On this page, you will find Separation of Substances Class 6 Notes Science Chapter 5 Pdf free download. CBSE NCERT Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 5 Separation of Substances will seemingly help them to revise the important concepts in less time.
CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Notes Separation of Substances
Separation of Substances Class 6 Notes Understanding the Lesson
1. A mixture is a substance that contains particles of two or more types of substances mixed together.
2. There are two types of mixtures: heterogeneous and homogeneous.
3. Mixture are needed to be separated
- to remove undesirable substances.
- to get desirable substances.
- to obtain highly pure substances.
4. We have so many methods to separate the components of mixture.
5. Methods of separation may be classified into following groups:
- Separation of solids from solids.
- Separation of insoluble solids from liquids.
- Separation of soluble solids from liquids.
- Separation of two immiscible liquids.
6. Handpicking is the method in which the constituents are separated by simply picking them by hand.
7. In handpicking, the solid undesirable components that are less in quantity are picked up and separated.
8. The process of separating grains from the stalks is called threshing. Farmers beat the bundles of stalks attached to the grains with a stick. Animals like bullocks are allowed to crush the stalks and then the grains are separated from stalks.
9. Separation of stalks from grains is also done by machines called threshers.
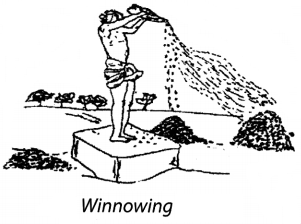
10. Winnowing is the method of separating the lighter components of a mixture from the heavier ones with the help of blowing air.
11. The mixture is made to fall from a height. Husk particles being light in weight are blown away by the wind.
12. Sieving is the process of separating the bigger particles from the smaller ones with the help of sieve.
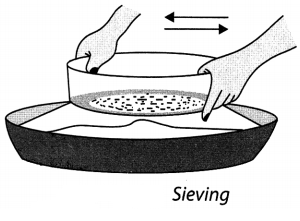
13. We choose a sieve having holes larger than the size of the particles of one component and smaller than other.
14. The mixture is shaken on the sieve so that the particles smaller than the holes of the sieve pass through the holes and fall down and the particles larger than its holes remain on it.
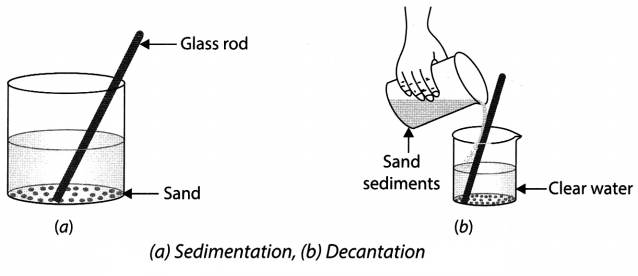
15. When the heavier component in a mixture settles after water is added to it, the process is called sedimentation.
16. The Process of separating a liquid (top layer) from settled solid (sediment) without disturbing it is called decantation.
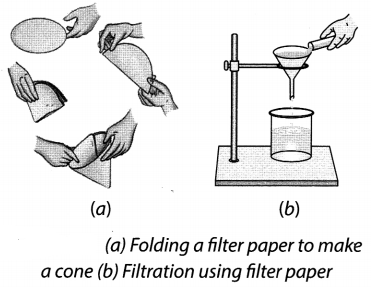
17. Filtration is the process of separating an insoluble solid from a liquid with the help of a filter paper or strainer.
18. We use filter paper or strainer for the process of filtration.
19. When a liquid is heated, it converts from liquid into vapour form. This is called evaporation.
20. Evaporation is a continuous process which takes place wherever water is present. This process is used to separate dissolved salt from water.
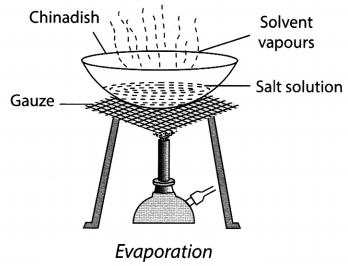
21. If during evaporation, heating is stopped just before the mixture completely dries up and we let it cool, crystals of the pure substance will be formed. This process is called crystallisation.
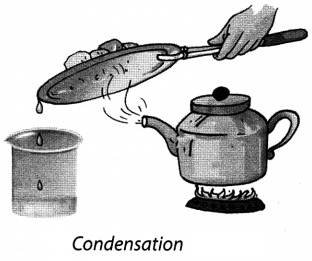
22. The process of conversion of water vapour into its liquid form is called condensation.
23. Condensation is reverse of evaporation.
24. A saturated solution is the solution which cannot dissolve any more solute in it at a given temperature.
25. The maximum amount of a solute that can be dissolved in a fixed amount of solvent at a particular temperature, is called solubility.
26. Sometimes, when more than two substances are mixed, one method of separation is not sufficient. We have to use more than one method.
27. Drinking water that reaches us also passes through many processes of purification.
Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Notes Important Terms
Churning: The process of agitation or stirring of a liquid to separate the lighter particles of a suspended solid from the liquid is called churning.
Condensation: The process of conversion of water vapour into its liquid form is called condensation.
Decantation: The process of separating a liquid (top layer) from a settled solid (sediment) without disturbing it is called decantation.
Evaporation: The process of removing water from a mixture either by heating on flame or direct sunlight is called evaporation.
Filtration: The process of separating an insoluble solid from a liquid with the help of a filter paper and funnel or strainer.
Handpicking: The method in which the constituents are separated by simply picking them up by hand, is called handpicking.
Saturated solution: A saturated solution is the solution which cannot dissolve any more solute in it at a given temperature.
Sedimentation: When the heavier component in a mixture settles after water is added to it, the process is called sedimentation.
Sieving: The process of separating the bigger particles from the smaller ones with the help of a sieve is called sieving.
Solution: A solution is a uniform mixture of two or more substances out of which any of its components cannot be identified separately.
Threshing: The process of separating grains from the stalks is called threshing.
Winnowing: The method of separating the lighter components of a mixture from the heavier ones with the help of blowing air is called winnowing.