On this page, you will find Surface Areas and Volumes Class 9 Notes Maths Chapter 13 Pdf free download. CBSE NCERT Class 9 Maths Notes Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes will seemingly help them to revise the important concepts in less time.
CBSE Class 9 Maths Chapter 13 Notes Surface Areas and Volumes
Surface Areas and Volumes Class 9 Notes Understanding the Lesson
Cuboid: With length T, breadth ‘b’ and height ‘h’
(a) Volume = lbh
(b) Total surface area = 2(lb + bh + hl)
(c) Lateral surface area = 2h(l + b) (c)
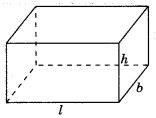
(d) Diagonal = \(\sqrt{l^{2}+b^{2}+h^{2}}\)
(e) Perimeter = 4(l + b + h)
Cube: With side ‘a’
(a) Volume = a3
(b) Total surface area = 6a2
(c) Lateral surface area = 4a2
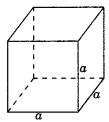
(d) Diagonal = \(\sqrt{3} a\)
(e) Perimeter = 12a
Right circular cylinder: With radius ‘r’ and height ‘h’
(a) Volume = πr2h
(b) Curved surface area = 2πrh
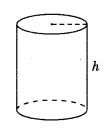
(c) Total surface area = 2πr(h + r)
Right circular cone: With radius ‘r’, height ‘h’ and slant height ‘l’
(a) Volume = \(\frac{1}{3}\) πr2 h or \(\frac{1}{3}\) x (Area of the base) x height
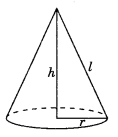
(b) Curved surface area = πrl, where \(l=\sqrt{h^{2}+r^{2}}\)
(c) Total surface area = πr(l + r)
Sphere: With radius ‘r’
(a) Volume =\(\frac{4}{3}\) πr3
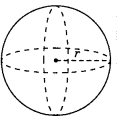
(b) Surface area = 4πr2
Hemisphere: With radius ‘r’
(a) Volume = \(\frac{2}{3}\)πr3
(b) Curved surface area = 2πr2
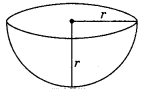
(c) Total surface area = 3πr2