Learninsta presents the core concepts of Biology with high-quality research papers and topical review articles.
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (Std)
Sexually transmitted diseases (STD) or Venereal diseases (VD) or Reproductive tract infections (RTI) are called as Sexually transmitted infections (STI). Normally STI are transmitted from person to person during intimate sexual contact with an infected partner.
Infections like Hepatitis-B and HIV are transmitted sexually as well as by sharing of infusion needles, surgical instruments, etc with infected people, blood transfusion or from infected mother to baby.
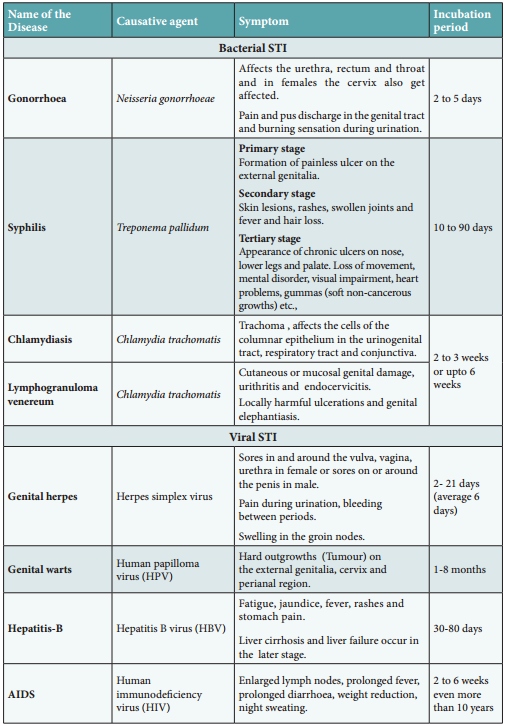
People in the age of 15 to 24 years are prone to these infections. The bacterial STI are gonorrhoea, syphilis, chancroid, chlamydiasis and lymphogranuloma venereum. The viral STI are genital herpes, genital warts, Hepatitis-B and AIDS.
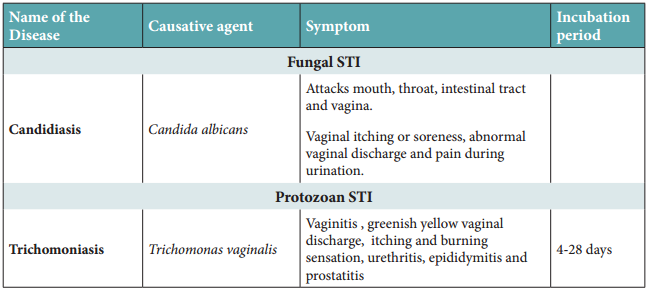
Trichomoniasis is a protozoan STI, and candidiasis is a fungal STI. STI caused by bacteria, fungi and protozoa or parasites, can be treated with antibiotics or other medicines, whereas STI caused by virus cannot be treated but the symptoms can be controlled by antiviral medications. Latex condoms usage greatly reduces the risk, but does not completely eliminate the risk of transmission of STI.
Prevention of STDs
- Avoid sex with unknown partner/multiple partners.
- Use condoms.
- In case of doubt, consult a doctor for diagnosis and get complete treatment.
Cervical cancer
Cervical cancer is caused by a sexually transmitted virus called Human Papilloma virus (HPV). HPV may cause abnormal growth of cervical cells or cervical dysplasia. The most common symptoms and signs of cervical cancer are pelvic pain, increased vaginal discharge and abnormal vaginal bleeding. The risk factors for cervical cancer include
- Having multiple sexual partners
- Prolonged use of contraceptive pills
Cervical cancer can be diagnosed by a Papanicolaou smear (PAP smear) combined with an HPV test. X-Ray, CT scan, MRI and a PET scan may also be used to determine the stage of cancer. The treatment options for cervical cancer include radiation therapy, surgery and chemotherapy. Modern screening techniques can detect precancerous changes in the cervix.
Therefore screening is recommended for women above 30 years once in a year. Cervical cancer can be prevented with vaccination. Primary prevention begins with HPV vaccination of girls aged 9 – 13 years, before they become sexually active. Modification in lifestyle can also help in preventing cervical cancer. Healthy diet, avoiding tobacco usage, preventing early marriages, practicing monogamy and regular exercise minimize the risk of cervical cancer.