Chapter 7 Control and Coordination Class 10 Science Important Questions with Answers PDF will help you in scoring more marks. This consists of 1 mark Questions, 3 Mark Numericals Questions, 5 Marks Numerical Questions and previous year questions from Chemical Reactions and Equations Chapter.
Control and Coordination Class 10 Important Questions and Answers Science Chapter 7
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Write the function of hormone thyroxine in our bodies. (CBSE Delhi 2004)
Answer:
It controls basal metabolic rate and regulates metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins.
More Resources
- Previous Year Question Papers for CBSE Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science
- Value Based Questions in Science for Class 10
- HOTS Questions for Class 10 Science
Question 2.
Name the part of hind brain which takes part in regulation of respiration. (CBSE Delhi 2004)
Answer:
Medulla oblongata.
Question 3.
Which hormonze helps in lowering the level of blood glucose in human beings ? (CBSE Delhi 2004)
Answer:
Insulin.
Question 4.
We suddenly withdraw our hand when a pin pricks. Name the type of response involved in this action.
(CBSE Delhi 2004)
Answer:
Reflex action.
Question 5.
Which hormone is responsible for the development of moustache and beard in man ? (CBSE Foreign 2004)
Answer:
Testosterone.
Question 6.
Which type of glands in human body secrete hormones ? State any one location for them.
(CBSE Foreign 2004)
Answer:
Endocrine or ductless glands, e.g, thyroid in neck region around trachea.
Question 7.
Name the structural and functional units of human nervous system. (CBSE A.I. 2004 C)
Answer:
Neuron.
Question 8.
What is neuron ? (CBSE Delhi 2007)
Answer:
Neuron or nerve cell is a structural and functional unit of nervous system that is specialised to receive, conduct and transmit impulses.
Question 9.
What are phytohormones ? (CBSE A.I. 2007, CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
Phytohormones are chemical substances other than nutrients produced naturally in plants which regulate growth, development, differentiation and a number of physiological processes, e.g., auxin, gibberellins, abscisic acid, cytokinins.
Question 10.
Name the largest cell present in human body. (CBSE Delhi 2008)
Answer:
Neuron (length 90-100 cm).
Question 11.
What is the function of the hormone secreted by the endocrine gland pituitary ? (CBSE Foreign 2008)
Answer:
It generally controls the secretory activity of another endocrine gland, e.g., TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) on thyroid for release of thyroxine.
Question 12.
Why is the use of iodised salt advisable ? (CBSE Delhi 2008, CCE 2014, 2015)
Answer:
Iodine is an essential component of diet as it is required for synthesis of hormone thyroxine needed for proper metabolism of protein, fat and carbohydrates. Deficiency causes goitre, cretinism and myxoedema.
Question 13.
Name two tissues that provide control and coordination in multicellular animals. (CBSE Delhi 2009)
Answer:
- Nervous tissue
- Endocrine tissue.
Question 14.
Define reflex action. (CBSE Delhi 2009, CCE 2012, 2015)
Answer:
It is an automatic, spontaneous nerve mediated response to a stimulus without consulting the will of the individual.
Question 15.
Define chemotropism. (CBSE A.I. 2009, 2010, CCE 2011, 2012, 2013)
Answer:
Chemotropism. It is directional growth movement of curvature that occurs in response to a chemical stimulus. Ex. movement of pollen tube in style.
Question 16.
A young green plant receives sunlight from one direction only. What will happen to its shoots and roots ?
(CBSE Delhi 2009 C)
Answer:
(a) Shoots bend towards the source of light—positive phototropism.
(b) Roots bend away from the source of light—negative phototropism.
Question 17.
Name the plant hormones which help or promote
- Cell division
- Growth of stem
- Inhibits growth. (CBSE Delhi 2009 C, CCE 2012, 2013)
Answer:
- Cell division. Cytokinins.
- Growth of stem. Gibberellins.
- Inhibits growth. Abscisic acid.
Question 18.
Name the gland which secretes growth hormone.
Answer:
Pituitary gland.
Question 19.
How is the spinal cord protected in human body ?
Answer:
Overlying meninges and vertebral column.
Question 20.
A potted plant is made to lie horizontally on the ground. Which part of the plant will show
- Positive geotropism
- Negative geotropism ? (CBSE Delhi 2010)
Answer:
- Positive Geotropism: Root
- Negative Geotropism: Stem.
Question 21.
Name the hormone that helps in regulating level of sugar in our blood. Name the gland that secretes it.
(CBSE AI 2010)
Answer:
Hormone: Insulin.
Gland: Pancreas.
Question 22.
Mention the function of hind brain in humans.
Answer:
- Posture and equilibrium
- Reflexes, blood pressure, heart beat, breathing.
Question 23.
Name any two types of tropisms.
Answer:
Phototropism, geotropism.
Question 24.
Mention the function of adrenaline hormone.
Answer:
To prepare the body for meeting an emergency.
Question 25.
State the main function of abscisic acid in plants.
Answer:
Inhibition of growth and induction of dormancy for overcoming stress conditions.
Question 26.
Which hormone is injected to a diabetic patient and why ? (CCE 2010)
Answer:
Insulin is injected to a diabetic patient in order to meet deficiency of the hormone that is essential for uptake of glucose by cells.
Question 27.
Name the hormone secreted by an endocrine gland during emergency. Name the gland.
Answer:
Hormone: Adrenaline.
Gland: Medulla of adrenals.
Question 28.
What do we call the movement of shoot towards light ?
Answer:
Positive phototropism.
Question 29.
Name the plant hormone responsible for elongation of cells.
Answer:
Auxin.
Question 30.
Which part of the brain controls posture and balance of the body ?
Answer:
Cerebellum.
Question 31.
Name the part of the neuron through which the information travels as an electric impulse.
Answer:
Axon or nerve fibre.
Question 32.
Name the part of the neuron where information is acquired.
Answer:
Dendrite.
Question 33.
What is synapse ?
Answer:
Synapse is a narrow fluid-filled gap which functions as communicating junction between axon end of one neuron and dendrite tip of next neuron.
All information of our environment is detected by specialised tip of some nerve cells.
Question 34.
Mention the name given to such tips and also mention where they are located. (CCE 2012, 2013)
Answer:
Receptors. Receptors are located in sense organs—skin, inner ears, eyes, nose, tongue.
Question 35.
While watering a rose plant, a thorn pricked Ritas hand. How would she respond to this situation ? Provide the term for such a response. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Rita will immediately withdraw her hand from the rose plant even before feeling the pain. The phenomenon is called reflex action.
Question 36.
What is meant by tropic movements ? (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Tropic movements are directional paratonie curvature movements of growth which generally occur in cylin¬drical organs with direction of movement being determined by the direction of stimulus.
Question 37.
A boy runs on seeing a stray dog. His breathing becomes very fast and blood pressure also increases. Name the hormone found to be high in his blood and the gland which produces it. (CCE 2012, 2013)
Answer:
Hormone. Adrenaline. Gland. Adrenal medulla.
Question 38.
How shoot and root of a plant respond to light ? (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Shoot: It is positively phototropic to unilateral light.
Root: It is either neutral or negatively phototropic to unilateral light.
Question 39.
State the main function of abscisic acid in plants.
Answer:
Abscisic acid is a growth inhibitor that induces dormancy in buds and seeds.
Question 40.
How do the shoot and root of a plant respond to the pull of earths gravity ? (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Main shoot is negatively geotropic while main root is positively geotropic. Their branches are generally plagiogeotropic.
Question 41.
Name two components of central nervous system in humans. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Brain and spinal cord.
Question 42.
Mention the part of the body where gustatory and olfactory receptors are located. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Gustatory Receptors. Mostly tongue.
Olfactory Receptors. Olfactory epithelium in upper part of nasal chambers or nose.
Question 43.
Name the sensory receptors found in the nose and on the tongue. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Gustatory Receptors. Mostly tongue.
Olfactory Receptors. Olfactory epithelium in upper part of nasal chambers or nose.
Question 44.
Which body organ is surrounded by meninges. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
Brain and spinal cord (central nervous system).
Question 45.
In multicellular organisms how the various activities are controlled and coordinated ? (CCE 2013)
Answer:
By nervous and hormonal systems collectively called neuroendocrine system.
Question 46.
Define phototropism. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
It is directional movement of curvature which occurs in plants in response to unilateral exposure to light.
Question 47.
Which system facilitates communication between central nervous system and other parts of the body ?
(CCE 2013, 2014)
Answer:
Peripheral nervous system (PNS).
Question 48.
In case of a spinal cord injury, identify the signals that will be disrupted. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
Neuromuscular signals from areas served by spinal cord, viz., limb movement, sensations of touch and pain, spinal reflexes.
Question 49.
Name the tissue in animals which provides control and co-ordination to them. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Nervous tissue.
Question 40.
Differentiate between the movement of leaves of the sensitive plant and the movement of a shoot towards light. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Movement of leaves of sensitive plant is hapnonastic turgor movement while movement of shoot towards light is phototrophic growth movement.
Question 51.
Name one plant hormone which inhibits growth. Write its one function. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Abscisic acid. It includes dormancy in buds and seeds.
Question 52.
State the role of the brain in reflex action. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
It functions as a relay centre for transferring impulse from sensory to motor neurons in several reflex actions called cerebral reflexes, e.g, closure of eyes exposed to flash of light, salivation at the sight or smell of food. In spinal reflexes it acts as information collecting and evaluation centre without any direct involvement in reflex action.
Question 53.
Mention the part of brain which controls the involuntary action like blood pressure, salvination, etc.
(CCE 2015)
Answer:
Medulla oblongata.
Question 54.
Name the part of the neuron
- Where information is acquired
- Through which information travels. (CCE 2016)
Answer:
- Dendrites
- Axon.
Question 55.
Name the hormone in humans which regulates carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism in the body. Mention the site where it is synthesised. (CCE 2016)
Answer:
Hormone—Thyroxine. Site—Thyroid.
Question 56.
(a) State the function of the following plant hormones :
- Abscisic acid
- Cytokinin.
(b) Define chemotropism. (CCE 2016)
Answer:
(a)
- Function of Abscisic Acid. Inhibits growth and induces dormancy.
- Function of Cytokinin. Cell division, Differentiation and countering apical dominance.
(b) Chemotropism: It is directional growth movement of curvature that occurs in response to a chemical stimulus. Ex. movement of pollen tube in style.
Short Answer Questions (2 Marks Each)
Question 1.
Name two hormones secreted by pancreas. Write one function of each hormone named.
(CBSE Delhi 2007)
Answer:
Insulin (secreted by (3-cells of islet of Langerhans)
Recognition of glucose by cells for absorption and conversion of glucose into glycogen in liver and muscles.
Glucagon (secreted by a-cells of islet of Langerhans)
Formation of glucose from glycogen and other sources and its release into blood.
Question 2.
Name the hormone responsible for regulation of
- Metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins
- Balance of calcium and phosphate
- Blood pressure
- Water and electrolyte balance.
(CBSE Delhi 2008)
Answer:
- Thyroxine
- Parathormone (also calcitonin)
- Adrenaline
- ADH or vasopressin and aldosterone (a mineralocorticoid).
Question 3.
What is reflex action ? Explain the mechanism of reflex action with a suitable example.
(CBSE Foreign 2008, CCE 2012, 2015)
Answer:
Reflex Action: It is an automatic nerve mediated response to a stimulus without consulting the will of the individual, e.g., withdrawal of hand on being pricked or coming in contact with hot surface.
Mechanism: The stimulus for reflex action is picked up by a receptor located in the organ on which stimulus is acting. One or more sensory neurons carry the impulse from receptor to the central nervous system (e.g., spinal cord). CNS functions as modulator. It transfers the sensory nerve impulse to one or more motor neurons. The motor neurons carry the impulse to effectors which provide a proper response to the stimulus.
Stimulus ———>Receptor ———>Sensory neurons ——–>CNS ——–>Motor neurons ——-> Effectors
———>Response.
Question 4.
Name the three major regions of human brain. Which part of brain maintains posture and equilibrium of the body ? (CBSE Foreign 2008)
Answer:
Major Regions of Brain
- Fore Brain: Olfactory lobes (2), Cerebrum (2 cerebral hemispheres) and diencephalon.
- Mid Brain: Cerebral peduncles (crura cerebri) and four quadrigemina.
- Hind Brain: Cerebellum, pons and medulla oblongata.
Question 5.
Maintenance of Posture and Equilibrium. Cerebellum.
(a) Distinguish between voluntary and involuntary actions of our body.
(b) Choose involuntary actions, amongst the following :
Reading, Beating of heart, Salivation in the mouth on viewing tasty food, Talking.(CBSE Foreign 2008)
Answer:
(a) Differences between Voluntary and Involuntary Actions
| Voluntary Actions | Involuntary Actions |
| 1. Will. They are under control of the will.
2. Muscles. The actions are performed with the help of striated muscles. 3. Activities. They are connected with the functioning of external organs. |
They are performed without consulting the will.
The actions are performed with the help of smooth muscles. They are connected with the functioning of internal organs. |
(b) Beating of heart, salivation in the mouth on viewing of tasty food.
Question 6.
Explain the cause of shoots of the plant bending towards light ? (CBSE Delhi 2008, CCE 2010, 2011)
Answer:
Stems are positively phototropic and bend towards the direction of light. The movement is due to occurrence of more auxin on the darker side and lesser auxin on the illuminated side. As a result, there is more growth on the darker side which causes the stem to bend towards light.
Question 7.
What are nastic and curvature movements ? Give one example of each. (CBSE Delhi 2009)
Answer:
(a) Nastic Movements: They are non-directional curvatures movements of turgor or growth where the movements are determined by the structure of the responding organ irrespective of the direction of stimulus which is generally diffuse. Ex. Drooping and folding of leaves in Sensitive Plant in response to shock (seismonasty).
(b) Curvature Movements: They are changes in orientation of some plant parts in relation to others caused by intrinsic or external stimuli. Ex. Sleep movement or nyctinasty of legume leaves, bending of stems towards light (or positive phototropism of stems).
Question 8.
Draw a diagram of a nerve cell and label on it following :
(a) Nucleus
(b) Dendrites (CBSE Delhi 2009 C, CCE 2010)
Answer:
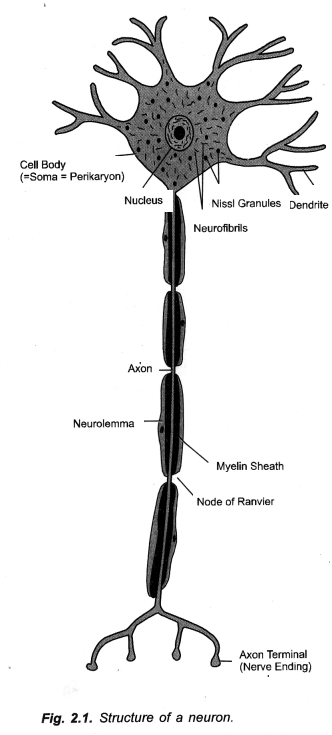
Question 9.
What are plant hormones ? Write two functions of auxin. (CBSE A. I. 2009 C)
Answer:
Definition: Phytohormones are chemical substances other than nutrients produced naturally in plants which regulate growth, development, differentiation and a number of physiological processes, e.g., auxin, gibberellins, abscisic acid, cytokinins.
Function of Auxin:
- Cell Enlargement. They bring about growth of cells. In shoots auxin is effective above a concentration of 10 ppm while in roots the required concentration is 0-0001 ppm.
- Several plant movements are mediated by differential distribution of auxin, e.g., geotropism, phototropism.
Question 10.
Name the two main regions of our central nervous system. Which one of them plays a major role in sending command to muscles to act without involving thinking process ? Name the phenomenon involved.
(CBSE A.I. 2010)
Answer:
- Brain and spinal cord,
- Spinal cord plays a major role in mediating muscle action without involving thinking process,
- The phenomenon is called reflex action.
Question 11.
Name the hormone secreted by human testes. State its functions. (CBSE A.I. 2010)
Answer:
Hormone: Testosterone.
Functions:
- Development of male sex characteristics and secondary sex organs during puberty,
- Maintenance of male sex characteristics and male sex organs thereafter.
Question 12.
Name and explain the function of the hormone secreted by the pituitaiy gland in humans. (CBSE A.I. 2010)
Answer:
Pituitary gland secretes several hormones,
- Somatotrophic or growth hormone stimulates growth by increased anabolic activity, enlargement of long bones, muscles and visceral organs, synthesis of more proteins and retention of calcium.
- FSH (follicle stimulating hormone) stimulates sperm formation in testes and development of ovarian follicles in ovaries.
Question 13.
Explain how the human body responds to secretion of adrenaline into blood. (CCE 2010)
Answer:
Adrenaline reduces blood supply to skin and digestive system but increases the same to skeletal or voluntary muscles. There is increase in breathing rate and heart beat. The body becomes ready to deal with an emergency. Further, endocrine system controls and coordinates many processes of the body where nervous system has no role, e.g., cell permeability, cell division, cell growth, cell differentiation, development of sex organs, secondary sex characters and several other activities. Any discrepancy can lead to a disorder, e.g, dwarfism and gigantism, hypothyroidism (simple goitre, cretinism, myxedema), hyperthyroidism (exophthalmia).
Question 14.
Name the gland and hormone secreted by the gland which are associated with the following problems :
(i) A girl has grown extremely tall
(ii) A woman has swollen neck. (CCE 2014, 2015)
Answer:
(i) Pituitary, excessive secretion of growth hormone causing gigantism.
(ii) Thyroid, reduced secretion of thyroxine causing hypothyroidism or goitre.
Question 15.
A doctor advised a patient to go on a diet without sugar and take insulin injections also. Name the disease he is suffering from. Why has he been given the two advices ? (CCE 2014)
Answer:
Disease. Diabetes mellitus. The disease is due to insufficiency of insulin secretion which results in nonabsorption of glucose by cells and its nonconversion into glycogen in liver and muscles. Excess sugar present in blood is partly passed out alongwith urine. Sugar free diet will reduce quantity of sugar in the blood. Injections of insulin will help the cells to pick up glucose for their metabolism and allow liver and muscles to convert it into glycogen.
Question 16.
Name the following :
- A gland present in females but not in males,
- A gland that secretes hormones as well as digestive juice or enzyme,
- A gland associated with brain,
- A gland that is associated with kidneys. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
- Ovary/Mammry glands
- Pancreas
- Pituitary
- Adrenal.
Question 17.
Trace the sequence of events through a reflex arc with occur when a bright light is focussed on your eyes.
(CCE 2015)
Answer:
Cerebral reflex: It functions as a relay centre for transferring impulse from sensory to motor neurons in several reflex actions called cerebral reflexes,
Reflex Arc: Reflex action requires a stimulus, a receptor organ, sensory neurons, a part of central nervous system, motor neurons and effector organ. The pathway taken by a stimulus to travel from receptor organ to effector organ is known as reflex arc. Its components are as follows (Fig. 2.4).
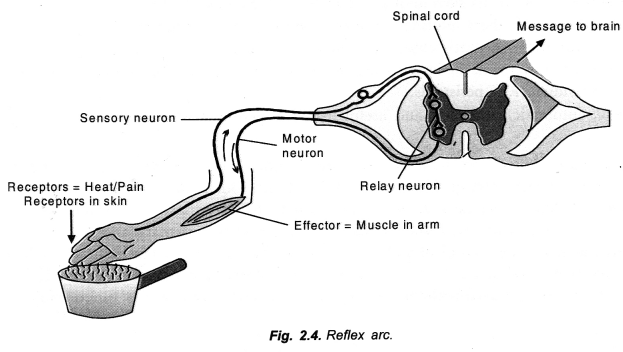
Stimulus——>Receptor organ ——> Sensory neurons ——> CNS——> Motor neurons ——> Effector organ——>Response.
Receptor Organ: It is a tissue or organ which receives the stimulus for initiating nerve impulse, e.g., skin, eye, ear.
Question 18.
State the source of secretion and function of the following hormones :
- Thyroxine
- Insulin
- Growth hormone. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Source :
- Thyroxine — Thyroid,
- Insulin — Pancreas,
- Growth hormone — Pituitary.
Function :
- Thyroxine: Regulates metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins, release of energy and body activity.
- Insulin: Regulates blood glucose by its absorption in liver, muscles (for formation of glycogen) and individual cells (for metabolic activity).
- Growth Hormone (GH) or Somatotrophic Hormone: Regulates growth and development of the body through anabolic activity for growth of bones, muscles and visceral organs.
Question 19.
Write the function of the following :
- Sensory Neuron
- Cranium
- Vertebral column
- Motor Neuron. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
- Sensory Neuron. Picking up sensation from the receptor and passing it to CNS.
- Cranium. Protection of brain.
- Vertebral Column. Protection spinal cord.
- Motor Neuron. Taking message from CNS to muscle, gland or organ to perform its function.
Question 20.
Draw a neat and labelled diagram of neuro-muscular juction. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
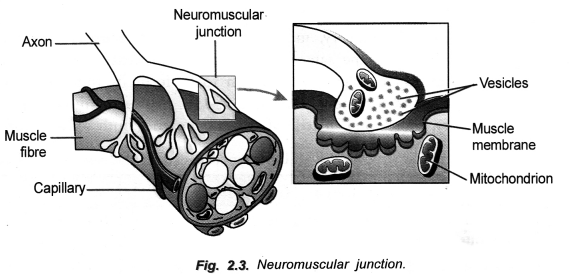
Question 21.
Identify the parts of a neuron
- Where information is acquired,
- Through which information travels
- Where the impulse must be converted into a chemical signal. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
- Dendrites
- Axon
- Synapse, neuromuscular junction.
Question 22.
What is reflex arc ? Why have reflex arcs evolved in animals ? (CCE 2016)
Answer:
Reflex arc is the pathway taken by a stimulus to travel from the receptor organ to the effector organ through CNS without consulting the will of the individual. It produces a quick, immediate and involuntary response where delay can be harmful. Reflex arcs evolved in animals as a survival mechanism before the development of intelligence.
Question 23.
Name the hormone which is released when we are in a scary situation. Write two effects of the hormone on our body that enable the body to deal with the situation. (CCE 2016)
Answer:
Adrenaline (from adrenal medulla): Adrenaline/emergency hormone/triple Fhormone
- Reduces blood supply to peripheral blood vessels and gastrointestinal tract,
- More blood flows to skeletal and heart muscles.
- Increases breathing and gives more oxygen to muscles,
- Increases heart rate,
- Mobilises more glucose to muscles for higher activity.
Question 24.
How does our body maintain sugar level ? (CCE 2016)
Answer:
Sugar level is maintained with the help of two hormones secreted by pancreas.
Insulin (secreted by (3-cells of islet of Langerhans)
Recognition of glucose by cells for absorption and conversion of glucose into glycogen in liver and muscles.
Glucagon (secreted by a-cells of islet of Langerhans)
Formation of glucose from glycogen and other sources and its release into blood.
Question 25.
State the sequence of events through a reflex arc which occur when bright light is focussed on your eyes.
(CCE 2016)
Answer:
The sensation of bright light is picked up by receptors present over the eyes. The sensation travels to superior quadrigemina through sensory neurons. The impulse is here transferred to motor neurons that reach the pupil and eye lids to close the eyes.
Short Answer Questions (3 Marks Each)
Question 1.
Define hormones. Name the hormone secreted by thyroid. Write its functions. Why is the use of iodised salt advised to us ? (CBSE Delhi 2008, CCE 2011)
Answer:
Definition: Nervous stimulation is for only short duration while certain activities require prolonged stimulation. Therefore, multicellular animals have also a second system of communication called endocrine system. Endocrine system operates through chemicals called hormones.
Hormone of Thyroid. Thyroxine.
Functions of Thyroxine: It controls
- Basal metabolic rate or BMR.
- Metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins.
- Physical activity
- Body temperature
- Heart beat
- Development
- Nervous activity.
Iodised Salt: Iodine is essential for formation of thyroxine. In its deficiency, thyroid undergoes overgrowth causing goitre. Common salt is iodised to prevent occurrence of goitre.
Question 2.
Which animal or plant hormone is associated with the following :
- Increased sugar level in blood.
- Changes at puberty in boys
- Inhibits growth of plants.
- Rapid development of fruits
- Dwarfism
- Goitre. (CBSE Delhi 2008 C)
Answer:
- Increased sugar level in blood. (Deficiency of) Insulin,
- Changes at puberty in boys. Testosterone.
- Inhibits growth of plants. Abscisic acid,
- Rapid development of fruits. Auxin.
- Dwarfism. Deficiency of somatotrophic or growth hormone
- Goitre. Deficiency of Thyroxine.
Question 3.
What is phototropism ? How does it occur in plants ? Describe an activity to demonstrate phototropism.
(CBSE A.I. 2009, 2010, CCE 2012, 2014, 2015)
Answer:
Definition of Phototropism. It is directional growth movement of curvature which occurs in plants in response to stimulus of unilateral light.
How does it occur ? Phototropism is caused by increased auxin on shaded side and decreased auxin on illuminated side. Increased auxin causes increased’growth in shoot (which bends towards light, positive phototropism) and reduced growth in roots (when bends away from light, negative phototropism). Demonstration of Phototropism.
Question 4.
What is hydrotropism ? Describe an experiment to demonstrate hydrotropism. (CBSE A.I. 2009)
Answer:
Definition of Hydrotropism: Hydrotropism is directional movement of curvature which occurs in response to unilateral stimulus of water.
Experiment:
Apparatus: Trough with perforated base, saw dust, water, seeds of Pea/Gram, wooden support.
Procedure: Take a trough with perforated base. Fill it with saw dust. Moisten the same. Sow several seeds of Pea or Gram. Place the trough in slanting position by means of a wooden block. Keep the saw dust moist by sprinkling water at intervals. Observe after 2-3 days.
Observation: As the radicles come out of the seeds, they are seen to move towards the perforations. They come out of the pores and hang downwardly for some time under the influence of gravity. However, after some growth they bend back and enter the perforations to reach moist saw dust in complete disregard of gravity (Fig. 2.11).
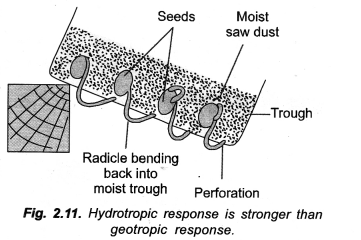
Inference: Bending of radicles back into moist saw dust is hydrotropic movement. It occurs despite being against the force of gravity.
Question 5.
How does feed back mechanism regulate hormone secretion ?
Answer:
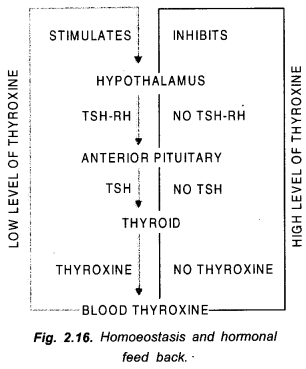
Feed back system is a regulatory mechanism in which presence of certain level of substance promotes or inhibits its further formation. Common control is through negative feed back. Here regulation is through opposite action. Positive feed is rare as during uterine contraction at child birth. Regulation of thyroxine production by its concentration in blood is an example of negative hormonal feed back system. Concentration of thyroxine in blood is detected by hypothalamus. If it is low, hypothalamus produces TSH-RH. The latter stimulates pituitary gland to produce TSH or thyroid stimulating hormone. TSH passes into circulatory z system and reaches thyroid. Thyroid begins to secrete more thyroxine.
Question 6.
(a) If the cerebellum is not functioning properly, what are the activities of our body affected ?
(b) How do muscle cells move ? (CCE 2010)
Answer:
(a) Posture and equilibrium (balance) of the body.
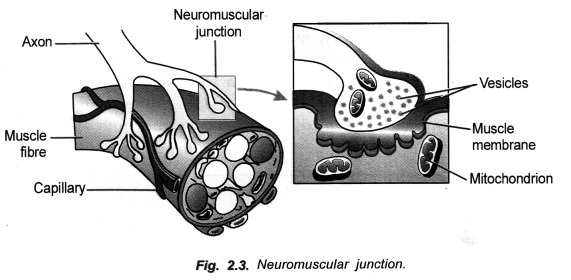
(b) It is the place of apposition of motor end plate of a neuron with the surface of the muscle. Motor end plate consists of a number of knobbed branches. A knob or bouton is plugged into shallow depression present on surface of muscle fibre called sole plate. A narrow space or synaptic cleft occurs between the two.
On excitation the knob of motor end plate passes out acetylcholine which reaches the Ach receptors on the surface of muscle. The excitation spreads over the whole muscle fibre. The latter contracts.
Question 7.
If you keep the potted plant horizontally for 2-3 days, what type of movements would be shown by the shoot and root after 2-3 days. Why ? (CCE 2010)
Answer:
The plant shows geotropic response. The terminal part of the shoot bends upwardly. It is negative geotropic response. The terminal part of the root bends downwardly. It is positive geotropic response. The response is due to more auxin on the lower side which causes more growth on the lower side of the stem and no growth on the lower side of the root.
Question 8.
(a) What is endocrine gland ?
(b) Name any two endocrine glands present in a human body and write hormones secreted by them.
(CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Endocrine gland is an isolated gland which does not have a duct for draining out its scretion but instead pours the same into circulatory system for reaching the target sites.
(b)
- Thyroid-Hormone thyroxine
- Islets of Langerhans in Pancreas-Hormones insulin and glucagon.
Question 9.
Which part of nervous system controls reflex arcs ? With the help of a diagram trace the sequence of events which occur when we touch a hot object. Mention the part of the neuron that acquires information and the form in which information travels. (CCE 2010, 2011, 2015)
Answer:
Control of reflex arcs is carried out by CNS, chiefly spinal cord.
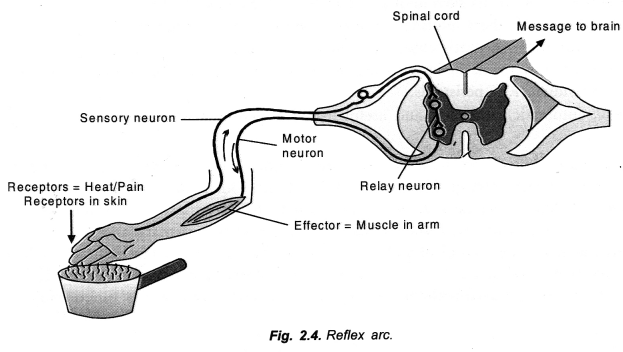
Sequence of Events. The hot object functions as a stimulus. The stimulus is received by receptors present in the skin. Sensory neurons carry the information as electrical impulse from the receptors to the CNS. CNS possesses relay neurons that transfer the information as electrical impulse to motor neurons. The motor neurons conduct the impulse to effector organs which in this case are muscles that pull away the arm before the information reaches brain.
Question 10.
Name the hormone synthesised at the shoot tips. How does it help the plant to respond to light ?
(CCE 2011)
Answer:
Hormone Synthesised at shoot tip. Auxin.
The shoot responds to unilateral light by bending towards it. This is caused by migration and synthesis of more auxin on the shaded side as compared to the illuminated side. Higher concentration of auxin on the shaded side causes more growth as compared to illuminated side. This bends the shoot towards the light.
Question 11.
(a) Which hormone is responsible for the changes noticed in males at puberty ?
(b) Deficiency of which hormone leads to dwarfism
(c) Name the hormone which is injected to a diabetic patient. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Testosterone
(b) Growth hormone/somatotrophic hormone
(c) Insulin.
Question 12.
(a) What is the structural and functional unit of nervous system ? Name its any two components.
(b) Which structure in a neuron helps to conduct a nerve impulse
- towards the cell body
- away from cell body. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
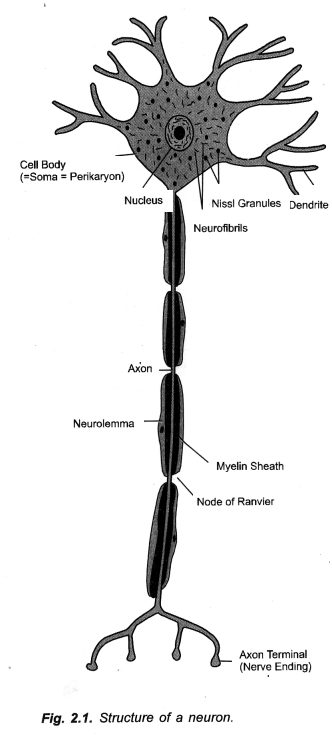
(a) Neuron. Components. Dendrites, cell body and axon.
(b)
- Dendrites
- Axon.
Question 13.
Ram has met with an accident. After that he has lost the capacity to
- walk in straight line
- smell anything
- Does not feel full after eating. Which part of the brain is damaged in each case ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
- Hind brain-Cerebellum
- Fore brain-cerebrum (temporal lobes).
- Fore brain—hypothalamus.
Question 14.
How does our body respond when adrenaline is secreted into the blood ? (CCE 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014)
Answer:
Adrenaline/emergency hormone/triple F hormone
- Reduces blood supply to peripheral blood vessels and gastrointestinal tract,
- More blood flows to skeletal and heart muscles.
- Increases breathing and gives more oxygen to muscles,
- Increases heart rate,
- Mobilises more glucose to muscles for higher activity.
Question 15.
(a) What is tropism ?
(b) How is brain protected in our body ?
(c) Name the part of brain responsible for precision of voluntary actions and maintaining body posture and
balance of the body. (CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
(a) Tropism. It is the phenomenon of directional paratonie growth movement of curvature in which the direction of movement is determined by the direction of stimulus, e.g., phototropism, geotropism, hydrotropism.
(b) Protection of Brain,
- Bony box or skull on the outside,
- Meninges over the brain.
- Presence of cerebrospinal fluid both outside and inside the brain to absorb shocks.
(c) Cerebellum.
Question 16.
State the sequence of changes that takes place in a human body when it prepares itself to protect from a scary or dangerous situation. (CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
Both sympathetic nervous system and hormone adrenaline of adrenal medulla work together in preparing the body for protection from a scary or dangerous situation.
- Heart beats faster so as to provide more blood and its contained oxygen and glucose to muscles,
- Blood supply to peripheral vessels and digestive tract is reduced. More blood becomes available to skeletal muscles.
- Breathing rate increases due to dilation of bronchioles, increased activity of diaphragm and rib-muscles.
Question 17.
(a) Which plant hormone is present in greater concentration in the areas of rapid cell division ?
(b) Give one example of a plant growth promoter and plant growth inhibitor. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Cytokinin.
(b)
- Plant Growth Promoter—Auxin/Gibberellin.
- Plant Growth Inhibitor—Abscisic acid (ABA).
Question 18.
(a) Which organ secretes a hormone when blood sugar rises in our body ?
(b) Name the hormone and name one enzyme released by this organ. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Pancreas
(b)
- Insulin
- Trypsin/pancreatic amylase/lipase.
Question 19.
(a) Which part of the brain controls involuntary actions ?
(b) Write the function of any two regions of it. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Involuntary actions are mostly controlled by hind brain.
(b)
- Medulla Oblongata: It regulates rate of breathing, rate of heart beat, blood pressure and reflexes like swallowing, vomiting, coughing, sneezing, salivation and peristalsis.
- Cerebellum: Maintaining equilibrium or posture in various activities of the body and coordinating muscular activity of the body.
Question 20.
(a) Name the hormones secreted by thyroid, pancreas and adrenal glands. Write one function of each of these hormones. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
| Thyroid | Thyroxine | Regulates carbohydrate fat and protein metabolism, release of energy and body activity. |
| Pancreas | Insulin | Regulates blood sugar by promoting absorption and storage |
| Glucagon | Release of glucose from storage regions. | |
| Adrenal | Adrenaline | Preparing the body for emergency. |
| Noradrenaline | Moderating body activities. |
Question 21.
(a) If the cerebellum is not functioning properly, state the activities of our body that are affected,
(b) How do muscle cells move ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Maintenance of posture or balance of body and coordination of body activities will be impaired.
(b) Excitation of neuron is transferred to muscle at the neuromuscular junction by the release of acetylcholine from the knobs of its motor end plate. Acetylcholine is picked up by Ach receptors present on the surface of muscle fibre. This induces the mucles fibre to contract.
Question 22.
Why does the shoot of the plant bend towards light when it is kept inside a card-board box with a small hole ?
(CCE 2011)
Answer:
Light coming from the hole in card-board falls on one side of shoot. Auxin diffuses from the illuminated side to shaded side. Higher concentration of auxin brings about more growth on the shaded side. As a result, the shoot bends towards the side of the hole.
Question 23.
(a) What is geotropism ?
(b) Describe an experiment to demonstrate positive and negative geotropism. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Geotropism : It is directional growth movement of curvature which occurs in response to force of gravity. Main root shows positive geotropism while main stem shows negative geotropism.
(b) Experiment. Place a well watered potted plant on its side (horizontally) in sunlight. Keep watering the plant on alternate days. Observe after 3-4 days. The terminal part of the shoot bends upwardly. It shows negative geotropic response. The terminal part of the root bends downwardly. It shows positive geotropic response.
Question 24.
(a) Define tropic movement.
(b) Why do multicellular organisms need another means of communication between cells besides nervous
coordination ? (CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
(a) Tropic Movement: It is directional paratonie growth movement of curvature in which direction of movement is determined by the direction of the stimulus. They mostly occur in cylindrical organs. Growth response occurs due to differences in the distribution of auxin.
(b) Need For Another System of Communication. Nervous system cannot meet all the requirments of a multicellular organism because
- Nerve impulse cannot reach every cell of the body,
- Nervous stimulation is for only short duration while certain activities require prolonged stimulation.
Therefore, multicellular animals have also a second system of communication called endocrine system. Endocrine system operates through chemicals called hormones. Hormonal secretion passes to all parts of the body but the hormone triggers activity in cells that have recceptors for them. The information can pass persistently. Further, endocrine system controls some processes where nervous system cannot have any role, e.g., cell growth, cell differentiation, development.
Question 25.
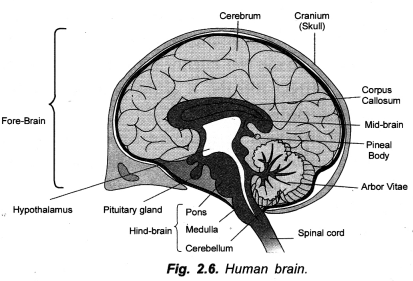
Draw a diagram of human brain and label cerebrum, cerebellum, medulla and fore brian on it.
(CCE 2012)
Answer:
Question 26.
List in tabular form three differences between nervous control and chemical control. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
| Endocrine System/ Chemical Control | Nervous SystemTControl |
| 1. Passage of Information. It is through chemicals called hormones. | It is through electrical conduction. |
| 2. Sensory Receptors. Absent. | Present. |
| 3. Rapidity. The system is comparatively slower. | The system is rapid. |
| 4. Connection. The system is not connected to target sites directly. | The system is directly connected to every part under its control. |
| 5. Response. The response is slow and produced by all the cells of target tissues. | The response is quick and limited to those cells that are innervated. |
| 6. Growth and Development. The system controls growth and development. | It has little role in growth and development. |
| 7. Components. It consists of glands and their secretions. | It consists of neurons, nerves and nervous organs. |
| 8. Effects. The effect of chemical message lasts for longer period. | The effect of nervous message is of short duration. |
| 9. Action. It is involuntary. | It can be voluntary or involuntary. |
Question 27.
Draw a diagram of reflex arc and label on it sensory neuron, motor neuron, relay neuron and receptors.
(CCE 2012)
Answer:
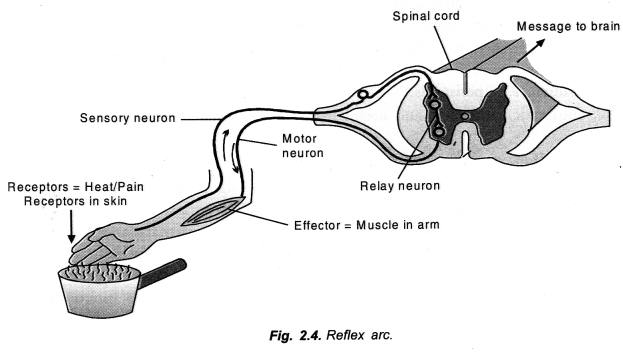
Question 28.
List in tabular form three differences in the movement of leaves of a touch-me-not plant when touched and movement of a tendril towards a support. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
| Leaf Movement in Mimosa | Tendril Movement Towards Support |
| 1. Type. It is a turgor movement. | It is a growth movement. |
| 2. Stimulus. It is a paratonie movement that occurs in response to stimulus of touch. | It is an autonomic movement caused by intrinsic factor. |
| 3. Nature. It is a nastic movement that results in folding and drooping of leaves. | It is a nutation movement that results in bringing tendril in contact with support. |
Question 29.
A gland secretes a particular hormone. The deficiency’of this hormone in the body causes a particular disease in which the blood sugar level rises,
- Name the gland and the hormone secreted by it.
- Mention the role played by this hormone.
- Name the disease caused due to deficiency of this hormone. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
- Pancreas, insulin,
- Insulin makes the body cells receptive to glucose which is then absorbed by them from the blood. In liver and muscles, it also helps in conversion of absorbed glucose into glycogen.
- Diabetes mellitus.
Question 30.
Mention the role of each of the following :
- Cerebellum
- Fore brain
- Medulla. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
- Cerebellum: Maintaining equilibrium or posture in various activities of the body and coordinating muscular activity of the body.
- Seat of intelligence and control of movements,
- Medulla Oblongata: It regulates rate of breathing, rate of heart beat, blood pressure and reflexes like swallowing, vomiting, coughing, sneezing, salivation and peristalsis.
Question 31.
(a) Draw the structure of a neuron and label the nucleus and cell body,
(b) Name the part of neuron
- Where information is acquired
- Through which information travels as an electric impulse. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a)
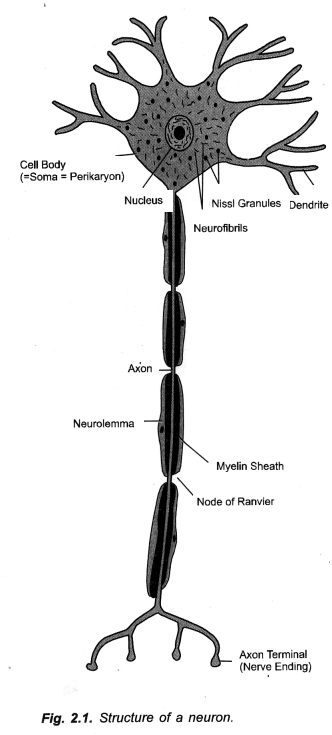
(b)
- Information Acquired. Dendrites,
- Information Travels as Electric Impulse. Axon.
Question 32.
How the timing and amount of hormone released is regulated ? Explain with the help of an example.
(CCE 2012, 2015)
Answer:
The timing and amount of hormone released depends upon feed back system. The requirement of hormone is monitored by a regulatory organ which may be gland itself (e.g., pancreas) or hypothalamus. For example, after meals the glucose content of blood rises. This stimulates P-cells of islets of Langerhans to secrete insulin. Insulin promotes glucose absorption by individual cells, formation of glycogen in liver and muscles. As the glucose level in the blood decreases, secretion of insulin is also reduced.
Question 33.
(a) Identify the enducrine glands a, b, c and d in the given diagram.
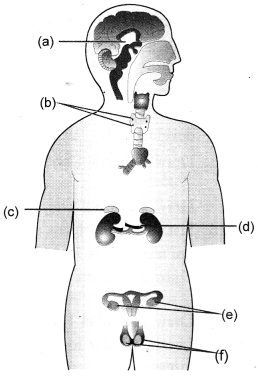
(b) List the functions of parts d and f (CCE 2012, 2013)
Answer:
(a) a—pituitary,
b—parathyroids,
c—adrenal,
d—kidney.
(b) Kidney:
- Produces erythropoietin that stimulates bone marrow to form more RBCs.
- Produces renin that raises blood pressure to increase ulfrafiltration.
- Formation of urine by extracting metabolic wastes from blood.
Testes:
- Formation of sperms,
- Secretion of testosterone that stimulates formation and maintenance of male sex traits.
Question 34.
In the given diagram of reflex arc
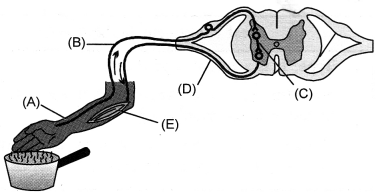
(a) Name the parts labelled A, B, C and D.
(b) Write the function of B and E. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) A—receptor
B—sensory neuron
C—relay neuron
D—motor neuron.
(b)
- Function of B: To pick up impulse from receptor and.pass it to CNS (here spinal cord).
- Function of E: It is effector muscle which is activated by motor impulse to provide response or relfex action.
Question 35.
Name a hormone secreted by
(a) Pancreas
(b) Pituitary
(c) Thyroid. State one function of each of the hormones.
(CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Pancreas. Insulin. Control of glucose absorption by individual cells and formation of glycogen in liver as well as muscles.
(b) Pituitary. Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH). Formation of ova and sperms in sex organs.
(c) Thyroid. Thyroxine. Control of basal metabolism, regulation of protein, fat and carbohydrate metabolism, consumption of energy, development and differentiation.
Question 36.
(a) Name the hormone which is secreted by growing plants when they detect light. Mention its site of secretion in plant,
(b) Explain why plants appear ro bend towards light ?
(c) Name the diseases caused by deficiency of
- Iodine
- Insulin. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Auxin. Site of Secretion. Stem tip.
(b) Shoot bends towards light as more auxin accumulates on the darker side as compared to illuminated side.
(c)
- Deficiency of Iodine. Goitre,
- Deficiency of Insulin. Diabetes mellitus.
Question 37.
(a) How is brain protected from injury and shock ? (CCE 2013)
(b) Name two parts of hind brain and state the function of each. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Protection of Brain. Brain is protected by
- Bony cranium
- Meninges
- Cerebrospinal fluid present in subarachnoid space and ventricles of brain.
(b)
- Medulla Oblongata: It regulates rate of breathing, rate of heart beat, blood pressure and reflexes like swallowing, vomiting, coughing, sneezing, salivation and peristalsis.
- Cerebellum: Maintaining equilibrium or posture in various activities of the body and coordinating muscular activity of the body.
Question 38.
Name the property that causes tendril to circle around the object ? Explain how it happens and how is plant benefitted by it. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Property: Thigmotropism.
(b) Mechanism: Less auxin occurs on the side of contact as compared to the free side. More growth occurs on the free side.
As a result of more growth on the free side, the tendril coils around the support.
(c) Benefit: As the tendrils encircle the support, the plant can climb higher and higher to expose its leaves properly to sun.
Question 39.
Smitas father has been advised by a doctor to reduce his sugar intake;
- Name the disease he is suffering from and name the hormone whose deficiency causes it.
- Identify the gland that secretes it and mention the function of this hormone.
- Explain how the time and amount of secretion of this hormone is regulated in human system. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
- Diabetes mellitus: Hormone Deficiency. Insulin.
- Gland: Pancreas ((3-cells of islets of Langerhans). Insulin activates glucose receptors of body cells for its absorption. In liver and muscles, it stimulates conversion of glucose to glycogen.
- As glucose level in blood rises after a meal, the [3-cells of islets of Langerhans are stimulated to secrete insulin. As glucose level falls in blood, insulin secretion is reduced.
Question 40.
(a) Name the part of brain which controls
- Voluntary actions
- Involuntary actions,
(b) What is the significance of peripheral nervous system ? Name the components of this nervous system and distinguish between the origin of the two. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Voluntary Actions. Cerebellum. Involuntary Actions. Medulla oblongata. Fore brain has controls over many involuntary and voluntary actions.
(b) Peripheral Nervous System: It is soild lateral part of nervous system that develops from CNS and connects different parts of the body with CNS. Peripheral nervous system has two components, voluntary and involuntary. Voluntary peripheral nerous system is under the control of will. It consists of cranial nerves from brain and spinal nerves from spinal cord. Involuntary peripheral nervous system works independent of will. It develops from some cranial and spinal nerves. Involuntary peripheral nervous system is also called autonomic nervous system. It has two parts, sympathetic (for emergency) and parasympathetic (for moderation). They control the functioning of various internal body parts.
Question 41.
Brain and spinal cord are two vital organs of our body. How is our body designed to protect them ?
(CCE 2013)
Answer:
- They lie inside bony cases, brain inside cranium and spinal cord inside vertebral column,
- Both are covered by meninges—duramen, arachnoid and piamater.
- Cerebrospinal fluid occurs both inside and outside them.
Question 42.
(a) How do muscle cells move ?
(b) Name any two types of tropism.
(c) Define tropism.
(d) Which type of impulses are generally shown by human cells ? (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a) Excitation of neuron is transferred to muscle at the neuromuscular junction by the release of acetylcholine from the knobs of its motor end plate. Acetylcholine is picked up by Ach receptors present on the surface of muscle fibre. This induces the mucles fibre to contract.
(b) Geotropism, Phototropism
(c) Tropism: It is the phenomenon of directional paratonie growth movement of curvature in which the direction of movement is determined by the direction of stimulus, e.g., phototropism, geotropism, hydrotropism.
(d) Electrical.
Question 43.
(a) Complete the following table
| Hormone | Function |
|
Abscisic Acid (ii) Thyroxine (iv) |
(i) Cell division in plants (iii) Stress management |
(b) Give an example of chemotropism. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a)
(i) Inhibits growth and induces dormancy
(ii) Cytokinin
(iii) Controls basal metabolic rate (BMR)
(iv) Adrenaline.
(b) Movement of pollen tube in style and ovary.
Question 44.
After consuming a lot of alcohol, Manish could not walk properly and was vomiting. His friend Sunil stopped his car and tried to help him by dropping him home
(a) Which part of the brain gets affected by consuming alcohol ?
(b) Which part of the nervous system controls the reflex action ?
(c) Which two values are shown by Sunil by helping him. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a) Cerebellum
(b) Central nervous system like spinal cord
(c)
- Sunil knows the after-effects of excessive alcohol intake,
- He is trying to protect his friend from any mishap on the way. Sunil is showing both comradeship and social sense.
Question 45.
(a) Name the major parts of the brain.
(b) Name the part of brain responsible for maintaining the posture and balance of the body.
(c) Which tropic movement is responsible for the growth of pollen tubes towards ovules ? (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a) Major Parts of Brain
Fore-Brain: Olfactory lobes (2), Cerebral hemispheres (2) or cerebrum, Diencephalon.
Mid-Brain: Cerebral peduncles, Corpora quadrigemina.
Hind Brain: Pons, Cerebellum, Medulla oblongata.
(b) Cerebellum
(c) Chemotropism.
Question 46.
(a) How does tendril coil around the support ?
(b) Define geotropism. (CCE 2013, 2014)
Answer:
(a) Thigmotropism or curvature movement that occurs in response to contact. Less auxin is present in the region of contact. The free side having more auxin shows more growth. This causes the tendril to coil over the support.
(b) Geotropism : It is directional growth movement of curvature which occurs in response to force of gravity. Main root shows positive geotropism while main stem shows negative geotropism.
Question 47.
(a) Define nerve impulse and reflex arc.
(b) Which structure in a neuron helps to conduct a nerve impulse
- towards the cell body
- away from cell body. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a) Nerve Impulse. It is a self propagated electrical current that travels from one end to another end of a neuron/nerve for the passage of a message.
Reflex Arc: The pathway taken by a stimulus to travel from receptor organ to effector organ in a reflex action is called reflex arc.
(b)
- Dendrites
- Axon.
Question 48.
(a) What is significance of reflex actions ?
(b) Which signals will get disrupted in case of a spinal cord injury. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a) Significance of Reflex actions:
- It checks overloading and overtaxing of brain.
- Survival Value. Reflex actions have survival value.
- Quick Response. There is an immediate response to otherwise harmful stimuli without the brain having analysed the same.
- Conditioned Reflexes. With the help of conditioned reflexes we perform a number of our activities, g., reading, writing, typing, pedalling, playing a musical instrument.
(b)
- Sensory impulses from the area innervated by injured portion,
- Transmission of motor impulses through the injured portion,
- Reflex action in the area of injury. Sensations and movements are restricted.
Question 49.
With the help of schematic diagram trace the events which occur when you suddenly touch a hot pan. What is the path followed by reflex action known as ?
Answer:
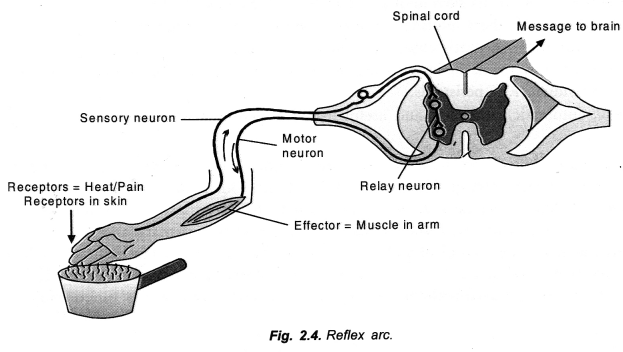
For Events: Control of reflex arcs is carried out by CNS, chiefly spinal cord.
Sequence of Events. The hot object functions as a stimulus. The stimulus is received by receptors present in the skin. Sensory neurons carry the information as electrical impulse from the receptors to the CNS. CNS possesses relay neurons that transfer the information as electrical impulse to motor neurons. The motor neurons conduct the impulse to effector organs which in this case are muscles that pull away the arm before the information reaches brain.
Path. Reflex arc.
Question 50.
Two examples of plant movements are shown

(a) State the stimulus which is common for movement in both the cases
(b) Mention separately for both, whether the movement takes place away or at the point where stimulus is received.
(c) State one reason for movement in each case.
Answer:
(a) Stimulus. Touch.
(b) In Sensitive Plant, the leaf shows movement away from place of contact, at the bases of pinnules, pinnae (pulvinules) and petiole (pulvinus). In tendril the movement takes place in the region of contact.
(c) In Sensitive Plant movement occurs due to loss of water or turgidity by certain cells. In tendril it is due to auxin induced greater growth of cells on the side not in contact with object.
Question 51.
Write three points of difference between reflex action and walking. (CCE 2014, 2015)
Answer:
| Reflex | Walking/Voluntary |
| 1. Origin. Reflex action is inborn and present in an individual right from birth.
2. Control. It is automatic. An individual cannot control it. 3. Intensity. It cannot be changed. 4. Value. It has survival and protective value. |
It is acquired through learning.
It is under control of the will or brain. It can be changed. It has various functions, generally other than survival and protection. |
Question 52.
Illustrate with the help of a diagram the effect of auxin in different parts of a plant. (CCE 2014)
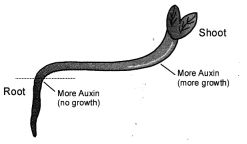
Answer:
In stem auxin stimulates more growth when its concentration reaches above Root 10 ppm. In roots the optimum concentration required for growth is 0-0001 ppm. Higher value is inhibitory.
Question 53.
How does the plant detect the touch and how do the leaves move in response ? (CCE 2015)
Answer:
The stimulus of touch is converted into electro-cheftiical potential or synthesis of chemical called turgarin.
The same travels to the bases of pinnules, pinnae and petiole. The thin walled cells present on upper side of pinnule bases and lower side of pinna bases and petiole are stimulated to eject K+ ions and then water. They shrink in size and cause folding and drooping movements.
Question 54.
(a) Write two points of difference between enzymes and hormones.
(b) Name one endocrine gland in our body which performs dual function. Write its functions.
Answer:
(a)
| Hormones | Enzymes |
| 1.Glands. They are produced by endocrine or ductless glands.
2.Chemical Nature. Hormones are chemically amino acids, peptides, proteinaceous, fatty icids or steroids. 3. Translocation. They are transported from the site of production to the site of action through circulatory system. 4. Activity. Hormones inhibit or initiate activity. 5.Catalytic action. They do not catalyse reactions. 6. Consumption of Hormones. They are consumed at the end of process. |
Enzymes are produced by exocrine glands.
They are usually proteinaceous in nature.There is no role of circulatory system as the site of action is near the site of production. Enzymes have no such role. They catalyse reactions. Enzymes are not consumed. They can be used time and again. |
(b) Testis :
- Secretion of hormone testosterone,
- Formation of sperms.
Question 55.
Name the system which facilitates communication between central nervous system and other parts of the body. Mention two types of nerves it consists of alongwith their organs of origin. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
- Peripheral nervous system.
- It has two components, cranical nerves and spinal nerves. There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves which arise from brain. Spinal nerves are 31 pairs. They develop from spinal cord.
Question 56.
Write two different types of movements shown by the plants. Explain them by giving one example for each.
(CCE 2015)
Answer:
Response of Plants to External Stimuli. Plants are fixed. They cannot run away from stressful conditions nor move to area of favourable conditions. They respond to external stimuli by
- Turgor movements and
- Growth movements.
Turgor Movements: Change in hydration of certain cells gives rise to these movements, e.g, closure and opening of stomata, nyctinasty or sleep movements in legumes, hydronasty in many grasses, seismonasty in Sensitive Plant.
Growth Movements: They are of two types, nondirectional or nastic and directional or tropic.
Nondirectional growth movement is related to struture of the responding organ and not the direction of stimulus, e.g, opening and closing of flowers. Directional growth movement is related to the direction of stimulus, e.g, phototropism, geotropism.
Question 57.
(a) An old man is advised by his doctor to take less sugar in his diet. Name the disease from which the man is suffering. Mention the hormone due to imbalance of which he is suffering from this disease. Which endocrime gland secretes this hormone ?
(b) Name the endocrime gland which secretes growth hormone. What will be the effect of the following on a person :
- Deficiency of growth hormone,
- Excess secretion of growth hormone. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Ans.
(a)
- Diabetes mellitus. Hormone Deficiency. Insulin.
- Gland. Pancreas ((3-cells of islets of Langerhans). Insulin activates glucose receptors of body cells for its absorption. In liver and muscles, it stimulates conversion of glucose to glycogen.
- As glucose level in blood rises after a meal, the [3-cells of islets of Langerhans are stimulated to secrete insulin. As glucose level falls in blood, insulin secretion is reduced.
(b) Pituitary gland
- Dwarfism
- Gigantism.
Question 58.
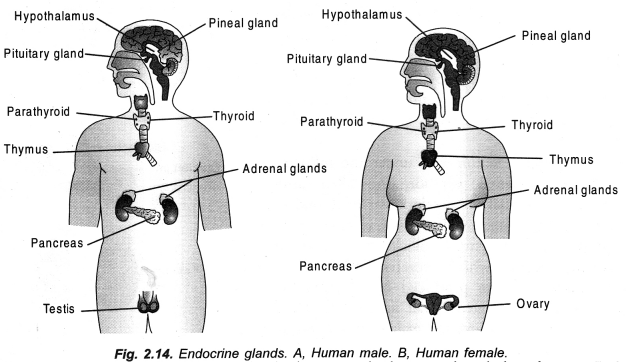
Draw a diagram showing the correct position of pancreas, thyroid gland, pituitary gland, adrenal gland in human being. (CCE 2015, 2016)
Answer:
Question 59.
Name and state briefly one function each of any three phytohormones. (CCE 2016)
Answer:
Five types — auxin, gibberelin, cytokinin, ethylene and abscisic acid.
Auxin: Cell enlargement, root formation, apical dominance, inhibition of abscission, fruit growth.
Gibberellin: Growth in stem and leaves, higher fruit yield, overcoming dormancy.
Cytokinin: Essential for cell division, differentiation, prevention of senescence and overcoming apical dominance.
Ethylene: Promotes transverse growth, fruit ripening and overcoming dormancy of some parts.
Abscisic Acid (ABA): Induces dormancy, senescence and abscission, checking excessive activity of growth promoting hormones, closure of stomata under water stress.
Question 60.
Mention the part of the brain which
- Enables us to ride a bicycle
- Changes the size of the pupil of eye
- Maintains blood pressure of the body
- Maintains posture and equilibrium of the body
- Regulates respiration
- Detects the smell of agarbatti. (CCE 2016)
Answer:
- Cerebellum
- Superior corpora quadrigemina
- Medulla oblongata
- Cerebellum
- Medulla oblongata
- Temporal lobe.
Question 61.
How does the plant shoot bends when the plant is placed in a room having only one open window ? Explain briefly. (CCE 2016)
Answer:
The plant will be receiving light from one side. The unidirectional light caues positive phototrophic response from the shoot. More auxin is formed on the shaded side of the shoot apex. As a result more growth occurs on the shaded side than the illuminated side. This results in bending of the shoot towards the direction of light.
Question 62.
“As the blood sugar level in our body falls, insulin secretion is reduced”.
Justify the statement in the reference of feedback mechanism that regulates the timing and amount of hormone released. (CCE 2016)
Answer:
Insulin secretion by pancreas is linked to the concentration of sugar in the blood. After a meals, as the glucose concentration becomes high in the blood, insulin is secreted. It activates glucose receptors of the body cells. They absorb glucose for their use. In liver and muscles, the absorbed glucose is converted into glycogen. This reduces the glucose concentration in blood. Insulin secretion by pancreas is also reduced because the P-cells of its endocrine region are not being stimulated to secrete.
Question 63.
Draw a nerve cell and label on it the following : Nucleus, Dendrite, Axon. (CCE 2016)
Answer:
Question 64.
Write two different types of movements shown by plants. Explain them by giving one example for each. (CCE 2016)
Answer:
Nastic and trophic
Nastic Movements: They are non-directional curvatures movements of turgor or growth where the movements are determined by the structure of the responding organ irrespective of the direction of stimulus which is generally diffuse. Ex. Drooping and folding of leaves in Sensitive Plant in response to shock (seismonasty).
Tropic Movements: It is the phenomenon of directional paratonie growth movement of curvature in which the direction of movement is determined by the direction of stimulus, e.g., phototropism, geotropism, hydrotropism.
Long Answer Questions (5 Marks Each)
Question 1.
(a) What is reflex action ? Give its two examples. Illustrate the pathway followed by a message from the
receptor in a reflex arc. (CBSE Delhi 2006 C, CCE 2010, 2015)
(b) Name the actions of sympathetic and parasympathetic systems on eye. (CBSE Delhi 2006 C)
Answer:
(a) Reflex Action: It is an automatic, spontaneous nerve mediated response to a stimulus without consulting the will of the individual.
e.g., withdrawal of hand on being pricked or coming in contact with hot surface.
(b) Effect on Pupil,
- Sympathetic—dilation
- Parasympathetic—constriction.
Question 2.
(a) What are “hormones” ?
(b) List four characteristics of hormones
(c) Name the hormone required for the following :
- Functioning of mammary glands
- Regulation of calcium and phosphate
- Lowering of blood glucose
- Development of moustache and beard in human malc.(CBSE A.I. 2006 C, CCE 2015)
Answer:
(a) Definition: Hormones (Gk. hormein— to excite) are chemical messengers or informational molecules produced by ductless glands which are translocated by circulatory system to other body parts for inducing and coordinating their activities including growth. First hormone, secretin, was discovered by Bayliss and Starling (1902). The term hormone was coined by Starling (1905)
(b) Characteristics:
- Hormones are produced by endocrine or ductless glands.
- They are poured into circulatory system for passage to different body parts.
- Target Sites. Hormones act on specific cells, tissues and organs called target sites, generally away from the place of their synthesis. ‘
- They function as chemical messengers or informational molecules that trigger specific chemical and physiological processes of target cells.
- Slow Action. Since hormones reach the target sites through blood, their effect appears after a lag period. They are slow acting with the exception of adrenaline.
- Chemical Nature. Hormones are small sized organic molecules which are of diverse origin— proteins, peptides, amino acids, amines and steroids.
- Non-nutrient Nature. Hormones are nonnutrient in nature. They have no role in providing energy or body building materials. Hormones take part in stimulation or inhibition of physiological processes.
- The hormones are effective in very low concentration, e.g., adrenaline one in 300 million parts.
- It is very specific. TSH acts only on thyroid while thyroxine affects all body parts.
- Hormones are generally produced in response to specific stimuli.
- Hormones are ultimately broken down or consumed during their activity in target cells.
- Deficiency or Excess. Both deficiency and excess of hormone are harmful, often leading to serious disorders.
(c)
- Functioning of Mammary Glands. Prolactin.
- Regulation of Calcium and Phosphate in Blood. Parathormone.
- Lowering of Blood Glucose. Insulin.
- Development of Moustache and Beard in Human Male. Testosterone.
Question 3.
(a) What is
- Phototropism and
- Geotropism ?
With labelled diagrams describe an activity to show that light and gravity change the direction that plant parts grow in.
(b) Mention the role of each of the following plant hormones :
- Auxin
- Abscisic acid. (CBSE A.I. 2008, CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a)
- Definition of Phototropism: It is directional growth movement of curvature which occurs in plants in response to stimulus of unilateral light.
- Definition of Geotropism: It is directional growth movement of curvature which occurs in response to force of gravity. Main root shows positive geotropism while main stem shows negative geotropism.
Activity: Phototropism and Geotropism- Take two potted plants. Place one plant near a window. Keep the other pot tilted horizontally in the open. Water the plants on alternate days. Observe after a week. Potted plant kept near the window shows bending of young stems towards the window. They are positively phototropic. In the horizontal pot, the stem bends upward as it is negatively geotropic. Its root if taken out, shows downward bending indicating its positive geotropic nature.
(b)
- Role of Auxin. It promotes cell enlargement, fruit growth, apical dominance, rooting of cuttings, prevention of abscission and differential growth during tropic movements.
- Role of Abscisic Acid. It checks excessive activity of auxin and gibberellins, closes stomata in water deficiency, induces dormancy of buds and seeds.
Question 4.
(a) Name the hormone which is injected to a diabetic patient.
(b) Why should we use iodised salt in our diet ?
(c) If iodine is insufficient in one’s diet, what might be the deficiency disease and its symptoms.
(CCE 2010, 2011)
Answer:
(a) Diabetic Patient. Hormone injected is insulin.
(b) Iodised Salt. Iodine is essential for synthesis of hormone thyroxine in thyroid gland. Thyroxine controls basal metabolic rate, metabolism of protein fat and carbohydrates, activity, body temperature, heart beat and body development.
(c) Deficiency of Iodine. Reduced thyroxine which causes goitre, cretinism and myxoedema. In goitre, there is enlargement of thyroid that results in swelling of neck.
Question 5.
(a) What is reflex arc ?
(b) What are the components of reflex arc ?
(c) How do muscle cells move ?
(CCE 2010, 2011)
Answer:
(a) Reflex Arc: The pathway taken by a stimulus to travel from receptor organ to effector organ in a reflex action is called reflex arc.
(b) Components of Reflex Arc:
Stimulus —> Receptor —> Sensory neuron —> Relay Neuron (CNS) —> Motor neuron —> Effectors —> Response.
(c) Movement of Muscle cells:
It is the place of apposition of motor end plate of a neuron with the surface of the muscle. Motor end plate consists of a number of knobbed branches. A knob or bouton is plugged into shallow depression present on surface of muscle fibre called sole plate. A narrow space or synaptic cleft occurs between the two.
On excitation the knob of motor end plate passes out acetylcholine which reaches the Ach receptors on the surface of muscle. The excitation spreads over the whole muscle fibre. The latter contracts.
Question 6.
Mention the part of brain involved in the following :
- Walking in a straight line,
- Picking up a pencil.
- Blood pressure
- A question is being asked by the teacher in a class.
- Change in size of the pupil in response to intensity of light. (CCE 2014, 2015)
Answer:
- Walking in Straight Line. Cerebellum.
- Picking up a Pencil. Cerebellum.
- Blood Pressure. Medulla oblongata.
- Question being Asked by Teacher. Frontal (Broca’s motor area of speech) lobe of fore brain.
- Change in Pupil. Superior corpora quadrigemina.
Question 7.
Define tropism. Explain four kinds of tropism with one example each. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
Tropism: It is the phenomenon of directional paratonie growth movement of curvature in which the direction of movement is determined by the direction of stimulus, e.g., phototropism, geotropism, hydrotropism.
Four Kinds
- Geotropism: It is directional growth movement of curvature which occurs in response to force of gravity. Main root shows positive geotropism while main stem shows negative geotropism.
- Phototropism: It is directional growth movement of curvature which occurs in plants in response to stimulus of unilateral light.
- Thigmotropism: Thigmotropism or curvature movement that occurs in response to contact. Less auxin is present in the region of contact. The free side having more auxin shows more growth. This causes the tendril to coil over the support.
- Hydrotropism: It is directional growth movement of curvature which occurs in response to unilateral stimulus of water. Roots are positively hydrotropic.
Question 8.
(a) Define reflex action. State its significance.
(b) How do plants respond to external stimuli ? (CCE 2014)
Answer:
(a) Reflex Action: It is an automatic nerve mediated response to a stimulus without consulting the will of the individual, e.g., withdrawal of hand on being pricked or coming in contact with hot surface.
Significance,
- It provides very quick response to stimuli which require immediate remedy,
- Reflex action relieves the brain of overloading or overtaxing.
- It has survival value.
(b) Response of Plants to External Stimuli. Plants are fixed. They cannot run away from stressful conditions nor move to area of favourable conditions. They respond to external stimuli by
- Turgor movements and
- Growth movements.
Turgor Movements: Change in hydration of certain cells gives rise to these movements, e.g, closure and opening of stomata, nyctinasty or sleep movements in legumes, hydronasty in many grasses, seismonasty in Sensitive Plant.
Growth Movements: They are of two types, nondirectional or nastic and directional or tropic.
Nondirectional growth movement is related to struture of the responding organ and not the direction of stimulus, e.g, opening and closing of flowers. Directional growth movement is related to the direction of stimulus, e.g, phototropism, geotropism.
Question 9.
(a) Name one organ each where growth hormone is synthesised in man and plant.
(b) List the sequence of events that occur when a plant is exposed to unidirectional light leading to bending of a growing shoot. Also name the hormone and the type of movement. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
(a)
- Growth Hormone in Man (GH, Somatotrophic Hormone). Anterior pituitary.
- Growth hormone in Plants (Auxin). Shoot tip.
(b) A plant exposed to unidirectional light shows bending of shoot towards the source of light. It is due to higher growth on the shaded side as compared to the illuminated side.
Hormone. Higher growth is caused by hormone auxin which is synthesised at the shoot tip. More of it is synthesised on the shaded side. Some auxin also diffuses from illuminated to shaded side.
Type of Movement. Positive phototropism.
Question 10.
(a) State two points of difference between cerebrum and cerebellum.
(b) Explain the mechanism of reflex action. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
(a) Differences between Cerebrum and Cerebellum.
| Cerebrum | Cerebellum |
| 1. Part. It is a part of fore brain. | It is part of hind brain. |
| 2. Size. Cerebrum constitutes 80% of brain. | It constitutes 12-5% of brain. |
| 3. Position. It forms the front, superior and lateral sides of the brain. | It lies in the posterior region of brain. |
| 4. Components. Cerebrum is made of two parts called cerebral hemispheres. | Cerebellum has three parts, two lateral cerebellar hemispheres and one central vermis. |
| 5. Cavities. It contains two cavities called lateral ventricles. | A cavity is nearly absent. |
| 6. Seat. It is seat of intelligence and memory. | It coordinates muscular activity. |
| 7. Control. Cerebrum controls intelligence, movements, speech, sight, smell, taste, hearing and other sensations. | Cerebellum maintains equilibrium of the body. |
| 8. Nature. Cerebrum is centre of both voluntary and involuntary activities. | It provides precision to voluntary activities. |
(b) Mechanism of Reflex Action:
Mechanism. The stimulus for reflex action is picked up by a receptor located in the organ on which stimulus is acting. One or more sensory neurons carry the impulse from receptor to the central nervous system (e.g., spinal cord). CNS functions as modulator. It transfers the sensory nerve impulse to one or more motor neurons. The motor neurons carry the impulse to effectors which provide a proper response to the stimulus.
Stimulus Receptor ——–>Sensory neurons ———>CNS ——–>Motor neurons ———-> Effectors ———->Response.
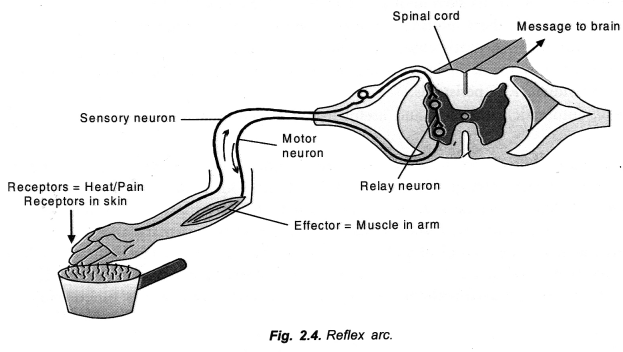
Question 11.
Name the hormone which is secreted by the adrenal gland. Explain the function of this hormone when we have to deal with scary situation. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Adrenaline: It works in co-ordination with sympathetic nervous system to deal with scary situation. Function.
Both sympathetic nervous system and hormone adrenaline of adrenal medulla work together in preparing the body for protection from a scary or dangerous situation.
- Heart beats faster so as to provide more blood and its contained oxygen and glucose to muscles,
- Blood supply to peripheral vessels and digestive tract is reduced. More blood becomes available to skeletal muscles.
- Breathing rate increases due to dilation of bronchioles, increased activity of diaphragm and rib-muscles.
Question 12.
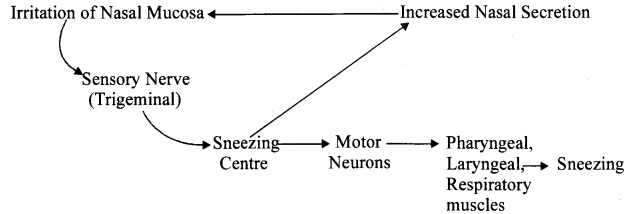
(a) Define reflex arc. Draw a flow chart showing the events which occur during sneezing.
(b) List four plant hormones. Write function of each. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
(a) Reflex arc: The pathway taken by a stimulus to travel from receptor organ to effector organ in a reflex action is called reflex arc.
Flow chart of Sneeze Reflex :
(b) Plant hormones : Five types — auxin, gibberelin, cytokinin, ethylene and abscisic acid.
Auxin: Cell enlargement, root formation, apical dominance, inhibition of abscission, fruit growth.
Gibberellin: Growth in stem and leaves, higher fruit yield, overcoming dormancy.
Cytokinin: Essential for cell division, differentiation, prevention of senescence and overcoming apical dominance.
Ethylene: Promotes transverse growth, fruit ripening and overcoming dormancy of some parts.
Abscisic Acid (ABA): Induces dormancy, senescence and abscission, checking excessive activity of growth promoting hormones, closure of stomata under water stress.
Question 13.
Define phytohormones. How do plants respond to external stimulus ? (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Phytohormones : Phytohormones are chemical substances other than nutrients produced naturally in plants which regulate growth, development, differentiation and a number of physiological processes, e.g., auxin, gibberellins, abscisic acid, cytokinins.
Response of plants to external stimuli: Plants are fixed. They cannot run away from stressful conditions nor move to area of favourable conditions. They respond to external stimuli by
- Turgor movements and
- Growth movements.
Question 14.
(a) Name the hormone which is released into blood when its sugar level rises. Name the organ which produces the hormone and its effect on blood sugar level. Also mention the digestive enzymes secreted by this organ with one function each.
(b) Explain the need of chemical communication in multicellular organisms. (CCE 2016)
Answer:
(a)
- Insulin,
- It is secreted by pancreas ((3-cells of islets of Langerhans).
- Insulin activates glucose receptors of body cells for its absorption. It also stimulates liver and muscles to convert absorbed glucose into glycogen,
- Pancreas secretes three enzymes— trypsin (as trypsinogen), lipase and amylase. Trypsin breaks down proteins, peptones and proteeses into peptides. Pancreatic lipase hydrolysis lipids into fatty acids and glycerol. Pancreatic amylase acts on complex carbohydrates to form maltose.
(b) Multicellular organisms require a system of chemical communication as it can reach every cell of the body and stimulate the cells to perform particular functions. Different cells respond to particular chemicals for which they have receptors. This helps different structures of the body to perform particular functions, e.g., glucose absorption with the help of insulin, glycogen breakdown and glucose formation with the help of glucagon, cell division by cytokinin, cell growth by auxin, etc.
Question 15.
(a) Define nerve impulse. Name the structure that helps to conduct a nerve impulses
- Towards cell body
- Away from cell body.
(b) Why have organisms adapted to use electrical impulse to transmit messages.
(c) State two limitations about the use of electrical impulses. (CCE 2016)
Answer:
(a) Nerve Impulse. It is a self propagated electrical current that travels from one end to another of a neuron for the passage of message,
- Dendrites
- Axon.
(b) Electrical impulses are fast, hardly taking 1 msec for passage. There is no spill-over to external medium, nor any after-effect. As a result the same nerve can carry a new impulse soon after.
(c) In electrical impulse there is one type of transmission while certain messages are to be blocked or inhibited. This is carried out at synapse by means of different types of neurotransmitters.
Hope given Previous Year Question Papers for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control and Coordination are helpful to complete your science homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online science tutoring for you.