Here we are providing Class 12 Political Science Important Extra Questions and Answers Chapter 9 Recent Developments in Indian Politics. Political Science Class 12 Important Questions are the best resource for students which helps in class 12 board exams.
Class 12 Political Science Chapter 9 Important Extra Questions Recent Developments in Indian Politics
Recent Developments in Indian Politics Important Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
How many seats were secured by R.J.P. and the Congress in the elections of 2019?
Answer:
B.J.P. secured 303 seats in the Lok Sabha elections of 2019, while Indian National Congress secured 52 seats.
Question 2.
Highlight any two effects of the elections in 1989 on the politics of India. (Imp.) (C.B.S.E. 2014)
Answer:
The two effects of the elections in 1989 on the politics of India were as follows:
- Firstly, the defeat of the Congress Party.
- The role of Regional parties increased in the elections.
Question 3.
Are Regional Parties necessary? Give any two arguments in support of your answer. (C.B.S.E. 1996)
Answer:
Regional Parties are necessary for India due to the following reasons:
- India is a Continental polity with a wide range of socio-cultural and ethnic diversities. Under conditions of democratic culture, these diversifies are bound to indeed aspire for political economy.
- The emergence of regional economic imbalance in India is also responsible for the emergence of regional parties.
Question 4.
Political equations in the coalition government are unstable. How was this concept reflected in the formation of the National Front Government in 1989 and the United Front Government in 1996? (C.B.S.E. 2012 Outside Delhi)
Answer:
In November 1989, five parties; National Front comprising Janata Dal, Congress (S), and three regional parties, he., Telugu Desarn, DMK, and AGP formed the government headed by V.P. Singh with the outside support extended by the BJP and the left parties. In November 1990, V.P. Singh’s government reduced into minority and V.P. Singh resigned. In 1996, Janta Dal formed a United Front. With the consent of Congress and CPI (M), the Chief Minister of Karnataka, H.D. Deve Gowda was asked to lead the coalition as Prime Minister. His term was from June 1, 1996, to April 21, 1997. In 1997, the Congress Party withdrew the support.
Question 5.
What does a coalition government mean? Mention any one example of such a government. (Imp.) (C.B.S.E. 2013)
Answer:
A coalition government is formed when many small political parties or groups in a house agree to join hands on a common platform by sinking their broad differences and form a majority in the house.
For example, the UPA government formed in 2004 was a coalition government.
Recent Developments in Indian Politics Important Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type (2 Marks)
Question 1.
Name the two alliance fronts that formed the government at the center in 1989 and 1996 respectively. (Imp.) (C.B.S.E. 2014)
Answer:
- National Front
- United Front.
Question 2.
In 2019 who formed the government?
Answer:
B.J.P. formed a Coalition government known as NDA.
Question 3.
Which political party emerged as the single largest party in the 1996 Parliamentary elections?
Answer:
The Bharatiya Janata Party.
Question 4.
From 1989 until the elections of 2004 which party has been gaining strength in Lok Sabha. (C.B.S.E. 200S)
Answer:
From 1989 until the election of 2004 Bharatiya Janata Party has been gaining strength in Lok Sabha.
Question 5.
Name any two political parties, which were the components of the Third Front for the Lok Sabha elections in 2009.
Answer:
- C.P.I.
- C. P. M
- Bahujan Samaj Party
- Telugu Desam Party.
Question 6.
Who is the present Prime Minister of India? (Imp.)
Answer:
Sh. Narendra Modi.
Question 7.
From which year did the era • of coalition government at the center begin in India? (C.B.S.E. 2013)
Answer:
The era of the coalition government, at the center, began in India in 1989.
Question 8.
In which year did the Congress Party win 415 seats in the Lok Sabha? Who became the Prime Minister? (C.B.S.E. 2012 Delhi)
Answer:
The Congress Party won 415 seats in 1984 and Sh. Rajeev Gandhi became the Prime Minister.
Question 9.
Explain the concept of a ‘coalition Government’. (C.B.S.E. 2018)
Answer:
A coalition government is formed when many small political parties or groups in a house agree to join hands on a common platform by sinking their broad differences and form a majority in the house.
Question 10.
Identify anyone similarity between the united front Government of 1996 and the National Front Government of 1989. (C.B.S.E. 2019)
Answer:
Both the Government of 1989 and 1996 included Janta Dal and Several other regional Parties. Choose the correct answer:
Question 11.
In which year was Janata Dal formed?
(a) 1975
(b) 1982
(c) 1985
(d) 1988.
Answer:
(d) 1988.
Question 12.
Who headed the coalition government of 1989?
(a) Chandra Shekhar
(b) V.P. Singh
(c) I.K. Gujral
(d) Rajiv Gandhi.
Answer:
(b) V.P. Singh.
Recent Developments in Indian Politics Important Extra Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Write a short note on NDA.
Answer:
On 15th May 1999 in an effort to project Unity and Cohesion, BJP and its allies including the DMK and the Indian Lok Dal floated a National Democratic Alliance with a common manifesto for contesting Lok Sabha elections under the leadership of Mr. Atal Behari Vajpayee. National Democratic Alliance promised to give a stable, honest, transparent, and efficient government, capable of accomplished all-round development. In the 13th Lok Sabha elections, NDA secured 297 seats.
The NDA elected Mr. Atal Behari Vajpayee its leader and the government was formed under its leadership. In the 14th Lok Sabha elections, NDA secured 186 seats. In the 15th Lok Sabha elections, NDA secured 159 seats. NDA secured 334 seats in the 16th Lok Sabha election held in 2014 and formed the government under the leadership of Sh. Narendra Modi. NDA again formed the Government under the leadership of Sh. Narendra Modi in 2019.
Question 2.
Write a short note on United Progressive Alliance Government. (Imp.)
Answer:
In the general elections of 2004, the ruling BJP was stunned by the scale of defeat and Congress was astounded by the edge they got over the rivals. The country’s first-ever Congress-led Coalition called the United Progressive Alliance government was formed under the leadership of Dr. Manmohan Singh. The United Progressive Alliance and its supporting left parties unveiled the Common Minimum Programme, laying down six principles for governance for the government.
“The UPA makes a solemn pledge to the people of our country to provide a government that is corporation free, transparent and accountable at all times to provide an administration that is responsible and responsive at all times,” said the Prime Minister while releasing the document. However, the Prime Minister admitted the differences with the U.P.A, especially with the R.JD over women’s reservation.
Question 3.
Describe briefly any four main developments, witnessed by the country from 1989 to 1992. (C.B.S.E. 2008)
Or
Describe any four major developments in Indian Politics since 1989. (Imp.) (C.B.S.E. 2015)
Answer:
1. National Front. In Nov. 1989, the elections to the 9th Lok Sabha were held and no political party secured a clear majority. The five-party National Front, comprising Janata Dal, Congress (S), and three regional parties i.e., Telugu Desam, DMK, and AGP, formed the government headed by V.P. Singh with the outside support extended by the BJP and the left parties.
2. Congress (I) Government. Elections to the 10th Lok Sabha were held in May- June 1991 and the Hung Lok Sabha emerged for the second time in succession. No single party secured a clear majority in the Lok Sabha. Congress (I) formed the government under the leadership of P.V. Narsimha Rao.
3. Ram Mandir Issue. In June-July 1990 the BJP and Vishwa Hindu Parishad decided to construct Ram Mandir. In the meantime L.K. Advani started Rath Yatra from Somnath (Gujarat) to Ayodhya (U.P.). In Bihar, the Advani Yatra was stopped and he was arrested. BJP delegation led by Atal Behari Vajpayee met the President on 23rd October 1990 and presented a letter withdrawing support to the V.P. Singh government.
4. Mandal Commission Report. Prime Minister V.P. Singh announced, all of a sudden, the acceptance of the Mandal Report on August 7, 1990, in the Parliament. But this move of V.P. Singh alienated him from his senior-most colleagues. The student community launched a massive movement throughout the country against the implementation of the Mandal report.
Question 4.
Explain any four reasons for the emergence of the Coalition era in the Indian Democratic System. (C.B.S.E. Sample Paper)
Or
When and why did a long phase of Coalition politics begin in India? (C.B.S.E. 2012 Delhi)
Answer:
In India, the coalition era started in 1989 and became one of the most important features of the Indian political system.
The following reasons led to the emergence of the Coalition era in the Indian Democratic System:
- The coalition era came in the Indian democratic system with the split and failure of Congress in winning a majority.
- To build up a strong front against Congress, several political parties met that led to the formation of a coalition government.
- The greed for power and position led to the emergence of the coalition era.
- Disputes between Centre and State also caused the emergence of the coalition era in Indian democracy.
Question 5.
Write a short note on Hung Parliament.
Answer:
Hung Parliament is that parliament when no party gets a clear majority in the Lok Sabha. Since 1989 India is facing the problem of the Hung Parliament. In 1989, elections to the 9th Lok Sabha were held but no political party secured an absolute majority. Hence, no single political party was in a position to form the government. In the 10th, 11th, 12th, 13th, and 14th Lok Sabha elections no single political party secured a clear majority and thus coalition government was formed. After the 10th, 11th, and 12th Lok Sabha elections, the government was weak and unstable.
But after the 13the Lok Sabha election coalition government (NDA government) was led by Sh. Atal Behari Vajpayee and it completed full five years. After the 14th Lok Sabha election, a coalition government was formed under the leadership of Dr. Manmohan Singh. After the 15th Lok Sabha elections, again coalition government was formed under the leadership of Dr. Manmohan Singh. According to Prof. Rajni Kothari, “The emergence of Hung parliament and legislature over the past decade is a manifestation of people’s disenchantment with the political parties and parliamentary democracy”.
Question 6.
In what way do the coalition governments prove to be more democratic than the one-party governments? (Imp.) (C.B.S.E. 2015)
Answer:
- Coalition government represents all shades of public opinion. Different communities get proper representation in the government.
- Coalition government protects the rights and liberties of the minorities.
- In a coalition government, various parties, accommodate each other.
- The coalition government, restrict the dictatorship of one-party rule.
Question 7.
Explain the impact of coalition | government on Indian Politics. (C.B.S.E. 2011 Delhi)
Answer:
The following are the impact of the coalition government on Indian politics.
- The coalition government brought political instability in India.
- Coalition ministries were very much large in size because they had to accommodate the interests of all the different partners.
- Coalition government created tension between center and states.
- It was during the coalition era that the relation between the coalition ministry and the respective governors became strained.
Question 8.
Mention, any four Prime Minister of India and name their respective coalitions that led the union Government from 1989 to 1999. (C.B.S.E. 2018)
Answer:
| S.No Name of Prime Minister | Name of Coalitions |
| 1. Sh. V.P. Singh | National Front |
| 2. Sh. H.D. Devegowda | United Front |
| 3. Sh. Inder Kumar Gujral | United Front |
| 4. Sh. Atal Bihari Vajpayee | National Democratic Alliance |
Recent Developments in Indian Politics Important Extra Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1.
Assess any three benefits of the coalition government in India since 1989. (C.B.S.E. 2019)
Answer:
Following are the benefits of the coalitions government in India since 1989.
1. Representation of all shades of opinion. An important benefit of the coalition government is that in the government all shades of opinion get representation. There exist various political parties that represent different shades of opinion and each party gets somewhat represented in the government. The members of each political party support their view-point in the government. This way the government becomes such an institution that represents every type of view-point.
2. Nation is not divided into two halves. In a coalition government, the political parties do not bitterly criticize one another because after the resignation of the cabinet no single party is confident of forming the government. Therefore Nation is not divided into two halves.
3. Partner itself put check on the government: Another benefit of the coalition government in India since 1989, that partner of the coalition government, itself put a check on the autocratic activities of the government.
Question 2.
Analyze five developments that made a long-lasting impact on Indian Politics during the 1980s. (C.B.S.E. Sample Q.P. 2017)
Or
Analyze any three developments towards the end of the 1980s that were to make a long-lasting impact on the politics of India. (C.B.S.E. 2019)
Answer:
Following are the developments that made a long-lasting impact on Indian Politics during the 1980s:
1. The first major development was the defeat of the Congress Party their defeat marked the end of the ‘Congress System’.
2. Prime Minister V.P. Singh announced, all of a sudden, the acceptance of the Mandal Report on August 7, 1990, in the Parliament. But this move of V.P. Singh alienated him from his senior-most colleagues. The student community launched a massive movement throughout the country against the implementation of the Mandal report.
3. The Third Major development was the announcement of the New Economic Policy. With adopting the New Economic Policy, India Joined the Globalization and Liberalization Process.
4. In June-July 1990 the BJP and Vishwa Hindu Parishad decided to construct Ram Mandir. In the meantime L.K. Advani started Rath Yatra from Somnath (Gujarat) to Ayodhya (U.P.). In Bihar, the Advani Yatra was stopped and he was arrested. BJP delegation led by Atal Behari Vajpayee met the President on 23rd October 1990 and presented a letter withdrawing support to the V.P. Singh government.
5. The fifth major development was the assassination of Rajiv Gandhi in May 1991, Which led to a change in leadership of the Congress Party.
Question 3.
Describe any three major developments that left a long-lasting impact on the politics of India after the death of Rajiv Gandhi. (C.B.S.E. 2017)
Answer:
1. Weakened the Congress: After the death of Rajiv Gandhi, Congress was not able to get leadership from the Nehru family and it gave decline to the Congress. Thus, began an era of a multi-party system. No single party secured a clear cut majority, this development initiated an era of coalition governments at the center, in which regional political parties play a crucial role in informing the ruling alliance.
2. Introducing New Economic Policies: In 1991 New Economic Policy was introduced by Dr. Manmohan Singh with this New Policy era of the liberal and the open market was started in India.
3. Ayodhya dispute: In 1992 Ayodhya issue is another important development that left a long-lasting impact on the politics of India.
Question 4.
In the midst of severe competition and many conflicts, a consensus appears to have emerged among most political parties of India.” In the light of these statements, analyze any three elements of growing consensus. (Sample Paper Outside Delhi)
Or
Highlight any three issues on which a broad agreement has emerged among most of the political parties in India. (C.B.S.E. 2013)
Or
Describe any three points of consensus that emerged among most political parties in India in spite of severe competition and conflicts. (Imp.) (C.B.S.E. 2015)
Or
Describe any three elements of growing consensus among most of the political parties of India after 1989. (C.B.S.E. 2017)
Answer:
India is a Sovereign, Socialist, Secular, Democratic Republic country. In India, parliamentary democracy is established. For the successful working of parliamentary democracy, political parties are inevitable. In India, multiple party system exists. Election Commission recognized 7 national parties and 53 state-level parties.
Each party wants to capture power. Thus, there is competition and conflicts among the political parties. Conflicts are there because each political party has its own ideology, policies, and programs. However, in the midst of severe competition and many conflicts, a consensus has emerged among political parties on the following:
1. Full Faith in Constitutional System: All the political parties have full faith in the Constitutional system of India. For the registration of political parties, it is essential that the party should have true faith and allegiance to the Constitution of India.
2. Faith in Democracy and Secularism: All political parties have full faith in democratic values. Political parties are interested in capturing political power but through democratic methods. Mrs. Indira Gandhi imposed an emergency on 25th June 1975, but ultimately she held the election in a free and fair manner. Congress party was defeated in the election because they were responsible for emergency restrictions on the rights and liberties of the people.
3. Policy of Non-alignment: There is a consensus on the policy of non-alignment. Non-alignment is the basic principle of India’s foreign policy. Not only Congress but non-Congress governments at the center also followed the policy of non-alignment.
Question 5.
“Communalism is a bane for democracy in India.” How can we curb it? (C.B.S.E. 2005 Set I, II, III Delhi)
Or
‘Communalism is a curse’. How can it be curbed? Give any five suggestions. (C.B.S.E. 2005 C)
Answer:
Communalism is a bane for democracy in India. Communalism is the bane for democracy in India because of the following reasons:
- Several political parties in India have been formed on the basis of religion.
- Communal feelings play a vital role in elections. Almost all political parties field their candidates on the basis of caste and community.
- Voters are also influenced by religion while casting their votes. Generally, the Muslim or Sikh voters vote in favor of candidates belonging to their religions.
- Not only religion-based political parties are active in Indian politics but also religious-oriented pressure groups are doing their own role in communalizing the social and political atmosphere of our country.
- The communal riots have become an integral part of Indian politics, which are against democratic norms.
Methods to Curb Communalism. The following steps are suggested to curb communalism in India:
1. Right Type of Education. Communalism is a mental malady and hence needs a mental remedy. Through well-designed textbooks, articles, pamphlets, and other means, the educational system should be used for checking communalism.
2. Right use of Media. T.V., Radio, and Media should avoid the coverage of news and views likely to promote communal hatred. Radio, T.V., mass-media should spread the message of secularism, religious toleration, and fraternity.
3. Efficient And Strong. State machinery should be efficient, strong, and impartial enough to put down communalism. The government should not yield to communal pressures.
4. Political parties should be decriminalized. Election Commission should not give recognition to communal parties.
5. Religion should be separated from politics. To curb communalism, the central government has prohibited the use of religious places for political means.
6. Government should take steps to protect the rights of minorities. This will give minorities a sense of security; resultantly they will not encourage communalism.
7. Government should punish the communalist agents and for this special courts should be established.
8. Government should treat all religions equally and respect them. This will help in curbing communalism differences.
9. People of different religions should also respect other religions. They should practice religious toleration.
10. social and religious organizations should not have discriminatory feelings against any religion or religious act.
Question 6.
Write a note on the 16th Lok Sabha election held in 2014.
Answer:
In India the 16th Lok Sabha Elections April- May 2014 were conducted in 9 stages. The main features of this election are as follows:
- Enhancement in the Election Expenditure- The Central Government enhanced the Election expenditure limit in Feb 2014. Now a candidate for contesting the Lok Sabha seat can spend a maximum of 70 Lacs Rupees whereas in legislative Assembly election a candidate can spend a maximum of 28 Lacs Rupees on his/her election.
- Highest Percentage of Polling/Voting-In 16th Lok Sabha election highest 66.38% vote-polling was recorded.
- Nota Button used-in 16th Lok Sabha election 60 Lacs voters used the Nota (None of the above) button.
- Number of Voters-During the 16th Lok Sabha election, the number of total voters was 81 crore 40 Lacs. By which nearly 55 crores voters cast their votes.
- The number of Political Parties-During the 16th Lok Sabha election the number of Political Parties was 1687 in which 6 National Parties were included.
- Women candidates were elected-In the 16th Lok-Sabha elections maximum of 61 women were elected.
The results of these elections are given below:
| Name of Party | Seats |
| 1. Bhartiya Janata Party | 282 |
| 2. Bhartiya Communist Party | 01 |
| 3. Bhartiya Communist Party MARXIAN | 09 |
| 4. Indian National Congress | 44 |
| 5. Nationalist Congress Party | 06 |
| 6. Aam Admi Party | 04 |
| 7. All India Anna Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam-ANDMK | 37 |
| 8. All India N.R. Congress | 01 |
| 9. All India Trinamool Congress | 34 |
| 10. All India United Democratic Front | 03 |
| 11. Biju Janata Dal | 20 |
| 12. Indian Nationalist Lok Dal | 02 |
| 13. Indian Union Muslim League | 02 |
| 14. P.D.P. | 03 |
| 15. Janata Dal (S) | 02 |
| 16. Janata Dal (U) | 02 |
| 17. Jharkhand Mukti Morcha | 02 |
| 18. Kerala Congress (M) | 01 |
| 19. Lok Jan Shakti Party | 06 |
| 20. Naga Peoples Front | 01 |
| 21. Naga Peoples Party | 01 |
| 22. Pattali Makkal Katchi | 01 |
| 23. National Janata Dal | 04 |
| 24. Revolutionary Socialist Party | 01 |
| 25. Samajwadi Party | 05 |
| 26. Shiromani Akali Dal | 04 |
| 27. Shiv Sena | 18 |
| 28. Sikkim Democratic Front | 01 |
| 29. Telangana Rashtra Samithi | 11 |
| 30. Telugu Desam Party | 16 |
| 31. I-Mujlis-Ittehadul Muslimeen | 01 |
| 32. Apna Dal | 02 |
| 33. Rashtriya Lok Samata Party | 03 |
| 34. Sevabhamani Paksha | 01 |
| 35. YSR Congress Party | 09 |
| 36. Independents | 03 |
7. Sh Narendra Modi Emerged as Prime Minister. In the 16th Lok Sabha Elections, Bhartiya Janta Party won 282 seats and whereas NDA Coalition got 334 Seats. And the leader of BJP and NDA Sh. Narendra Modi was administered the oath of Prime Ministership on 26 May 2014.
8. Formation of Council of Ministers. On 26, May 2014 Prime Minister Narendra Modi formed his Council of Ministers in which 23 Cabinet Ministers, 10 Independent Charge Ministers, and 12 State Ministers were included.
Question 7.
Write a note on the 17th Lok Sabha election held in 2019.
Answer:
In India, the 17th Lok Sabha Elections were conducted in April-May 2019, in 7 stages. The main features of this election are as follows:
- Highest Percentage of Polling/Voting-In 17th Lok Sabha election highest 67.11% vote-polling was recorded.
- Number of Voters- During the 17th Lok Sabha election, the number of total voters was 90 crore.
- Women candidates were elected in the 17th Lok-Sabha elections 78 women were elected in these elections.
- Total 10 Lakh polling booths were made by the election commission.
- V.V.P.A.T was used along with E.V.M. all over India.
The results of these elections are given below:
| Party | Won |
| Aam Aadmi Party | 1 |
| AJSU Party | 1 |
| All India Anna Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam | 1 |
| All India Majlls-E-Ittehadul Muslimeen | 2 |
| All India Trinamool Congress | 22 |
| All India United Democratic Front | 1 |
| Bahujan Samaj Party | 10 |
| Bharatiya Janta Party | 303 |
| Biju Janta Dal | 12 |
| Communist Party of India | 2 |
| Communist Party of India (Marxist) | 3 |
| Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam | 23 |
| Indian National Congress | 52 |
| Indian Union Muslim League | 3 |
| Jammu & Kashmir National Conference | 3 |
| Janta Dal (Secular) | 1 |
| Janta Dal (United) | 16 |
| Jharkhand Mukti Morcha | 1 |
| Kerala Congress (M) | 1 |
| Lok Jan Shakti Party | 6 |
| Mizo Nation Front | 1 |
| Naga Peoples Front | 1 |
| National People’s Party | 1 |
| Nationalist Congress Party | 5 |
| National Democratic Progressive party | 1 |
| Revolutionary Socialist Party | 1 |
| Samajwadi Party | 5 |
| Shiromani Akali Dal | 2 |
| Shivsena | 18 |
| Sikkim Krantikari Morcha | 1 |
| Telangana Rashtra Samithi | 9 |
| Telugu Desam | 3 |
| Yuvajana Sramika Rythu Congress Party | 22 |
| Other | 8 |
| Total | 542 |
6. Sh. Narendra Modi Emerged as Prime Minister. In the 17th Lok Sabha Elections, Bharatiya Janata Party won 303 seats and whereas NDA Coalition got 355 Seats. Therefore the leader of BJP and NDA Sh. Narendra Modi was administered the oath of Prime Ministership on 30 May 2019.
7. Formation of Council of Ministers. On 30, May 2019 Prime Minister Sh. Narendra Modi formed his Council of Ministers in which 53 Ministers, 24 Cabinet Ministers, 9 Independent Charge Ministers, and 24 State Ministers were included
Question 8.
In the 2014 elections, people have j voted for a stable government at the center. Do you think that the era of the coalition has ended? Support your j answer with suitable arguments. (C.B.S.E. 20IS)
Answer:
During April-May 2014, B.J.P. won with 282 seats in the Lok Sabha elections and under the magnetic personality of Sh. Narendra Modi people have voted for a stable government at the center. Though after 1984, for the first time, the rule of the complete majority is established, one cannot conclude that an era of the coalition government has ended. However, in this election B.J.P received support from other NDA coalition parties thus accounting for 336 seats in the 2014 elections.
Firstly, Regional political parties are having their full importance, and these parties fully influence and play their role in the National Politics of the country.
Secondly, though BJP got a complete majority in the center, yet there is a coalition government in the center also and allies are Shiromani Akali Dal and Shiv Sena and Telugu Desam, etc.
In many states, the coalition government has been formed where the parties have failed to win a clear majority.
Question 9.
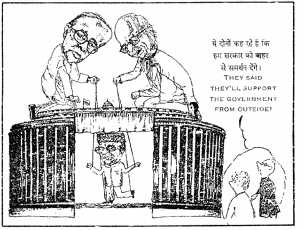
Study the above cartoon carefully and answer the following questions:
(i) Who was head of the Government formed by the National Front in 1989?
Answer:
Sh V.P. Singh was head of the government formed by the National Front in 1989.
(ii) Why was the government formed by him called a puppet government?
Answer:
The government formed by Sh. V.P. Singh called a puppet government because the government was supported by
other parties, especially by Left and B.J.P.
(iii) Identify the puppeteers pulling the strings and the political parties they belong to. (C.B.S.E. 2016)
Answer:
| Name of the Leader | Political Parties |
| (a) Sh. Jyoti Basu | C. P.M. |
| (b) Sh. Lai Krishna Advani | B.J.P. |
Question 10. Study the cartoon given below and answer the following questions:

(i) Identify any four national leaders from the above cartoon and mention the serial number of each.
Answer:
- Sh. Rajiv Gandhi
- Sh. V.P. Singh;
- Sh. Lai Krishan Advani
- Ch. Devi Lai.
(ii) Which was the most con¬troversial issue of the period related to leader No. 2 as Prime Minister of India?
Answer:
The most controversial issue of the period related to leader No. 2 (Sh. V.P. Singh) was to implement the recommendation of the Mandal Commission.
(iii) What was the position of the party led by leader No. 1 in the Lok Sabha elections of 1989? (C.B.S.E. 2016)
Answer:
Leader No. 1’s (Sh. Rajiv Gandhi) party, (Congress Party) won 197 seats.
Recent Developments in Indian Politics Important Extra Questions HOTS
Question 1.
What do you know about NDA?
Answer:
NDA stands for National Democratic Alliance. It was formed by Bharatiya Janata Party and its and its allies in May 1999. It was formed under the leadership of Atal Behari Vajpayee. In the 13th Lok Sabha elections, NDA secured 297 seats. The NDA elected Mr. Atal Behari Vajpayee its leader and the government was formed under his leadership.
Question 2.
What do you know about United Front (U.F.)?
Answer:
United Front was formed in 1996 by Janata Dal and its allies. Samajwadi Party, D.M.K., Assam Gana Parishad, Tamil Manila Congress, Communist Party of India, and Telugu Desam Party were the main members of U.F. United Front formed India’s government between 1996 and 1998. H.D. Deve Gowda was the Prime Minister of the United Front government from June 1, 1996, to April 21, 1997.
Question 3.
How far is it correct to say that the coalition government in India has helped in arriving at some consensus?
Answer:
After 1989, the coalition government has become a regular feature of the Indian political system. After the Lok Sabha election of 2009, the coalition government under the leadership of Dr. Manmohan Singh was formed. It is correct to some extent that the coalition government in India has helped in arriving at some consensus.
Question 4.
Are Regional Parties necessary? Give any two arguments in support of your answer.
Answer:
Regional Parties are necessary for India due to the following reasons:
- India is a Continental polity with a wide range of socio-cultural and ethnic diversities. Under conditions of democratic culture, these diversities are bound to indeed aspire for political economy.
- The emergence of regional economic imbalance in India is also responsible for the emergence of regional parties.