Electronic Configuration of Noble Elements:
Noble gases have a completely filled valence shell and hence are chemically inert. The usual number of valence electrons in the atom of noble gases is 8 except helium in which it is 2.
Cause of Chemical Reactivity:
The reactivity of an element can be explained as the tendency of an atom to attain a completely filled valence shell.
The atoms combine with one another to achieve the inert gas electron configuration and become more stable. Atoms therefore form chemical bonds to achieve stability by acquiring the inert gas electron configuration. An atom can achieve the inert gas electron configuration in the following ways:
- By losing one or more electrons to another atom.
- By gaining one or more electrons from another atom.
- By sharing one or more electrons with another atom.
Ions:
An ion is an electrically charged atom or group of atoms. An ion is formed by the loss of electrons (sodium ion, Na+, magnesium ion, Mg2+) or gain of electrons (chloride ion, CT, oxide ion, O2-) by an atom. There are two types of ions:- cations and anions.
Cation:
A positively charged ion is known as cation. Sodium-ion, Na+and magnesium ion, Mg2+ are cations because they are positively charged ions since the number of protons in the nucleus is more-than the number of electrons due to which there is a net positive charge on the atom. A cation has less electrons than protons.
![]()
Anion:
A negatively charged ion is known as anion. Chloride ion, Cl” and oxide ion, O2- c.e joined by the addition of electrons due to which t! ere is a net negative charge on the atom. An anion has more electrons than protons.
Ionic Compounds:
When metals react with non-metals, they form compounds by the transfer of electrons from a metal to a non-metal. Such compounds are known as ionic or electrovalent compounds.
Ionic Bond:
The chemical bond formed by the transfer of electrons from one atom to another is known as an ionic bond. An ionic bond is formed when a metal reacts with a non-metal and the transfer of electrons takes place from metal atoms to non-metal atoms.
The metal atom develops a positive charge after donating electrons and thus becomes a cation.
The non-metal atom, on the other hand, becomes a negatively charged ion, anion, after gaining or accepting electrons.
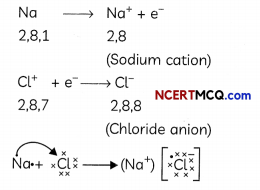
Formation of Sodium Chloride (NaCl):
Sodium donates one electron to a chlorine atom and forms a sodium ion, Na+.
Formation of Sodium-ion, Na+: The atomic number of sodium is 11. Its electronic configuration is: 2, 8, 1 Since it does not have an octet, it is not very stable. In order to become stable, the sodium atom donates its 1 outermost electron to some other atom.

Formation of Chloride ion, Cl–: Chlorine atom takes one electron from the sodium atom and forms a negatively charged ion, CT.
Cl + e– → Cl–
![]()
Sodium chloride is an ionic compound and contains ionic bonds. Both these ions, being oppositely charged, attract each other and are held by strong electrostatic forces of attraction to form an ionic compound. Ionic compounds do not exist as molecules but as aggregates of oppositely charged ions.
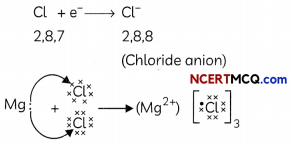
Formation of Magnesium Chloride (MgCl2):
Magnesium donates two electrons to two chlorine atoms and forms a magnesium ion, Mg2+. Similarly, 2 chlorine atoms take one electron each from the magnesium atom and form 2 negativeLy charged ions, Cl”.
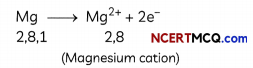
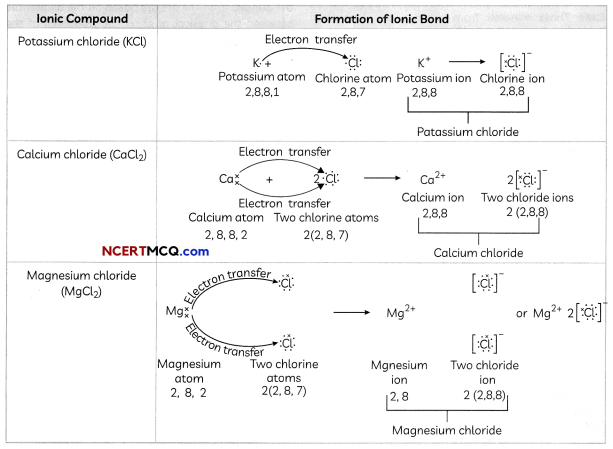
Formation of Some Common Ionic Compounds
![]()
Properties of Ionic Compounds
The general properties of ionic compounds are summarised below:
| Property name | Property Shown by Ionic Compounds |
| 1. Physical nature | Ionic compounds are generally crystalline solids and hard due to the strong force of attraction between the positive and negative ions. They are generally brittle. |
| 2. Melting and boiling points | They have high melting and boiling points as a large amount of energy is required to break the strong inter-ionic attraction. |
| 3. Solubility | These are generally soluble in water but insoluble in organic solvents Like ether, kerosene, petrol etc. |
| 4. Conduction of electricity | These conduct electricity in the molten state as the electrostatic forces of attraction between the oppositely charged ions are overcome due to the heat.
Moreover, they also conduct electricity when dissolved in water as its solution in water contains ions. However, these do not conduct electricity in the solid state due to their rigid structure. |