China. India and China decided to establish a security dialogue mechanism and decided to give new impetus to the decisions of the Joint Working Group. It was also decided to celebrate the 50th anniversary of the establishment of Indo-China diplomatic relations in an appropriate manner.
Visit of the Indian President to China. Indian President K.R. Naryanan visited China on May 28, 2000 (May 28 to June 3). India and China favoured a ‘fair and reasonable boundary dispute’ and decided to set up an Eminent Persons Group (EPG) to enhance over-all bilateral ties.
Chinese Leader Li Peng’s visit to India (Jan.2001). Chinese Leader Li Peng said, “The purpose of my visit is to enhance trust, boost friendship and strengthen co-operation.”
Visit of the Chinese Prime Minister to India: Chinese Premier Zhu Rongji visited India in January 2002. The two countries discussed a number of confidence-building measures.
Visit of the Indian Prime Minister to China: In June 2003, Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee visited China. During his visit, India and China signed the Cross Border Trade Agreement.
China’s stand on Sikkim: Sikkim has been an issue of conflict between India and China. But in May 2004 China put a step towards friendship and mutual trust. Beijing has for the first time officially stopped showing Sikkim as a separate country in Asia. This step of China has raised Indo-China relations to a qualitatively new plain.
Joint Indo-China Military Exercise: The first Indo-Chinese Joint Military Exercise began on December 21, 2007, and came to a conclusion on December 25, 2007, in Kunming (China). The focus of the exercise was on the anti-terrorism drill.
Visit of Indian P.M. to China: Indian Prime Minister Dr Manmohan Singh visited China on January 13, 2008. Indian Prime Minister and Chinese Premier signed a joint statement titled, ‘A Shared Vision for the 21st century’ on 14th Jan. 2008. The Shared Vision contains some new issues such are bilateral co-operation in civil nuclear energy, Chinese support for India’s desire to play a greater role in the United Nation Security Council, etc.
Improvement in Indo-China Relations: During these years of Indo-China relations the level of mutual trust between the two countries has been raised. Chinese Vice-Foreign Minister Wang Yi has said during an interview that “China-India relations are developing very well. Especially we have improved our mutual trust, which is important for bilateral relations”.
China’s stand on Arunachal Pradesh: Arunachal Pradesh is an integral part of India. But on November 11, 2008, Qin Gang, foreign ministry spokesman rejected India’s assertion that Arunachal Pradesh is its integral part and insisted that China never recognised the ‘illegal’ Mac Mohan line and that the status of the border state was never officially demarcated. But Prime Minister Dr Manmohan Singh rejected China’s claim and stated Arunachal is ‘Our land of the rising sun’.
Visit of Chinese Premier Wen Jiabao: Chinese Premier Wen Jiabao visited India on December 15, 2010. Premier Wen Jiabao declared that the world had enough space for India and China to prosper and pledged to promote ties between the two Asian giants. The two countries set a new bilateral trade target of $100 billion by 2015 and take measures to promote greater exports to China with a view to reducing India’s increasing trade deficit.
Prime Minister Manmohan Singh’s Meeting with Chinese P.M. Wen Jiabao on November 18, 2011, at Bali. A range of issues, including the situation along the line of actual control and trade were discussed. Prime Minister Manmohan Singh stated that India is committed to developing the ‘best of relations’ with China while the Chinese P.M. underlined that both countries should work ‘hand-in-hand’ to ensure that the 21st century belongs to Asia.
P.M. Manmohan Singh’s visit to China: On 23rd October 2013 India and China took a leap towards reducing tension across the border and promised to strengthen cooperation on trans-border rivers, even as New Delhi delayed pact for a liberalised visa regime. The Border Defence Cooperation Agreement was among the nine pacts that the two countries signed in Beijing.
Chinese President’s visit to India. In September 2014, Chinese President Xi Jinping visited India. During this visit, both countries signed 12 Agreements.
Indian P.M. visit to China. In May 2015, Indian Prime Minister Sh. Narendra Modi visited China. During this visit, both countries signed 24 important agreements.
In Oct 2016 Chinese President visited India to attend ‘BRICS’ Summit, similarly Indian Prime Minister Sh. Narendra Modi visited China in September 2017 to attend 9th ‘BRICS’ summit. During there visit, both leaders held bilateral meeting also and discuss some important bilateral issues.
In June 2018 Indian Prime Minister Sh. Narendra Modi visited China. During this visited both countries discuss bilateral and regional issues.
In Oct 2019 Chinese President visited India. During this visit, both countries discuss trade, regional security and terrorism.
Conclusion: The relations between the two countries should be based on complete equality and mutual respect in the spirit of the U.N. Charter. Both could learn from each other’s experience since the two countries were in need of rapid development.
Question 6.
Study the picture given below carefully and answer the following questions: (C.B.S.E. 2019)

(i) The given image refers to which policy of India since 1991?
Answer:
The given image refers to look east policy of India since 1991.
(ii) Explain the significance of this policy as shown in the image above.
Answer:
The significance of this policy is that the relation between India and ASEAN becomes very cordial. Through look East Policy, India get various advantages in ASEAN countries.
(iii) Evaluate India’s role in ASEAN.
Answer:
The role of India in ASEAN is very important. India emphasis on bilateral trade between India and ASEAN in ASEAN summit-level conference. India also encourages free trade goods and services system between India and ASEAN. India also criticises terrorism in ASEAN summit.
Note: The following questions are for the Visually Impaired Candidates only, in lieu of the above question.
(1) What is the full form of ASEAN?
Answer:
The full form of ASEAN is the Association of Southeast Asian Nations.
(2) Evaluate India’s role in ASEAN.
Answer:
For this, see Study the picture given below carefully and answer the following questions: (C.B.S.E. 2019)
(i) The given image refers to which policy of India since 1991?
Answer:
The given image refers to look east policy of India since 1991.
(ii) Explain the significance of this policy as shown in the image above.
Answer:
The significance of this policy is that the relation between India and ASEAN becomes very cordial. Through look East Policy, India get various advantages in ASEAN countries.
(iii) Evaluate India’s role in ASEAN.
Answer:
The role of India in ASEAN is very important. India emphasis on bilateral trade between India and ASEAN in ASEAN summit-level conference. India also encourages free trade goods and services system between India and ASEAN. India also criticises terrorism in ASEAN summit.
(3) What did the Chinese do to break from their economic stagnation?
Answer:
For this, see
Explain the New Economic Policy of China since 1978. (C.B.S.E. 2013)
Or
“China followed its own path in j introducing a market economy”. Justify this statement with four suitable arguments? (C.B.S.E. Sample paper 2018)
Answer
(i) In 1978, Deng Xiaoping adopted the ‘Open Door’ policy and economic reforms in China.
(ii) China started privatisation in the agricultural sector in 1982.
(iii) China started privatisation in the industrial sector in 1998.
(iv) Trade barriers were removed from the Special Economic Zone where foreign investors could set up their enterprises.
Question 7.
Study the cartoon given above carefully and answer the following questions: (C.B.S.E. 2019)
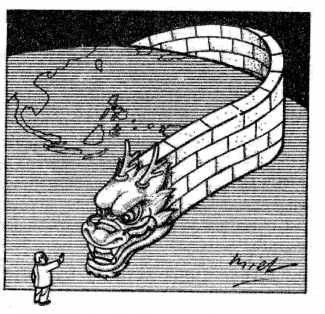
(i) Which part of this cartoon is related to China?
Answer:
In this cartoon, Dragon is related to China.
(ii) Assess the strength of China on the basis of the cartoon.
Answer:
China is growing as a great power. It is the world’s projected to overtake the U.S. as the world’s largest economy by 2040. However, it is not suitable conditions for India.
(iii) “China may be the next superpower in the world.” Justify the statement with two arguments.
Answer:
(a) In the economic sphere, China’s economy is growing very fast.
(b) Military power of China is very strong.
Note: The following questions are for the Visually Impaired Candidates only in lieu of Above question
(1) In your opinion, where does China stand as an economic power?
Answer:
China stands 2nd in the world as an economic power.
(2) Assess any two conditions which make the United States of America, a superpower.
Answer:
(a) Economically U.S.A. is very strong.
(b) Military point of view the U.S.A. is very strong.
(3) “China may be the next superpower in the world.” Justify the statement with two arguments.
Answer:
For this, see point
(i) Which part of this cartoon is related to China?
Answer:
In this cartoon, Dragon is related to China.
(ii) Assess the strength of China on the basis of the cartoon.
Answer:
China is growing as a great power. It is the world’s projected to overtake the U.S. as the world’s largest economy by 2040. However, it is not suitable conditions for India.
(iii) “China may be the next superpower in the world.” Justify the statement with two arguments.
Answer:
(a) In the economic sphere, China’s economy is growing very fast.
(b) Military power of China is very strong.
Question 8.
Study the cartoon given below carefully and answer the following questions: (C.B.S.E. 2018)

(a) Which country does this cartoon refer to?
Answer:
This cartoon belongs to China
(b) Evaluate any two changes in the economic policies of this country form ‘then’ to ‘now’
Answer:
For this see:
Explain the New Economic Policy of China since 1978. (C.B.S.E. 2013)
Or
“China followed its own path in j introducing a market economy”. Justify this statement with four suitable arguments? (C.B.S.E. Sample paper 2018)
Answer
- In 1978, Deng Xiaoping adopted the ‘Open Door’ policy and economic reforms in China.
- China started privatisation in the agricultural sector in 1982.
- China started privatisation in the industrial sector in 1998.
- Trade barriers were removed from the Special Economic Zone where foreign investors could set up their enterprises.
(c) Assess any two outcomes of the latest changes that took place in this country.
Answer:
- The Chines economy including both industry and agriculture grew at a forte rate.
- China emerged as an economic superpower in Asia.
Note: The following questions are for visually impaired candidates only, in lieu above question
(20.1) What is the full form of ASEAN?
Answer:
The full form of ASEAN is the Association of South-East Asian Nations.
(20.2) State the main objective of the ASEAN.
Answer:
The main objective of ASEAN was to accelerate economic growth and through that social progress and cultural development.
(20.3) What does the ‘ASEAN Way’ mean?
Answer:
ASEAN way is a form of interaction among ASEAN members that is informal and cooperative.
Alternative Centres of Power Important Extra Questions HOTS
Question 1.
Mention two drawbacks of China’s new economic policy.
Answer:
- China has made great economic growth but the benefits of growth have not reached to the common man.
- Corruption in administration is increasing day-by-day.
Question 2.
Mention two features of the European Union.
Answer:
- In the contemporary world, it is the oldest regional organisation.
- European Union stands for democracy, world peace, human rights and friendly relations amongst the nations. It is opposed to war.
Question 3.
Write two aims of the European Union.
Answer:
- The main aim of the European Union was to establish an economic and political organisation of the European states.
- A common currency of all the member states shall be created.
Question 4.
Illustrate two major points of dispute with China.
Answer:
- A major dispute is a border dispute which involves the demarcation of the 4200 km. the long border at the foot of Himalayas.
- Chinese aggression on Indian border on October 20, 1962, and the continuing violations of our borders.
Question 5.
Write two weaknesses in the European Union.
Answer:
- European Union has failed to adopt a common constitution. Prime Minister Churchill’s dream of the United States of Europe could not become a reality.
- The common currency of the European Union is not adopted by all the member states.
Question 6.
What do you understand by ‘Marshall Plan’?
Answer:
For the reconstruction of the economics of Western Europe, America started a plan known as the ‘Marshall Plan’. The Communists and even France under De Gaulle considered this plan as a cover to establish U.S. dominance in Western Europe. All the sixteen non-communist European nations which received aid from the Marshall Plan formed an organisation for European Economic Co-operation on April 15, 1948.