Chapter 15 Our Environment Class 10 Science Important Questions with Answers PDF will help you in scoring more marks. This consists of 1 mark Questions, 3 Mark Numericals Questions, 5 Marks Numerical Questions and previous year questions from Chemical Reactions and Equations Chapter.
Our Environment Class 10 Important Questions and Answers Science Chapter 15
Very Short Answer Questions (1 Mark Each)
Question 1.
What is environment ? (CBSE Foreign 2006, 2016, CCE 2012)
Answer:
It is sum total of all external factors, substances, conditions and living beings that surround the organisms and influence the same without becoming their part.
More Resources
- Previous Year Question Papers for CBSE Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science
- Value Based Questions in Science for Class 10
- HOTS Questions for Class 10 Science
Question 2.
Why is ozone layer getting depleted at higher levels of the atmosphere ? (CBSE Delhi 2008 C, CCE 2011)
Answer:
Presence of ozone depleting chemicals like chlorofluorocarbons.
Question 3.
Name any two abiotic components of an environment. (CBSE Delhi 2008 C)
Answer:
(a) Climatic factors (light, temperature, rainfall).
(b) Edaphic factors (soil and its conditions).
Question 4.
What are two main components of our environment ? (CBSE Delhi 2009, CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Biotic Components, e.g., producers, herbivores, carnivores, decomposers.
(b) Abiotic Components e.g., climatic factors, edaphic factors, topographic factors, inorganic nutrients and organic substances.
Question 5.
Which compounds are responsible for the depletion of ozone layer ? (CBSE A.I. 2009)
Answer:
Ozone depleting substances like chlorofluorocarbons, halons, methane, N2O, Chlorine, Carbon tetrachloride.
Question 6.
Why are green plants called producers ? (CBSE A.I. 2009, Delhi 2016, CCE 2011)
Answer:
Green plants are also called producers because only they can synthesise organic food from inorganic raw materials with the help of solar energy in the process of photosynthesis. This food is not only used by green plants but also all other organisms called consumers.
Question 7.
The flow of energy in the food chain is unidirectional. Why ? (CCE 2011 )
Answer:
There is dissipation of energy at every step of its transfer and transformation so that energy cannot flow back
in the reverse direction. It flows from sun to plants, plants to animals, animals to animls, organic remains to decomposers and dissipation as heat at every stage.
Question 8.
Use of paper is more environment friendly than the use of polythene for packaging. Justify. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Paper bags are biodegradable while polythene is nonbiodegradable.
Question 9.
In a food chain comprising frogs, insects, birds and grass, which one of the organisms is likely to have maximum concentration of harmful non-biodegradable chemicals in the body. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Birds, as they form the topmost trophic level where the non-biodegradable chemicals will have maximum biomagnification.
Question 10.
State one advantage of using disposable paper cups over disposable plastic cups. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Disposable paper cups are biodegradable while disposable plastic cups are non-biodegradable.
Question 11.
Give an example of food chain of four trophic levels that exists in a grassland. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
![]()
Question 12.
Write the full form of CFC. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Chlorofluorocarbon.
Question 13.
In a certain study conducted on the occurrence of DDT along food chains in an ecosystem, the concentration of DDT in grass was found to be 0-5 ppm. In sheep, it was 2 ppm and in man it was 10 ppm. Why was the concentration of DDT maximum in case of man ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
DDT is a non-biodegradable chemical which not only accumulates in each trophic level but also undergoes biomagnification with the rise in trophic level. DDT concentration is maximum in man as man is occupying the highest trophic level.
Question 14.
Why there has been a large hue and cry against the use of CFCs ? (CCE 2011, CBSE Foreign 2016)
Answer:
CFCs (Chlorofluorocarbons) pass on to the upper layers of atmosphere, i.e., stratosphere, where ozone layer is based. CFCs cause depletion of ozone layer that allows harmful UV radiations to reach the surface of the earth causing skin cancers and defective eye sight.
Question 15.
Select the biodegradable wastes : DDT, crop residue, leather, glass. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Crop residue, leather.
Question 16.
In a food chain consisting of snake, insect, grass and frog, assign an appropriate trophic level to frog.
(CCE 2011, CBSEA.I. 2016)
Answer:
![]()
Question 17.
What are the three ‘Rs’ in saving the environment ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Reduce, recycle and reuse.
Question 18.
In the following food chain, 5 J of energy is available to man. How much energy was available at the producer level ?(CCE 2011)
![]()
Answer:
Man 5 J, sheep 5 x 10 = 50 J, plants 50 x 10 = 500 J.
Question 19.
Name the disease caused in human beings due to depletion of ozone layer in the atmosphere. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Skin cancer.
Question 20.
Name any two non-biodegradable wastes. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Waste plastic articles, polythene bags, many pesticides like DDT.
Question 21.
Define the term biomagnification. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Biomagnification is the increase in the level of a non-biodegradable substance with each successive rise in the trophic level of a food chain.
Question 22.
What is depicted in the scheme ? (CCE 2011)
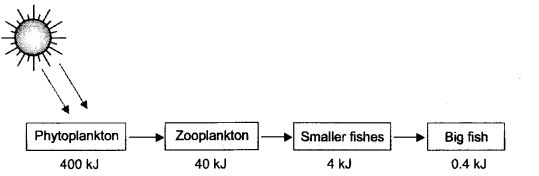
Answer:
It is a food chain that is depicting 10% law of energy.
Question 23.
Ozone is deadly poisonous. Still it performs an essential function. How ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Ozone present in the ozone layer of the stratosphere dissipates and hence filters out high energy UV radiations (100 —320 nm) of the sun and protects the earth from the same.
Question 24.
Which of the following belong to the first trophic level : Grasshopper, Rose plant, Neem plant, Cockcroach, Vulture. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Rose plant, Neem plant.
Question 25.
What would happen to the environment if decomposers were not present ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Organic remains will pile up and all the biogenetic nutrients will get tied up in organic matter with no further scope of manufacture of more organic matter.
Question 26.
Which one of the following organisms comprising a food chain will possibly have the maximum concentration of harmful chemicals in its body :
Peacock, Frog, Grass, Snake, Grasshopper. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Peacock as it lies at the top of food chain :
Grass ———> Grasshopper ———> Frog ———> Snake ———> Peacock.
Question 27.
Phytoplankton ———> Zooplankton ———> Fish ———> Fish eating Bird.
In this food chain which organisms will have
- Maximum available energy
- Maximum concentration of pesticides. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
- Phytoplankton
- Fish eating birds.
Question 28.
List two man-made ecosystems. (CCE 2011, CBSE Foreign 2017)
Answer:
Cropland, aquarium.
Question 29.
Which of the following materials are biodegradable : Glass, leather, glucose, silver foil ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Leather, glucose.
Question 30.
Mention any two methods of garbage disposal. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Composting, manure and biogas.
Question 31.
Why is depletion of ozone layer a cause of concern ? (CCE 2011, CBSEA.I. 2016)
Answer:
Depletion of ozone layer is causing increased number of skin cancers, cataracts and reduced immunity in human beings.
Question 32.
How can we help in reducing the problem of waste disposal ? List any two ways. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
- Separation of biodegradable and non-biodegradable wastes,
- Preparation of compost or vermicompost from biodegradable waste and handing over the recyclable non-biodegradable wastes to rag pickers.
Question 33.
Which one of the following food habits is better and why :
(a) Plant ———> Man
(b) Plant ———> Goat ———> Man. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Plant ———> Man as it makes more energy available (ten percent law).
Question 34.
Name the type of compounds which are used as refrigerants and in fire extinguishers that deplete the ozone layer in the atmosphere. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Chlorofluorocarbons (as refrigerants) and halons (in fire extinguishers).
Question 35.
Producers always occupy the first trophic level in any food chain. Why ? (CCE2011, C.B S.E. Foreign 2016)
Answer:
Only producers have the ability to trap solar energy and manufacture organic food through the process of photosynthesis.
Question 36.
A list of organisms is given below : Peacock, Snake, Gross, Frog, Grasshopper. Construct a food chain showing snake at the fourth place. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
![]()
Question 37.
“Save the tiger” campaign is being over-emphasized these days by our Government. What may be the possible reason ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
To maintain the ecological balance which is effected through biocontrols.
Question 38.
Why are plastics non-biodegradable substances ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Plastics are non-biodegradable substances as they cannot be broken down by decomposers. Their wastes pile up‘ . . . .
Question 39.
What step is being taken to limit the damage to ozone layer ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Stopping manufacture of chlorofluorocarbons and halons and replacing them with ozone friendly substances.
Question 40.
Which gas shields the surface of earth from harmful radiations of the sun ? Why are UV radiations harmful to organisms ? (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Ozone.
Harmful Effects of UV Radiation.
- Skin cancer, cataract and fall of immunity in humans.
- More mutations, fall in photosynthesis, blinding of animals, killing of their young ones.
Question 41.
List two raw materials used by living organisms of the first trophic level for making food. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
CO2, H2O and minerals. Energy is obtained from sun.
Question 42.
Which of the following are biodegradable : Gold coin, glass, nylon cloth, oil, silver foil, leather. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Oil. leather.
Question 43.
In the food chain comprising Tiger, Plants and Goats, which will
(a) Transfer the maximum amount of energy
(b) Receive minimum amount of energy ? (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Transfer of Maximum Energy. Plants
(b) Receive Minimum Energy. Lion.
Question 44.
Identify producers from the following : Frog, Blue-green algae, Grass hopper, Fish, Grass. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Blue-green algae, Grass.
Question 45.
Draw a line diagram to show flow of solar energy in ecosystem. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
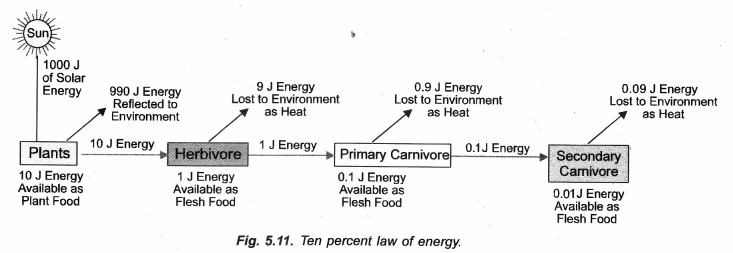
Question 46.
What is 10% law in the context of energy transfer in food chains ? (CCE 2012)
Answer:
10% Law (Lindeman, 1942). Energy available decreases by 90% with the rise in trophic level so that higher trophic level comes to have only 10% of energy present in lower trophic level.
Question 47.
Why do man-made materials like plastics persist for a long time in our environment ? (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Man made materials like plastics are non-biodegradable because decomposers do not have enzymes to degrade them.
Question 48.
A geographical area contains organisms like snake, grass hopper, peacock, grass and frog. If pesticides was used in this area to kill insects which among the organisms will have maximum amount of pesticide. Name the phenomenon involved. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Peacock will have maximum concentration of pesticide as it lies at the top of food chain. The phenomenon involved in increase in pesticide concentration at higher trophic level is called biomagnification.
Question 49.
Name any two non-biodegradable wastes generated daily in household activities. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Milk pouches, polythene bags.
Question 50.
State a way to prevent accumulation of harmful chemicals in our bodies. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
- Use of organic foods.
- RO treated drinking water.
- Minimum use of pesticides at home. Instead, stress should be on cleanliness and double doors.
Question 51.
Write the appropriate names of trophic levels Z and X in the figure. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
X: Primary consumer.
Z: Tertiary consumer.
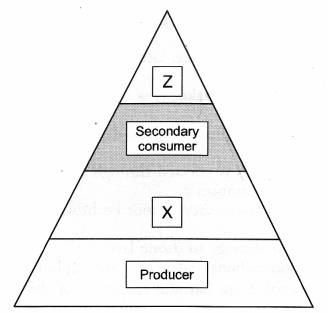
Question 52.
Which chemical is used as fire extinguishers ? How is it harmful ? (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Halon or bromine containing gas, e.g., bromochlorodifluoromethane.
It causes depletion of ozone in the stratosphere.
Question 53.
Pick up non-biodegradable substance from the following : Animal bones, wool, paper, glass. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Glass.
Question 54.
What is ecosystem ? (CCE 2012, CBSE Delhi 2017)
Answer:
Ecosystem is self sustained ecological system which consists of a distinct biotic community and the physical environment both interacting and exchanging materials between them.
Question 55.
Select the biotic components of the environment from the following : Fungi, Soil, Mango Tree, Temperature. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Fungi, Mango tree.
Question 56.
Why is the Government stressing upon the use of jute/cloth carry bags ? (CCE 2012)
Answer:
- Cloth bags are stronger and more durable as compared to plastic bags.
- They are washable.
- They are reused time and again.
- Cloth bags do not pollute environment.
- They are made of biodegradable material which can also be recycled.
Question 57.
Why should biodegradable and nonbiodegradable wastes be discarded in two separate dust bins ? (CCE 2013)
Answer:
So that the two can be easily disposed off without causing much littering and stink
- Disposable directly to composting and gasification plants,
- Nondisposable for separation into recyclable and nonrecyclable (landfill) components.
Question 58.
What will be the amount of energy available to the organisms of the second trophic level of food chain, if the energy available at the first trophic level in 10,000 Joules ? (CCE 2015)
Answer:
1000 Joules (10% Law).
Question 59.
Which of the following are always at the second trophic level of food, chains : Carnivores, Autotrophs, Herbivores ? (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Herbivores.
Question 60.
From the following list find out the organism which is likely to have maximum concentration of pesticide in the body-Grass, grasshopper, frog, snake and hawk. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Hawk, because it lies at the top of food chain where maximum bio-magnification of pesticide concentration will occur.
Question 61.
Suggest a food chain in which one of the trophic level is occupied by humans. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Wheat ———> Human; Grass ———> Goat ———> Human.
Question 62.
Differentiate between the food habits of organisms belonging to first and second trophic levels.
Answer:
Organisms of first trophic are producers. Organisms of second trophic level are herbivores. Producers are autotrophic, i.e., manufacture their own food from inorganic raw materials. Herbivores are animals which feed on producers for obtaining food and its contained energy.
Question 63.
List two natural ecosystems. (CBSE Delhi 2016, Foreign 2017)
Answer:
Forest, lake/pond.
Question 64.
List two biotic components of biosphere. (CBSE Delhi 2016)
Answer:
Plants, animals, microorganisms
Question 65.
Why is forest/lake considered a natural ecosystem ? (CBSE Delhi 2017)
Answer:
It is a self sustained ecological system.
Question 66.
In the following food chain, 100 J of energy is available to the lion. How much energy was available to the producer ? (CBSE A.I. 2017)
Answer:
Plants ———> Deer ———> Lion.
Energy available to deer = 100J x 10 = 1000 J
Energy available to plants = 1000 x 10 = 10,000 J.
Question 67.
In the following food chain, plants provide 500J of energy to rats. How much of energy will be available to hawks from snakes ?
Plants ———> Rats ———> Snakes ———> Hawks (CBSE A.I. 2017)
Answer:
Energy available to snakes from rats
500 J % 10 = 50 J
Energy available to hawks = 50 J% 10 = 5J.
Question 68.
In the following food chain, 20000J of energy was available to the plants. How much energy would be available to man in this chain ?
Plant ———> Sheep ———> Man (CBSE A.I. 2017)
Answer:
Out of the energy available to plants, the amount of energy trapped by them and available to sheep is 1%. 20000 x 100% = 200J
Energy available to sheep = 200 10 = 20 J
Energy available to man = 20 x 10% = 2 J.
Question 69.
List any two abiotic components of an ecosystem.
Answer:
Water, minerals, sunlight.
Short Answer Questions (2 Marks)
Question 1.
Construct an aquatic chain showing four trophic levels.
Answer:
Phytoplankton ———> Zooplankton ———> Small Carnivorous Fish –
Question 2.
Explain “biological magnification” with the help of an example.
Answer:
Biological magnification is increase in the concentration of a chemical per unit weight of the organisms with the successive rise in trophic level. In one study it was found that concentration of harmful chemical like DDT will increase 80,000 times the concentration present in water.
![]()
Question 3.
A high concentration of harmful chemical is highly injurious, even fatal, to higher trophic level organisms. Mention the basis of classifying substances as biodegradable and non-biodegradable. Give two examples of each. (CBSE Foreing 2010)
Answer:
Substances are classified into biodegradable and non-biodegradable on the basis of their disposability or nondisposability by saprophytic organisms.
Biodegradable. Used tea leaves, waste paper.
Non-biodegradable. DDT, silver/aluminium foil.
Question 4.
What is ozone ? How does it protect the organisms on the earth ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Ozone is triatomic form of oxygen, O3. It forms a protective ozone layer in the stratosphere. Ozone layer absorbs the very harmful component of ultraviolet radiations (100 – 320 nm) and thus protect the organisms on the earth.
Question 5.
Observe the food chain :
Plant (1000 kj) ———> Goat ———> Lion
(a) If autotrophs occupying the first trophic level are called producers, what are herbivores called as ?
(b) How much energy does the lion get in the above food chain ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Primary consumers
(b) 10 kj (10% law, 1000 ———> 100 ———> 10).
Question 6.
“The maximum concentration of harmful chemicals accumulates in human beings ?” State the phenomenon involved and justify this statement. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Human beings are omnivorous and lie at the tip of almost every food chain. They are also long lived. Harmful chemicals reach in higher concentration through biomagnification and continue to accumulate in their bodies. Therefore, non-biodegradable chemicals occur in maximum concentration in human beings.
Question 7.
In the food chain Grass ———>Deer ———> Lion operating in a forest, what will happen if all the
(a) Lions are removed
(b) Deer are removed. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Removal of Lions. It will cause spurt in population of deer so much so that whole of grass can disappear resulting in conversion of the area into desert and death of the deer as well.
(b) Removal of Deer Lions will die of starvation.
Question 8.
Define
(a) Biomass
(b) Anaerobic degradation. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Biomass. It is the amount of living matter, measured as fresh or dry weight.
(b) Anaerobic Degradation. There is slowing down of rate of decomposition of organic remains which will pile up. Offensive odours may occur due to putrefaction of proteins while fermentation of carbohydrates gives rise to alcohols and organic acids that may kill the microbes. It is, however, useful in production of biogas.
Question 9.
We often observe domestic waste decomposing in the bylanes of residential colonies. Suggest ways to make people realize that the improper disposal of waste is harmful to the environment. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
Domestic waste is often thrown outside the living quarters or some common place near the homes for municipal staff to pick up and dispose the same. The waste is, however, spread by stray cattle, pigs and dogs and is left to decompose. It is an improper method of waste disposal being harmful to environment as well as to all of us. It produces stink and becomes a source of several diseases. The scattered decomposing waste attracts flies, mosquitoes and rats.
Therefore, a proper waste disposal method involving biodegradable in covered green bins and nonbiodegradable in covered blue bins be adopted. The municipal staff can take the wastes from the bins.
Question 10.
Explain how ozone is formed in the atmosphere ? How does it protect living beings from harmful radiations of the sun ? (CCE 2013)
Answer:
- Ozone is formed in the upper atmosphere by the action of ultraviolet (UV) radiations over oxygen (O2)
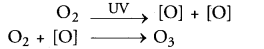
- Ozone present in the upper atmosphere protects us from extremely harmful high energy ultraviolet radiations (100-320 nm) by dissipating their energy.
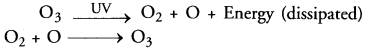
Question 11.
Why is Government of India imposing a ban on the use of polythene bags ? Suggest two alternates to these bags and explain how this ban is likely to improve the environment. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
Polythene is nonbiodegradable. Use of polythene bags often chokes drains and kills animals feeding on garbage besides piling up in garbage disposal sites.
Alternates: Use of cloth bags and paper bags.
Environment: Cloth bags can be used and reused. Both cloth and paper bags are biodegradable.
Question 12.
List two reasons to show that the existence of decomposers is essential in an ecosystem. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
- They function as saprophytes and cleanse the earth of organic remains.
- Decomposers release minerals tied up in organic remains. They thus help in recycling of biogeochemicals. Recycling of paper, metal, plastic and e-waste is done at most of the places.
Question 13.
Mention the positive impact of this recycling process on environment. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
- There will be reduced use of resources.
- There will be little pollution from these wastes as they are picked up for recycling as soon they are produced.
Question 14.
It is said that there is need to put a complete ban on the products containing aerosols. What are aerosols ?
Why is there a demand to put a ban on them ? (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Aerosols are mist producing propellants used in sprays like deodrants, perfumes, after shaves, etc. They are commonly made of chlorofluorocarbons which are strongest ozone depleting substances. Therefore, there is a demand for putting a ban on them.
Question 15.
Food web is shown as a series of branching lines of food chains. Explain and justify the statement.
(CCE 20I5)
Answer:
Food web is a network of food chains occurring in an ecosystem which get connected at different trophic levels so as to form feeding connections or alternatives amongst different organisms of the community.
Because the food chain are connected at different trophic levels, connectives appear as branching lines of food chains.
Question 16.
Rohan was watching television when his mother instructed him to empty the home garbage bin which had become full, into public garbage bin. Rohan emptied the home garbage bin in front of his house as the public garbage bin was little far off. His mother saw him doing so. She tried to explain him the problems associated with improper garbage disposal.
(a) Mention any 2 problems, society faces due to improper garbage disposal.
(b) Mention two values displayed by Rohan’s mother. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
(a)
- The garbage will be scattered by cattle and dogs, resulting in unhygienic condition.
- Stink or foul smell will be produced by the decaying garbage due to emission of foul gases.
- The decaying garbage becomes breeding place of flies and other pests which spread a number of diseases.
(b) Values :
- Care for sanitary conditions all around.
- Social consciousness
- Teaching good habits.
Question 17.
Recycling is considered as a welcome practice to deal with the environmental problems. Justify the statement with two arguments ? (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Recycling is treatment of waste material so as to make it suitable for reuse, e.g., metallic articles, broken glass, paper, etc.
- There will be reduced use of resources.
- There will be little pollution from these wastes as they are picked up for recycling as soon they are produced.
Question 18.
We as an individual can contribue by becoming environmental friendly. What practices we can adopt in order to do so. (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
- Use of cloth bags instead of polythene or plastic bags.
- Separation of biodegradable and non-biodegradable in green and blue coloured bins.
- Use of compact fluorescent lamps instead of incandescent lamps.
- Harvesting of rain water and preventing wastage of resources.
Short Answer Questions (3 Marks Each)
Question 1.
Why are some substances biodegradable and some non-biodegradable ? (CBSE A.L 2007)
Answer:
Substances which can be degraded and disposed off naturally by saprophytic organisms or decomposers are called biodegradable, e.g, organic remains, garbage, sewage, livestock waste. Substances which cannot be degraded by saprophytes are known as non-biodegradable. They are mostly man-made articles like pesticides, plastic, polythene, synthetic fibres, etc. Biodegradable articles are formed naturally in biosphere. Decomposer organisms feed on them by secreting digestive juices and absorbing the solubilised substances. Biogenetic nutrients are released in the process called mineralisation. Non-biodegradable articles pile up in nature because decomposers do not have enzymes to degrade them.
Question 2.
“Damage to the ozone layer is a cause of concern.” Justify the statement. Suggest any two steps to limit this damage. (CBSE Delhi 2008 C)
Answer:
Cause of Concern: Ozone layer present in the stratosphere has thinned out by about 8% over the equator and more so over the antarctica where a big ozone hole appears every year. This has increased the level of UV-B radiations reaching the earth by 15-20%. These radiations are causing increased number of skin cancers, cataracts and reduced immunity in human beings. There is increased incidence of blinding of animals, death of young ones, reduced photosynthesis, higher number of mutations and damage to articles.
Steps to Limit Damage,
- Ban on production and use of halons.
- Ban on production and use of chlorofluorocarbons.
Question 3.
Distinguish between biodegradable and non-biodegradable substances. List two effects of each of them in our environment. (CBSE Delhi 2008 C)
Answer:
(a) Differences between Biodegradable and Non-biodegradable Substances:
|
Biodegradable Wastes |
Non-biodegradable Wastes |
| 1. Origin. They are biological in origin. | They are commonly man-made. |
| 2. Degradability. The wastes are degraded by microorganisms. | They are not degraded by microorganisms. |
| 3. Accumulation. They do not accumulate in nature. | They pile up and accumulate in nature. |
| 4. Biomagnification. The biodegradable wastes do not show biomagnification. | The soluble non-degradable wastes enter food chains and undergo biomagnification. |
| 5. Resource. The wastes can be converted into resource. | Some wastes can be recycled. |
| Examples. Garbage, livestock wastes, sewage. | Examples. Plastic, polythene, glass, nickel, cadmium, several pesticides. |
(b) Effects of Biodegradable Substances:
- Stink: Within a day or so waste biodegradable substances begin to stink and produce foul gases.
- Pests and Pathogens: The decaying biodegradable substances become breeding places of flies and many other pests. They also contain a number of pathogens. Flies and other pests carry the germs to all the places visited by them resulting in spread of diseases.
(c) Effects of Non-biodegradable Substances:
- Dumping Area: Dumping of non-biodegradable substances on a piece of land converts the same into barren land. It is also called landscape pollution.
- Biological Magnification: Pesticides, heavy metals and other chemicals enter water and food chains. They accumulate in toxic proportions and harm all kinds of living organisms. Their concentration also increases with rise in trophic level. Human beings are harmed the most because man lies at the top of every food chain.
Question 4.
Why are bacteria and fungi called decomposers ? List any two advantages of decomposers to the environment.
(CCE 2011)
Answer:
Answer:
(a) Decomposers: Most of the bacteria and fungi are saprophytes. They obtain their nourishment from organic remains. For this they secrete digestive enzymes over the remains. The remains are converted into soluble absorbable form. This results in decomposition of organic matter. Therefore, bacteria and fungi are called decomposers.
(b) Advantages:
- Scavengers: Decomposers function as scavengers by removing organic remains and cleansing the earth.
- Mineralisation: Decomposers release inorganic nutrients trapped in organic remains. The same are recycled.
Question 5.
How is ozone formed in the upper atmosphere ? Why is damage to ozone layer cause of concern to us.
What causes this damage ? (CBSE A.I. 2008, 2008 C, Delhi 2009 C)
Answer:
(a) Formation of Ozone in Upper Atmosphere. High energy UV radiations split oxygen molecules into oxygen atoms. The latter react with oxygen molecules to form ozone (Molina and Molina, 1992)
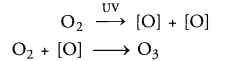
(b) Damage to Ozone Layer Cause of Concern:
Ozone layer present in the stratosphere has thinned out by about 8% over the equator and more so over the antarctica where a big ozone hole appears every year. This has increased the level of UV-B radiations reaching the earth by 15-20%. These radiations are causing increased number of skin cancers, cataracts and reduced immunity in human beings. There is increased incidence of blinding of animals, death of young ones, reduced photosynthesis, higher number of mutations and damage to articles
(c) Causes of Damage. Presence of ozone depleting substances or ODS in the stratosphere ———> Halons,
chlorofluorocarbons, N2O, Methane, Chlorine, Carbon tetrachloride.
Question 6.
State in brief two ways in which nonbiodegradable substances would affect the environment. List two methods of safe disposal of the nonbiodegradable waste. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
Effects on Environment:
- Dumping Area: Dumping of non-biodegradable substances on a piece of land converts the same into barren land. It is also called landscape pollution.
- Biological Magnification: Pesticides, heavy metals and other chemicals enter water and food chains. They accumulate in toxic proportions and harm all kinds of living organisms. Their concentration also increases with rise in trophic level. Human beings are harmed the most because man lies at the top of every food chain.
Safe Disposal:
- Recycling: Metal, plastic and glass articles can be sent for recycling,
- Sanitary Landfills: The nonrecyclable articles are dumped in specially prepared low lying area, compacted and covered by a layer of earth, lime and bleaching powder.
Question 7.
(a) What is an ecosystem ? List its two main components.
(b) We do not clean ponds or lakes but an aquarium needs to be cleaned regularly. Explain. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a) Ecosystem: It is self contained ecological system, which consists of a distinct, biotic community and the physical environment both interacting and exchanging materials between them.
Main Components,
- Biotic, e.g., producers, consumers
- Abiotic, e.g., climatic factors, inorganic nutrients.
(b) Cleaning an aquarium:
An aquarium is an artificial system which is also incomplete due to absence of producers, food chains and decomposers. There is no recycling and self cleaning. However, a pond or a lake is a self sustained, natural and complete ecosystem where there is perfect recycling of nutrients.
Question 8.
“Our food grains such as wheat and rice, the vegetables and fruits and even meat are found to contain varying amounts of pesticide residues”. State the reason to explain how and why it happens ? (CCE 2014)
Answer:
Crops are often sprayed with pesticides in order to prevent loss due to attack of pests. The sprayed pesticides enter the food crops, soil, vegetation and water. As a result grains like wheat and rice, vegetables, fruits and meat of animals come to have varying amounts of pesticides.
Question 9.
“Energy flow in a food chain is unidirectional”. Justify this statement. Explain how the pesticides enter food chain and subsequently get into our body. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
Energy Flow is Unidirectional:
An ecosystem does not have its own source of energy. It receives the same from sun. Green plants or producers trap the solar energy and change it into chemical form during synthesis of food. Herbivores obtain energy from the food they take. A lot of energy dissipates during transfer and utilization of food energy by herbivores (10% law). From herbivores the food energy passes to primary carnivores. However, only about 10% of herbivore energy is passed into body mass of primary carnivores.
The rest is dissipated. From primary carnivores the energy passes into secondary carnivores (10%), etc. It is ultimately lost as heat.
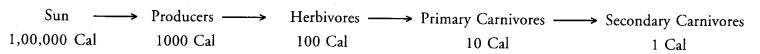
Since energy available decreases at every tophic level, very little of it is available at higher trophic levels. There is dissipation of energy at every step of its transfer and transformation. Hence it cannot flow in the reverse direction i.e., energy flow is unidirectional from sun to plants, plants to animals, animals to animals, organic remains to decomposers and dissipation as heat.
Pesticides: Pesticides are sprayed over crop plants in order to protect them from pests. They not only enter the crop plants but also pass into soil and reach water table as well as water bodies where they become part of food chain. With rise of trophic level the/ undergo biomagnification. Human beings obtain the pesticides from their food. They accumulate in human body in toxic amounts as human beings are long lived and continue to feed on pesticide contaminated foods.
Question 10.
Differentiate between biodegradable and non-biodegradable substances with the help of one example each. List two changes in habit that people must adopt to dispose non-biodegradable waste, for saving the environment. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Differences :
|
Biodegradable Wastes |
Non-biodegradable Wastes |
| 1. Origin. They are biological in origin. | They are commonly man-made. |
| 2. Degradability. The wastes are degraded by microorganisms. | They are not degraded by microorganisms. |
| 3. Accumulation. They do not accumulate in nature. | They pile up and accumulate in nature. |
| 4. Biomagnification. The biodegradable wastes do not show biomagnification. | The soluble non-degradable wastes enter food chains and undergo biomagnification. |
| 5. Resource. The wastes can be converted into resource. | Some wastes can be recycled. |
| Examples. Garbage, livestock wastes, sewage. | Examples. Plastic, polythene, glass, nickel, cadmium, several pesticides. |
Change in Habits :
- Reduce, reuse and recycle of non-biodegradable wastes can save the environment.
- Non-biodegradable materials which cannot be recycled are employed in sanitary land fills.
- Segregation of non-biodegradable wastes and putting them into separate dustbin (blue) for disposal.
- Use of cotton and jute bags for shopping, vegetables, fruits and other articles.
Question 11.
If all the wastes we generate are biodegradable, what effect will this have on the environment ? Write two values which will be imbibed if people are made to understand that generation of waste should be restricted to be biodegradable only. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
There will be no piling up of wastes nor any problem of their disposal. Bio-degradable wastes are natural and can be made to decompose naturally. Rather, it can produce useful materials like biogas and manure.
Values:
- No third pollution,
- Disappearance of many diseases.
- Greener earth and cleaner water.
Question 12.
After the examination, Rakesh with his friends went on a picnic to nearby park. All freinds carried cooked food packed in plastic bags or plastic cans. After eating the food, some freinds collected.the left over food and plastic bags, etc. and planned to dispose them off by burning. Rakesh inmediately checked them and suggested to segregated left over food and peels of fruits from plastic materials and respectively dispose them off separately in green and red dustbins placed into corner of the park.
(a) In your opinion, is burning plastic an eco-freindly method of waste disposal ? Why ? State the advantage of method suggested by Rakesh.
(b) How can we contribute in maintaining the parks and roads, neat and clean ? (CCE 2015)
Answer:
(a) No. Burning of plastic releases a number of toxic chemicals which are harmful to humans, animals and plants besides polluting the environment. Segregating the wastes and placing them in different bins (green for biodegradable and red for non-biodegradable wastes) is an eco-freindly disposal.
(b) Parks and roads can be kept neat and clean by keeping dust bins at selected places and asking the users to throw the wastes only in the bins meant for them.
Question 13.
Sita and Lata are neighbours in a colony. Sita maintains a compost pit by using bio-degradable household wastes. Lata throws the household waste in two separate dustbins.
(a) Whom do you support ? Why ?
(b) How is Sita justified.
(c) Maintaining two dustbins for bio-degradable and non-biodegradable wastes is a good idea.
How is Sita’s practice better than that of Lata ? (CCE 2015)
Answer:
(a) Sita. She is sparing the municipal committee of picking up biodegradable waste and transporting the same to disposable sites.
(b) Sita is producing her own compost for her home garden. She is not only saving money on purchase of manure and fertilizer but is also practising organic farming.
(c) Lata’s practice of keeping two separate bins of bio-degradable and non-biodegradable garbage is most suitable but Sita’s practice is better as it reduces the bulk of garbage and saves on money.
Question 14.
Give reason to justify the following :
(a) The existence of decomposers is essential in the biosphere.
(b) Flow of energy in a food chain is unidirectional. (CBSE Delhi 2016)
Answer:
(a)
- They function as saprophytes and cleanse the earth of organic remains.
- Decomposers release minerals tied up in organic remains. They thus help in recycling of biogeochemicals. Recycling of paper, metal, plastic and e-waste is done at most of the places.
(b) An ecosystem does not have its own source of energy. It receives the same from sun. Green plants or producers trap the solar energy and change it into chemical form during synthesis of food. Herbivores obtain energy from the food they take. A lot of energy dissipates during transfer and utilization of food energy by herbivores (10% law). From herbivores the food energy passes to primary carnivores. However, only about 10% of herbivore energy is passed into body mass of primary carnivores.
The rest is dissipated. From primary carnivores the energy passes into secondary carnivores (10%), etc. It is ultimately lost as heat.
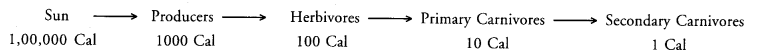
Since energy available decreases at every tophic level, very little of it is available at higher trophic levels. There is dissipation of energy at every step of its transfer and transformation. Hence it cannot flow in the reverse direction i.e., energy flow is unidirectional from sun to plants, plants to animals, animals to animals, organic remains to decomposers and dissipation as heat.
Question 15.
Your mother always thought that fruit juices are very healthy for everyone. One day she read in the newspaper that some brands of fruit juices in the market have been found to contain certain level of pesticides in them. She got worried as pesticides are injurious to our health.
(a) How would you explain to your mother about fruit juices getting contaminated with pesticides.
(b) It is said that when harmful pesticides enter our body as well as in the bodies of other organisms, they get accumulated and beyond a limit cause harm and damage to our organs. Name the phenomenon and write about it. (CBSE A.I. 2017)
Answer:
(a) During growth of plants and formation of fruits, the plants are often sprayed with pesticides to protect them from pests and pathogens.
- A small quantity of pesticides does enter the fruits and other parts of crop plants,
- A good quantity of pesticides seep into soil and reach the ground water. The pesticide contaminated ground water also enters the crop plants. It also causes contamination of fruit juices if such a water is used during preparation of juices.
(b) From fruit juices, other plant products and ground water the pesticides enter our bodies as well as bodies of other organisms which pass the same to humans through food chain. Beyond a certain level, the pesticides become toxic, harming our vital organs.
Definition. The increase in concentration of non-biodegradable substances in the bodies of organisms with time and rise in trophic level is called biomagnification.
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
(a) What is ozone ? How is it formed in the atmosphere ? Explain with equation.
(b) How is ozone layer useful ?
(c) Name the substances responsible for the depletion of ozone layer. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a) Ozone is triatomic form of oxygen, O3. Ozone is formed in the upper atmosphere by the action of ultraviolet (UV) radiations over oxygen (O2)
![]()
(b) The important ozone depleting substances or ODS are chlorofluorocarbons (CFC), methane, N2O, chlorine, halons and carbon tetrachloride.
Question 2.
(a) What are trophic levels in a food chain ?
(b) Explain the flow of energy through food chain.
(c) Write a four trophic level food chain and represented in the form of an ecological pyramid. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a) Trophic Levels. They are steps or divisions of food chain which are characterised by particular methods of obtaining food, e.g., producers (T1), herbivores (T2), primary carnivores (T3), etc.
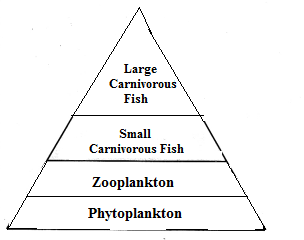
(b) Flow of Energy Through Food Chain. Energy enters a food chain through producers. Producers or green plants trap solar energy and convert it into chemical energy of food during photosynthesis. From producers energy passes into herbivores. A lot of energy dissipates during transfer and utilization of food energy by herbivores (10% law). From herbivores the food energy passes into primary carnivores, again with a lot of dissipation. Only about 10% of herbivore energy is passed into body mass of primary carnivores. From primary carnivores, nearly 10% energy passes into secondary carnivores and so on. It is ultimately lost as heat.

(c) Aquatic Four Trophic Level Food Chain.
Phytoplankton ———> Zooplankton ———> Small Carnivorous Fish ———> barge Carnivorous Fish.
Hope given Previous Year Question Papers for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment are helpful to complete your science homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online science tutoring for you.