Here we are providing Online Education for Physical and Chemical Changes Class 7 Extra Questions and Answers Science Chapter 6 was designed by subject expert teachers. https://ncertmcq.com/extra-questions-for-class-7-science/
Online Education for Class 7 Science Chapter 6 Extra Questions and Answers Physical and Chemical Changes
Physical And Chemical Changes Class 7 Worksheet With Answers Question 1.
Why is cutting of paper a physical change?
Answer:
Because properties of paper do not change on cutting.
Physical And Chemical Changes Class 7 Extra Questions With Answers Question 2.
A piece of chalk becomes powdery on pressing. Which type of change is it?
Answer:
Physical.
Class 7 Science Chapter 6 Extra Questions Question 3.
What is freezing mixture?
Answer:
A mixture of ice and common salt.
Class 7 Physical And Chemical Changes Extra Questions Question 4.
What happens when water is heated?
Answer:
It gets converted into vapours.
Chapter 6 Science Class 7 Extra Questions Question 5.
What are physical properties?
Answer:
Properties such as shape, size, colour and state of a substance are called its physical properties.
![]()
Class 7 Science Ch 6 Extra Questions Question 6.
In which type of change, no new substance is formed?
Answer:
Physical change.
Physical And Chemical Changes Class 7 Questions And Answers Question 7.
Write equation for burning of magnesium ribbon.
Answer:
Magnesium (Mg) + Oxygen (O2) → Magnesium Oxide (MgO)
Ncert Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 6 Extra Questions Question 8.
Which type of change is explosion of a firework?
Answer:
Chemical change.
Class 7 Science Chapter 6 Extra Questions And Answers Question 9.
What happens if a cut apple is kept open for a while?
Answer:
The open surface acquires a brown colour.
Questions On Physical And Chemical Changes Class 7 Question 10.
Write the necessary conditions for rusting.
Answer:
Presence of water vapour and air.
![]()
Ncert Class 7 Science Chapter 6 Extra Questions Question 11.
Is melting of ice a chemical change? Give reason.
Answer:
No. When ice melts into water, no new substance is formed. Only the physical form of ice is changed. So, it is not a chemical change.
Physical And Chemical Changes Extra Questions Question 12.
What happens when a hack-saw blade is heated?
Answer:
When a hack-saw blade is heated, it becomes red in colour. It starts emitting light.
Physical And Chemical Changes Class 7 Extra Questions Question 13.
What happens when magnesium oxide is dissolved in water? Write the chemical equation for the reaction.
Answer:
On dissolving magnesium oxide in water, magnesium hydroxide is produced.
This chemical change can be written in the form of the following equation :
Magnesium oxide (MgO) + Water (H2O) → Magnesium hydroxide [Mg(OH)].
Extra Questions Of Physical And Chemical Changes Class 7 Question 14.
Write two importances of chemical changes.
Answer:
- Extraction of all metals requires chemical changes.
- Useful new materials, such as plastics and detergents, are produced by chemical reactions.
Class 7 Chapter 6 Science Extra Questions Question 15.
Why is it advised not to play with fireworks?
Answer:
Explosion of a firework is a chemical change. Such an explosion produces heat, light, sound and harmful gases that pollute the atmosphere. That is why it is advised not to play with fireworks.
Chemical Substances And Processes Class 7 Extra Questions Question 16.
What is stainless steel?
Answer:
Stainless steel is an alloy of iron which does not rust, hence the name stainless steel. It is made by mixing iron with carbon and metals like chromium, nickel and manganese.
![]()
Extra Questions On Physical And Chemical Changes Class 7 Question 17.
What happens when iron nail is dipped into copper sulphate solution?
Answer:
The blue colour solution of copper sulphate changes into a green coloured solution. The change of colour of the solution front blue to green is due to the formation of iron\ sulphate, a new substance. The brown substance \deposit on the iron nail is copper, another new substance. We can write the reaction as :
Copper Sulphate solution (blue) + Iron → Jkon Sulphate solution (green) + Copper (brown deposit).
Class 7 Science Physical And Chemical Changes Extra Questions Question 18.
What happens when carbon dioxide is passed through lime water? Give chemical equation.
Answer:
When carbon dioxide is passed through lime water, calcium carbonate is formed, which makes lime water milky. The turning of lime water milky is a standard test of presence of carbon dioxide.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) + Lime water [Ca(OH)2] → Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3 + Water (H2O).
Science Class 7 Chapter 6 Extra Questions Question 19.
What does ozone do for us?
Answer:
It protects us from the harmful ultraviolet radiations which come from the sun. Ozone absorbs this radiation and breaks down to oxygen. If ultraviolet radiations were not absorbed by ozone, they would reach the earth’s surface and cause harm to us and other life forms. Ozone acts as a natural shield against these radiations.
Class 7th Science Chapter 6 Extra Questions Question 20.
Why has a fraction of ships iron to be replaced every year?
Answer:
Ships are made of iron and a part of them remains underwater. On the part above water also, water drops keep clinging to the ship’s outer surface. Moreover, the water of the sea contains many salts. The saltwater makes the process of rust formation faster. Therefore, ships suffer a lot of damage from rusting in spite of being painted. So much so, that a fraction of ship’s iron has to be replaced every year.
Question 21.
What happens when baking soda is added to vinegar and the resulting gas is passed through lime water?
Answer:
On adding baking soda to vinegar, a hissing sound is heard and bubbles are seen coming out. When this gas is passed through lime water, it turns milky.
The change in the test tube is as follows :
Vinegar (Acetic acid) + Baking soda (Sodium hydrogen carbonate) → Carbon dioxide + other substances
The reaction between carbon dioxide and lime water is as follows :
Carbon dioxide (CO2) + Lime water [Ca(OH)2] → Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3) + Water (H2O)
When carbon dioxide is passed through lime water, calcium carbonate is formed, which makes lime water milky. The turning of lime water milky is a standard test of carbon dioxide.
![]()
Question 22.
Make a list of ten changes you have noticed around you.
Answer:
- lighting of bulb
- moving of fan
- sound produced by radio
- changing of day and night
- changing of the shape of the moon
- changing of size of the puppy
- blooming of flowers
- melting of ice
- vaporisation of water
- lightning.
Question 23.
When a candle burns, both physical and chemical changes take place. Identify these changes. Give another example of a familiar process in which both the chemical and physical changes take place.
Answer:
Physical changes: The wax of the candle first melts, then vaporises and burns.
Melting of wax is a physical change since molten wax can be solidified back to the wax and there is no new substance formed.
Chemical changes: When wax vapours burn, smoke and carbon dioxide are formed which are new substances. So, it is a chemical change.
Example: Lightning torch bulb using dry cell is another example where both physical and chemical changes take place.
The lighting of the bulb is physical change since no new substance is formed there. The current from the dry cell is obtained by the chemical substances inside it. Here, the chemicals in the cell react with each other and produce light substances and hence the cell ultimately becomes useless. So, it is a chemical change.
Question 24.
How would you show that setting of curd is a chemical change?
Answer:
When soipe sour substance is added to milk or kept overnight, it turns into curd. The curd in no way can be converted into milk. Curd is a different substance than milk. So, formation of curd is a chemical change.
![]()
Question 25.
Explain why burning of wood and cutting it into small pieces are considered as two different types of changes.
Answer:
Burning of wood produces ash and smoke. Hence the properties of wood are changed and new substances are formed. So, it is a chemical change.
When a log of wood is cut into small pieces, no new substance is formed there. Each small piece bears the properties of wood. So, it is a physical change.
Question 26.
Describe how crystals of copper sulphate are prepared.
Answer:
A cupful of water is taken in a beaker and a few drops of dilute sulphuric acid are added into it. The water is heated. When it starts boiling copper sulphate powder is added slowly while stirring continuously. Copper sulphate powder is added continuously till no more powder can be dissolved. The solution is filtered and allowed to cool down. Crystals of copper sulphate slowly form at the bottom of the beaker.
Question 27.
Describe how crystals of copper sulphate are prepared.
Answer:
A cupful of water is taken in a beaker and a few drops of dilute sulphuric acid are added into it. The water is heated. When it starts boiling copper sulphate powder is added slowly while stirring continuously. Copper sulphate powder is added continuously till no more powder can be dissolved. The solution is filtered and allowed to cóol down. Crystals of copper sulphate slowly form at the bottom of the beaker.
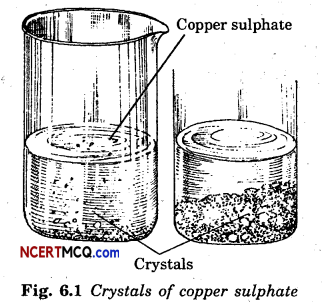
Question 28.
Explain how painting1of an iron gate prevents it from rusting
Answer:
For rusting, iron must be In contact with both air and moisture. When iron gate is painted, the layer of paint cuts the contact between air, moisture and iron. Thus, it prevents rusting.
![]()
Question 29.
Explain why rusting of iron objects is faster in coastal areas than in deserts.
Answer:
In coastal areas, there is more moisture in air due to the presence of sea. But in deserts, there is a scarcity of water and hence air is almost dry there. Both air and moisture are necessary conditions for rusting. So, rusting is faster in coastal areas than in deserts.
Question 30.
Describe two changes that are harmful. Explain why you consider them harmful? How can you prevent them?
Answer:
(i) Rusting: If a piece of iron is left in open for some time, it acquires a film of brownish substance. This substance is called rust and the process is called rusting.
Rusting is harmful because it destroys the iron objects. Iron is the most widely used metal and so rusting is such a serious problem. Prevention of rusting: Rusting can be prevented by preventing iron particles from coming in contact with oxygen, or water, or both.
- One simple way is to apply a coat of paint or grease. In fact, these coats should be applied regularly to prevent rusting.
- Another way is galvanisation, i.e., to deposit a layer of a metal like chromium or zinc on. iron.
(ii) Spoilage of food: Food items when kept carelessly, get spoiled. This is a chemical change and obviously harmful for us. Food is spoiled by microorganisms.
Prevention of food spoilage: Microorganisms do not survive at high or low temperatures. So, food items stored in refrigerator do not spoil. Also we should keep them covered so that microorganisms do not get any chance to enter and spoil them.
Question 31.
Prepare crystals of alum.
Answer:
A cupful of water is taken in a beaker and a few drops of dilute sulphuric acid are added into it. The water is heated. When it starts boiling alum powder is added slowly while stirring continuously. Alum powder is added continuously till no more powder can be dissolved. The solution is filtered and allowed to cool down. Crystals of alum slowly form at the bottom of the beaker.
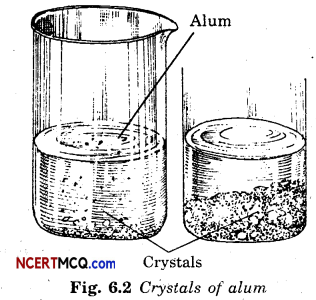
Question 32.
Collect information about the types of fuels used for cooking in your area. Discuss with your teachers /parents? others which fuels are less polluting and why?
Answer:
The different fuels used for cooking are wood, charcoal, cow-dung cak&, kerosene, biogas, LPG, etc.
Among all these, biogas and LPG are least polluting. Both of these burn completely and do not give smoke. Also, they do not leave any residue (ash, unburnt part, etc.) after burning. So, these fuels are less polluting.
![]()
Experiment:
Aim: To make crystals of copper sulphate from its powder.
Requirements: Beaker, burner, tripod stand, wire gauge, spoon, copper sulphate powder, water, filter paper, funnel, stand.
Procedure :
- The beaker is half-filled with water.
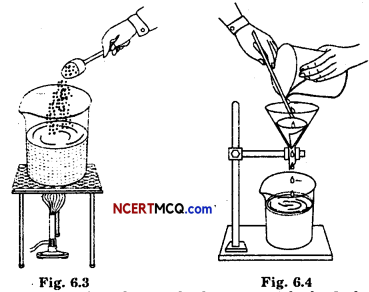
- It is placed over the burner with the help of tripod stand and wire gauge.
- The burner is lighted.
- When the water starts boiling, copper sulphate powder is added into it and stirred.
- Powder is added continuously till no more powder dissolve further.
- The solution is filtered.
- The filtrate is kept undisturbed and allowed to cool down.
Observation: Crystals of copper sulphate get deposited at the bottom of the beaker.
Multiple Choice Questions
1. When you cut a piece of paper into four square pieces, which of the following happens?
(i) There is a change in property of paper.
(ii) The paper can’t be got back by any method.
(iii) Change in physical properties takes place like shape and size.
(iv) None of the above.
Answer:
(iii) Change in physical properties takes place like shape and size.
2. When the paper is cut in pieces, what can be the changes?
(i) changes in shape and size
(ii) changes in state
(iii) changes in colour
(iv) changes in position
Answer:
(i) changes in shape and size.
3. The chalk can again be reversed from the chalk dust. Which type of change is this?
(i) Chemical change
(ii) Physical change
(iii) Both physical and chemical change
(iv) None of these.
Answer:
(iii) Both physical and chemical change.
![]()
4. On placing a mixture of ice and water in a freezer, water becomes solid ice once again. This type of change is called a :
(i) physical change
(ii) chemical change
(iii) periodic change
(iv) none of these.
Answer:
(i) physical change.
5. Hold an inverted pan by its handle over the steam at some distance from the boiling water. Observe the inner surface of the pan. What will you find?
(i) Entrapped steam.
(ii) Condensed water droplets at the surface.
(iii) Water vapours stuck to surface.
(iv) None of these.
Answer:
(ii) Condensed water droplets at the surface.
6. Steam get converted back to water by the process of :
(i) evaporation
(ii) condensation
(iii) sublimation
(iv) vaporisation.
Answer:
(ii) condensation.
![]()
7. When the tip of the hack-saw blade is kept on the flame, what changes occur?
(i) Change in shape
(ii) Change in state
(iii) Change in colour
(iv) Chemical change
Answer:
(iii) Change in colour.
8. When it (hack-saw blade) is cooled, what happens?
(i) It gets back to its original colour.
(ii) Its colour faints a bit.
(iii) It becomes extra dark in colour.
(iv) It becomes colourless.
Answer:
(i) It gets back to its original colour.
9. A physical change is generally :
(i) irreversible
(ii) reversible
(iii) change in composition of the object
(iv) none of these.
Answer:
(ii) reversible.
10. When magnesium is burnt in air with a brilliant white light, it forms :
(i) magnesium carbonate
(ii) magnesium hydroxide
(iii) magnesium oxide
(iv) magnesium cyanide.
Answer:
(iii) magnesium oxide.
11. When magnesium oxide is mixed with small quantity of water, it forms magnesium hydroxide, which is a/an :
(i) acid
(ii) base
(iii) salt
(iv) none of these.
Answer:
(ii) base.
12. Magnesium hydroxide, formed by dissolving magnesium oxide in water turns :
(i) red litmus blue
(ii) blue litmus red
(iii) red litmus green
(iv) no change.
Answer:
(i) red litmus blue.
![]()
13. Formula of magnesium oxide is :
(i) MgO2
(ii) MgO
(iii) MnO
(iv)MnO2.
Answer:
(ii) MgO.
14. Formulh of magnesium hydroxide is
(i) Mg(OH)2
(ii) MgOH
(iii) Mn(OH)2
(iv) MnOH.
Answer:
(i) Mg(OH)2.
15. The colour of copper sulphate solution is :
(i) blue
(ii) green
(iii) grey
(iv) brown.
Answer:
(i) blue.
16. The colour of iron sulphate solution is :
(i) blue
(ii) green
(iii) black
(iv) brown.
Answer:
(ii) green.
17. A few drops of dilute sulphuric acid are added into a solution of copper sulphate and a blade is put into it. The brown deposit on the shaving blade is :
(i) deposit of iron
(ii) deposit of iron rust
(iii) deposit of sulphur
(iv) deposit of copper.
Answer:
(iv) deposit of copper.
18. The change in the colour of copper sulphate solution, when blade is left in it for some time, is due to :
(i) reaction of copper sulphate with iron (blade)
(ii) reaction of sulphuric acid with iron (blade)
(iii) reaction of copper sulphate with sulphuric acid
(iv) none of these.
Answer:
(i) reaction of copper sulphate with iron (blade).
19. The end products of the reaction of copper sulphate solution and iron is/are :
(i) iron sulphate solution
(ii) copper
(iii) both iron sulphate solution and copper
(iv) copper and sulphuric acid.
Answer:
(iii) both iron sulphate solution and copper.
![]()
20. When a pinch of baking soda is added to a teaspoonful of vinegar, you would hear a hissing sound and see bubbles of a gas coming out. What reaction took place?
(i) Acetic acid + Sodium carbonate → Carbon dioxide + Other substances.
(ii) Acetic acid + Sodium hydrogen carbonate → Carbon dioxide + Other substances.
(iii) Acetic acid + Sodium hydrogen carbonate → Oxygen + other substances.
(iv) Acetic acid + Sodium carbonate → Oxygen + Other substances.
Answer:
(ii) Acetic acid + Sodium hydrogen carbonate → Carbon dioxide + Other substances.
21. On passing the gas evolved in the above-mentioned experiment through a solution of lime water, it turns milky. It is due to the formation of :
(i) calcium carbonate
(ii) calcium bicarbonate
(iii) calcium oxide
(iv) calcium hydroxide.
Answer:
(i) calcium carbonate.
22. Galvanisation is process of coating iron with for preventing rusting.
(i) paint
(ii) nickel
(iii) zinc
(iv) cadmium
Answer:
(iii) zinc.
Keywords:
→ Chemical change: The change in which substance(s) undergoes a change in their chemical properties or composition or both is called chemical change. Here, a new substance is formed.
→ Chemical reaction: It is a process, which changes the chemical properties or composition or both of substances.
![]()
→ Crystallisation: The process of making large crystals of pure substances from their solution is known as crystallisation.
→ Galvanisation: The process of depositing a layer of zinc on iron is called galvanisation.
→ Physical change: A change in which a substance undergoes a change in its physical properties is called a physical change. This change may be reversible. Here, no new substance is formed.
→ Rusting: The process of corrosion of iron is known as rusting.
