Learninsta presents the core concepts of Biology with high-quality research papers and topical review articles.
Principles of Ecology
The term “ecology” (oekologie) is derived from two Greek words – oikos (meaning house or dwelling place and logos meaning study) It was first proposed by Reiter (1868). However, the most widely accepted defiition of ecology was given by Ernest Haeckel (1869).

Alexandar von Humbolt – Father of Ecology
Eugene P. Odum – Father of modern Ecology
R. Misra – Father of Indian Ecology
Definitions of ecology
“The study of living organisms, both plants and animals, in their natural habitats or homes.” – Reiter (1885)
“Ecology is the study of the reciprocal relationship between living organisms and their environment.” – Earnest Haeckel (1889)
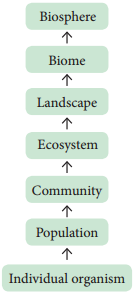
Ecological hierarchy
The interaction of organisms with their environment results in the establishment of grouping of organisms which is called ecological hierarchy or ecological levels of organization.
The basic unit of ecological hierarchy is an individual organism. The hierarchy of ecological systems is illustrated below:
Branches of Ecology:
Ecology is mainly divided into two branches, they are autecology and synecology.
- Autecology is the ecology of an individual species and is also called species ecology.
- Synecology is the ecology of a population or community with one or more species and also called as community ecology.
Many advances and developments in the field ecology resulted in various new dimensions and branches. Some of the advanced fields are Molecular ecology, Eco technology, Statistical ecology and Environmental toxicology.
Habitat and Niche
Habitat
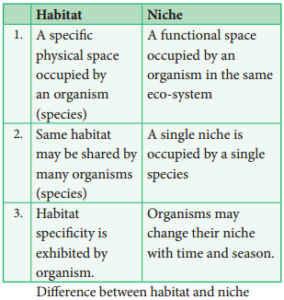
Habitat is a specifi physical place or locality occupied by an organism or any species which has a particular combination of abiotic or environmental factors. But the environment of any community is called Biotope.
Niche
An ecological niche refers to an organism’s place in the biotic environment and its functional role in an ecosystem. The term was coined by the naturalist Roswell Hill Johnson but Grinell (1917) was probably first to use this term. The habitat and niche of any organism is called Ecotope.
The differences between habitat and niche are as follows.
Ecological equivalents
Taxonomically diffrent species occupying similar habitats (Niches) in diffrent geographical regions are called Ecological equivalents.
Examples:
- Certain species of epiphytic orchids of Western Ghats of India differ from the epiphytic orchids of South America. But they are epiphytes.
- Species of the grass lands of Western Ghats of India differ from the grass species of temperate grass lands of Steppe in North America. But they are all ecologically primary producers and fulfiling similar roles in their respective communities.