Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals Class 10 Science Important Questions and Answers PDF will help you in scoring more marks. This consists of 1 mark Questions, 3 Mark Numericals Questions, 5 Marks Numerical Questions and previous year questions from Chemical Reactions and Equations Chapter.
Metals and Non-metals Class 10 Important Questions and Answers Science Chapter 3
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Name the metal which is most abundant in earth’s crust.
Answer:
Aluminium (Al) is the most abundant metal in the earth’s crust and is present to the extent of 8-1 per cent by mass.
More Resources
- Previous Year Question Papers for CBSE Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science
- Value Based Questions in Science for Class 10
- HOTS Questions for Class 10 Science
Question 2.
What is the difference between calcination and roasting ?
Answer:
Calcination is carried in the absence of air while roasting is done in excess of air.
Question 3.
What is the chemical formula of rust ?
Answer:
Rust is hydrated ferric oxide and its chemical formula is Fe2O3.xH2O.
Question 4.
Name the process used for the enrichment of sulphide ore.
Answer:
The process is called Froth Floatation process.
Question 5.
Out of zinc and iron, which evolves hydrogen more readily on reacting with dilute HCl ?
Answer:
Zinc evolves hydrogen more readily than iron on reacting with dilute HCl because it is placed above iron in the reactivity series.
Question 6.
How do alloys brass and bronze differ in composition ? (CBSE 2010)
Answer:
Constituents of brass are copper and zinc while those of bronze are copper and tin.
Question 7.
Does german silver contain silver in it ?
Answer:
German silver is an alloy of copper, zinc and nickel. It does not contain any silver in it.
Question 8.
Write the chemical formulae of the main ores of iron and aluminium.
Answer:
The main ore of iron is haematite (Fe2CO3) while that of aluminium is bauxite (Al2O3.2H2O).
Question 9.
Name the non-metal which can conduct electricity.
Answer:
Graphite, an allotropie form of carbon conducts electricity.
Question 10.
Write the names of two neutral oxides. (CBSE 2010)
Answer:
Two neutral oxides are : carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrous oxide (N2O).
Question 11.
Name the chemical formula of zinc blende and galena.
Answer:
Zinc blende is zinc sulphide (ZnS) while galena is lead sulphide (PbS).
Question 12.
Write one example each of :
- a metal having low melting point and a metal having high melting point.
- a metal which is a poor conductor of electricity and a non-metal which is a good conductor of electricity.
Answer:
- Gallium (Ga) is a metal with very low melting point (302 K). Diamond (carbon) is a non-metal with very high melting point. (4000 K)
- Metal lead (Pb) is a poor conductor of electricity whereas graphite (carbon) is a good conductor of electricity.
Question 13.
Which acts as anode in the electro-refining of metals ?
Answer:
A plate of impure metal acts as anode in the electro-refining of metals.
Question 14.
What is the name of the bond formed when a metal atom combines with the atom of a non-metal ? (CBSE 2010)
Answer:
Bond formed is ionic or electrovalent.
Question 15.
How will you account for the high melting points of salts ?
Answer:
The high melting points of salts are due to their closely packed structures and also due to stronger forces of attraction in the oppositely charged ions.
Question 16.
Name two metals which exist in the native or free state.
Answer:
Metals gold (Au) and platinum (Pt) exist in the free or native state.
Question 17.
What reaction takes place when manganese dioxide is heated with aluminium powder ?
Answer:
3MnO2(s) + 4Al(s) ————> 3Mn(l) + 2Al2O3(s)
Question 18.
Can rusting of iron nail occur in distilled water ?
Answer:
No, because distilled water has no dissolved oxygen in it.
Question 19.
Which metal is the best conductor of electricity ? (CBSE 2010)
Answer:
Silver (Ag) is the best conductor of electricity.
Question 20.
Which metal is used in amalgams ?
Answer:
Mercury (Hg) is used in amalgams that are also alloys in nature.
Question 21.
Why are metals conducting in nature ?
Answer:
The conductivity of metals is due to the movement of electrons. These are mobile even in the solid state.
Question 22.
Why do metals generally appear to be dull ?
Answer:
When metals are kept exposed to air for sometime, oxygen present in air slowly combines with the metal to form metal oxide. It is deposited as a layer on the surface of metals. They appear to be dull.
Question 23.
Name two non-metals which exist in the solid state and two non-metals which exist in the gaseous state.
Answer:
Solid State : Sulphur, phosphorus;
Gaseous state : Nitrogen, oxygen.
Question 24.
Name the metal whose foils are used for the packing of food materials.
Answer:
Aluminium foils are used for the purpose.
Question 25.
The electronic configuration of an elements ‘E’ (Z = 16) is 2, 8, 6. Will it lose six electrons or gain two electrons ?
Answer:
It will gain two electrons.
Question 26.
Alloys are used in electrically heating devices rather than pure metals. Give one reason.
(CBSE All India 2009)
Answer:
Alloys are generally the combination of two or more metals. Since metals are good conductors of electricity, a combination of metals i.e., alloy is expected to be a better conductor of electricity than the pure metal,
Question 27.
A shining metal ‘X’ on heating in air becomes black in colour. Name the black coloured compound formed and identify ‘X’.
Answer:
The black coloured compound is copper (II) oxide or cupric oxide. The metal ‘X’ is copper.
![]()
Question 28.
Why do silver articles become black after some time ?
Answer:
Traces of hydrogen sulphide (H2S) gas are present in air/atmosphere. It slowly reacts with silver to form silver sulphide which is black. As a result, silver ornaments lose their shine after sometime.
Question 29.
Name a metal other than aluminium that is covered with a layer of oxide film.
Answer:
Iron (Fe) is also covered with a layer of its oxide (Fe2O3) when kept exposed to air for a long time.
Question 30.
What is the common feature in the electronic configuration of metal atoms ?
Answer:
The metal atoms in general have one, two or maximum of three valence electrons which they can easily lose to form cations or positive ions.
Question 31.
What are ionic compounds ?
Answer:
These are the compounds in which the constituent particles are ions (cation and anions) attracted to each other by strong forces of attraction.
Question 32.
Name one metal and one non-metal which exist in liquid state at room temperature ?
Answer:
Mercury (metal) and bromine (non-metal) exist as liquid at room temperature.
Question 33.
What changes do you observe in the iron nails and colour of copper sulphate solution if the nails are dipped in CuSO4 solution for 15 minutes ?
Answer:
Iron nails turn to brown and the solution becomes light green.
Question 34.
What are amphoteric oxides ? Give an example.
Answer:
These are the oxides which act both as acids and bases. For example, zinc oxide (ZnO).
Question 35.
Name a non-metal which is lustrous and a metal which is non-lustrous.
Answer:
Bromine (non-metal) is lustrous. Sodium (metal) is non-lustrous due to the formation of an oxide layer on its surface.
Question 36.
Give the electronic configuration of an element having atomic number 11. (CBSE 2010)
Answer:
The element with atomic number (Z) 11 is sodium (Na). Its electronic configuration is 2, 8, 1.
Question 37.
Why are metals good conductors of electricity while non-metals are not ? (CBSE 2010, 2012)
Answer:
The metal atoms can easily release electrons to conduct electric current. The atoms of non-metals are not in a position to do so and therefore, are not conducting.
Short Answer Questions
Question 38.
Which important properties of aluminium are responsible for its great demand in industry ?
Answer:
The properties of aluminium metal responsible for its great demand in industry are :
- The metal is a good conductor of electricity.
- The metal is not attacked by water.
- The metal is a powerful reducing agent.
Question 39.
Name an alloy of
- Aluminium used in construction of air crafts.
- Lead in joining metals for electric welding.
- Copper used in household vessels.
Answer:
- The alloy is duralumin : A1 (93%), Cu (4%), Mg (0.5%), Mn (0.5%).
- The alloy is solder : Pb (50%), Sn (50%)
- The alloy is brass : Cu (80%), Zn (20%)
Question 40.
All ores are minerals but all minerals are not ores. Justify.
Answer:
In the earth’s crust, metals are present in the form of minerals and there are more than one mineral for a particular metal. However, metal may not be extracted from all of them. The mineral from which a metal can be profitably and conveniently extracted is known as ore. This clearly means that all ores are minerals but all minerals are not ores. For example, the different minerals of iron are :
Haematite : Fe2O3 ;
Limonite : Fe2O3.3H2O;
Siderite : FeCO3 ;
Iron pyrites : FeS2
Iron is extracted from haematite (Fe2CO3). Haematite mineral is the ore of iron while other minerals are not the ores.
Question 41.
(a) An iron knife kept in blue copper sulphate solution turns the blue solution into light green. Explain.
(b) An athlete won a bronze medal in a race competition. After some days, he found that the medal had lost its lustre due to the formation of a greenish layer on it. Name the metals present in the medal. What is the reason for the appearance of a greenish layer on its surface ?
Answer:
(a) Iron lies above copper in the activity series. This means that iron or iron knife will displace copper from copper sulphate solution. As a result of the reaction, ferrous sulphate will be formed and the solution will be light green in colour.
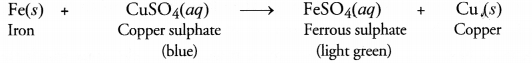
(b) The bronze medal is an alloy and the constituting metals are copper and tin.
The loss of lustre by the medal is due to the formation of a coating of green layer. This layer is at basic copper carbonate.
Question 42.
Why is titanium called a strategic metal ? Mention two of its properties which make it so special.
Answer:
Titanium is called strategic metal because it is used for making certain war equipments. The properties which make the metal so special are :
- It is light in weight but at the same time stronger than the other metals.
- It is not affected by corrosion even if kept in the open for a very long time.
Question 43.
A copper plate was dipped into a solution of AgNO3. After sometime, a black layer was deposited on the copper plate. State the reason for it. Write the chemical equation for the reaction involved.
Answer:
Copper lies above silver in the activity series. This means that copper is more reactive than silver. Therefore, copper had replaced silver from AgNO3 solution. Silver got deposited on the copper plate and changed to black after sometime because silver and also some salts of silver are sensitive to light. They readily become blackish on standing or on exposure to air.
![]()
Question 44.
On placing a piece of zinc metal in a solution of mercuric chloride, it acquires a silvery surface but when it is placed in a solution of magnesium sulphate, no change is observed. State the reason for the behaviour of zinc metal.
Answer:
Zinc lies above mercury in the activity series and can easily replace it from mercuric chloride solution. Mercury formed in the reaction gets deposited on the surface of zinc to give it a silvery look.
![]()
But zinc is placed below magnesium in the activity series. Therefore, no chemical reaction occurs between zinc and magnesium sulphate solution.
Question 45.
Which method of concentration of ore is preferred in the following cases and why ?
- The ore has higher density particles mixed with a large bulk of low density impurities.
- The ore consists of copper sulphide intermixed with clay particles.
Give an example of amalgam.
Answer:
- The concentration of ore can be done by gravity separation method.
- The concentration of ore is done by Froth Floatation process.
An amalgam of mercury with silver or gold called dental alloy is used to fill cavities in the teeth.
Question 46.
Name an ore of zinc other than zinc oxide. By which process can this ore be converted into zinc oxide ?
Answer:
The ore of zinc other than zinc oxide (zincite) is zinc carbonate (calamine). It has the formula ZnCO3 Calamine is converted into zinc oxide by calcination i.e., by heating strongly in the absence of air.
![]()
Question 47.
Give reasons for the following :
Metals replace hydrogen from dilute acids whereas non-metals do not. (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
Metals are electropositive in nature. Their atoms readily lose electrons to form positive ions. The electrons are accepted by H+ ions of the acid to evolve hydrogen gas. For example,
Zn(s) ———-> Zn2+(aq) + 2e– ;
2H+(aq) + 2e– ————> H2(g)
Non-metals are electronegative in nature. This means that their atoms can take up electrons and cannot lose them. Therefore, they do not evolve hydrogen on reacting with dilute acids.
Question 48.
(a) Why is ZnO called an atmospheric oxide? Name another atmospheric oxide?
(b) Whar are alkalies? Give one exampleof alkalies?
Answer:
(a)
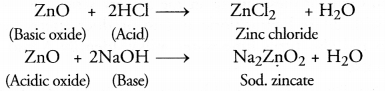
Aluminium oxide (Al2O3) is another amphoteric oxide.
(b) Water soluble hydroxides of metals are known as alkalis. For example, NaOH.
Question 49.
(a) What is the activity series of metals ? Arrange the metals Zn, Mg, Al, Cu and Fe in a decreasing order of reactivity.
(b) What would you observe when you put
- some zinc pieces into blue copper sulphate solution ?
- some copper pieces into green ferrous sulphate solution ?
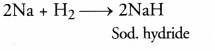
(c) Name a metal which combines with hydrogen gas. Name the compound formed.
Answer:
(a) We find that zinc occupies a much higher position in the acitivity series as compared to copper. It is expected to displace copper present in the aqueous solution of its salt (e.g. CuSO4).
![]()
(b)
- Blue colour of copper sulphate solution would slowly disappear.
- No change would be noticed.
(c) Sodium combines with hydrogen to form sodium hydride.
Question 50.
(a) Are all pure liquids bad conductors of electricity ?
Name a liquid which is a good conductor of electricity but does not undergo electrolysis on passing electric current.
If pure water is used, no electrolysis takes place. Why ?
Answer:
Name one practical application based on the phenomenon of electrolysis.
No, there are exceptions also. Mercury in pure state a good conductor of electricity.
Mercury is a good conductor of electricity but does not undergo electrolysis.
Pure water (H2O) does not dissociate into ions on passing electric current.
Question 51.
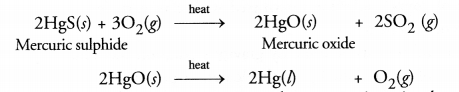
What is the main ore of mercury ? How is mercury obtained by this ore?
Answer:
The main ore of mercury is cinnabar (HgS). Mercury is obtained from it by heating with excess of air or oxygen.
Question 52.
(a) Using a simple experiment, how can you prove that magnesium is placed above zinc in the reactivity ?
(b) Why cannot copper metal liberate hydrogen on reacting with dil. HCl ?
Answer:
(a) In a glass tube, take about 10 mL of aqueous solution of zinc sulphate. It is colourless. Dip a small and dry piece of magnesium ribbon in the solution. It slowly dissolves and greyish mass gets deposited at the bottom of the tube. This shows that magnesium is more reactive than zinc or it is placed above zinc in the activity series.
![]()
(b) Copper lies below hydrogen in the reactivity series and cannot lose electrons to H+ ions of the acid. This means that hydrogen gas cannot be liberated.
Question 53.
The way metals like sodium, magnesium and iron react with air and water, is an indication of their relative positions in the ‘reactivity series’. Is this statement true ? Justify your answer with examples. (CBSE 2014)
Answer:
Yes, the statement is true. We can have an idea about the relative positions of these metals in the reactivity series. For example,
(a) Sodium reacts violently even with cold water and with air or oxygen it readily combines.
(b) Magnesium reacts with hot water and with air or oxygen upon heating.
(c) Iron reacts with steam only and with air it reacts very slowly
This shows that the relative positions of these metals in the activity series are : sodium, magnesium, iron.
Question 54.
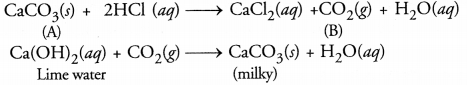
Metallic compound A reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to produce effervescence and a gas B. The gas B extinguishes a burning candle and also turns lime water milky. Identify A and B. Write balanced chemical equations for the reactions involved.
Answer:
The available information suggests that the gas B is CO2 since it turns lime water milky. The compound A is the carbonate or bicarbonate of some metal (e.g. calcium earbonate) The equations for the reactions involved are given :
Question 55.
Identify the oxides from the following which turn blue litmus into red.
CO2, Na2O, CaO, SO2, NO2.
What is the nature of these oxides ?
Answer:
These are the oxides of non-metals and are CO2, SO2 and NO2. These are called acidic oxides since they form acids when dissolved in water. Their aqueous solution in water turns blue litmus red.
Question 56.
Name the chemical compounds formed on the surface of silver, copper and iron metals when exposed for sometime to atmosphere.
Answer:
- On the surface of silver : Black silver sulphide (Ag2S).
- On the surface of copper : Green basic copper carbonate (Cu(OH)2-CuCO3)
- On the surface of iron : Brown rust i.e., Hydrated ferric oxide (Fe2O3.xH2O).
Long Answer Questions
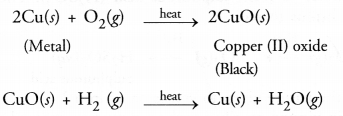
Question 57.
When the powder of a common metal is heated in an open china dish, its colour turns black. However, when hydrogen gas is passed over the hot black substance formed, it regains its original colour. Based on this information, answer the following questions :
- What type of chemical reaction takes place in each of the two given steps ?
- Name the metal initially taken in the powder form. Write balanced chemical equations for both these reactions.
Answer:
- The available information suggests the metal is copper. In open air, its is oxidised to form copper (II) oxide which is black in colour. The reaction is known as oxidation reaction. On passing hydrogen gas over the hot substance, the original colour of the metal is regained. It is an example of reduction reaction.
- The balanced chemical equations for the reactions are :
Question 58.
(a) Which of the following metals would give hydrogen when added to dilute hydrochloricacid?
- iron
- copper
- magnesium ?
(b)Explain why do surfaces of some metals acquire a dull appearance when exposed to air for a long lime.
Answer:
(a) Both iron (Fe) and magnesium (Mg) will evolve hydrogen on reacting with dilute hydrochloric acid. These are active metals and are placed above hydrogen in the activity series. As copper is placed below hydrogen in the series, it will not evolve hydrogen.
(b) Surfaces of some metals acquire a dull appearance when exposed to air for a long time and they lose their lustre. This is due to the formation of layer of oxides, hydroxides, carbonates etc. on the surface For example, surface of aluminium metal becomes dull white due to the formation of coating oi aluminium oxide (Al2O3). Similarly, the surface of copper acquires a greenish colour since a layer oi basic copper carbonate with the formula Cu(OH)2CuCO3 is deposited on the surface.
Question 59.
How will your demonstrate that the ionic compounds do not conduct electricity in the solid state and can do so in solution.
Answer:
- In a glass beaker, take small amount of solid sodium chloride.
- Dip two graphite rods (electrodes) in the solution.
- Connect these rods to a battery through a bulb and a switch.
- Switch on the battery. The bulb will not glow. This show that no current has passed through the solid sodium chloride.
- Now, add some water to the salt so that it may dissolve.
- Repeat the operation. The bulb will immediately glow showing that current has passed through the salt solution.
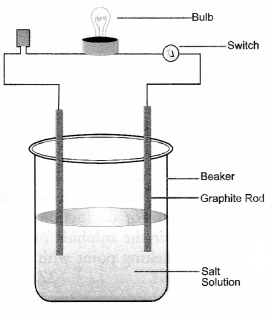
Explanation: Sodium chloride (NaCl) is a crystalline solid and the current is carried by the mobility (movement) of ions. Since the ions do not move in the solid state, the salt is not conducting. In aqueous solution, both Na+ and Cl- ions can move and the salt will be conducting in the solution. That is why the bulb glows.
Question 60.
With a suitable activity show that sulphur burns in air to form a compound which is acidic in nature.
Answer:
- Take a small amount of sulphur powder on a spatula.
- Now burn this powder by placing a tube in a inverted position over the spatula as shown in the figure.
- The fumes produced as a result of burning of sulphur will get collected in the tube.
- Place the tube in vertical position and immediately add some water to it.
- Shake the tube so that the fumes may completely dissolve.
- Add a few drops of blue litmus to a portion of the solution. It will acquire red colour which shows that it is of acidic nature.
- To another portion, add a few drops of red litmus solution. No colour change will be noticed. This shows that the solution is not acidic.
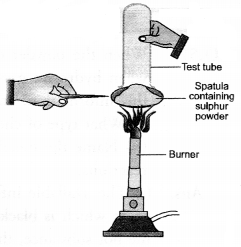
Explanation : Sulphur burns in air to form sulphur dioxide which escapes from the tube as fumes with pungent and suffocating smell. The gas produced readily dissolves in water to form sulphurous acid (H2SO3). The solution is therefore, acidic. It will change the colour of blue litmus to red.
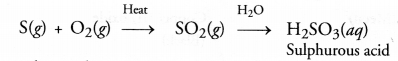
Question 61.
(a) Define corrosion; what is the nature given to corrosion of iron ?
(b) Name the colour of coating formed on silver and copper when exposed to air.
(c) List two damages caused by corrosion and suggest, how these can be prevented.
Answer:
(a) For definition of corrosion: The process of slow eating up of a metal by the gases and water vapours present in air due to formation of certain chemical compounds. Corrosion of iron is known as rusting.
(b) Coating deposited on the surface of silver metal is of silver sulphide (Ag2S). It is black in colour. The coating deposited on copper surface is of basic copper carbonate Cu(OH)2CuCO3. It is green in colour.
(c) Corrosion of metals particularly the rusting of iron is very harmful. The structures made from iron are generally placed in the open. These are slowly corroded or rusted. This reduces their strength gradually. They become prone to accidents and are therefore, quite dangerous. A lot of care and money is involved in their maintenance. However, corrosion of aluminium has advantage. The metal placed high in the activity series is quite reactive. It combines with the oxygen present in air to form aluminium oxide (Al2O3).
Question 62.
Give reasons for the following :
- Zinc can displace copper from copper sulphate solution.
- Silver articles become black after sometime when exposed to air.
- A metal sulphide is converted to its oxide to extract the metal from sulphide ore.
Answer:
- Zinc is placed above copper in the activity series. Therefore, it can easily displace copper from copper sulphate solution.
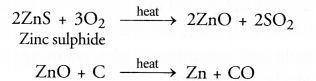
Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) ————> ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s) - Air contains traces of hydrogen sulphide (H2S) gas. Silver has a tendency to combine with H2S to form silver sulphide (Ag2S) which is black in colour. On account of this, silver articles become black after some time when kept exposed to air.
- A metal sulphide is normally converted into oxide by heating with excess of air or oxygen. This process is called roasting. Actually, the oxide of metal which is formed cap be easily reduced to the metallic form by reduction with carbon or some electropositive element. For example,
Question 63.
(a) Distinguish between ‘roasting’ and ‘calcination’. Which of the two is used for sulphide ores and why ?
(b) Write a chemical equation to illustrate the use of aluminium for joining cracked railway lines.
(c) Name the anode, the cathode and the electrolyte used in the electrolytic refining of impure copper.
Answer:
(a) For distinction between calcination and roasting,
|
Calcination |
Roasting |
| (i) Calcination is carried in absence of air or oxygen. | Roasting is carried in the presence of excess of air. |
| (ii) As a result of calcination, the carbonate ore is converted to the oxide form. | As a result of roasting, the sulphide ore is converted to the oxide form. |
| ZnCO3(s) —— > ZnO(s) + CO2(g) | 2ZnS(s)+3O2(g)—– > 2ZnO(s)+2SO2(g) |
For the sulphide ores, the process of roasting is commonly used. It is carried by heating the ore helow its melting point with excess of air. As a result, the sulphide ore is converted to its oxide form. For example,
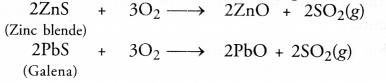
(b) Cracked railway lines can be joined or welded with the help of thermit welding. Thermit is a mixture of ferric oxide and aluminium powder. The chemical equation involved is :
![]()
(c) In the electrolytic refining of copper ;
Anode : A rod of impure copper.
Cathode : A rod of pure copper.
Electrolyte : An aqueous solution of copper sulphate containing a small amount of sulphuric acid.
Question 64.
(a) Give an example of a metal which
- is a liquid at room temperature.
- is kept immersed in kerosene for storing.
- is both malleable and ductile.
- is the best conductor of heat.
(b) Name the process of obtaining a pure metal from an impure metal through electrolysis. Suppose you have to refine copper using this process, then explain with the help of a labelled diagram the process of purification, mentioning in brief the materials used as (i) anode (ii) cathode and (iii) electrolyte.
Answer:
(a)
- Mercury (Hg) is liquid at room temperature :
- Sodium (Na) is kept immersed in kerosene for storing.
- Aluminium (Al) is malleable and ductile
- Silver (Ag) is the best conductor of heat.
(b) The process is known as electro-refining. For the electro-refining of copper,
The conversion of a crude metal into pure metal is known as metal refining.
The refining can be done in a number of ways but the most common among these is the electro-refining and is discussed.
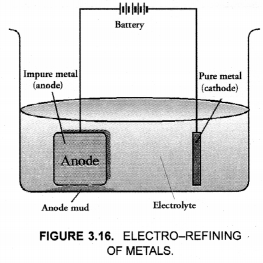
This method is commonly used for the purification of the metals like Cu, Ag, Zn, Ni etc. The impure metal is converted into a block which is made anode in an electrolytic cell in which a plate of pure metal acts as the cathode as shown in the Figure 3.16.
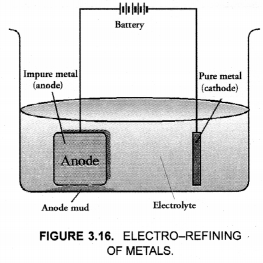 The electrolyte is the solution of the soluble salt of the same metal, preferably a double salt. On passing electric current, metal ions from the electrolyte are reduced to the metal which is deposited on the cathode. An equivalent amount of the pure metal from the anode gets oxidised and the metal ions (or cations) go into the solution. This keeps on till the whole of the metal from the anode dissolves and deposits on cathode, leaving behind impurities in the form of a mud called anode mud.
The electrolyte is the solution of the soluble salt of the same metal, preferably a double salt. On passing electric current, metal ions from the electrolyte are reduced to the metal which is deposited on the cathode. An equivalent amount of the pure metal from the anode gets oxidised and the metal ions (or cations) go into the solution. This keeps on till the whole of the metal from the anode dissolves and deposits on cathode, leaving behind impurities in the form of a mud called anode mud.
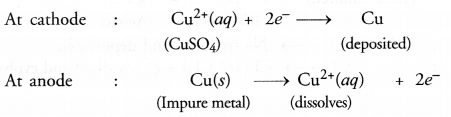
For example, in the electro-refining of crude copper, impure metal is made anode and a plate of pure copper acts as the cathode. These are connected through a battery in the external circuit as shown in the figure. The electrolyte is aqueous solution of copper sulphate containing a small amount of sulphuric acid. On passing current, the following changes occur.
Question 65.
(a) Write the balanced chemical equations for the extraction of copper metal from its ore. What is the reducing agent used ?
(b) Which reducing agent can be used in the extraction of metals placed at the top of the reactivity series ? Give the name of the process also.
(c) What is the chemical substance formed as green coating when copper reacts with atmospheric gases in moist conditions ?
Answer:
(a) Copper is isolated from its sulphide ore known as copper glance (Cu2S) by heating with excess of air or oxygen.
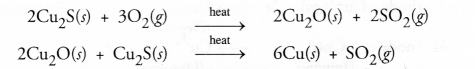
Cuprous oxide (Cu2O) acts as reducing agent and this process is known as auto-reduction.
(b) These metals (K, Na, Ca, Mg etc.) can be isolated by carrying out the process of electrolysis (electrolytic reduction) from their molten salts.
(c) The green coating is of basic copper carbonate. It is formed as follows :
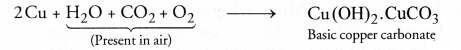
Question 66.
(a) Which method will you use to reduce the following ? Explain by giving a suitable example.
(i) Oxides of less reactive metals
(ii) Oxides of moderately reactive metals
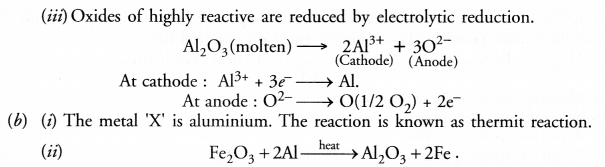
(iii) Oxides of highly reactive metals.
(b) The reaction between metal ‘X’ and Fe2O3 is highly exothermic and is used to join railway tracks.
(i) Identify metal ‘X’ and name the reaction.
(ii) Write the chemical equation of its reaction with Fe2O
Answer:
(a) (i) Oxides of less reactive metals can be reduced either by auto-reduction or upon heating. For example,
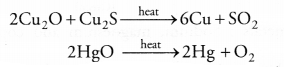
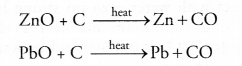
(ii) Oxides of moderately reactive metals can be reduced with coke. This is known as smelting. For example,
Question 67.
(a) Most metals do not react with bases but zinc metal does. Suggest a reason. Write an equation for the reaction between Zn and NaOH.
(b) When a metal X is treated with cold water, it gives a base Y with molecular formula XOH (Molecular mass = 40) and liberates a gas Z which easily catches fire. Identify X, Y and Z.
Answer:
(a) We know that zinc oxide (ZnO) is of amphoteric nature. The metal zinc also behaves similarly. It reacts with both acids and alkalies. For example,
![]()
(b) Molecular mass of base Y = 40 Atomic mass of X = 40 – (16 + 1) = 23
The metal X is sodium (Na). The salt Y is NaOH and liberated gas Z is, hydrogen.
![]()
Question 68.
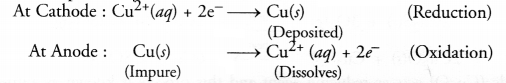
With reference to electrorefining of impure copper, answer the following :
(a) Draw a neat and labelled diagram required for the purpose of electrorefining.
(b) What is the electrolyte used ?
(c) Name the cathode and anode used.
(d) What happens at cathode and anode ?
Answer:
(a) For the labelled diagram,
(b) An aqueous solution of copper sulphate containing a small amount of sulphuric acid is used as the
Hope given Previous Year Question Papers for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals helpful to you.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. We try to provide online math tutoring for you.